Oil Pollution
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is oil pollution?
Pollution caused by petroleum products
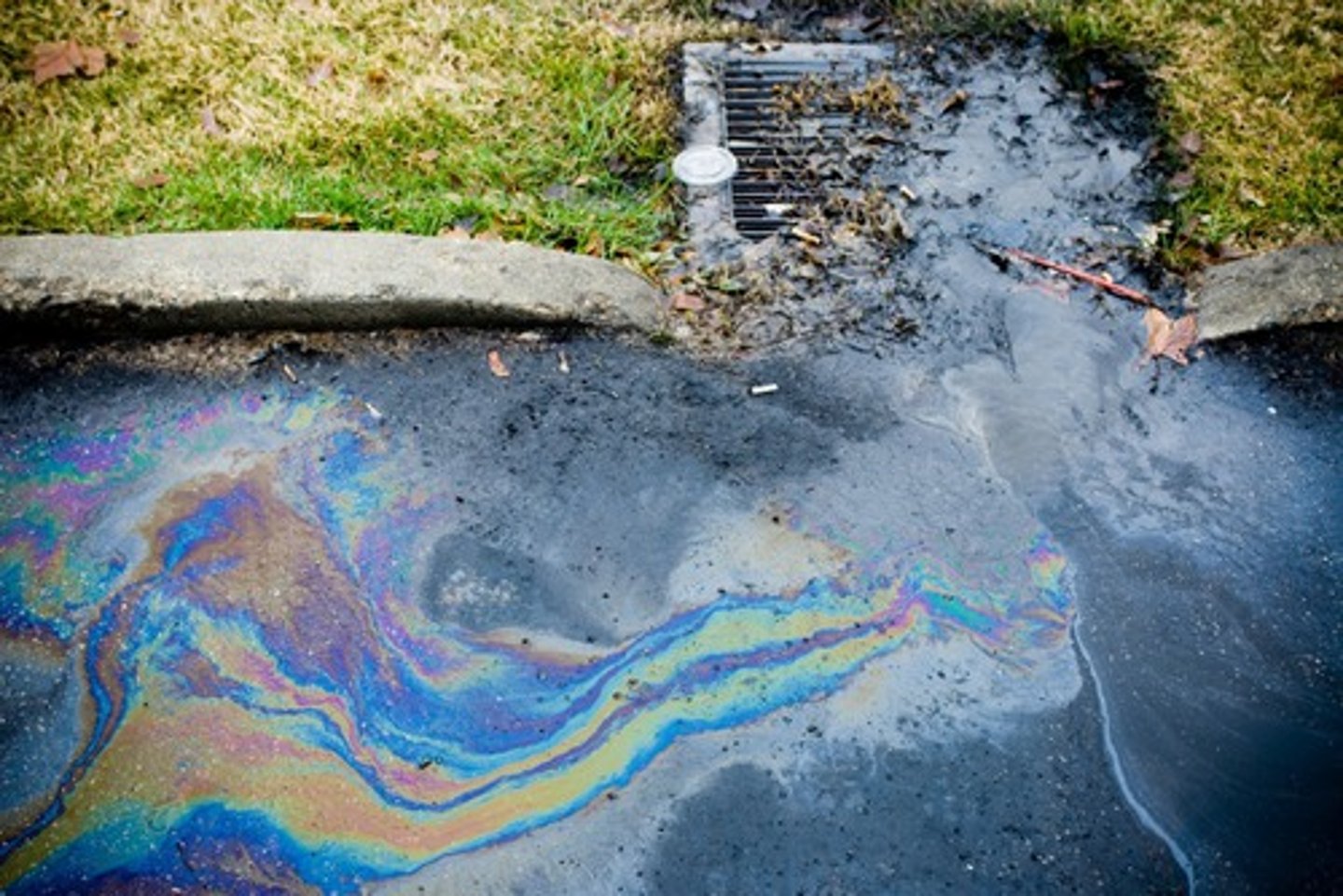

Sources of Oil Pollution
• Waste lubricating oil.
• Ship tank washing.
• Ship tanker accidents.
• Other ship accidents.
• Oil refinery spills.
• Pipeline leaks.
• Leakage during drilling
• Waste lubricating oil.
Vehicle engine lubricating oil which leaks or is deliberately discarded into the environment
Industry machine oil which is washed into drains or mixed with other effluents
• Ship tank washing.
Discharge of waste water from washing tanks on ship tankers
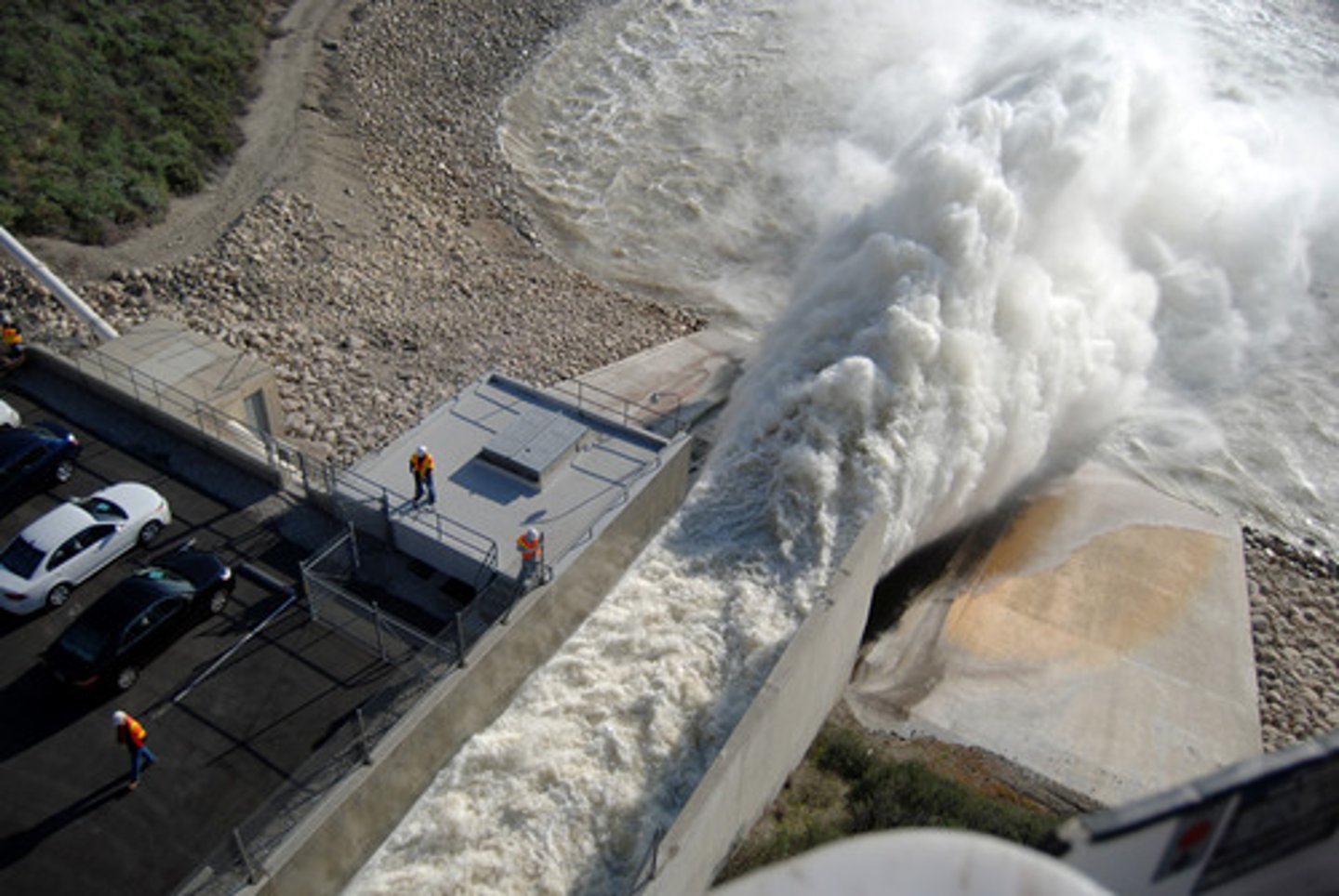

