unit 0
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
persian empire (photo)
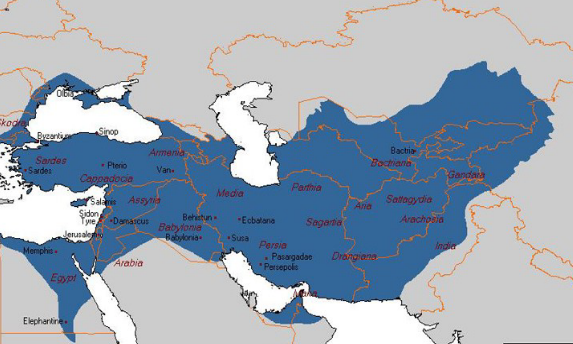
persia empire bullet points
military & administration powerhouse
like god
single central administration
cyrpurs & satraps
built beauracracy
religious tolerance
in modern iran
multi-ethnic
alchemeid
cyprus the great
ruler of persian empire
satraps
got stuff done on behalf of emporer, persia. policites enforced by these people.
persian empire thought their emporer was basically ___
god
complex bureaucracy
made my persians. had adminsatrators, tax collectors, record keepers, etc. had people do certain things for the govt.
persia had tolerance of their people’s religion and culture, which made things easier since no one felt oppressed of their individuality (to a degree)
persia had tolerance of their people’s religion and culture, which made things easier since no one felt oppressed of their individuality (to a degree)
zoastrianism
persian religion
monotheistic
zoroaster
in iran (most)
to gain knowledge = good
human free will & the ability to choose good or eveil
ignorance = bad
universal battle of Good & Evil
there is universal good and evil
good for the sake of good
how did zoastrianism bettered the __ empire?
persian
it helped to push knowledge forward and therefore the progress of the empire. knowledge & good
greek empire (west & east) photo
greeks were ___ of persians
polar-opposites
greek characteristics bullet points
democracy
citizen particpatoin
polytheism
city-states
athens
without divine monarch. vase w/ hate (full democracy), lots of slavery
sparta
had senates, 1 king home another goes to war
peloponnesian war bullet points
between athens and sparta.
war of power
other city-states allied with either athens or sparta
greek city-states lacked ___
unity
greek city states had the same cultural thread in pursuing
medicine, science philosphy, etc. first knowledge “aquired” by the greeks
hellenistic period
period of the greeks where there was mass expansion of greek culture and political dominance. greek rule
machedonian phillipp ii
