Acid and Bases and example compounds to recognize
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Arrhenius base
Produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in water
Bronsted-Lowry acid
Proton (H+) donor
Bronsted-Lowry base
Proton (H+) acceptor
Conjugate acid-base pair rule
A strong acid has weak conjugate base and a weak acid has a stronger conjugate base.
Auto-ionization of water (Kw)
Kw= 1.0×10^-14 at 25 degrees Celsius
Ka x Kb=
Ka x Kb=Kw= 1.0 × 10^-14
pH +pOH=
14 at 25 degrees Celsius
pH formula
pH= -log[H+]
pOH formula
pOH= -log[OH-]
pKa formula
pKa= -log Ka
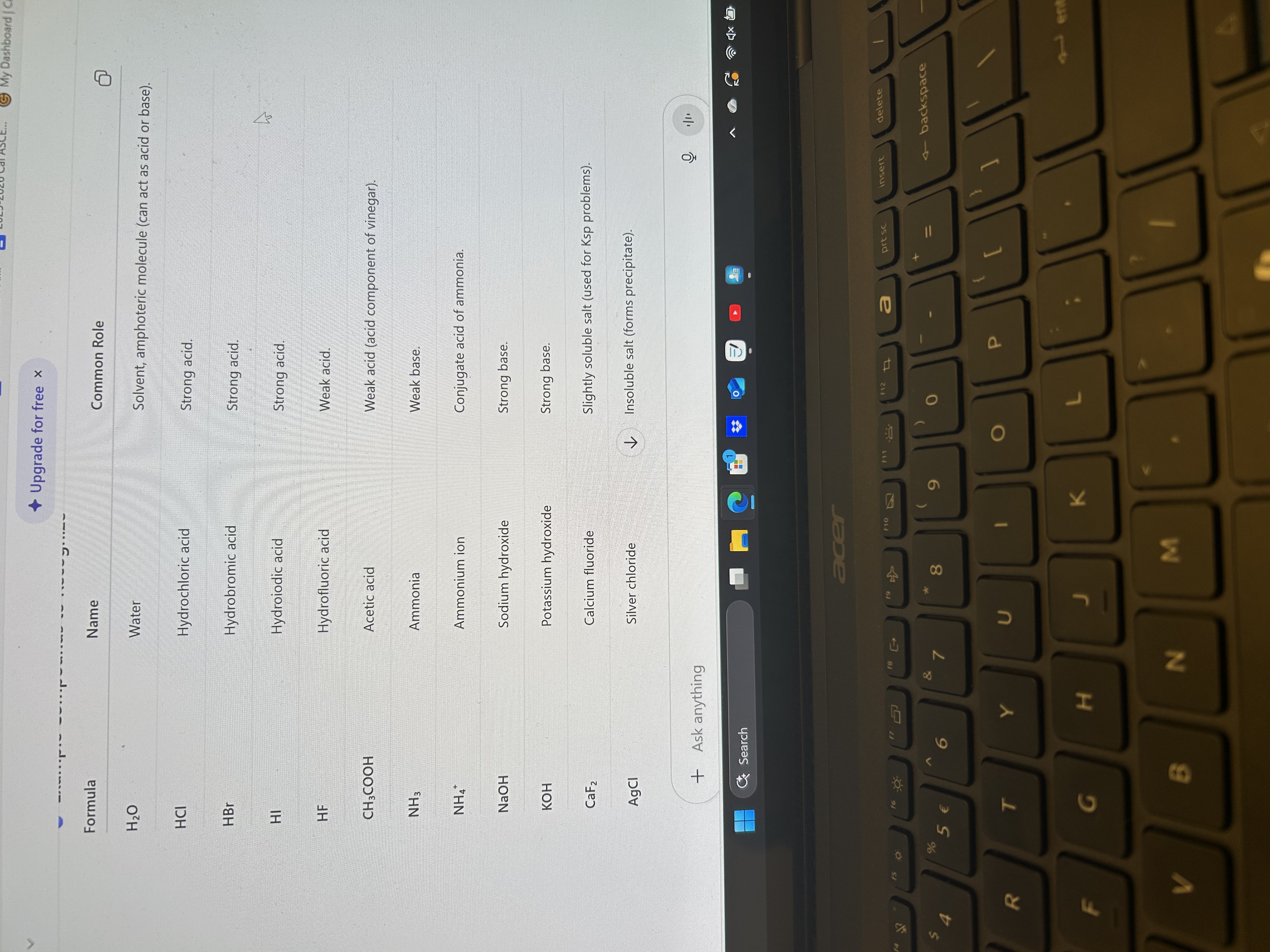
Examples of strong acids?
HCl
HBr
HI
HNO3
H2SO4(first H+ only)
HClO4
Strong bases examples
NaOH
KOH
(Ca(OH)2)
(Ba(OH)2)
Ka>1 × 10^-3 means?
Strong acid ( almost complete dissociation)
Ka<1 × 10^-6 means?
Weak acid use small x approximation.
Relationship between Ka and pKa
Lower pKa the stronger the acid is
Relationship between Kb and pKb
Lower pKb stronger the base
(S)
Solid
Example NaCl sodium chloride Cristal
(l)
Liquid
Example: H2O(l) water
(g)
Gas
Example CO2 carbon dioxide
(aq)
Aqueous (dissolved in water)
Example: Na+ sodium ion in solution
Name all of them