Consumer Attitudes, Self-Concept, and Information Search Strategies in Marketing
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What does the cognitive component of consumer attitude consist of?
A consumer's beliefs about an object, including features and benefits.
Why should marketers promote benefits rather than features?
Because benefits are evaluative beliefs that are more persuasive than nonevaluative feature beliefs.
What is the Multiattribute Attitude Model?
A model that assesses consumer attitudes based on multiple attributes, often using a weighted average.
What is a limitation of the weighted average model in the Multiattribute Attitude Model?
It assumes that more or less of an attribute is always better, which is not true for all attributes.
What are the two types of benefits marketers distinguish between in the affective component?
Utilitarian (functional) benefits and hedonic (emotional) benefits.
How do marketers measure the affective component?
Often through verbal scales similar to those used for cognitive components.
What does the behavioral component of an attitude reflect?
One's tendency to respond in a certain manner toward an object or activity.
What is the difference between direct and indirect approaches in measuring behavior?
Direct approaches involve straightforward questioning, while indirect approaches use less direct questions to reduce bias.
What are some factors that may cause inconsistencies between beliefs, feelings, and actual behavior?
Lack of need, lack of ability, relative attitudes, attitude ambivalence, weak beliefs, and interpersonal influences.
What are the four basic marketing strategies to change the cognitive component of an attitude?
Change beliefs, shift importance, add beliefs, and change ideal.
What is classical conditioning in the context of changing the affective component?
Pairing a liked stimulus, such as music, with a brand to transfer positive feelings to the brand.
How can affect toward an advertisement influence consumer attitudes?
Liking the ad (Aad) generally increases the tendency to like the brand (Abr).
What is the mere exposure effect?
The phenomenon where repeated exposure to a brand can lead to increased liking of that brand.
What is the significance of repetition in affect-based marketing campaigns?
Repetition is critical for enhancing affect and influencing purchase behavior.
How can behavior precede the development of cognition and affect?
Behavior can lead directly to affect, cognitions, or both simultaneously.
What individual factors can influence attitude change?
Gender, need for cognition, consumer knowledge, ethnicity, and regulatory focus.
What is the role of situational characteristics in attitude change?
They interact with individual factors and marketing activities to influence attitude change.
What is attitude ambivalence?
Holding mixed beliefs and/or feelings about an attitude object.
What is the importance of the behavioral component in marketing?
It reflects response tendencies or behavioral intentions that marketers aim to influence.
What is the goal of marketers when attempting to influence consumer behavior?
To provide information and stimuli that can indirectly influence behavior.
What is the significance of the attitude index in the Multiattribute Attitude Model?
It allows for comparison of attitudes towards competing brands.
How do marketers attempt to shift importance in consumer attitudes?
By convincing consumers that attributes where their brands excel are the most important.
What is the effect of weak beliefs and affect on consumer attitudes?
They can lead to changes in attitudes if consumers receive new information while shopping.
What is the relationship between cognitive and affective components in marketing?
Marketers can influence liking (affective) without directly changing beliefs (cognitive).
What is the impact of emotional appeals in advertising?
They can enhance attitude change by creating strong affective responses.
What is the role of behavior in relation to cognition and affect?
Behavior may precede or occur in contrast to cognitive and affective components.
What is operant conditioning's role in changing behavior?
Changing behavior prior to changing affect or cognition is primarily based on operant conditioning.
What is the key marketing task regarding consumer behavior?
To induce people to purchase or consume a product while ensuring that it is rewarding.
What factors influence attitude change?
Individual characteristics (like gender, consumer knowledge) and situational factors (like program context and viewer distraction).
What does the elaboration likelihood model (ELM) explain?
It explains how attitudes are formed and changed under varying conditions of involvement.
What is the central route to attitude change?
It occurs with high involvement, where consumers consciously process relevant message elements.
What is the peripheral route to attitude change?
It occurs with low involvement, where consumers form impressions based on readily available cues.
What type of information is effective in high-involvement situations?
Detailed factual information (central cues).