• Ship tanker accidents.
In old ships, tankers had a single layer of steel between oil and the sea. Any damage to the steel hull could allow the release of oil into the sea.

• Other ship accidents.
Oil tankers collide, causing damage to tankers and they let oil spill onto the sea.
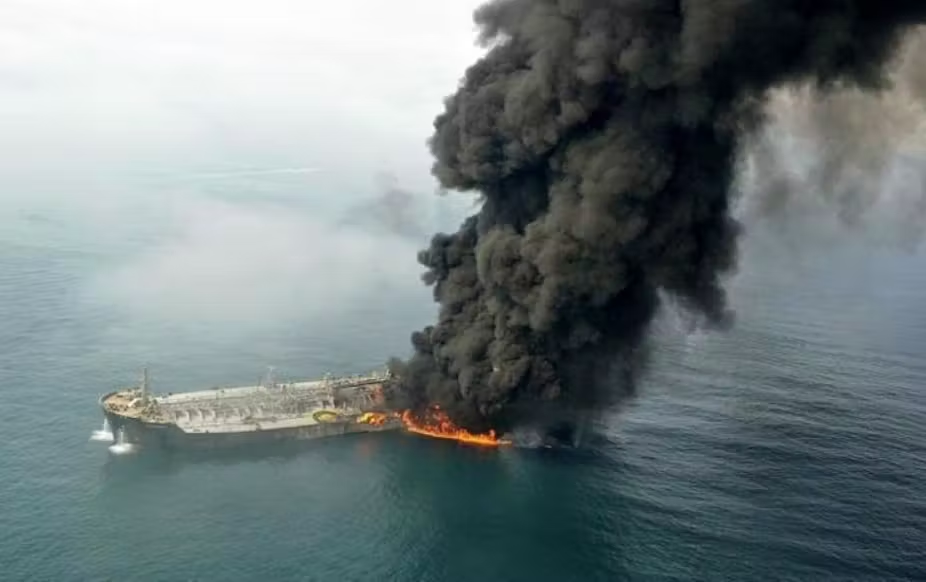

