IGCSE Geography Economic Activity and energy
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the 4 economic sectors?
1. Primary
2. Secondary
3. Tertiary
4. Quaternary
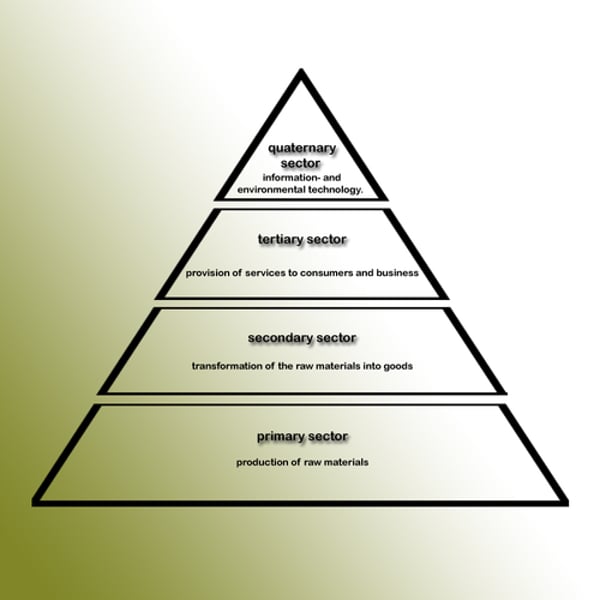
Describe the sectoral shift in the UK(HIC).
Before:
- Secondary Sector employed most people as it was an industrial country (Industrial Revolution)
- Primary Sector employed the least people.
- Quaternary sector was non- existent.
After:
- The Tertiary Sector now employs the most people due to the emergence of new industrial countries and to the fall of the industrial revolution.
- The primary sector still employs the least people.
- Rise in Quaternary sector employment.
factors affecting industrial location
Market, Good housing, Good schools and hospitals, nearby universities, cheap and skilled labour, flat land, water supply, flat and, climate
Describe the sectoral shift in China (MIC).
- Secondary sector dramatically increases, as China has a huge and very strong labor force.
- Primary sector employs the least people.
- Tertiary sector increases slowly in cities.
- Quaternary sector increasing.
Describe the sectoral shift in Ethiopia(LIC).
- Primary and Secondary sectors increased to employ the most individuals.
- Secondary sector employs the least people.
- Quaternary sector employs very little people.
Reasons for decline of employment in the primary sector
Cheap imports
Mechanisation
Depletion of resources
social change
reasons for decline of employment in the secondary sector
globalisation, mechanisation, government policies
reasons for growth in tertiary sectors
rise in demand for services linked to an increase of disposable incomes, decrease of employment in both other sectors, ageing population
Mechanisation
process of moving from a labour-intensive to a more capital-intensive method of production, employing more machines and fewer workers
Globalization
the process by which businesses or other organisations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.
Industrialization
The development of industries for the machine production of goods.
pre-industrial phase
- Primary sector leads the economy
- Agriculture the most important activity
Industrial phase
- secondary and tertiary sectors increase in productivity
- primary sector declines
post-industrial phase
- tertiary sector is now most important sector
- primary and secondary continue to decline
The Informal Sector
The economic sector that includes jobs that are not officially recognised by the government, and are usually self-employed with no taxes paid.
Give 4 examples of informal sector jobs.
- Shoe-shining.
- Selling unofficial products on the street.
- Drug Dealing.
- Weapon Trade.
What are the 5 reasons for the existence of the informal sector?
1. Poverty - Poor people will try to make money somehow to survive.
2. Unemployment - If there are no jobs available, people would have to employ themselves in order to make a living.
3. Lack of education - uneducated people have an extremely low probability of getting employed.
4. No state benefit - if the government cannot provide any help for unemployed people, they would have to find other ways to survive.
5. Low wages - some people cannot survive on low wages and need to make money.
Give 3 benefits of the informal sector.
1. Provides a wide range of cheap goods and services..
2. Provides the poor with means of survival.
3. Allows families to send children to receive education.
Give 3 downsides of the informal sector.
1. Can be illegal and dangerous.
2. Often exploits children.
3. The government doesn't benefit, meaning that the people receive no help.
Dharavi
Asias Largest Slum, in Mumbai, a city within a city, it its one unending stretch of narrow dirty lanes, open sewers and cramped huts, with 1 mill residents
De-industrialisation
The movement of secondary sector industries from HICs to MICs.
