Chemistry - 3 Structure and Bonding - 3.7 Giant Covalent Structures & 3.8 Fullerenes and Graphene
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
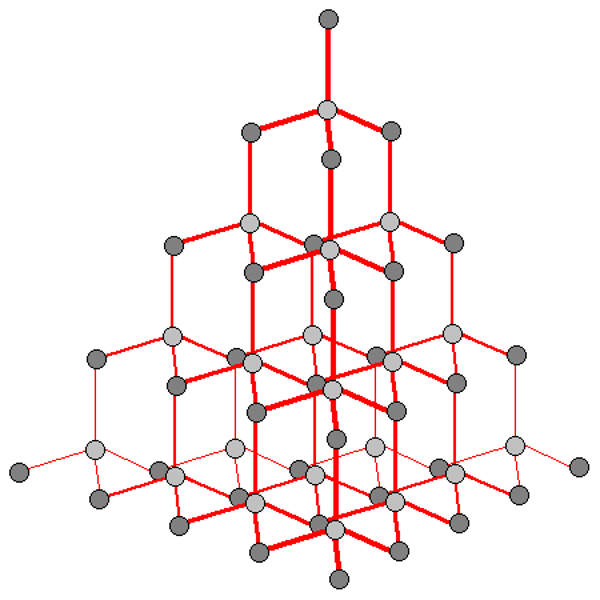
Diamond
formed by huge networks of covelently bonded carbon atoms, where each carbon atom is bonded to 4 others
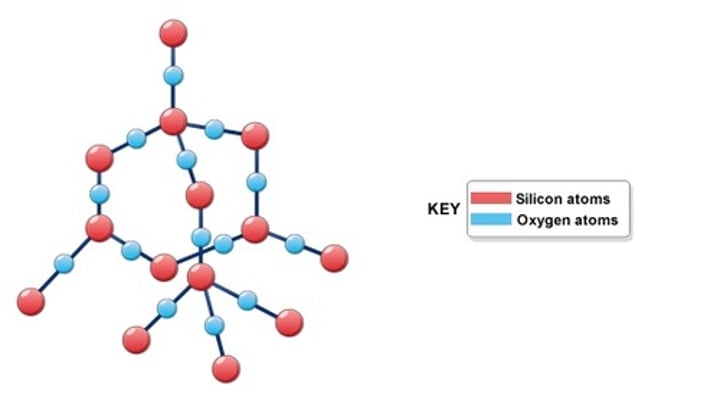
Silicon dioxide (SiO₂)
formed by huge networks of covalently bonded silicon and oxygen
Graphite
formed by huge networks of covalently bonded carbon atoms, where each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
Properties of substances with a giant covalent structure [3]:
- very high melting and boiling points
- insoluble in water
- (apart from graphite) hard and do not conduct electricity
In graphite [3]:
- each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
- they are arranged in hexagons
- they are arranged in layers without covalent bonds between them
Why does graphite conduct electricity (and thermal energy)? [5]
- each carbon atom is only bonded 3 times
- carbon atoms have 4 electrons in their other shell available for bonding
- this leaves 1 spare electron from each atom
- these electrons are delocalised and can move freely along the layers of graphite
- they can carry charges (and thermal energy)
Fullerene
a form of carbon that consists of atoms arranged in the shape of a hollow sphere
The structure of fullerenes is based on ... rings of carbon atoms
hexagona, pentagonal or heptagonal
Carbon nanotubes
tiny, hollow tubes made of carbon atoms (cylindrical fullerenes)
First fullerene [3]
- 60 carbon atoms
- called 'buckminsterfullerene' or 'bucky-ball'
- named after Buckminster Fuller, a Canadian architect who built a similar-looking building
Useful properties of carbon nanotubes [2]:
- high tensile strength
- high electrical and thermal conductivity
Uses for carbon nanotubes [2]:
- tennis rackets
- electronics
Bucky-onion
a fullerene with a ball within a ball
How could fullerenes be used? [3]
- deliver drugs or radioactive atoms (cancer treatment) to specific locations in the body
- lubricants
- catalysts (due to large surface area to volume ratio of nanoparticles)
Graphene
a single layer of graphite, one atom thick
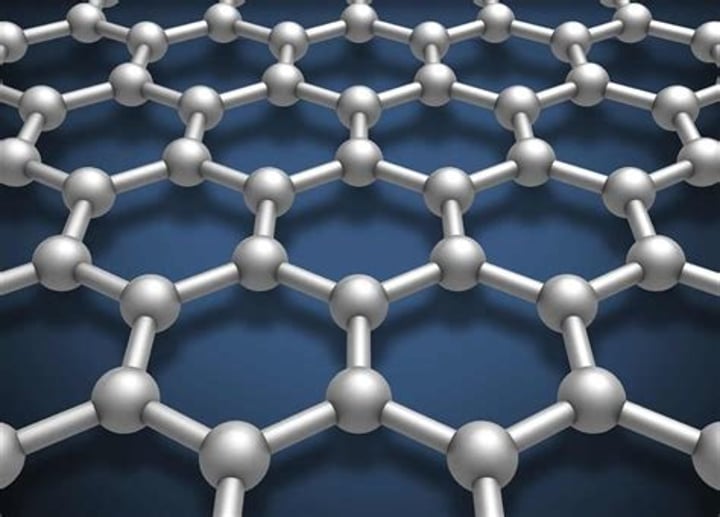
Properties of graphene [4]:
- excellent thermal and electrical conductor
- low density
- most reactive form of carbon
- incredibly strong