Practical Exam 2
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
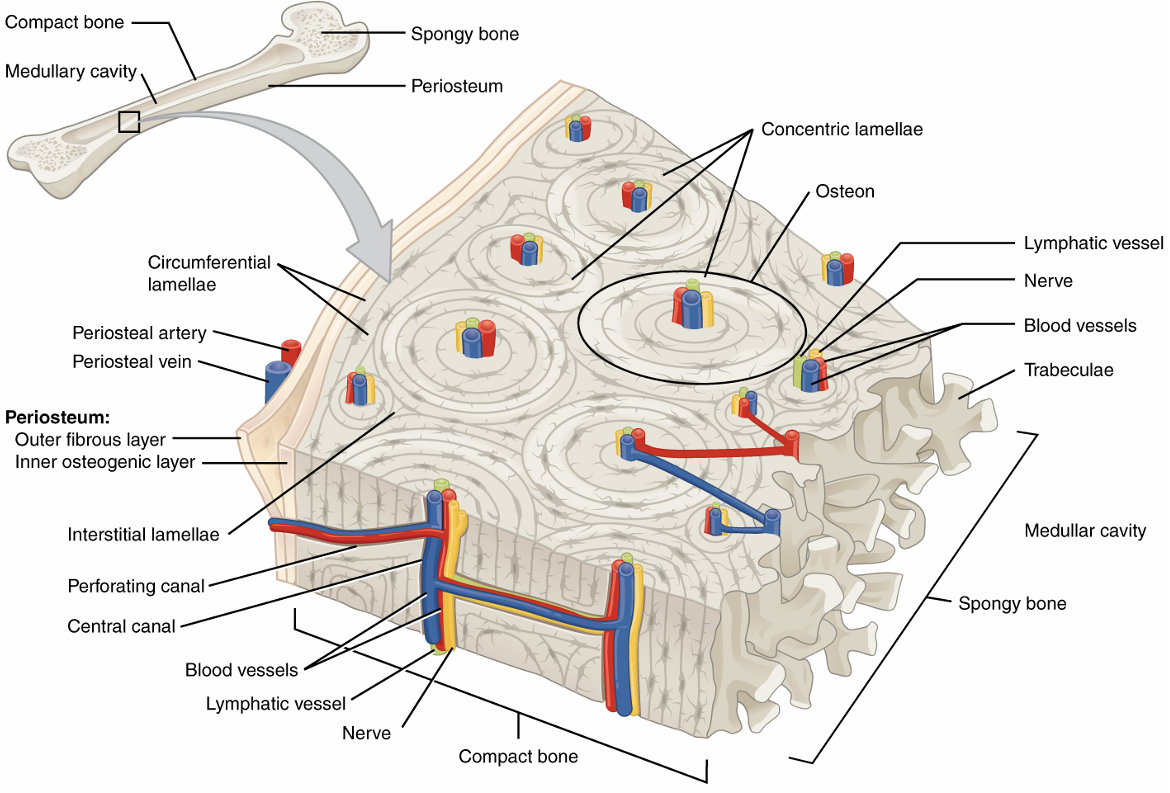
Microscopic Anatomy of Compact Bone
osteon/haversian system- cylindrical structures of multiple concentric lamellae around a central canal
central canal- passageway for nerves/vessels to supply osteon cells
lamellae- thin rings of bone tissue, collagen fibers run in opposite direction of adjacent rings
lacunae- hold osteocytes
canaliculi- tiny canals running from central canal to lacunae
circumferential lamellae- encircle all osteons
interstitial lamellae- fill in gaps between osteons
perforating canal- connect central canals, allow nerves/blood to enter the bone
periosteum- cover outside of bone
endosteum- lines medullary cavity
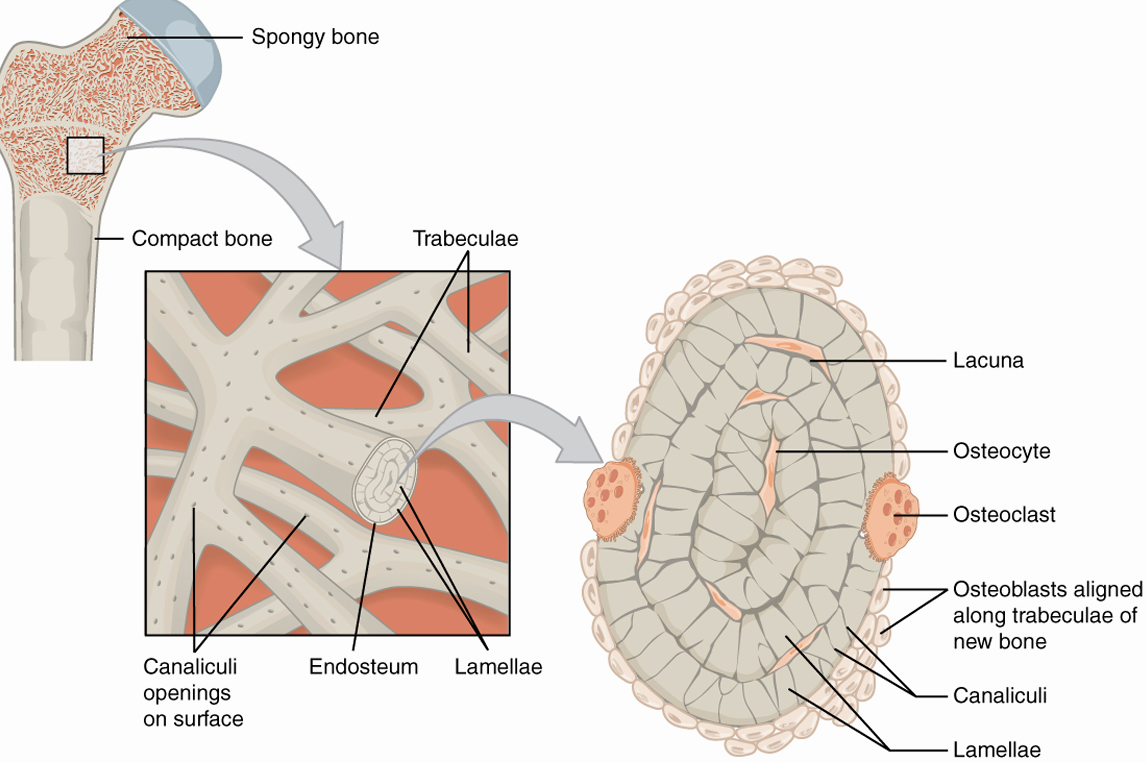
Microscopic Anatomy of Spongy Bone
trabeculae- mesh network of bone tissue
endosteum- thin, vascularized CT covering internal surfaces of bone
red marrow- fills the space between trabeculae