the king that united the greek sin the hellenistic period. his son continued his work
alexander the great
son of phillip king. greatest military campaign. macedon & greek federation led. ended persian rule
greek culture was embedded in cities by ___. locations
libraries. knowledge spread in central asia, north africa, middle east
settlers of greek cities in hellenistic period were called
alexandria
power of greek people were reserved to only __
men
legacy of greeks & persians
ofc philosophies and concepts
hellenistic states after Alexander had generals that took over. adopted persian gov
skepticism to get logic and observation
socrates, plato aristotle in writings and concetps
influenced arab, persian, indian,and western math
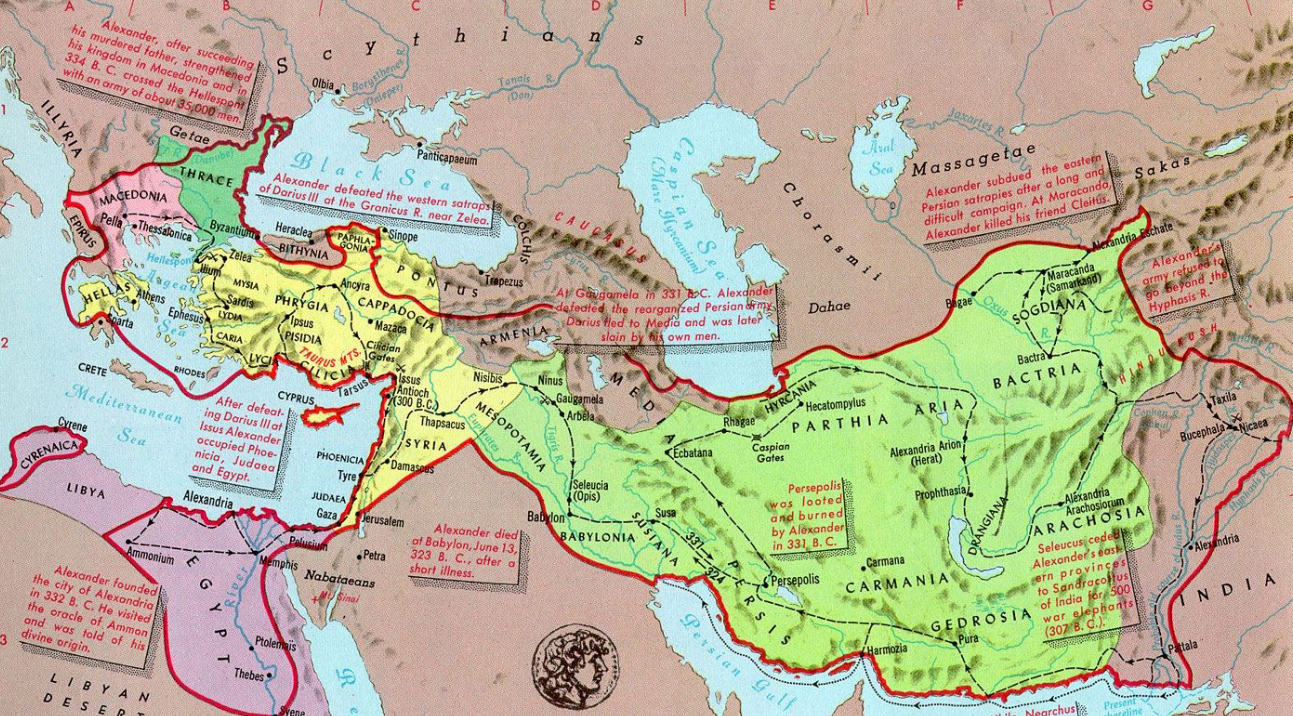
alexander the greats empire (greece photo)
roman republic (bullet points)
city-states
modern-day italy
conquered local latin cities - 500s BCE
ruled by elected senate
patricians (rich) & pleabs (everyone)
went to modern day spain → gaul (france)→ then to greek colonies
after greek armies, regional empires of carthage and macedona became opps
was able to eventually defeat carthage, punic wars
after carthage died, they targeted hellenistic states and became the rules of Meditteranean Sea
heavily borrowed from greek culture & administration
bureaucracy
punic wars (bullet points)
control over aegates & carthage
elephants & hannibal (general)
roman retaliation. boats & killed all men and enslaved women & children
julious caesar
intiated empire of rome. claimed to be emperor because just had an army. continued tradition of conquest
roman army size grew bec.
its rewards, land grants (from conguered land), etc.
upperclass elites in rome had
long estates, tax breaks, political positions
romans gave their citizenshipto
anyone that they conquered. aka not automatically slaves !!
if u were in trouble in rome
u were punished greatly
towards the end of rome, rome split in
west & east. they split becuase people were invading and they could’nt tfully protect themselves. east became byzantine empire and outlasted the west.
