PHYSCI REVIEWER FOR MIDTERMS
5.0(1)Studied by 9 people
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Last updated 11:58 AM on 4/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
BIG BANG
_____ created all the matter and energy in the universe.
2
New cards
HYDROGEN
The __**first atom**__ created moments after the Big Bang.
3
New cards
HELIUM
The __**alpha particle**__ created after the Big Bang.
4
New cards
NUCLEOSYNTHESIS
This is the process in which a nucleus is either combined with another nucleus or splits into small nuclei.
5
New cards
NUCLEAR FISSION
The process of splitting an atom into two or more smaller ones.
6
New cards
NUCLEAR FUSION
The process of combining two or more smaller atoms into a larger one.
7
New cards
RADIOACTIVITY
It is the emission of energetic particles of an atom.
8
New cards
ATOM
It comprises of 3 sub parts: protons + neutrons + orbiting electrons.
9
New cards
ISOTOPES
Particular element contains the same number, but different numbers of neutrons.
\
* Most of it occur naturally are stable
* Unstable _____ can become stable by releasing different types of particles (radioactive decay)
\
* Most of it occur naturally are stable
* Unstable _____ can become stable by releasing different types of particles (radioactive decay)
10
New cards
RADIOISOTOPES
An unstable form of a chemical element that releases radiation as it breaks down and becomes more stable. Radioisotopes may occur in nature or be made in a laboratory. In medicine, they are used in imaging tests and in treatment. Also called radionuclide.
11
New cards
**RADIOACTIVE DECAY RESULTS IN THE EMISSION OF EITHER:**
* Alpha particles
* Negative beta particles
* Positive beta particle
* Gamma-ray
* Negative beta particles
* Positive beta particle
* Gamma-ray
12
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**ALPHA DECAY**__
\-4 in MASS NUMBER; -2 in ATOMIC NUMBER
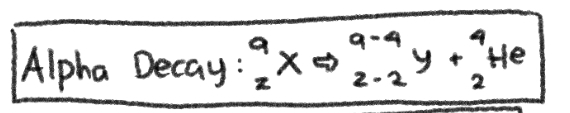
13
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**BETA DECAY**__
No Change in Mass NUMBER; +1 in ATOMIC NUMBER
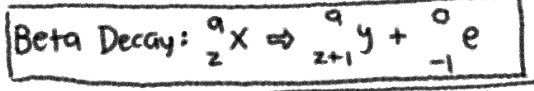
14
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**ELECTRON CAPTURE**__
No Change in MASS NUMBER; -1 in ATOMIC NUMBER
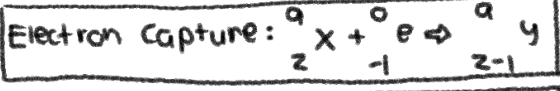
15
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**POSITRON EMISSION**__
No Change in MASS NUMBER; +1 in ATOMIC NUMBER
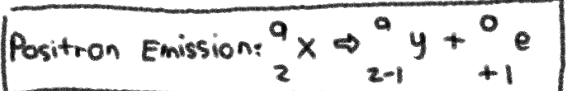
16
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**NEUTRON CAPTURE**__
\+1 in MASS NUMBER; No Change in ATOMIC NUMBER
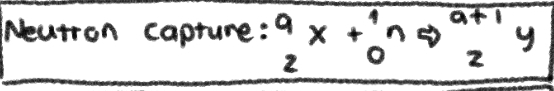
17
New cards
NUCLEAR REACTION of __**GAMMA DECAY**__
No Change in MASS NUMBER and ATOMIC NUMBER
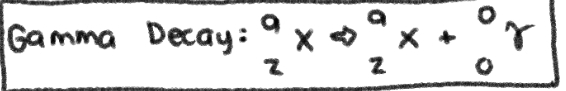
18
New cards
NUCLEAR STABILITY
* The strong nuclear force holds all nuclei together
* Otherwise protons would repel each other
* Neutrons space out protons and make the nucleus stable
* Not all isotopes are radioactive
* Only stable nuclei decay
* In smaller atoms, stable isotopes have equal numbers of protons and neutrons
* In larger atoms, stable isotopes will have more neutrons than protons
* Too many or too few neutrons makes the unstable nucleus
* Otherwise protons would repel each other
* Neutrons space out protons and make the nucleus stable
* Not all isotopes are radioactive
* Only stable nuclei decay