• Oil refinery spills.
Oil refinery centres that let oil leak and spill

Which of these are accidental releases?
• Ship tanker accidents.
• Other ship accidents.
• Pipeline leaks.
• Leakage during drilling
Effects
• Toxicity.
• Asphyxiation.
• Loss of insulation.
• Less time to feed young.
• Food chain effects.
• Toxicity.
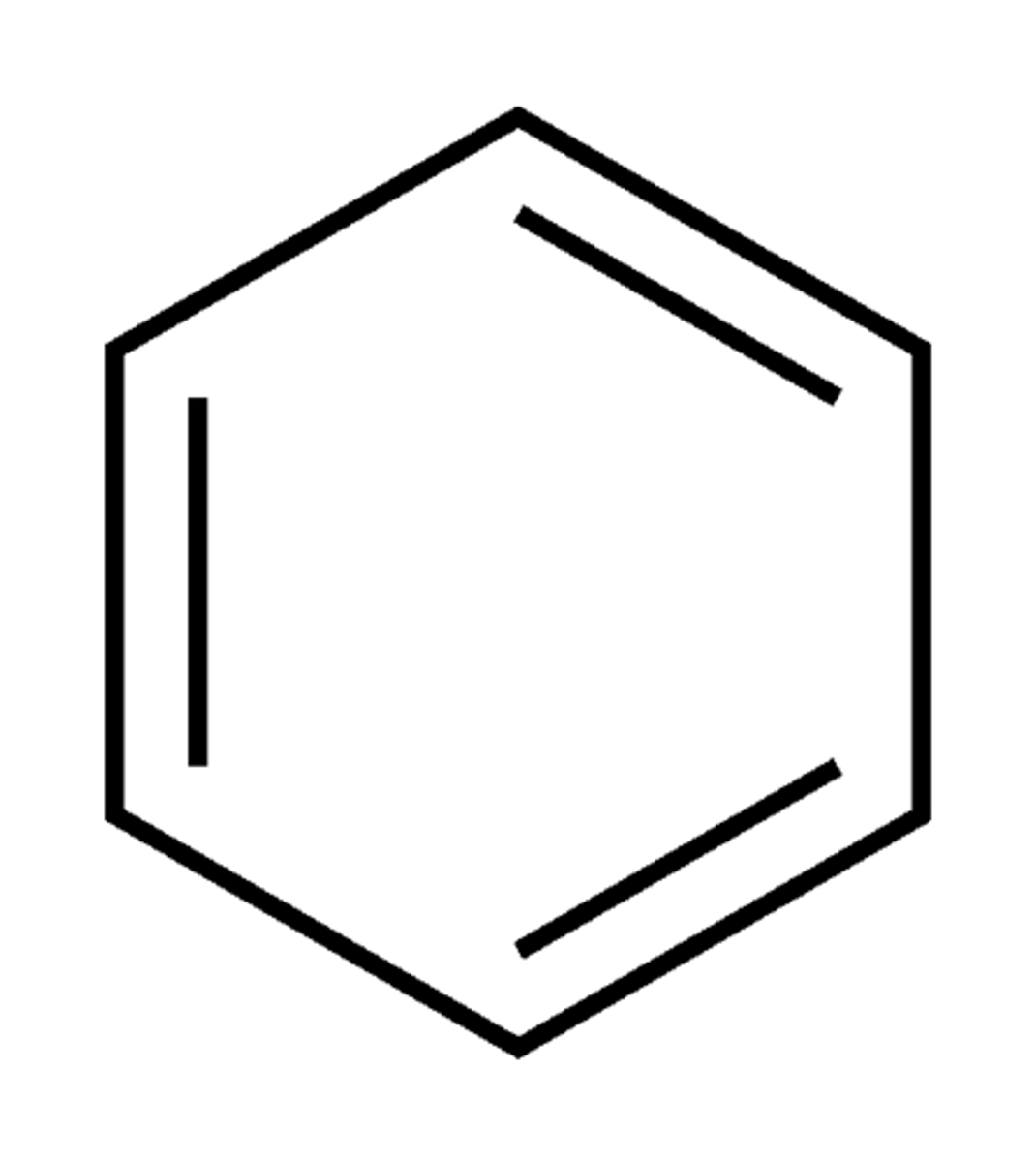
Crude oil components are benzene and xylene
Planktonic organisms that float near the water surface are most likely to be affected
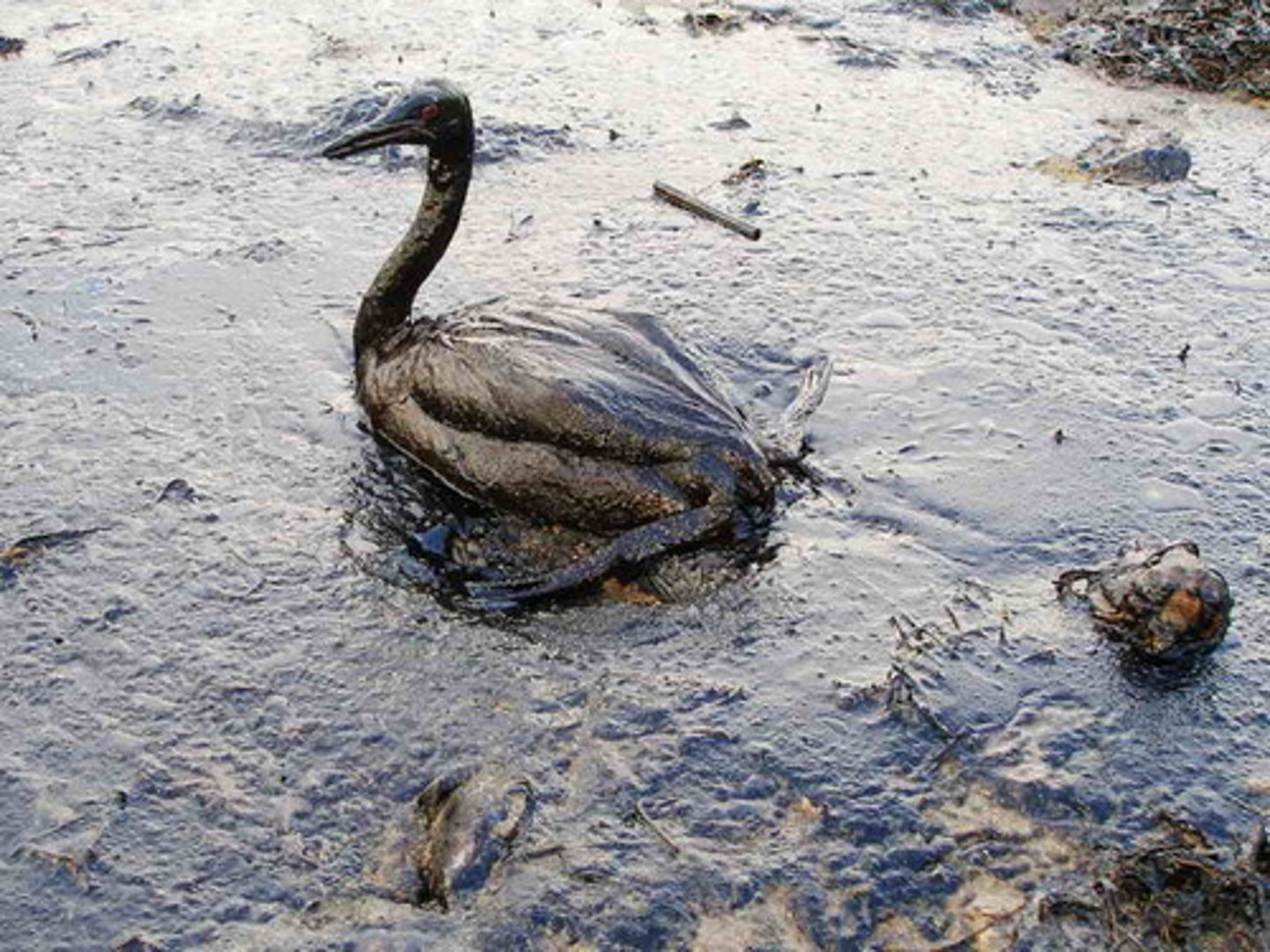
• Asphyxiation.
Oil is viscous and covers aquatic life on seashore and surface.
Molluscs and crustaceans can be asphyxiated
Algae would be unable to absorb sunlight and CO2 for photosynthesis
• Loss of insulation.
Oil causes birds' feathers to stick together so they lose their insulating properties, and the birds may die of hypothermia

