IB Physics 2.2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Q: What is a force?
A: A force is an action that causes deformation or a change in velocity/acceleration of an object.
Q: What is the unit of force?
A: Newton (N)
Q: What is weight?
A: The attractive gravitational force exerted by an object’s mass on another object. Formula: W=mg
Q: What is electrostatic force?
A: The attractive or repulsive force between two charged objects.
Q: What is magnetic force?
A: The attractive or repulsive force between magnetic objects.
Q: What is reaction (normal) force?
A: The perpendicular force a surface exerts on an object due to its weight.
Q: What is friction?
A: The force parallel to a surface that opposes motion between two surfaces.
Q: What is compression?
A: The force exerted when an object (like a spring or rod) is squished. Acts inward on both sides.
Q: What is tension?
A: The force exerted when an object (like a rope or spring) is stretched. Acts outward on both sides.
Q: What does a free body diagram show?
A: All the forces acting on an object
Q: How is the magnitude of a force shown on a free body diagram?
A: By the length of the arrow — longer arrow = larger force.
Q: Where is weight drawn from on a free body diagram?
A: From the center of the object
Q: In a terminal velocity free body diagram, what two forces are equal?
Weight and Drag
Q: For a block moving at constant velocity, what two forces are equal?
Applied Force = Friction
Weight = Reaction (Normal)
Q: State Newton’s First Law.
A: A body remains at rest or moves at constant velocity unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Q: What is equilibrium?
A: When all forces on an object balance out to zero.
Q: What are the two types of equilibrium?
A: Static: Object is stationary (e.g. Book on Table) B: Dynamic: Object moves at constant velocity
Q: State Newton’s Second Law
A: The resultant force on an object is proportional to its acceleration. Formula: F=ma
Q: What is the difference between mass and weight?
A: Mass: Amount of matter (kg) Weight: Gravitational force on mass
W=mg
Q: State Newton’s Third Law.
A: When object A exerts a force on object B object B exerts an equal and opposite force on A. F of A on B = - F of B on A
Q: What is the key condition for Newton’s Third Law?
A: The forces must be of the same type (e.g. both contact forces or both gravitational)
Q: What is static friction?
A: The force that prevents motion between stationary surfaces.
Q: Formula for maximum static friction?
A:
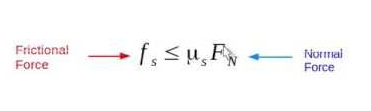
Q: What is dynamic (kinetic) friction?
A: The frictional force acting on moving surfaces.
Q: Formula for maximum dynamic friction?
A:
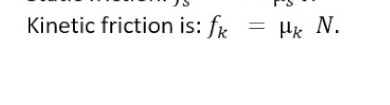
Q: Relationship between static and dynamic friction?
A: Static is Greater than Dynamic
Q: What does “smooth surface” mean in IB questions?
A: The surface has no friction acting on the object.
Q: What type of forces act in a spring?
A: Compression and tension — both can occur depending on how it’s stretched or compressed.
Q: What is the spring constant (k)?
A: A measure of a spring’s stiffness
Q: Formula for elastic (spring) force?
A: F=kΔx
Q: Why does spring force not follow F = ma directly?
A: Because the force changes with extension — it’s not constant.