Projections that are Sites of Muscle and Ligament Attachment
crest
epicondyle
line
spine
trochanter
tubercle
tuberosity
Crest
ridge
Epicondyle
raised area on or above a condyle
muscle/ligament attachment site
Line
slight, elongated ridge
Spine
sharp process
Trochanter
large, irregularly shaped process
Tubercle
small, rounded process
Tuberosity
rough surface
Projections that Fit into Joints
condyle
head
facet
Condyle
rounded surface
Head
prominent rounded surface
Facet
flat surface
Depressions and Openings Allowing Passage for Blood Vessels and Nerves
foramen
fossa
groove
Foramen
hole through bone
Fossa
elongated basin
Groove
furrow, narrow trench
Long Bone Examples
humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, phalanges, femur, tibia, fibula, metatarsals
Short Bone Examples
tarsals, carpals
Flat Bone Examples
skull bones, ribs, sternum, scapulae
Irregular Bone Examples
vertebrae, facial bones
Sesamoid Bone Example
patella
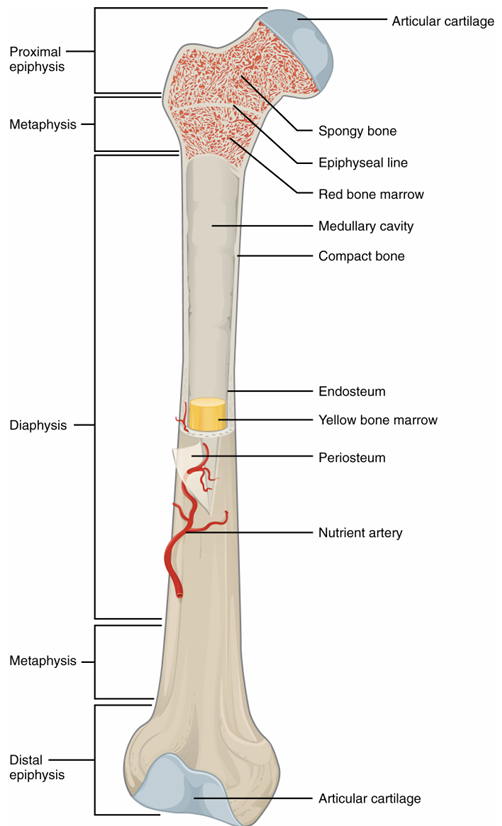