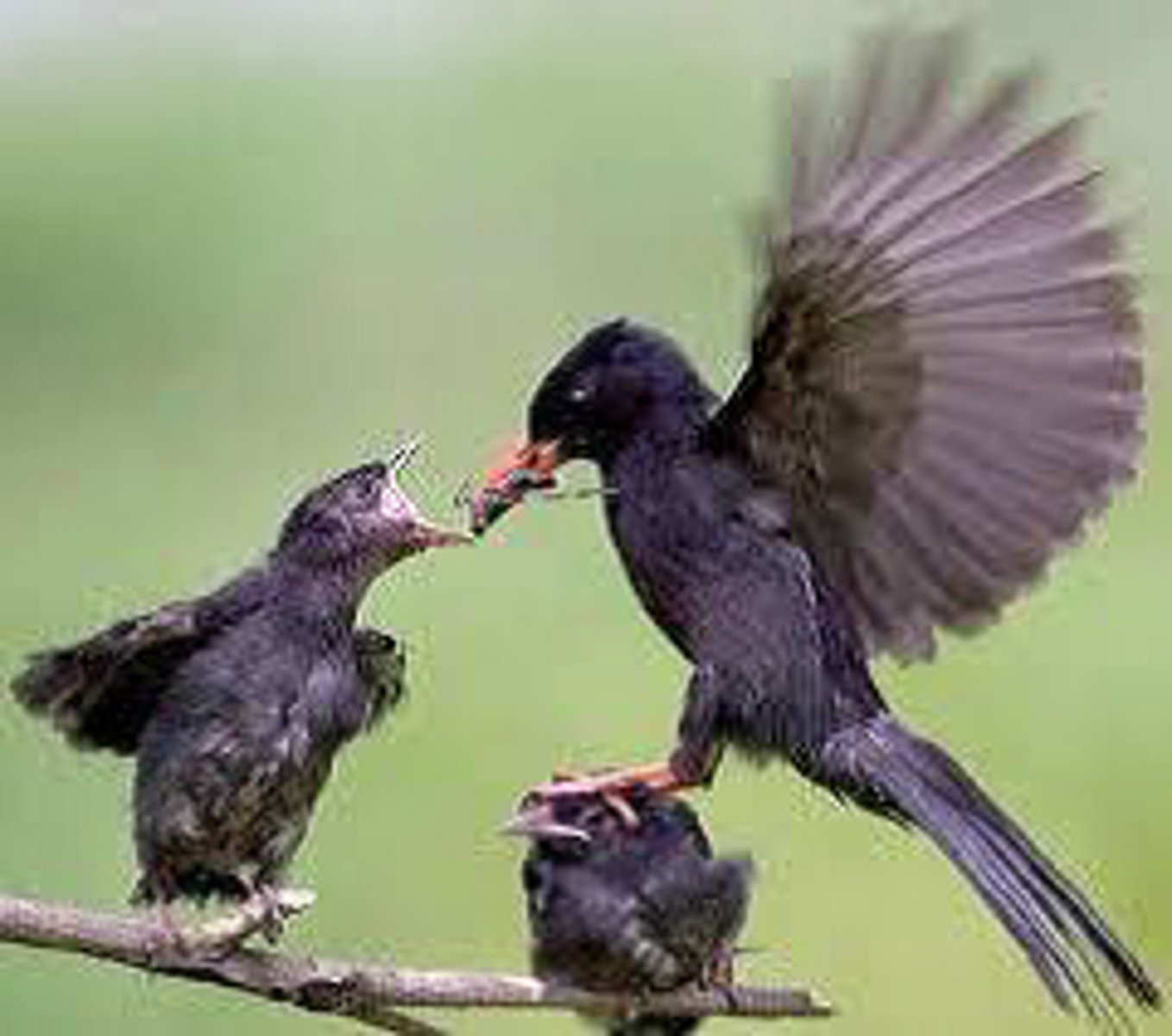
• Less time to feed young.
Birds can clean their feathers if there's only a little oil, but this takes time, reducing time being used to find food for themselves or their young

• Food chain effects.
Marine organisms sometimes find mates or food using smell. The oil has a narcotising, masking odour, making it difficult for the organisms.
Controls
1) Prevention of oil releases
2) Improved Oil Tanker Operation
3) Improved Tanker Design
4) Oil Interceptors
5) Bund Walls
6) Treatment of Oil Spills
1) Prevention of oil releases
• Recycling of waste oil.
How does recycling of waste oil help?
- Contaminants can be removed, and chemical reforming & distillation can produce commercially viable lubricants again
- Waste fuel that can't be recycled can be burnt as fuel, reducing demand
2) Improved Oil Tanker Operation
• Offshore shipping routes
• Improved navigation systems eg GPS
• Inert gas oil tank systems
• Recirculation of washing water
Offshore shipping routes
- Oil tankers have to stay a greater distance away from the shore when possible
- If a tanker has mechanical difficulties, like engine failure, this would give more time to deal with it before it may be carried ashore by water currents or winds

Improved navigation systems eg GPS
- GPS enable more accurate navigation
- AIS (automatic identification system) allows the positions of most ships to be monitored and coordinated to help avoid collisions
Inert gas oil tank systems
- When tankers use to unload their tanks at a terminal, the space left by the oil filled with air
- This can produce an explosive mix of air and oil vapours which leads to tankers releasing the remaining bit of oil as pollution
- Modern tankers now use cooled exhaust gases from the engines to replace the oil, and since there's no oxygen, explosions aren't possible
Recirculation of washing water
Tanks used to be washed out with seawater, then oil water was discharged into the sea
Now oil is recirculated in the tanks during unloading so that the built up tar sludges are mixed and removed with the cargo

