Aviation Weather Test 2 Study Lessons 6-9
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Water Vapor
Water in gas form
Where is half of all water vapor found?
Below 6,500 feet
How does composition change with an increase of water vapor?
All gases decrease and water (h20) would increase.
What does water vapor do?
Helps transfer heat energy and helps regulate the temperature of earth.
How is water vapor measured?
Relative humidity and dew point
What is ITCZ?
Inter-tropical convergence zone at equator and has many cumulonimbus clouds because of the intense heat at the equator which causes severe thunderstorms.
Why are the highest clouds found at the ITCZ?
More heat which equals more water vapor.
Hydrologic Cycle
Involves the continuous circulation of water in Earth’s atmosphere.
When is the water cycle considered balanced?
When the amount of water evaporating is the same amount that falls back as precipitation.
Evaporation
When liquid becomes a gas.
Where is the primary source of evaporation?
The oceans
Transpiration
the evaporation of water from plants. It is largely controlled by the humidity of the atmosphere and the moisture content of the soil.
Condensation
Water vapor (gas) becomes liquid.
Precipitation
Water that falls onto earth (ex. rain, snow,hail,etc.)
Runoff
Eccessive precipitation leading to the ground becoming saturated and not able to absorb more water which flows into streams and rivers.
Sensible heating
An object temperature changes without changing its phase. (ex. heating water to less than 100 degrees C to increase temp w/o changing phase/ making it boil).
Latent heat
The heat required (absorbed or released) for an object to change phase, expressed in joules per gram.
What phases involve the absorption of heat?
Melting, evaporation, sublimation
What phases involve the release of heat?
Freezing, condensation, deposition
Deposition
Water vapor turns into ice w/o becoming liquid. (ex. frost)
Sublimation
Solid to gas w/o passing through liquid (ex. dry ice)
Saturation
Max amount of water vapor an air parcel can hold at a given temp and pressure. (Saturated= air parcel is full) (Unsaturated= air parcel is not full).
What forms when saturation occurs and water vapor condenses?
Clouds, fog, dew
Relative Humidity
How full the air is with water vapor. Amount of water vapor that air can hold depends on air temperature (%).
What relative humidity comes with warm temps?
Low
What relative humidity comes with cold temps?
High
Relative Humidity Equation
Water vapor content/ capacity x 100
Dew point
Temperature air parcel must be cooled to allow for saturation/ turn into liquid like dew or fog. (degrees C)
What does a higher dew point=?
More moisture, regardless of current temperature.
Is relative humidity or dew point a better indicator of how humid it feels outside?
Dew point
Atmospheric Pressure
The force exerted by the weight of the atmosphere.
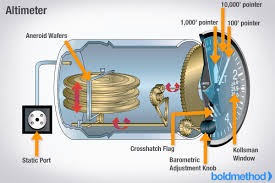
Barometer
Device that measures pressure.
What does a barometer do when high pressure is present?
Contract
What does a barometer do when low pressure is present (up at altitude)?
Expands
Standard pressure (mb)
1013.2mb
Standard pressure (inHg)
29.92 inHg
Station Pressure
Pressure measured at an airport, this is what is put into an altimeter.
Is pressure higher or lower at high altitudes?
Lower
When does pressure vary?
With altitude, tempurature, and water vapor
Mean sea level (MSL)
Common reference to compare station pressures between stations at different altitudes.
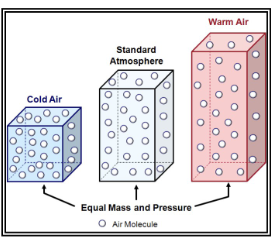
Density
How closley molecules are packed together. The closer they are the greater the density.
Is density high or low with high temperatures?
Low
Is density high or low with low temperatures?
High
How does volume change with density?
As volume increases, density decreases, as volume decreases density increases.
How does density effect pressure?
An air parcel with a high pressure is denser than an air parcel with a low pressure.
Does density increase or decrease with height?
Decrease
Is it better for the aircraft to fly in cold or hot weather?