Structure of Long Bone
epiphysis- head of bone
metaphysis- between epiphysis and diaphysis
diaphysis- shaft of bone
articular cartilage- caps the tops of bones
periosteum- outer lining
medullary cavity- hollow inside of shaft, yellow marrow
endosteum- inner lining
yellow bone marrow- in medullary cavity
compact bone- shell, makes up diaphysis and shell of epiphysis
spongy bone- inside of epiphysis
red bone marrow- inside of spongy bone
Parts of Axial Skeleton
skull
vertebral column
thoracic cage
Functions of Axial Skeleton
forms the longitudinal axis of the body
supports the head, neck, and trunk
protects the brain, spinal cord, and organs within the thorax
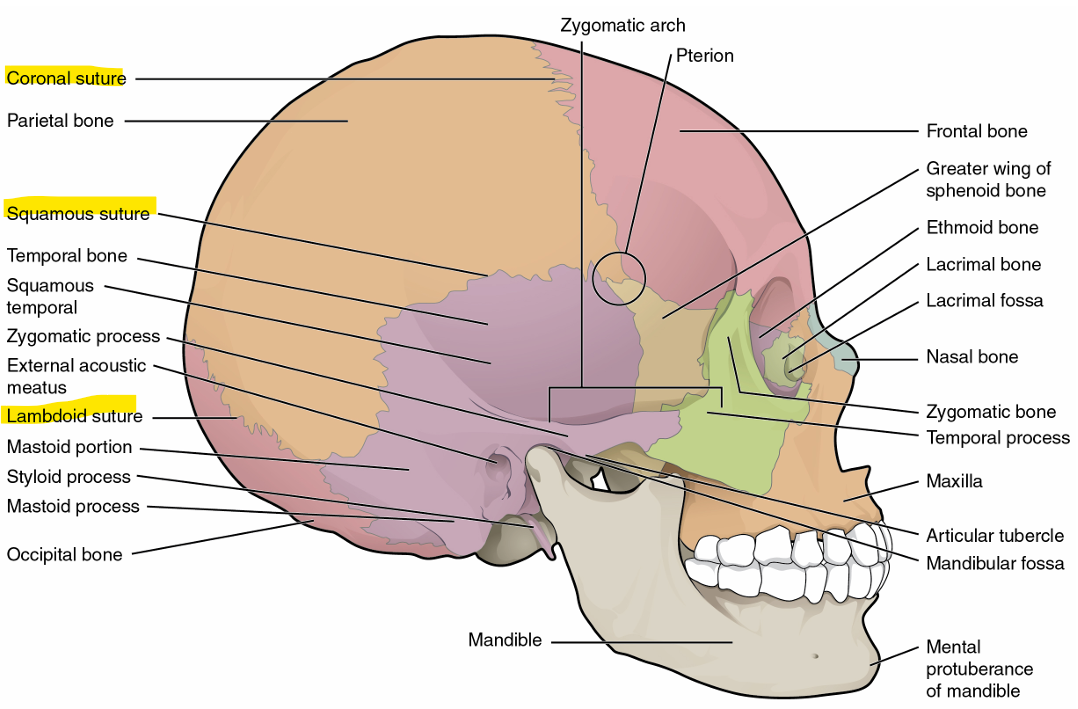
Cranial Bones
frontal bone → forehead, separated from parietal by coronal suture
parietal bones → upper lateral sides of skull, separated by sagittal suture
temporal bones → lower lateral sides of skull, separated from sagittal by squamous suture