3) Improved Tanker Design:
• Double hulls.
• Twin engines/rudders.
• Ship tanker design.
• Reduced leakage: equipment maintenance.
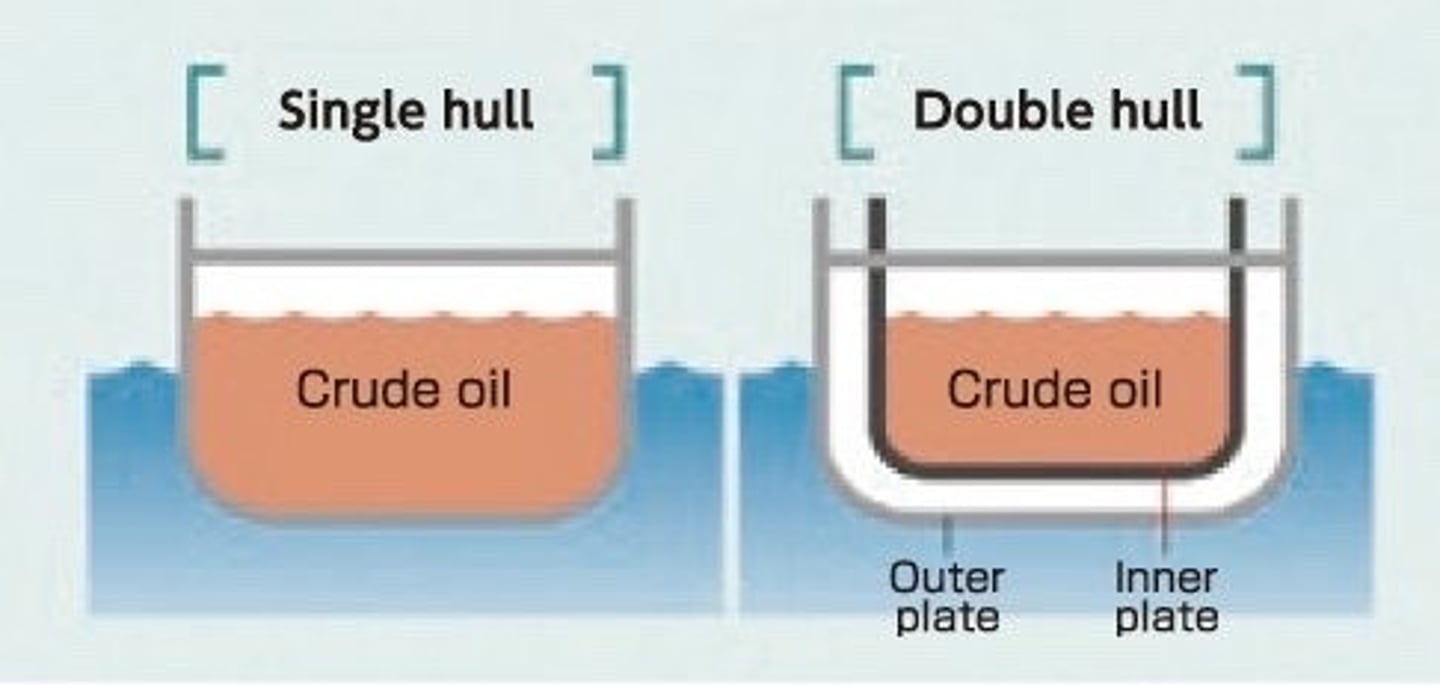
Double Hulls
- Tankers had a single layer of steel between oil and seawater
- Now they have twin hulls with a gap of up to 2m, therefore damage does not necessarily cause a spill
Twin engines/rudders
- Any mechanical failure on a tanker that affects propulsion or steering may result in the ship being carried by currents or wind
- Having twin engines/rudders can save the ship if one breaks down
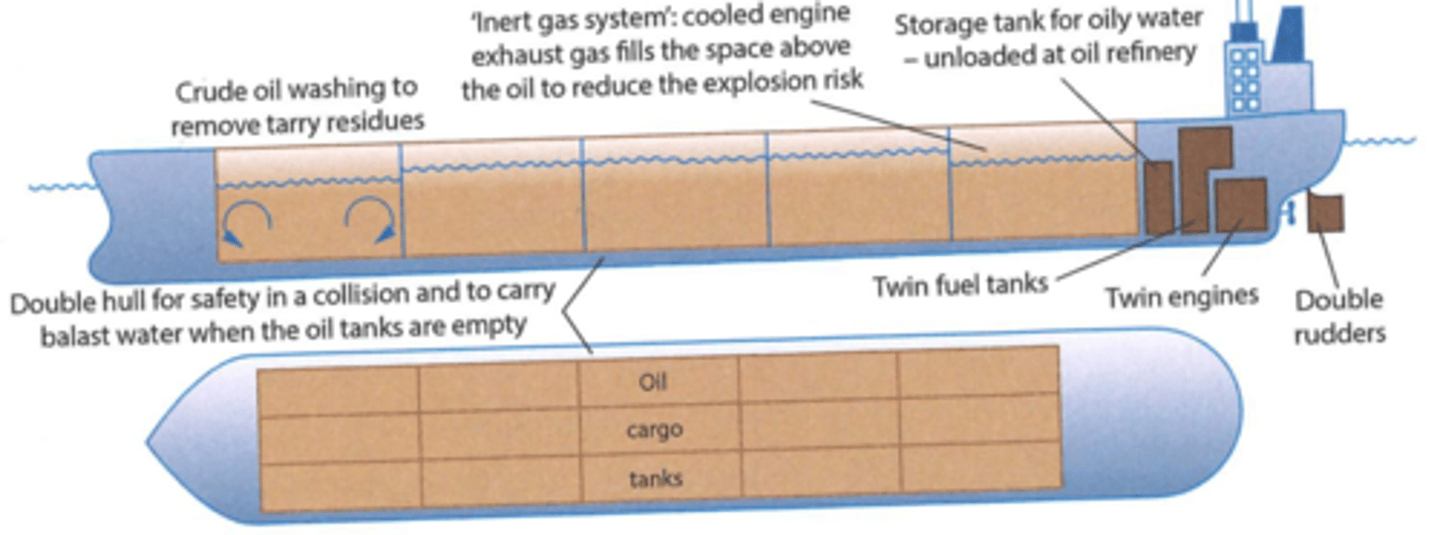
Ship tanker design
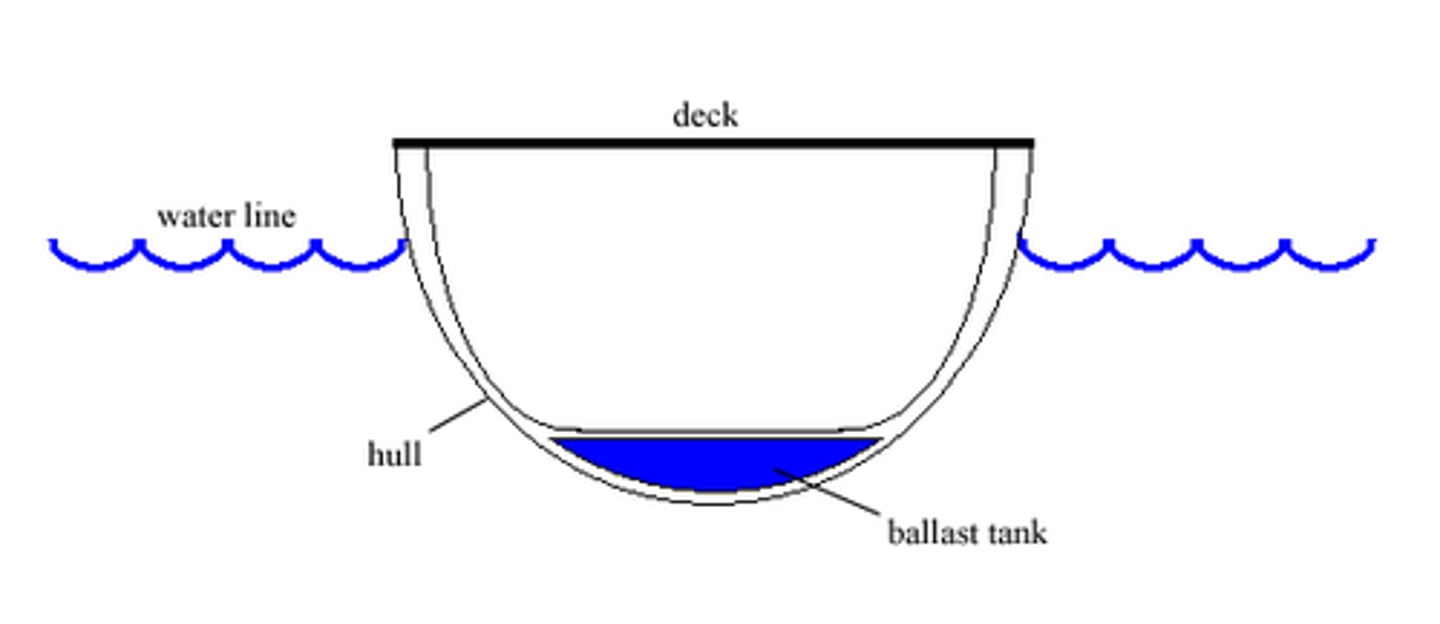
- When an oil tanker is not carrying oil, it must carry ballast water
- This means the hull will be kept down in the water and the propeller and rudder still work
- Also the ballast water is kept in a separate tank to the oil, so no pollution occurs when one empties the ballast tanks into sea
Reduced leakage: equipment maintenance
shi wont leak