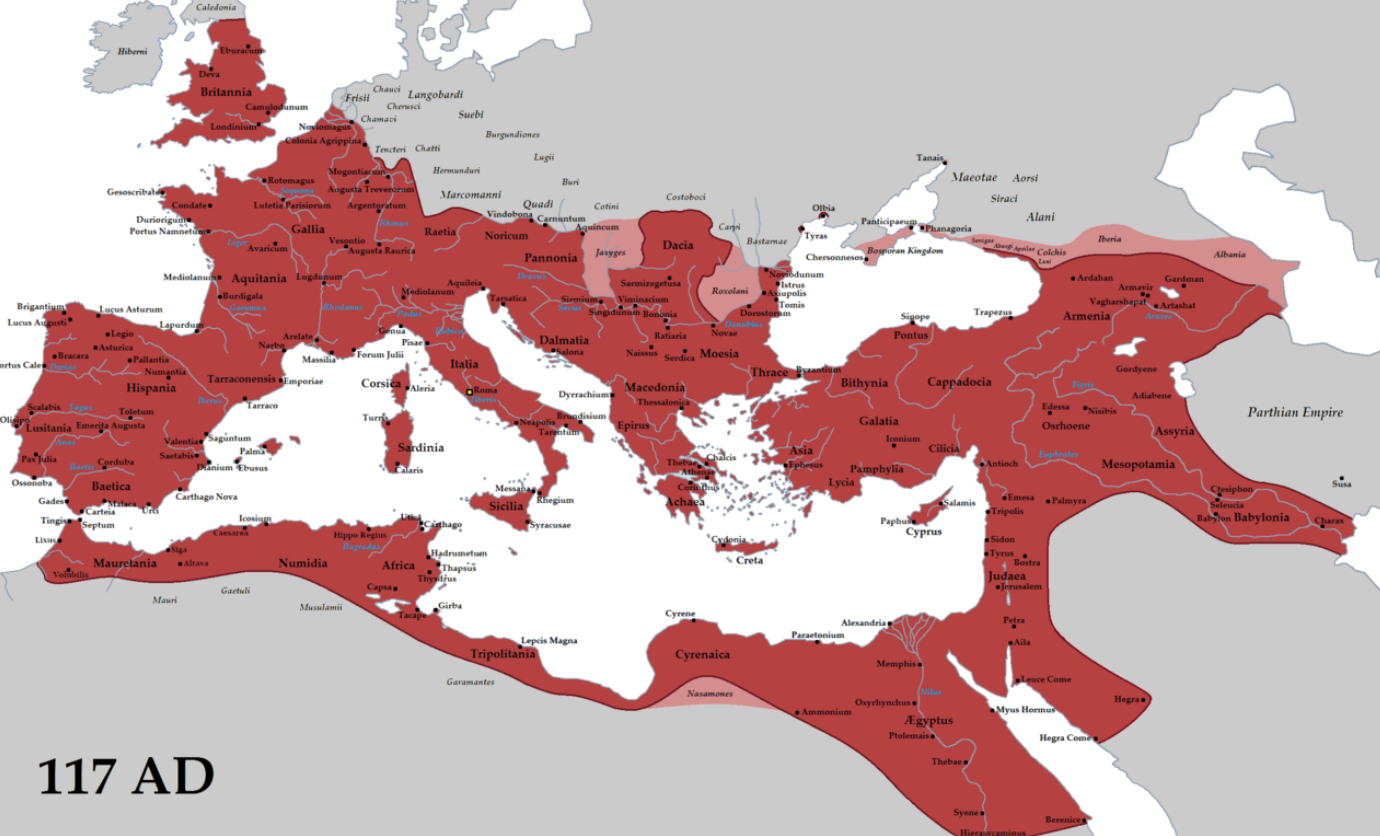
expansion of rome after caesar. photo
golden age of india
centralized india in 3rd century CE. known as gupta empire
sri gupta
king of gupta empire in india
golden age of india bullet points
had centralized state system
progress. math, poetry, science, etc.
created modern algebraic system, concept of zero, chess. earth rotates on axis, etc.
ended due to internal stike & hunnic invaders.
dynasty
line of rulers
warring states period and its effects
in china. constant war, death, famine, instability.