* In smaller atoms, stable isotopes have equal numbers of protons and neutrons
* In larger atoms, stable isotopes will have more neutrons than protons
* Too many or too few neutrons makes the unstable nucleus
19
New cards
REDSHIFT
* The wavelengths of the light emitted by distant objects is elongated as it travels to earth
* The longer he light travels, the more it gets _ed
* The longer he light travels, the more it gets _ed
20
New cards
__**ELEMENTS FORMED**__ AFTER CERTAIN CIRCUMSTANCES: (STELLAR FORMATION AND EVOLUTION Lesson)
* Big Bang Nucleosynthesis - Light Elements are Formed (HYDROGEN, HELIUM, LITHIUM, BERYLLIUM)
* Stellar Formation and Evolution - (BORON, CARBON, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, FLUORINE, NEON, IRON)
* Stellar Explosion/Supernova Nucleosynthesis - Elements Heavier Than Fe 56
* Laboratory - URANIUM 238
* Stellar Formation and Evolution - (BORON, CARBON, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, FLUORINE, NEON, IRON)
* Stellar Explosion/Supernova Nucleosynthesis - Elements Heavier Than Fe 56
* Laboratory - URANIUM 238
21
New cards
QUARK
Is a fundamental constituent of matter and defined as an elementary particle. These _____s combine to produce composite particles called hadrons, the most stable of which are neutrons and protons which are the components of atomic nuclei.
22
New cards
FORMATION OF __**LIGHT ELEMENTS**__

23
New cards
__**MAIN SEQUENCE STAR**__

24
New cards
__**RED GIANT**__

25
New cards
__**WHITE DWARF**__

26
New cards
**FORMATION OF HEAVY ELEMENTS FROM THE STAR**
* If a massive star has enough mass such as that temperature and pressure increase to a point where carbon fusion can occur.
* Neon then becomes concentrated at the core, then underwent fusion to produce oxygen.
* When oxygen becomes concentrated at the core, fusion continued, producing Silicon.
* The fusion of Si produced radioactive Ni, which then decayed to Iron. However, the production of elements stopped when Fe was formed.
* Neon then becomes concentrated at the core, then underwent fusion to produce oxygen.
* When oxygen becomes concentrated at the core, fusion continued, producing Silicon.
* The fusion of Si produced radioactive Ni, which then decayed to Iron. However, the production of elements stopped when Fe was formed.
27
New cards
STELLAR EXPLOSION
* As the red giant exhausted, its core started to collapse which eventually led to the explosion of a star.
* This explosion called a supernova releases a large amount of energy. It produced elements heavier than Fe through neutrons capture radioactive decay.
* This explosion called a supernova releases a large amount of energy. It produced elements heavier than Fe through neutrons capture radioactive decay.
28
New cards
Electron Distribution
It shows the distribution of electrons in the different orbitals in an atom.
29
New cards
Chemical Bonding
It is an electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of an atom.
30
New cards
Electron Configuration
It uses the symbols of the orbitals and the number of electrons that occupy each orbital.
31
New cards
ELECTRON CONFIGURATION MNEMONICS
S = 2 and Below; P = 6 and Below; D = 10 and Below; F = 14 and Below
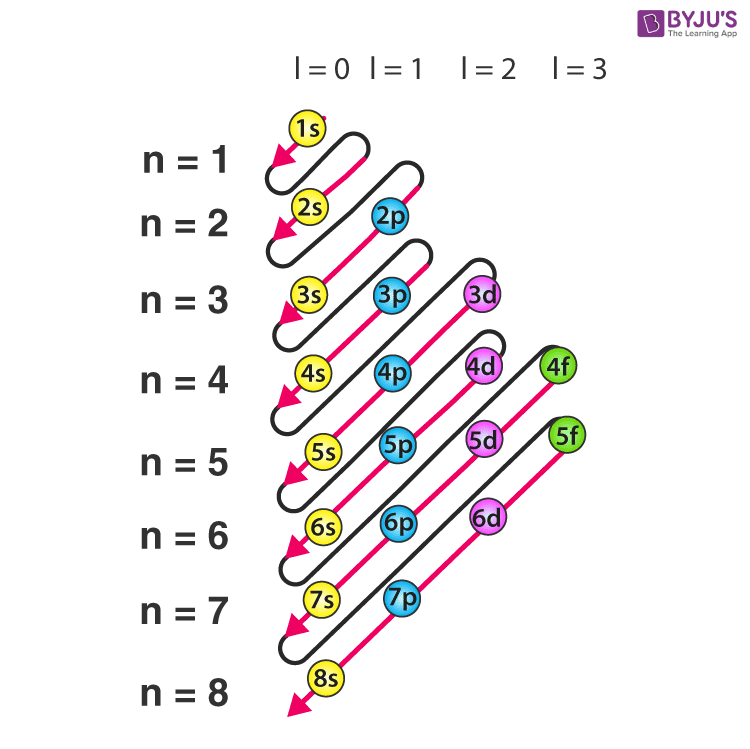
32
New cards
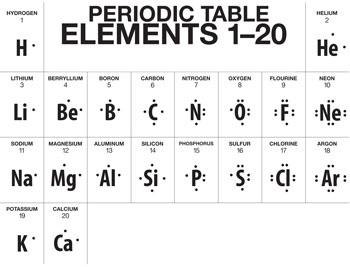
LEWIS DOT SYMBOL
* It consists of the symbol of an element surrounded by one or more dots.
