IMOS Module 5 - Concrete
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
UF IDS2935: Impacts of Material Science Fall 2024
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Cement v. concrete
cement is binder for concrete
concrete is the composite (clinker + sand + rock)
Clinker process
<700C = water is lost
700-900C = calcination (CaCO3 = CaO + CO2)
1150-1200C = liquid phase
1250-1450C = clinker nodules form
after cooling = add gypsum to control setting
clinker is ground into Portlad Cement
Bitumen
various mixtures of hydrocarbons with nonmetallic derivatives that occur naturally after heat-refining natural substances
Properties of Bitumen
polymeric material (carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur)
not a unique molecular composition
found as natural surface deposits
easily collected
easily processed
compositionally stable at <300F
Uses for Bitumen
applied as coating/adhesive
used for paving and roofing
Advantages of concrete
can be mixed offsite
cures at room temp.
moldable into any shape
cheap
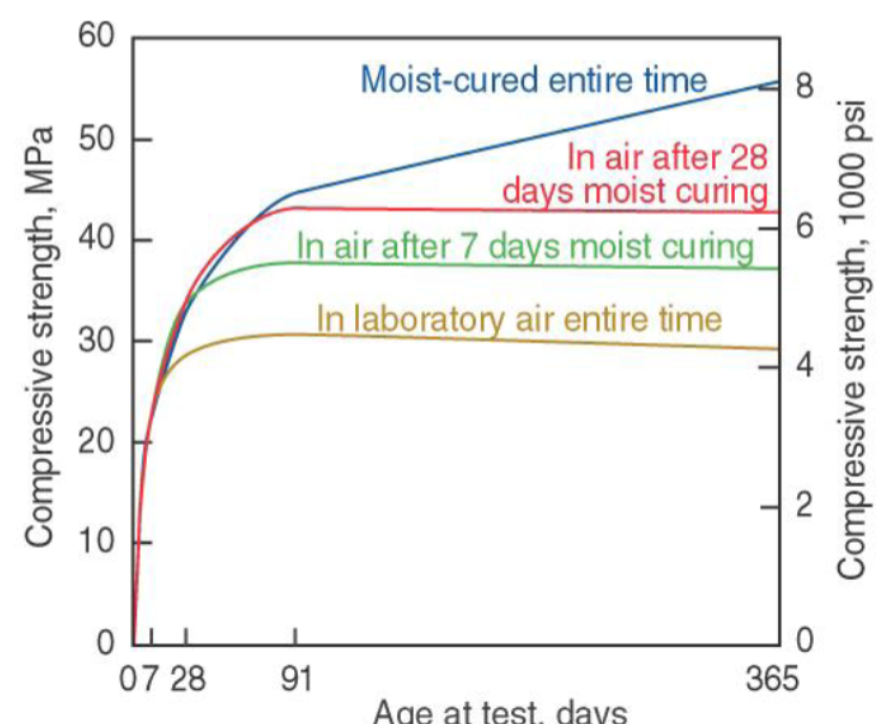
Disadvantages of concrete
relative durability
CO2 emission (7% of worldwide release)
1 ton of concrete = 1 ton of CO2
Future for concrete
use non-fossil fuels for heating (solar power)
green cement uses recycled material
zerocrete uses 100% recycled Flyash based cement
self-healing concrete uses bacteria and calcium lactate and heal cracks
Steel v. concrete