Give 6 causes of de-industrialisation.
- Cheaper and high availability of land.
- Cheaper and larger workforce.
- Cheaper energy.
- Cheaper and easier communications.
- Escaping strict regulations.
- Cheaper Transportation.
What were the effects of de-industrialisation on the UK(HIC)?
Benefits:
- Reduced Pollution
- Allowed the government to invest more in Quaternary industries, which has led to increased technology and research.
- Increased the employment of the Tertiary sector.
Downsides:
- Increased Unemployment.
- Increased government spending on welfare.
- Some derelict industrial buildings have been abandoned, where toxic chemicals have been used, hence posing a health risk.
What are the effects of de-industrialisation on China(MIC)?
Benefits:
- Increased levels of employment.
- Increased political power due to dramatically growing economy.
- Rapidly growing GDP/GNI.
Downsides:
- Dramatically increased air and water pollution.
- Loss of China's traditions and culture as western companies invade.
- Chinese cities becoming crowded as people searching for work move in.
CBD
Central Business District.
Describe the Tertiary and Quaternary sector growth cycle?
1. As the tertiary sector increases, the number of jobs increases.
2. This results in better quality jobs for more people.
3. Personal Income increases.
4. Hence personal spending increases as well.
5. Because of this, more people would bring their tertiary businesses to that location to earn more.
6. Causing the tertiary sector to increase, linking to the first point.
Describe the growth of the Tertiary sector in the UK.
1. As the secondary sector shrinks, the tertiary sector expands, providing more better quality jobs to people.
2. People's personal income income increases, increasing their personal spending.
3. This invites more tertiary businesses into the city and current businesses to expand.
4. This in turn expands the tertiary sector and shrinks the secondary sector again, and the cycle repeats.
Describe the growth of the Quaternary sector in the UK.
- The quaternary sector is born and begins to grow when the government begins to invest in building advanced education facilities such as specialist universities.
- Education facilities allow students to qualify for specialist careers.
- For these facilities to exist, the country requires HIC infrastructure and resources in order to be set up.
What are the 5 sectors of a city?
1. CBD - Central Business District
2. Inner city
3. outer city
4. Inner suburbs
5. Outer suburbs
What is an urban area's sphere of influence?
An area which depends on a given urban area for a particular good or service.
What is the urban fringe?
This is found at the edge of a town or city and is where town meets country. It is common for this area to have a mixture of land uses such as some housing, golf courses, allotments, business parks and airports.
Decentralisation
When an industry moves out from the CBD and relocates towards the urban fringe.
Give 5 benefits of decentralisation for economic development? (Reasons for why decentralisation is happening)
1. Cheaper Land
2. Room for expansion, less competition for space
3. Plenty of car parking space
4. Little Pollution
5. Attractive and clean environment.
6. More accessible for some
High Tech Industries
Industries that involve a highly skilled workforce whose products require a high level of research and development.
Why are high tech industries relatively footloose?
Because access to raw materials isn't very important as they mostly import light weight electronic components. They don't need to be in a certain location to receive them.
The Bio-technology Industry
A type of quaternary industry that combines biology and technology e.g. pharmaceutical industry
Explain why Britain has a growing biotechnology industry
- high calibre/good standard of scientists
- good links with universities
- as it continues to develop, more money can be spent on investment of this sector
What are the 3 factors that affect high-tech industries?
1. Location
2. Infrastructure
3. Transport Links
How does Location affect High-tech Industries?
- Closeness to education facilities such as Specialist universities attracts high grade graduates and undergraduates to work there.
- Being in a clean, attractive and calm environment, such as the rural urban fringe, attracts thinkers and students to work there.
How does Infrastructure affect High-tech Industries?
- Closeness to a major city provides the industry with good infrastructure.
- Access to social provisions is mandatory for a high-tech industry to exist.
How do transport links affect High-tech Industries?
- Access to Motorways and Highways provides the industry with an excellent transport link providing employees with access to the CBD and other desired regions.
- Availability of bus stations, train/metro stations and airports attract provide new and international students with cheap and easy methods of transportation and good transport links.
What are the 4 types of energy?