occipital bone → back of skull, separated from parietal by lambdoid suture
sphenoid bone → forms base of skull, looks like a bat, seen in back of eye cavity
ethmoid bone → single, midline bone that forms walls of upper nasal cavity and medial wall of the orbit
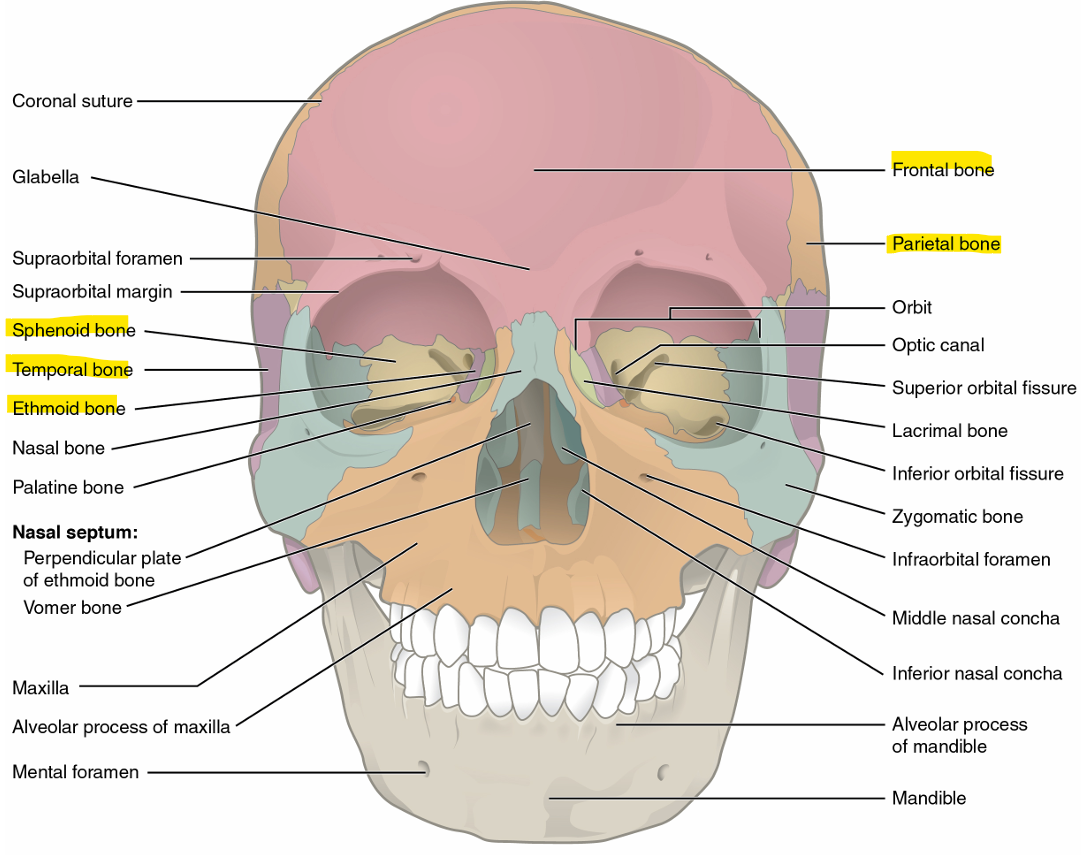
Sutures
coronal suture- joins frontal bones to parietal bones
sagittal suture- joins left and right parietal bones
lambdoid suture- joins occipital bone to parietal/temporal bones, upside-down V
squamous suture- joins parietal bones to temporal bones
Facial Bones
nasal bones (left and right) → form bony bridge of nose
maxilla (left and right) → upper jaw, hard palate, lateral base of nose
zygomatic bones (left and right) → cheekbone
mandible → lower jaw
lacrimal bones (left and right) → small bone that forms the anterior medial wall of orbit- part of orbit closest to the nasal bones
palatine bones (left and right) → lateral walls of nasal cavity- back portion of roof of mouth
