Pre lecture 6 - Hype and Hope vs hard evidence
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Unwarranted Hype
Excessive or premature excitement (even before evidence has been collected soemtimes) about scientific findings before sufficient evidence supports them.
often some organizations capitilize on premature exitement
media coverage and press releases may amplify preliminary or low-quality studies, leading to public and proffesional overestimation of findings.
Unwarranted Hype example
“Cure for alzheimers” on front of article - amplification of findings - very preliminary - or maybe they havent even studied it in human patients yet
Why is this cycle harmful to science?
Because repeated “breakthrough” or “new cure” claims that later fail make science seem unreliable and waste valuable public research money.
How can acute public health crises and untreatable diseases influence people’s behaviour?
They create strong demand for new solutions and increase people’s willingness to try unproven or experimental therapies.
usually diseases managed symptomaticcaly like type 1/II diabetes managed through insulin)
emotional narratives and the desperation of patients or caregivers are powerful motivators for pursuing treatments despite uncertain benefit.
How do policymakers and funders sometimes respond during urgent health crises?
They may lower their evidence standards, allowing faster approval or access to treatments that are only “good enough for now.”
becomes ready faster but risk of not knowing if its truly effective or safe in broad human population
Why is independently verifiable evidence essential in science?
It ensures patient safety and scientific reliability by confirming findings through independent, rigorously controlled studies.
What is a downside of demanding strong evidence before approving treatments?
It can delay lifesaving innovations, especially during rapidly evolving health crises or for rare conditions.
How common is it for promising therapies to succeed after replication in large trials?
Only about 10% of therapies remain effective when tested in large-scale trials.
several hundred small moelcule kinase inhibitors have failed in clinical trials
Example of drugs in clincial practise long before we fully understood their safety profile and mechanism of action
General anesthesia was used for 200 years before we understood how they alter consciousness and perception
Sensationalism
The exaggeration or misrepresentation of scientific findings to attract attention or create excitement, often at the expense of accuracy.
sensational claims distort the nature, timing or impact of scientific discoveries dueling unrelaistic expectations
oversimplification and ommision of uncertainty can undermine sound policy descisions.
sensational claims can drive inappropriate clinical practise changes or investments in the health economy that are difficlt to reverse
Whats the strongest form of evidence>
Empirical evidence
Evidence Triage
The rapid evaluation and prioritization of available research to determine which findings are most credible and relevant for decision-making, particularly in emergency settings.
the pressure to act quickly in health emergencues can lower standards dor evidence randking and acceptance
Evidence Hierarchy
A ranking of study designs by strength of evidence — from animal studies (weakest) to meta-analyses and clinical guidelines (strongest).
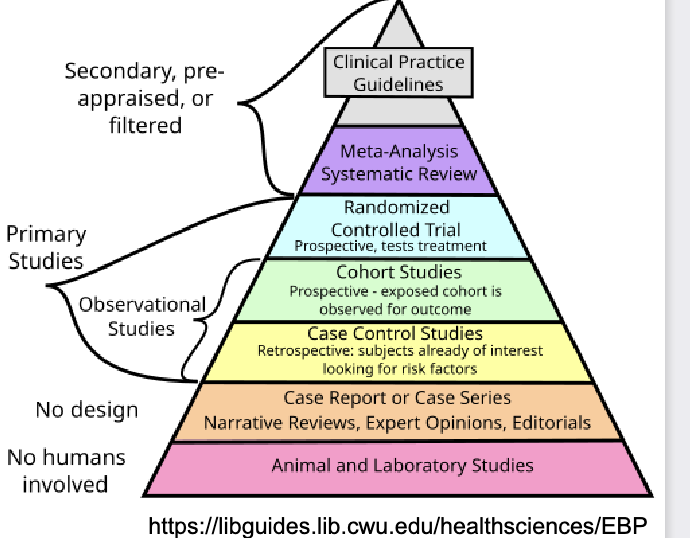
Triage
process of rapidly assessing and prioritzing a large volume of gathered evidence to focus on the most relevant information
Molnupiravir (Lagevrio)
An antiviral prodrug that introduces mutations into viral RNA to prevent replication; approved under emergency conditions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Prodrug
A compound that becomes pharmacologically active after being metabolized in the body.
How does molnupiravir work against viruses?
It’s incorporated into the viral RNA genome, causing random mutations that make the virus non-functional and easier for the body to clear. (eventually body clears virus until its no longer effecting cells)
mutations occur after the virus replicates inside the cell — leading to error accumulation in its RNA.