What type of cues are effective in low-involvement situations?
Simple affective and cognitive cues such as pictures and music (peripheral cues).
How do attitudes formed under the central route compare to those formed under the peripheral route?
Attitudes from the central route are stronger, more resistant to persuasion, and more predictive of behavior.
What is consumer resistance to persuasion?
Consumers are often skeptical and resist persuasion, especially if they hold strong attitudes.
What is self-concept?
The totality of an individual's thoughts and feelings about themselves.
What are the four basic parts of self-concept?
Actual self, ideal self, private self, and social self.
How does the independent self-concept differ from the interdependent self-concept?
Independent self-concept emphasizes personal goals and achievements, while interdependent self-concept emphasizes relationships and social roles.
What type of advertisements are effective for consumers with independent self-concepts?
Ads emphasizing autonomy and individualism.
What type of advertisements resonate with consumers with interdependent self-concepts?
Ads emphasizing group membership and social connections.
What is the extended self?
The self plus possessions, where individuals define themselves in part by their possessions.
What is the mere ownership effect?
The tendency of an owner to evaluate an object more favorably than a non-owner.
What is brand engagement?
The extent to which an individual includes important brands as part of their self-concept.
What is the semantic differential method used for?
To measure the actual, ideal, and social self-concepts of individuals.
How do consumers maintain and enhance their self-concepts?
Through the purchase and consumption of products, services, and media that align with their self-image.
What is self-image congruity?
The alignment between a consumer's self-concept and the brands they prefer.
When is self-image congruity likely to matter more?
For products with value-expressive symbolism and in public consumption situations.
What is self-image congruity in marketing?
It refers to the importance of consumers' self-image aligning with their perceptions of products, particularly for those who value others' opinions.
What criticism do marketers face regarding beauty standards?
Marketers are criticized for promoting ideals of beauty that may lead individuals to develop self-concepts overly reliant on physical appearance.
How do young women's self-concepts relate to beauty perceptions?
Young women often develop partly negative self-concepts due to societal beauty perceptions reinforced by advertising and media.
What is the definition of lifestyle in the context of consumer behavior?
Lifestyle encompasses how a person lives, influencing all aspects of consumption behavior.
What factors determine lifestyle?
Lifestyle determinants include demographics, subculture, social class, motives, personality, emotions, values, household life cycle, culture, and past experiences.
What are some components of lifestyle?
Components include activities, interests, likes/dislikes, attitudes, consumption patterns, expectations, and feelings.
How do lifestyles impact consumer behavior?
Lifestyles influence purchasing decisions, including how, when, where, and with whom consumers engage in consumption.
What distinguishes independents from interdependents in lifestyle choices?
Independents seek adventure and excitement, while interdependents engage more in home-related activities and domestic entertainment.
What is the relationship between individuals' desired lifestyles and their purchasing behaviors?
Individuals' desired lifestyles shape their needs and desires, influencing their purchase and usage behaviors.
How are psychographics and lifestyle studies related?
Psychographics and lifestyle studies are often used interchangeably to analyze consumer behavior based on attitudes, values, and interests.
What are the primary motivations identified in the VALS system?
The primary motivations are Ideals, Achievement, and Self-expression.