compression: good v. good
tension: good v. bad
thermal expansion coefficient is the same
alkaline environment reduces corrosion
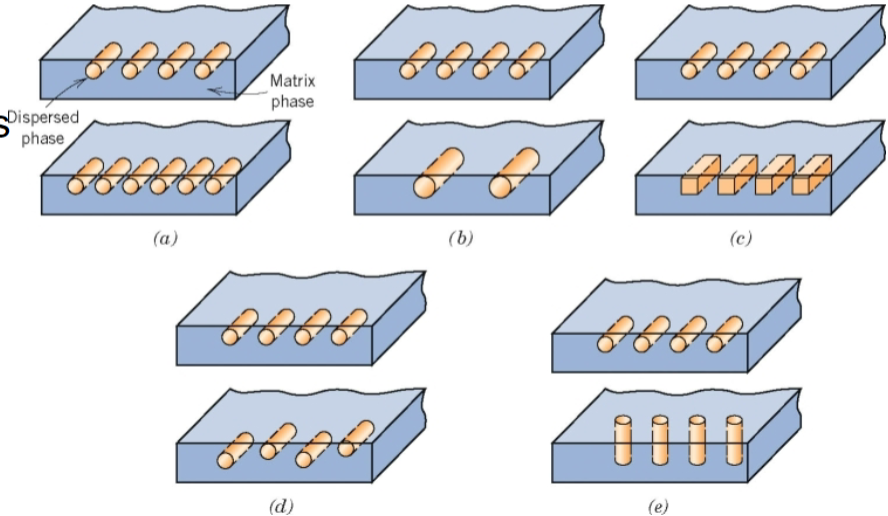
Composites
a material constructed from two or more components in greater physical or chemical properties are derived from the combination of compositions or structures
Properties of composites
componenets remain physically seperated
not naturally occuring
matrix and dispered phase
dependent on concentrartion, size, shape, distribution, orientation
concrete history
Ancient Greece used lime and pebbles
Romans use Roman concrete
Roman Empire falls and roman concrete recipe is lost
Middle Ages concrete is weak
John Smeaton discovers how to make cement hydraulic
USA uses cement for the Erie Canal
Portland Cement is invented
reinforced concrete is invented
first reinfoced concrete bridge is built in San Fransisco
Portland Cemenet
C + A + S + H + water + sand + rock
Roman concrete
used for compression structures (cantenary)
used different varieties for the dome of Parthenon
used for roads, buildings, aqueducts
sets underwater
self-healing properties
Roman concrete composition
quick lime formed from limestone and heat (CaCO3 = CaO + CO2)
fine pozzolana (volcanic ash replaces sand (Al2O3 + SiO2)
Water (H2O)
C+ A + S + H
Greek v. Roman architecture
doric
ionic
corinthian
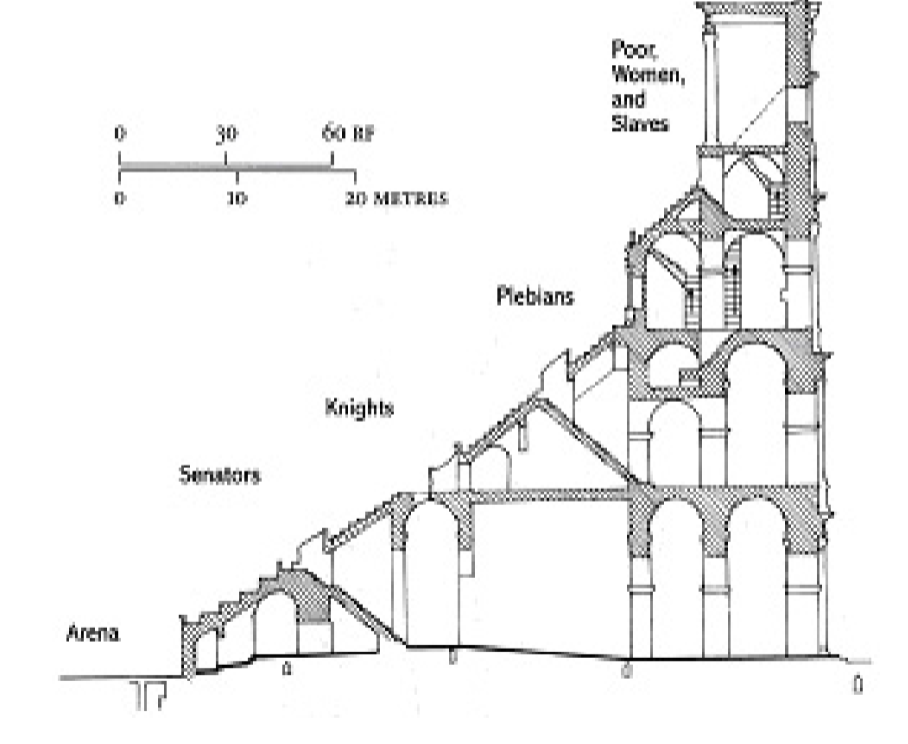
Class order of Romans
colessium seating reinforces class order