vomer → lower portion of nasal septum
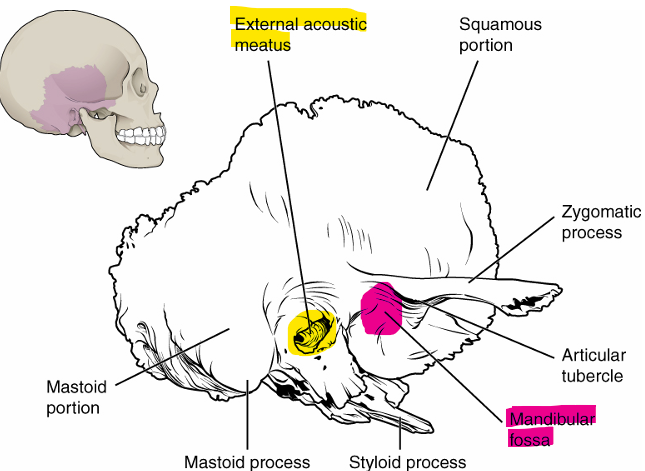
Temporal Bone Markings
external acoustic meatus → large opening on lateral side of skull, associated with ear
mandibular fossa → deep, oval shaped depression on external base of skull where mandible joins to
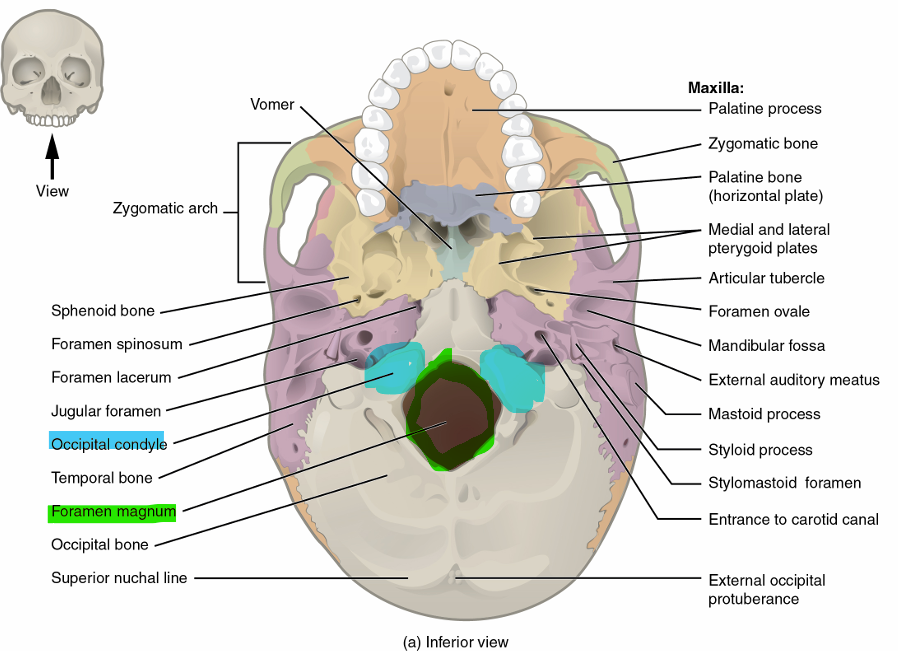
Occipital Bone Markings
foramen magnum → opening where spinal cord enters/exits brain
occipital condyles → sit on either side of foramen magnum, form joints w/ first vertebrae and support skull
Sphenoid Bone Markings
sella turcica → looks like a saddle, behind the nose in front of foramen magnum, holds the pituitary gland
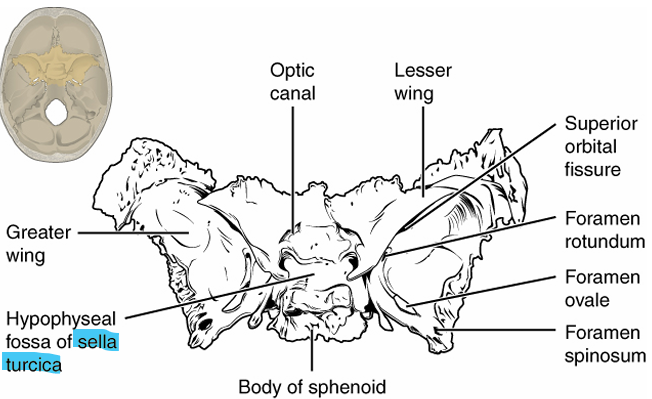
Maxillae Bone Markings
alveoli → forms upper jaw + contains the upper teeth
palatine process → roof of upper mouth
Mandible Bone Markings
alveoli → forms lower jaw + holds lower teeth
mandibular ramus → extends upwards to ear
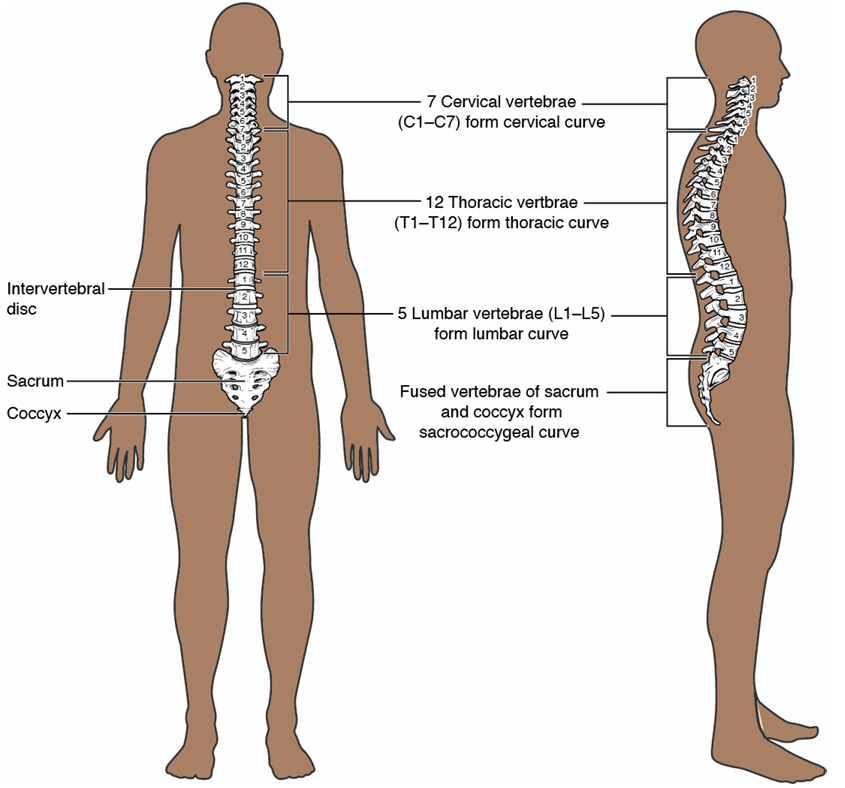
5 Divisions of Vertebral Column