* Each dot corresponds to every valence electron found in an atom of the element.
* Valence electrons refer to the electrons found in the outermost shell of an orbital.
* Valence electrons are the ones involved in chemical reactions.
* Each dot corresponds to every valence electron found in an atom of the element.
* Valence electrons refer to the electrons found in the outermost shell of an orbital.
* Valence electrons are the ones involved in chemical reactions.
33
New cards
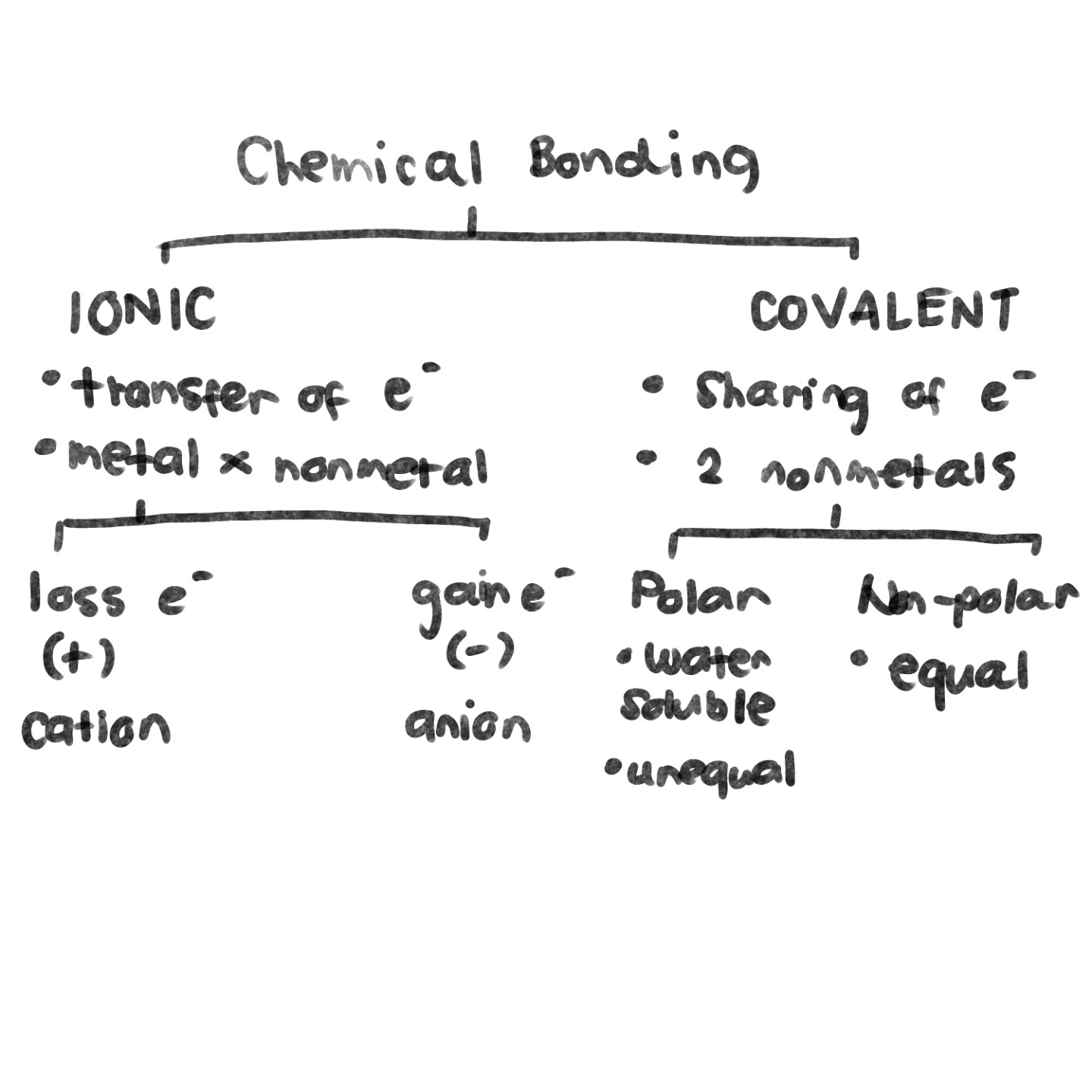
CHEMICAL BOND
Is an electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of an atom. This type of attraction is called an *Intramolecular force.*
* It can be ionic, covalent, and metallic.