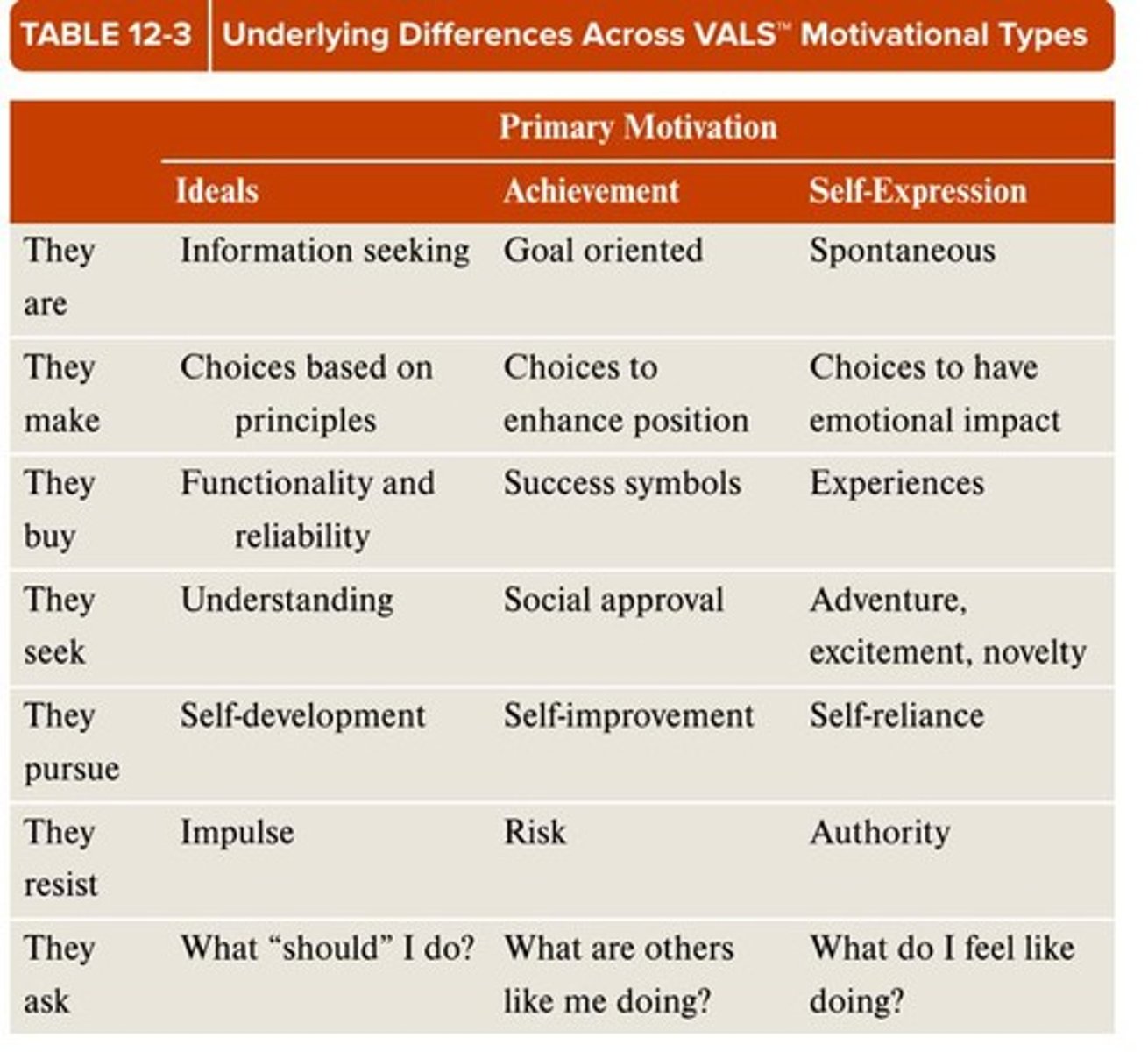
What characterizes the 'Innovators' segment in VALS?
Innovators are successful, sophisticated, and receptive to new ideas and technologies.
What defines the 'Thinkers' segment in VALS?
Thinkers are mature, reflective, and value durability and functionality in products.
How do 'Believers' differ from 'Achievers' in VALS?
Believers are traditional and conservative, while Achievers are goal-oriented and prefer premium products that signify success.
What is the focus of the 'Strivers' segment in VALS?
Strivers are trendy and fun-loving but have limited discretionary income, often emulating the purchases of wealthier individuals.
What is the significance of the second dimension in the VALS system?
The second dimension reflects the resources individuals have to pursue their dominant self-orientation, impacting their ability to act on motivations.
What are 'Technographics' in marketing segmentation?
Technographics categorize consumers based on their relationship with technology and its impact on their lives.
What characterizes the 'Wizards' segment in Technographics?