TOP
cervical (7)
thoracic (12)
lumbar (5)
sacrococcygeal (fused, 9 total)
BOTTOM
Primary Curvature
thoracic
sacrococcygeal
primary because they existed in their curved state in a newborn
Secondary Curvature
cervical
lumbar
secondary because they adapted as the newborn began walking + holding head up
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral bending of the vertebral column
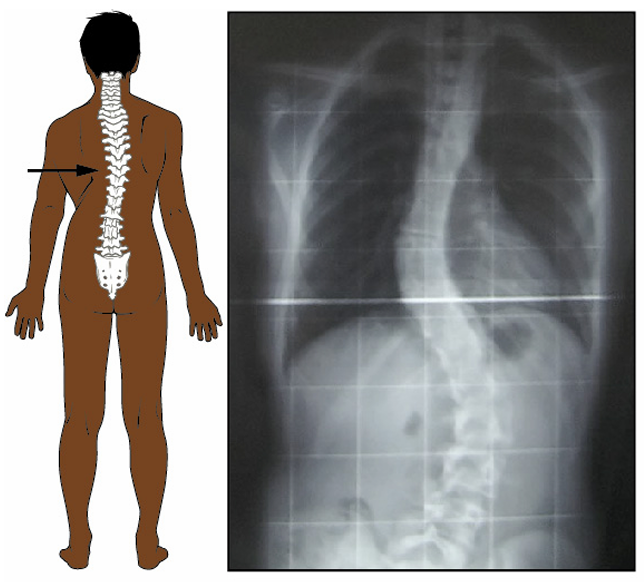
Kyphosis
exaggerated thoracic curve resulting in a hunchback appearancev
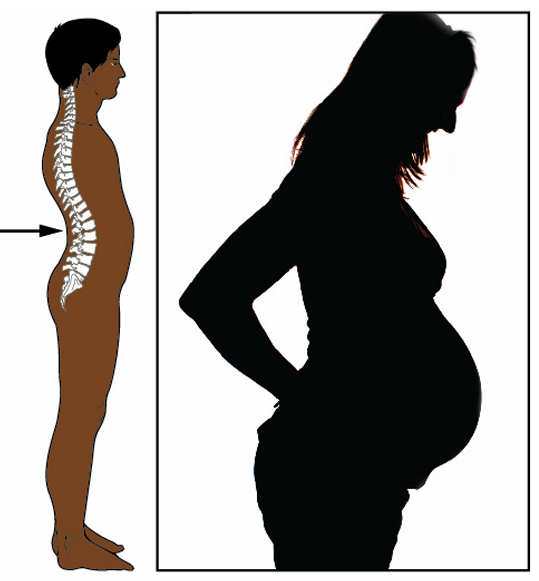
Lordosis
exaggerated lumbar curve resulting in a protruding stomach
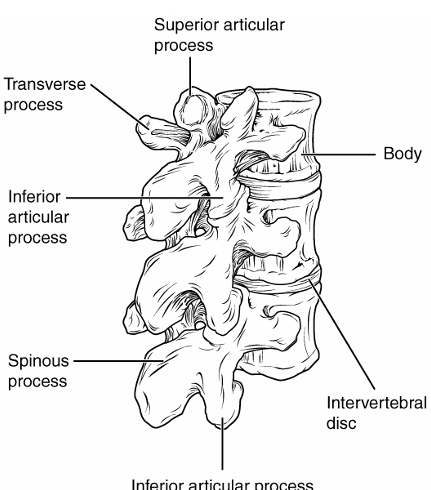
Features of Vertebra
body- anterior portion that supports weight
transverse process- project laterally
spinous process- singular, projects straight back
vertebral foramen- opening where spinal cord runs through
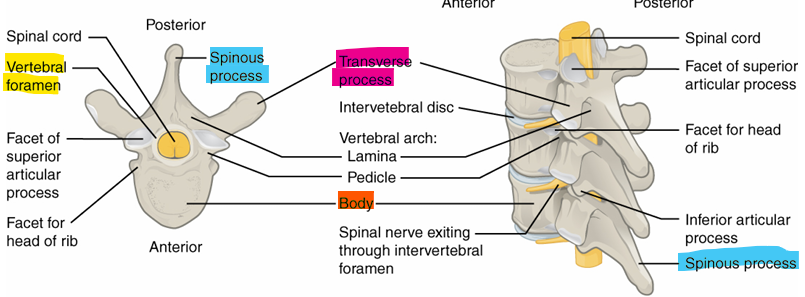
First Vertebra
name- C1 or atlas
shape- flat with a large hold, 2 smaller holes on side