because of this, people started to think. created:
confucianism & legalism
legalism
state should be built by moral law, secular laws, positions based on individual merit, not religiosity or class
confucianism:
believing that authorities should take care of the little ones, and the little ones should fully obey
qin dynasty bullet points
after warring period of china
defeated other kingoms
no record or contact with western empires (persia, greece, rome) they had to rely on themselves to create a large centralized empire in east asia
established foundations for state imperial (emperorial) systems for later chinese dynasties
shihuagdi
chinese admiistrator behind qin dynasty.
shihuangdi created
effective central bureaucracy
public roads
common currency
established formal written language
push back traditional enemy of china, xiongnu confederacy in the north
making peasants build first sections of great wall of china
chang’an
imperial capital city
han dynasty
confucianism survived thru qin
confucianism adopted in han dynasty as the official philosophy under emperor wu
fall by xiongu confederacy
liu bang (bullet points)
rebel that defeated his rivals and then controlled china.
made the golden age of china
expanded trade thru world and roman empire in the silk roads
mauryan empire
ashoka the great emperor was buddhist so his influence made india more buddhist. built temples, finances missionares, etc.
caste system was so rigid in hindusim that is created
buddhism
dhmaa
fulfilling duty in hinduism
brhama
the universe in hinduism`
judaism bullet points
started as polythestic
started having regional religious characteristics of mesopotamian region
Tanakh or Torah
zoroastrianism influenced judaism
after exile of babylon, they went back to israel and judah at the hands of th persian empire
the shift of theology was the second-temple judaism
following cyrpurs the great in the second temple in jerusalem
shifted to a more zoroastrianism model
2nd temple judaism bullet points
monotheism (yaweh)
enternal battle berween good and evil
we have free will to choose good and evil
promise of a future messiah to tip the scale to good
christianity
judaism laid a foundation for christianity
began around 20-33 CE
disciples in israel began following the miracles and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus was the incarnation of the Jewish messiah, though they though he would be some sort of military leader
promise of messiah was appealing especially since the oppresions experienced in Rome
led to revolt, Roman Empire opposed Chrisitnaity and its followers
missionaries like Paul spread Christianity to Rome and across other lands
missions and merchants continued to spread in Rome
islam bullet points
writings of the Prophet Muhammad (the Quran)
muhammad was a religous, social, and political leader
the last prophet
combines several features of arab paganism, zoroastrianism, and judeo-christian beliefs
people who follow and believe in the Quran, no matter any division (race, etc.) anyone can be Muslim
monotheistic
goal: to convert people to Islam, duty to help your community, etc
5 pillars of islam
there’s Allah and Muhammad is his messenger
5 times a day prayer
giving to charity/poor
go to mecca girlies (hajj) 🎀✨
fasting for Ramadan
prophet muhammad and his jourey (bullet points)
his audience included a lot of polytheistic religion
went to medina after they kicked him out of mecca; converted lots of arab pagans there
converted almost entire arab peninsula
ulama
scholars that had coolio jobs (judges, interpreters, admins, prayer leader, reciters of quran, preservers of islamic law)
sufis
thought that islamic civiliation was a distraction to what muhammad’s time was abt.
focused on mystical aspect
focused on trying to achieve union with allah
believed that the strucutre (5 times prayer, etc.) was good for daily life, but did little to feel the presence of god
mainstream in 11000 to 1800
rashidun caliphate
rashidun caliphate: period of rapid Islam expansion
after the death of Muhammad, Muslims would be led by a caliph
this splited Islam - Sunni & Shia
Sunni & Shia
dhimmis
payed additional taxes
had some limits, but there was religous tolerance
the rashidun caliphate established how muslimes viewed non-muslims
juzya tax:
caliph
civil and religous leader that determines religous and state policy
dhimmis
the protected people. they (Jew & Christians) were protected by the Muslim state byt were treated as second-class
juzya tax
taxes to the dhimmis unless they convert to islam
Sunni
Muhammad did not designate someone
Shia
minority, oppressed. Muhammad designated Hazrat Ali
ummah
community of believers. islam
pastoral socieities
the effect of the neolithic revolution led to pastoral societies
farming was difficult here (ex. grasslands, deserts)
depended on their domesticated animals ofc
ex. sheep, goats, cattle, horses, camels, reindeer
animals can turn into meat, fiber, hides, milk
also used for transport and warfare
known as herders, nomads, pastoral societies
in Central Asia, Arabian Peninsula, Sahara, parts of eastern and southern Africa
permanently settled farmers
the good society
no chiefs, kings, etc.