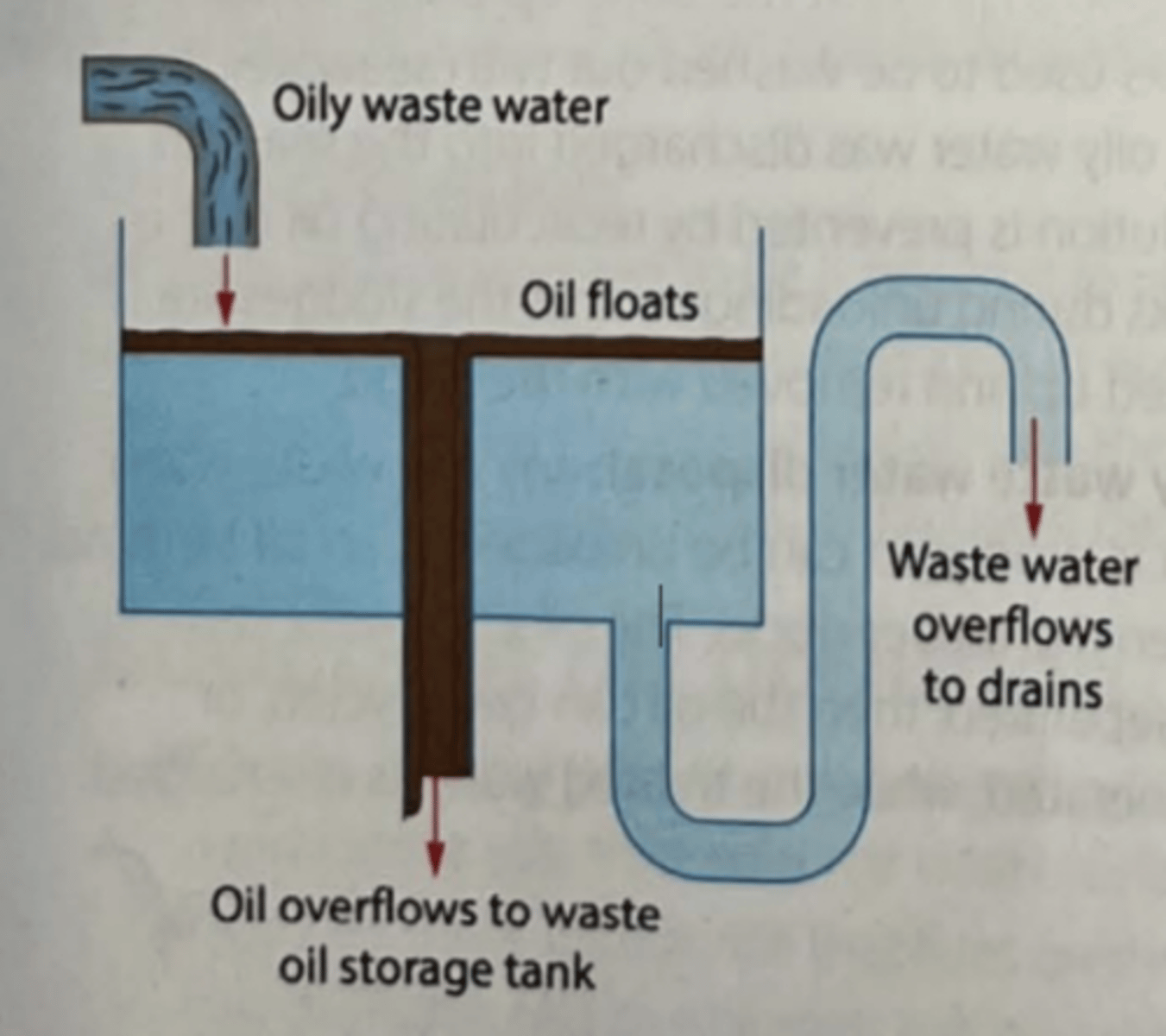
4) Oil Interceptors
Drainage water from roads or car parks will be flowed to oil interceptors
Water can flow into the drainage system whilst the oil is retained for treatment
5) Bund Walls
Oil storage tanks are surrounded by bund walls (impermeable bases) that would contain the oil if the tank were to split
The volume enclosed by a bund wall is greater than the tank, so the bund wall cannot overflow

6) Treatment of Oil Spills:
• inflatable booms
• skimmers
• absorbent materials
• polymerising materials
• dispersants
• steam cleaning
• bioremediation
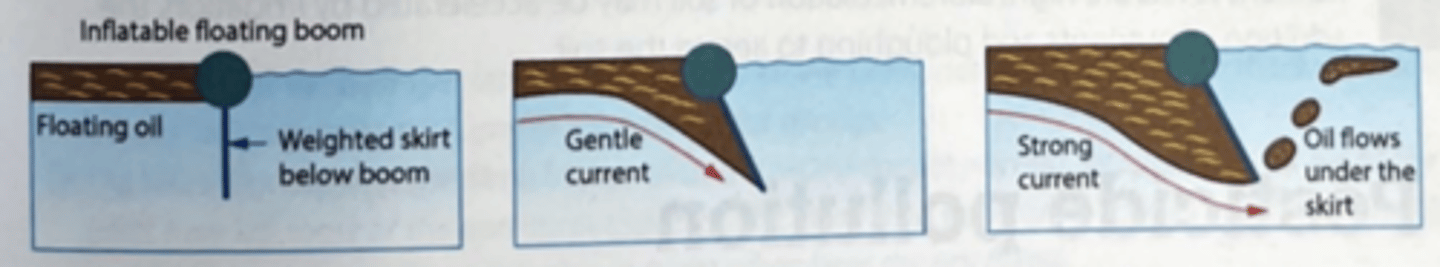
Inflatable Booms
Restricts the movement of floating oil
A skirt below the boom can retain oil if there is a water current
Does not work in open water where current or waves are too strong
Mainly used in sheltered areas to protect sensitive sites and reduce oil dispersal
Skimmers
Rotating metal discs that pick up oil and can be scraped off and stored for later disposal by incineration or landfill