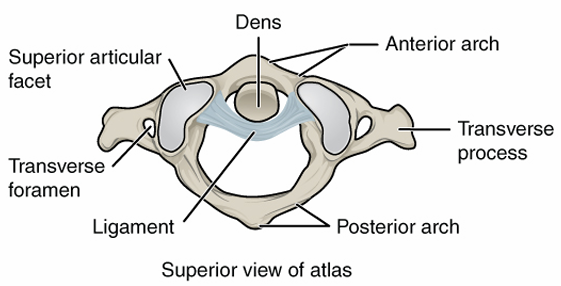
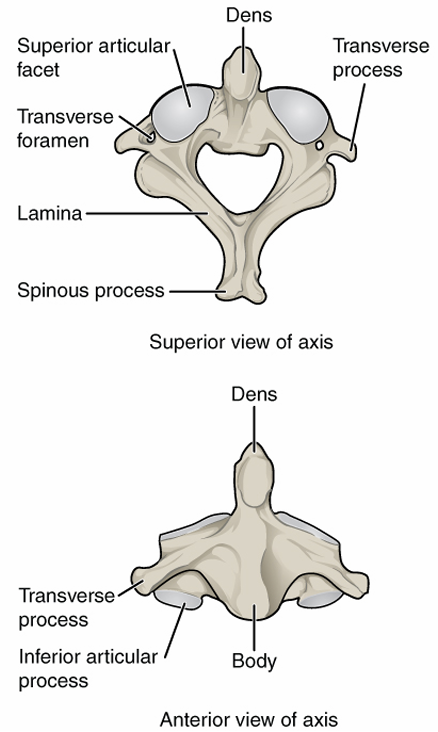
Second Vertebra
name- C2 or axis
shape- has a bone that protrudes up into atlas
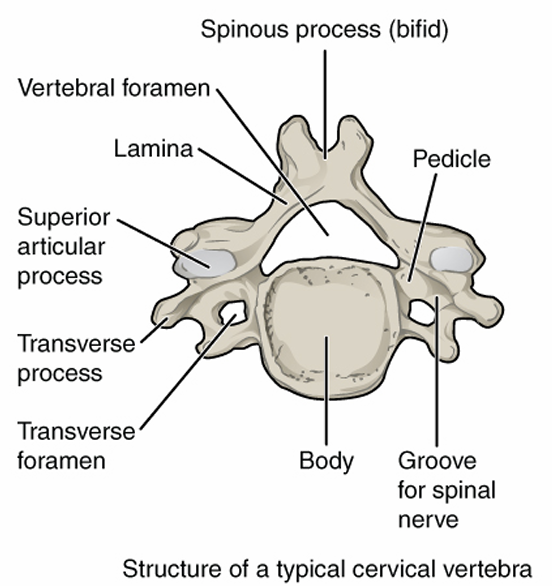
Cervical Vertebra Characteristics
body: small
vertebral foramen: large and triangular
spinous process: short, point posteriorly
transverse foramen: yes
Lumbar Vertebra Characteristics
body: intermediate
vertebral foramen: small, circular
spinous process: long, slender, point down
transverse foramen: no
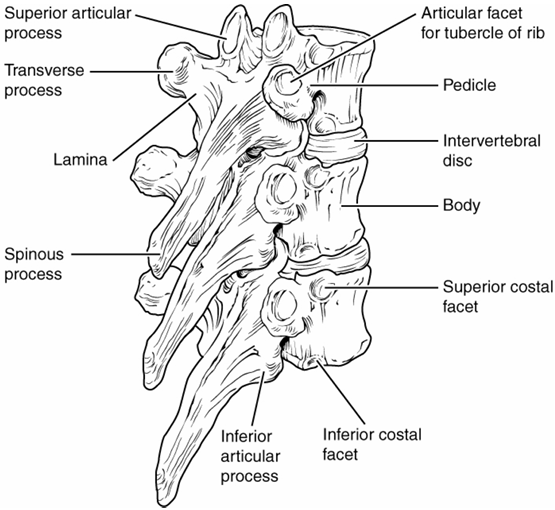
Thoracic Vertebra Characteristics
body: large and thick
vertebral foramen: intermediate, triangular
spinous process: short, thick, points back
transverse foramen: no
Sternum Regions
TOP
Manubrium → heart shaped top, connects to clavicles
Body → rectangular portion of tie
Xiphoid process → tip of the sword
True Ribs
their costal cartilage directly attaches to the sternum
RIBS 1-7
False Ribs