Cold
Is air with a greater amount of water vapor more or less dense than air with less water vapor?
less dense
Where do you enter the barometric pressure?
In the kollsman window
True altitude
Actual vertical distance above mean sea level.
Indicated altitude
What is indicated on the altimeter.
Pressure altitude
Altitude at standard temperature/ pressure (29.92)
Density Altitude
Pressure altitude corrected for non-standard temperatures.
Corrected altitude
Correcting true altitude for temperature
At what altitude does everyone set their altimeter to 29.92?
18,000 feet
What does higher density altitude do to aircraft performace?
Decreases performance
In what three ways does high density altitude reduce performance?
reduces power b/c engine takes in less air
reduces thrust b/c of less air for propeller
reduces lift because light air exerts less force on airplane
On cold days air is…
Denser which equals lower density altitude
On hot days air is…
Less dense which equals higher density altitudes.
Hadley Cell
Starts at equator and is a factor of tropical and subtropical climates.
Ferrel Cell
Mid latitude cell that distributes heat to polar and hadley cells.
Polar Cell
Cell over polar regions where air sinks once over pole
As air warms it…
Ascends, leading to low pressure at the surface.
As air cools it…
Descends, leading to high pressure at the surface.
Jet Streams
Narrow bands of strong wind in the upper levels of the atmosphere blowing from west to east. (found between each cell)
When are jet streams generally stronger?
In the winter
What do jet streams follow?
Boundaries of hot and cold air.
Where does the jet stream shift as the sun’s elevation increases in the spring?
North towards Canada
In autumn when the suns elevation decreases where does the jet stream move?
To the south towards the U.S.
How does high pressure move in the northern hemisphere?
Clockwise
How does low pressure move in the northern hemisphere?
Counterclockwise
Pressure gradient force
Force that pushes air from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure
What three forces affect the wind?
Pressure gradient force, coriolis force, friction
What pressure is exerted from cold air?
High pressure due to cold air being more dense .
What pressure is exerted from warm air?
Low pressure due to warm air being less dense.
How do pressures follow each other?
High follows low
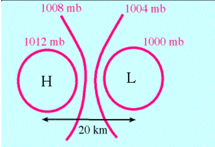
What does close spacing of isobars indicate?
Stronger pressure gradient force which results in stronger winds.
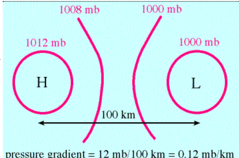
What does far spacing of isobars indicate?
Weaker pressure gradient force which results in weaker winds.
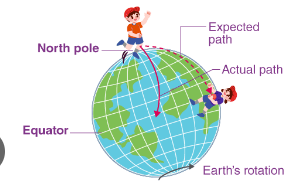
Coriolis force
Force that deflects air to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
What happens to the coriolis force as wind speed increases or decreases?
It increases or decreses with the wind.
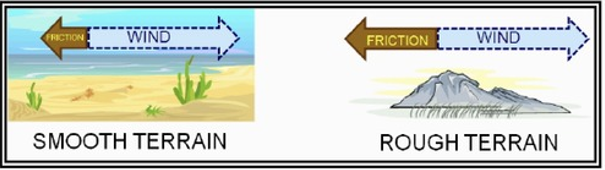
Friction
Slows down the wind.
When you go higher in the atmosphere is there more or less friction?
Less
Sea Breeze
Coastal local wind that blows from the sea to the land.
What causes sea breezes?
Temperature differences when the sea is colder than the land.
What is the sea breeze direction at surface?
From sea to land.
What is the sea breeze direction at altitude?
From land to sea.
Sea breeze front
Boundary where cold air and warm air meet.
What is Florida?
A peninsula
What occurs with a sea breeze collision?
Causes air to rise which creates thunderstorms.
Land breeze
Coastal wind that blows from land to sea at night when the land’s temperature is cooler than the ocean’s.
Lake breeze
A local wind that blows from the surface of a large lake onto the shores.
How does a shallow lake warm up?
Warms up rapidly and is less effective than a deep lake.