Absorbent materials
High surface area materials (like textile mops) can help absorb oil
The absorbent material & oil can then be removed and disposed of by incineration or in landfill sites

Polymerising materials
These cause oil molecules to join together, producing more solid materials that can be collected more easily
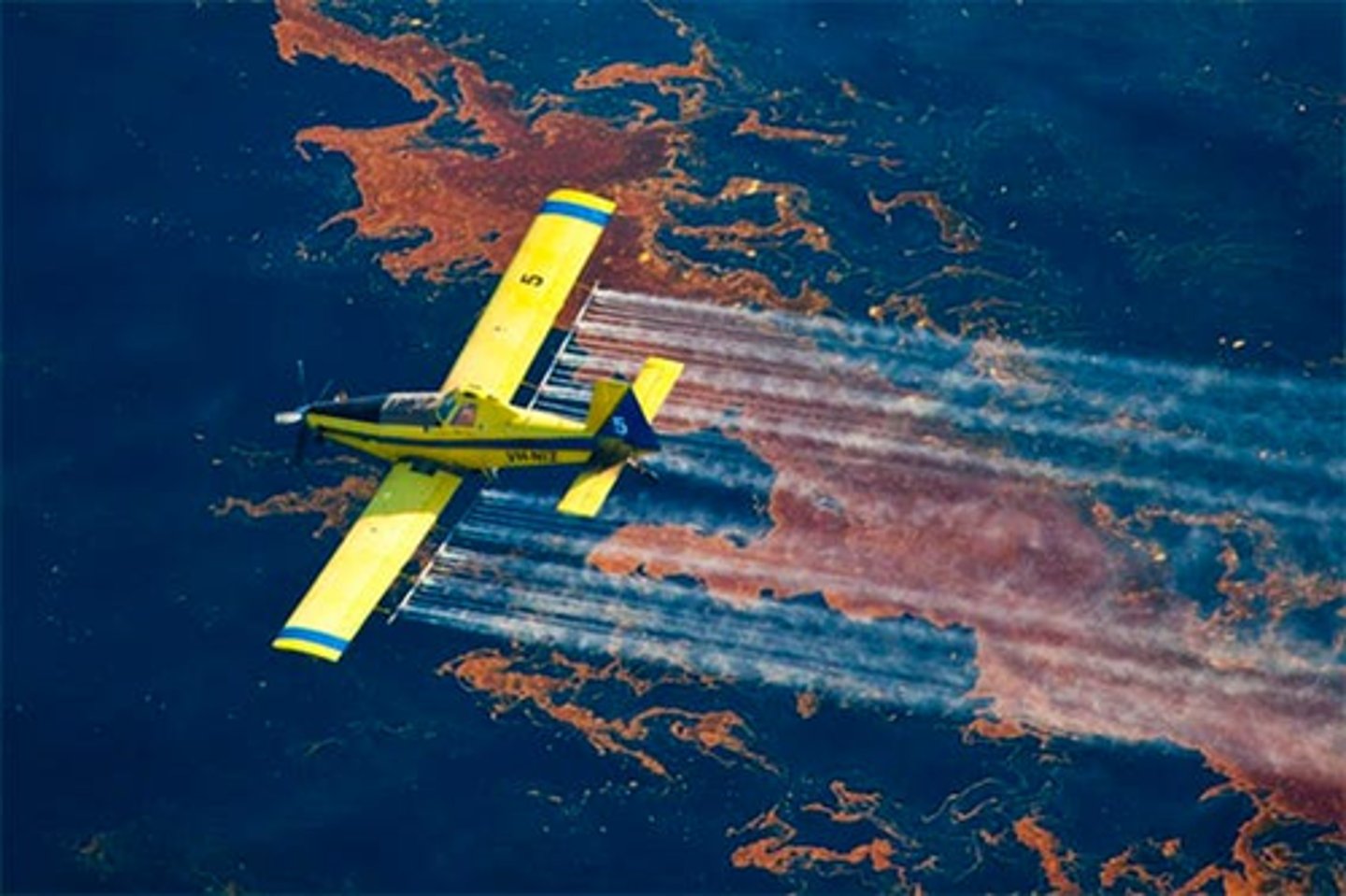
Dispersants
These break up the oil to produce an emulsion of oil droplets in water
They allow the oil to become more mobile and disperse, possibly to be broken down by bacteria
But they do not reduce the amount of oil pollution themselves
Spread by aircraft and ships