in Eurasia, Africa, Americas
organizing themselves in kinships (lineages)
incorporated not only immediate and extended family
had a good degree of social and gender equality 😱
had cultural, artistic, and religious traditions
interacted continuously with neighbors
chiefdoms
more inequality, but honestly not that bad (if chief is good)
chiefs had to give back to their community in order to persuade their followers
generosity, ritual status, personal charisma
chiefs usually derived from senior lineage (first son of ancestor)
chiefs led:
important rituals & ceremonies
organized community for warfare
economic life
resolve internal conflicts
the chiefs collected stuff from commoners (food, manufactured goods, raw materials) → warriors, craftsmen, religious specialists, etc.
North America: eastern woodlands
larges chiefdom: Cahokia
modern St. Louis around 1200 C.E.
China civilization:
Islamic civilization:
European civilization:
China civilization: made bureaucracy, silk production, papermaking, papermaking, printing, gunpowder.
Islamic civilization: math, medicine, astronomy, metallurgy, water management
European civilization: scientific & industrial revs.
the environment shapes the culture, but also the culture shapes the environment
ex. greece had city states rather than unified body - bec. of mountainous terrain
ex. the dense rain forests in the narrow area of Panama inhibited contact between civilizations
ex. oceans that separated Afro-Eurasian world from Western Hemisphere
ex. southern mesopotamia w/ intense ag. soil turned into salt, barley replaced wheat
ex. Chinese civ. expansion toward Yangzi River valley (after 200 C.E.) sucked all the life of the forest and made the elephants leave
ex. Maya civilization: shaped the land for agriculture, led to deforestation and erosion of hillsides along with its droughts. led to the collapse of Mayans
upanishads
collection of sacred texts (we dk the authors) between 800 & 400 BCE
atman
individual human soul
moksha
liberation
samsara
reincarnation
karma
sarmsara depended on your personal actions in your current life
bhakti movement
devotion to one or another god and/or goddesses
south india moving forward
intense adoration and identification
vishnu: protector and preserver of creation
shiva: destruction
this sort of set the caste system aside and just allowed people to connect to the divine
more accessible to normal people than the sacrifices of brahmins
less structure
poetic tradition
buddhism points
8-fold path: cure to unfullfillment
3 suffereings: old, death, pain
rejects caste system
theravada buddhism
teaching of the elders
portrayed buddha as very wise but not divine
gods do play a small part for enlightenment
this was very rigorous branch of buddhism.
time consuming meditation, focus on monks and nuns seclusion, absence of “worldy” comforts
mahyana buddhism
greater accessibility
wide range of people beyond monks
nirvana can be achieved in 1 lifetime
focused more on compassion instead of wisdom and insight
bodhisattvas:
bodhisattvas
fully enlightened beings who postponed their nirvana to help suffering humanity
tibetan buddhism
7th century C.E.
gave special authority to lamas: learned teachers
emphasized awareness and prep for death
fusion of native tibetan traditions + hinduism
ceremonies of heavenly beings, art, music, complex meditations, etc.
texts created were the tibetan book of the dead
describes the stages of transitioning from life to death to rebirth
buddhism disappeared in india in 1200
the wealth of building monastaries kept it separated from normal people
brahmin priests and islam after 1000 CE were more than buddhism
new kind of hinduism popped up
silk roads:
china and meditteranean world
sea roads
indian ocean and south china sea; connected southern china and east africa
sand roads
linked north africa and mediterranean world in west africa