Wizards are enthusiastic users of new technology, viewing it as essential to improving their lives.
What is the demographic profile of 'Novices' in Technographics?
Novices are mature adults and retirees who are disconnected from technology and prefer simple devices.
What is the cumulative effect of advertising on self-concept?
The cumulative effect of many ads, reinforced by mass media content, can negatively influence individuals' self-concepts.
What is the role of media patterns in lifestyle measurement?
Media patterns refer to the specific media consumers utilize, which can influence their lifestyle and consumption behaviors.
How do usage rates factor into lifestyle studies?
Usage rates measure consumption within a product category, categorizing consumers as heavy, medium, light users, or nonusers.
What is the impact of lifestyle on consumption behavior?
Lifestyle affects where, with whom, and how consumers engage in purchasing and consumption activities.
What is the significance of the household life cycle in lifestyle determination?
The household life cycle influences consumer needs and behaviors as individuals progress through different life stages.
What do Strivers value in products?
Stylish products that emulate the purchases of people with greater material wealth.
How do Experiencers approach technology?
They seek video and audio stimulation using new technologies and platforms.
What do Makers prioritize when choosing products?
Practicality and self-sufficiency, often preferring tough, rugged products.
What characterizes the lifestyle of Survivors?
They lead narrowly focused lives, primarily concerned about safety and security.
What is the first step in problem-solving according to consumer behavior?
Recognizing the problem and using long-term memory to determine potential solutions.
What is internal search in consumer decision-making?
The process of using relevant information from long-term memory to find solutions.
What happens if a satisfactory solution is not found during internal search?
The consumer engages in external search for additional information.
What are the benefits of conducting a search for information?
Finding lower prices or obtaining higher quality products.
What factors influence the amount of search a consumer engages in?
Purchase involvement and the complexity of the decision.
What is the difference between nominal and extended decision making?
Nominal involves recalling a single solution, while extended involves evaluating multiple alternatives.
What are the four categories of decision alternatives?
Awareness set, inert set, inept set, and evoked set.
What is the evoked set in consumer decision-making?
The brands or products that a consumer will evaluate for solving a specific problem.
What are the five primary sources of information for consumers?
Memory, personal sources, independent sources, marketing sources, and experiential sources.
How does online information impact offline sales?
Consumers are more likely to purchase a product offline if its website provides relevant information.
What role do search engines play in consumer behavior?
They are important tools for consumers to find information and begin product searches.
What is the significance of consumer reviews during online searches?
They are heavily utilized by consumers for performance information.
What are the strategic issues marketers face regarding online information search?
Driving information to consumers, driving consumers to information, and integrating online selling with existing channels.
What is permission-based email (PBE)?
An email marketing strategy where consumers opt-in to receive communications.
What is the expected growth of internet marketing spending by 2024?
It is expected to grow to almost $280 billion, accounting for over half of all media spending in the U.S.
What are view-throughs in online advertising?
Website visits that occur as a result of exposure to an online ad but do not occur at the time of exposure.
What role does relevance play in online advertising?
Relevance is a key driver of attention, interest, and engagement, influencing processing and click-through rates.
What is behavioral targeting?
Tracking consumer click patterns on a website to decide on banner ad placement.
What is search engine optimization (SEO)?
Techniques designed to ensure that a company's web pages are accessible to search engines and improve their chances of being found.
What percentage of U.S. adults have a mobile phone?
97 percent.
Who are the Prodigies in smartphone user segments?
5 percent of users who are constantly connected, mobile-centric tech trendsetters, and highly receptive to mobile ads.
What characterizes the Tribals segment of smartphone users?
13 percent of users who are hyperconnected, often with multiple devices, and strong influencers through social media.
What is the primary behavior of the Personals segment in smartphone usage?
11 percent of users who prefer direct messaging over social media and are more likely to purchase products advertised on their phones.
What defines the Pragmatists segment of smartphone users?
18 percent of users who manage home and work with their phones but are less likely to purchase items they see advertised.