1. Primary Energy
2. Secondary Energy
3. Non-Renewable Energy
4. Renewable Energy
Renewable Energy
Infinite energy that won't run out, and is usually a clean source of energy.
Non-renewable Energy
Finite energy that will run out, and is harmful to the environment as it releases a lot of greenhouse gases.
Energy Gap
A gap in energy production resulted by phasing out the use of fossil fuels for energy, causing production to be lower than consumption.
Efficiency
Making the most use out of something.
Give 4 reasons for Energy Efficiency.
1. Non-renewable energy is running out, so it must be used sparingly.
2. Non-renewable energy harms the environment, so it's better for the environment.
3. It's better for the economy in countries where energy sources are imported.
4. It's better for the economy in countries where energy is rare and expensive to produce.
Give 4 methods of applying energy efficiency.
1. Walking or cycling to work and school instead of using vehicles.
2. Shutting off electronic devices when idle and setting the to power saving mode.
3. Installing roof and wall insulation to prevent heat form escaping and use less energy for heating.
4. Use available public transport or Hybrid/Electric cars.
Non-renewable
One that is being formed slower than we are using it so we will run out of it.
Renewable
One that is being formed as fast as (of even faster than) we are using it.
Primary Energy
Fuels that provide energy without undergoing any conversion process E.g. fossil fuels, wood
Secondary Energy
Energy which is made from the processing of primary fuels E.g. electricity, petrol
Energy gap
This is the difference between a country's rising demand for energy and its ability to produce that energy from its own sources.
Fossil Fuels
Coal; oil and natural gas are focus fuels which are produced from organic material (plants and animals).
Energy Mix
The various sources of energy that make up the supply within a country.
Oil
Crude oil or petroleum is a mixture of different hydrocarbons. It was formed from plankton that previously floated in the ocean dying and falling to the seabed.
Peak Oil
The point at which we will have extracted more oil than there is left.
Coal
Sedimentary rock that formed from trees growing in tropical swamp forests. They are found in seams 1-4m thick and found between layers of other rocks.
Natural gas
Methane can form from plankton in the same way as oil accumulating in porous rocks
Nuclear power
Generated from using the radioactive material, uranium. The uranium atoms are split (nuclear fission) and release energy in the form of heat.
Geothermal power
Energy extracted from hot rocks or water beneath the Earth's surface.
Biofuels
This term includes any fuel which comes from biomass e.g. bioethanol, biodiesel, biogas and solid biofuels including firewood.
Hydro-electric
The use of falling water to turn turbines to generate power to create electricity.
Solar power
The use of the sun's energy by converting the light into electricity.
Wind power
The use of wind to turn turbines to generate power to create electricity.
Fuelwood
Trees are chopped down and the trunk and branches are burnt to generate heat for cooking.
Thermal power stations
Those powered by fossil fuels.
Economic Sector
A major division of the economy based on the type of economic activity.
Energy
Heat and motive power provided by the Sun and burning fuel; or by electricity, gas, steam and nuclear power.
Energy Consumption
The amount of energy used by individuals, groups or countries.
Energy Efficiency
Making the most of energy sources to cut down on waste and consumption.
Fossil Fuel
Carbon fuels that cannot be remade because it takes tens of millions of years to reform.
Global Shift
The movement of manufacturing from HICs to cheaper production locations in LICs.
High-tech Industry
Economic activities that rely on advanced scientific research and produce new, innovative and technologically advanced products.
Informal Employment
Types of work that are not officially recognised by the government.
Primary Sector
Economic activities concerned with natural resources, such as farming and mining.
Secondary Sector
Economic activities concerned with manufacturing and making things, such as electricity, buildings, cars and food.
Tertiary Sector
Economic activities concerned with providing a wide range of services and enable goods to be traded.
Quaternary Sector
Economic activities concerned with highly skilled and technological services, such as collecting and processing information and research and development (R&D).
Transnational Company (TNC)
A large company operating in a number of countries and are often involved in a variety of economic activities.
Case study: UK energy mix
- amount of energy used is decreasing
- becoming less reliant on fossil fuel and more so on renewable energy resources
-
Case study: India's energy mix
- energy consumption is growing
- very reliant on non-renewables
energy conservation
the practice of finding ways to use less energy or to use energy more efficiently
energy consumption
The use of energy as a source of heat or power or as a raw material input to a manufacturing process