* It can be ionic, covalent, and metallic.
34
New cards
IONIC BOND (EN ≥ 1.7 )
* It results from the transfer of one or more valence electrons from one atom to another.
* This bond exists between a metal and a nonmetal due to a large difference in their electronegative.
* This bond exists between a metal and a nonmetal due to a large difference in their electronegative.
35
New cards
POLAR COVALENT BOND (1.7 > EN > 0.4)
* It refers to the bond in which bounded atoms have an unequal sharing of electrons.
* This unequal sharing of electrons may be regarded as “partial electron transfer” or a shift in electron density.
* This unequal sharing of electrons may be regarded as “partial electron transfer” or a shift in electron density.
36
New cards
NONPOLAR COVALENT BOND (EN ≤ 0.4)
* It is a bond in which electrons are equally shared by the bonded atoms.
* This equal sharing of electrons indicates a balanced distribution of electrical charges.
* This equal sharing of electrons indicates a balanced distribution of electrical charges.
37
New cards
NOTES for CHEMICAL BONDING
An __**ANION**__ may be defined as an atom or molecule that is __*negatively charged*__. A __**CATION**__ may be defined as an atom or molecule that is __*positively charged*__.
38
New cards
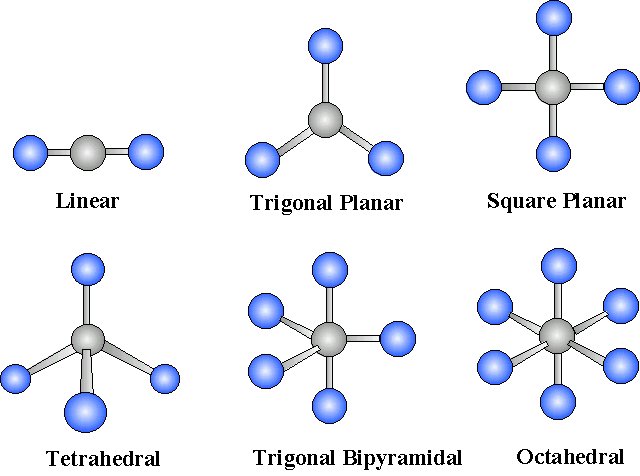
**VALENCE-SHELL ELECTRON PAIR REPULSION (VSEPR) MODEL**
The three-dimensional shape of a molecule can be predicted using its Lewis Structure together with VSEPR model.
39
New cards
SYMMETRICAL / NON-POLAR
* Linear
* Tetrahedral
* Trigonal Planar
* Trigonal Bipyramidal
* Octahedral
* Tetrahedral
* Trigonal Planar
* Trigonal Bipyramidal
* Octahedral
40
New cards
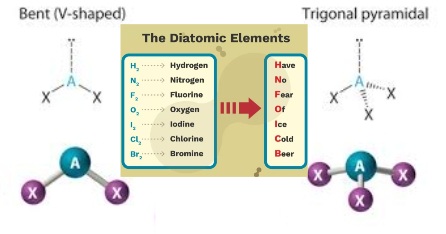
ASYMMETRICAL / POLAR
* Bent
* Trigonal Pyramidal
* Diatomic Elements
* Trigonal Pyramidal
* Diatomic Elements