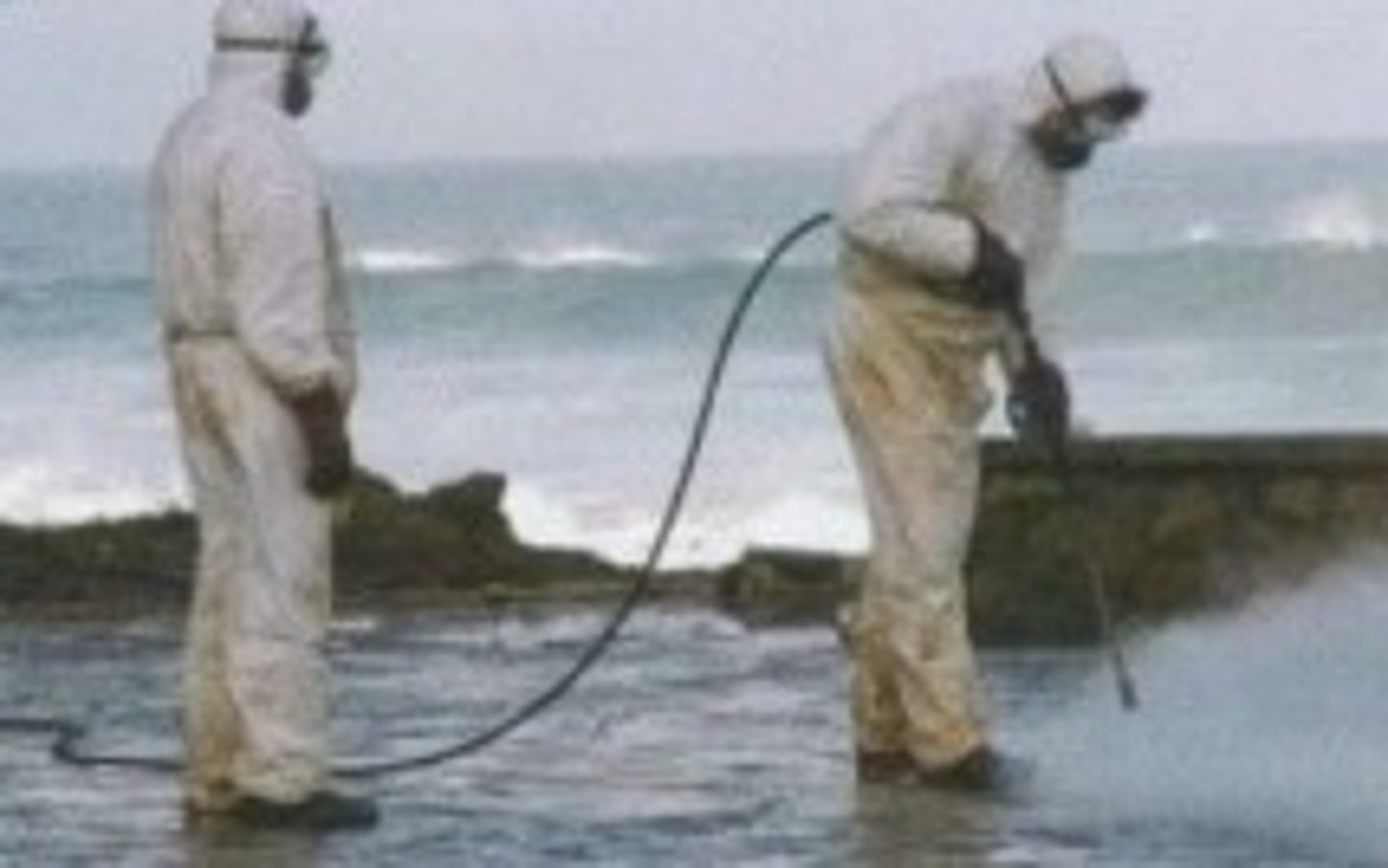
Steam cleaning
Oil on beaches can be washed off using steam
Does not destroy the oil, but removes it from particularly sensitive habitats
But tbh the steam may kill the organisms deeper in the sediments that weren't even affected by the oil

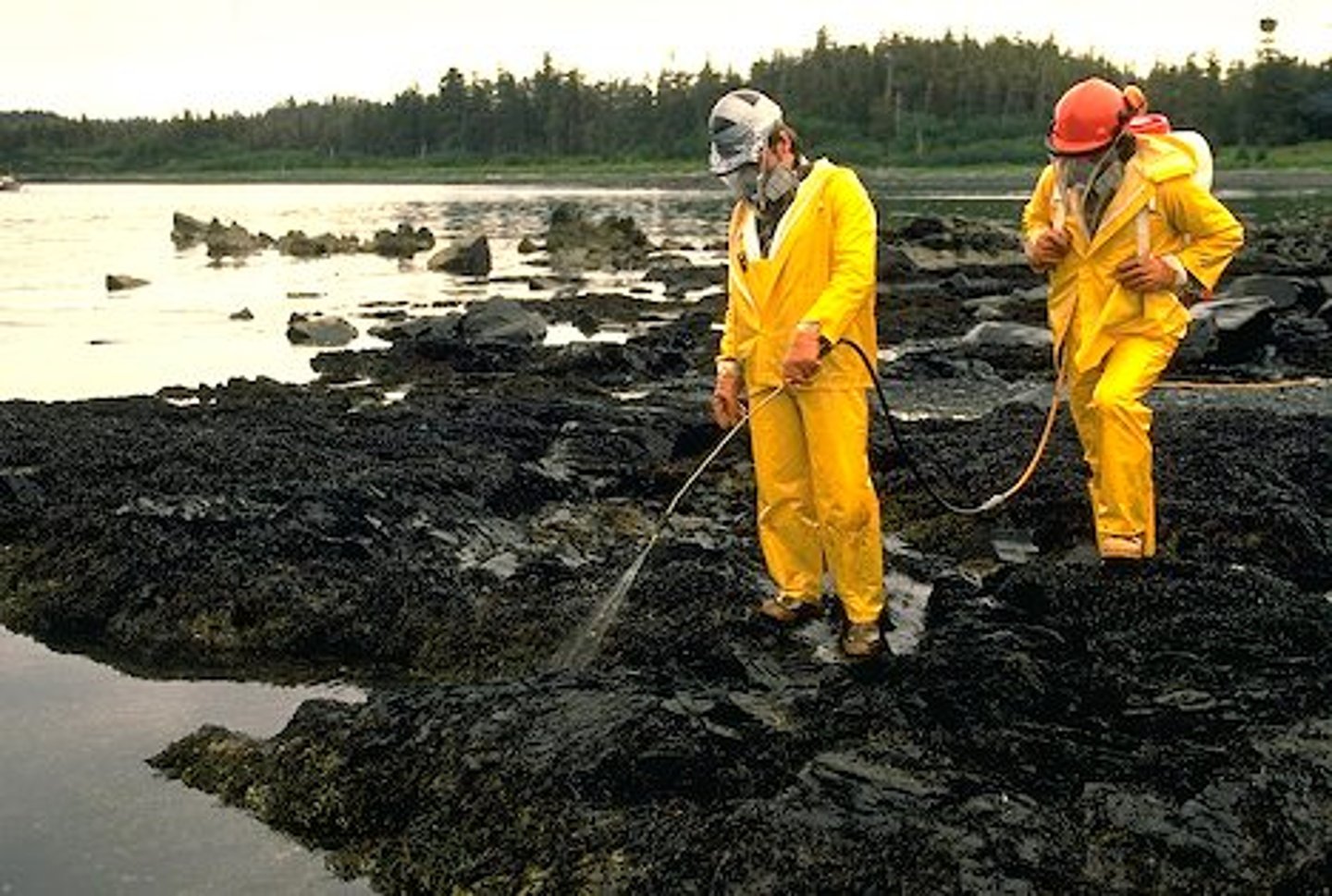
Bioremediation
Some bacteria break down hydrocarbons & help remove the residual pollution left after other clean up methods have been used
The rate of bacterial action depends on the ev conditions (temp, light level, oxygen level, nutrient level)

How can bioremediation of soil be accelerated?
- Through irrigation
- Addition of nutrients
- Ploughing to aerate the soil
Converting km² to m²
1 km² x 10⁶
Converting m² to cm²
1 m² x 10⁴