their costal cartilage is either not directly attached to sternum (shared) or not attached at all
RIBS 8-12
Floating Ribs
not attached to the sternum at all
RIBS 11+12
Appendicular Skeleton
bones of upper and lower extremities
bones of the pectoral girdle (clavicles and scapulas)
bones of the pelvic girdle (hip bones)
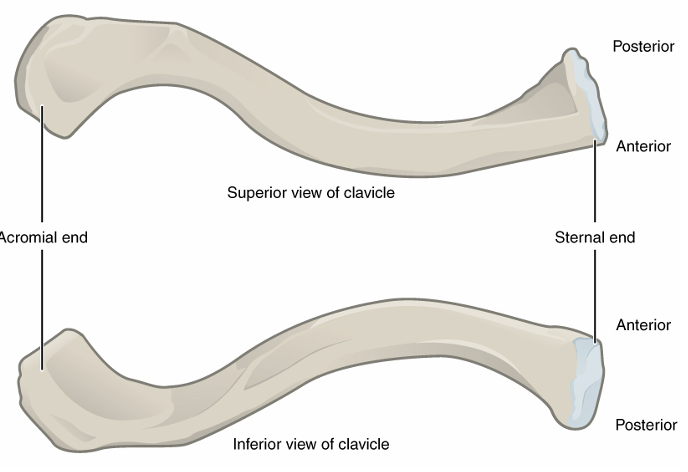
Clavicle
sternal end is flatter, attached to sternum
acromial end is rounded and slightly curved, attached to shoulder
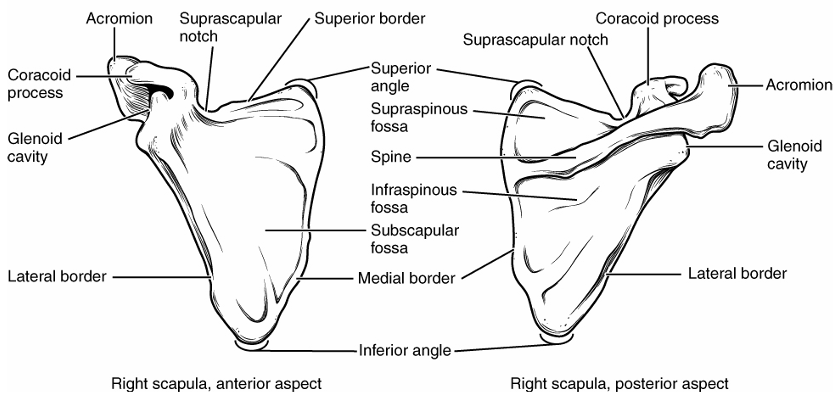
Scapula
glenoid cavity/fossa → articulates with head of humerus
spine → long prominent ridge on back portion
acromion → articulates with clavicle, end of spine that extends out
coracoid process → attachment site for biceps brachii
Humerus
head → top, articulates w/ shoulder
deltoid tuberosity → attachment site for deltoid
medial epicondyle → bottom projection of bone on inside (in anatomical), w/ ulna
lateral epicondyle → bottom projection of bone on outside, w/ radius
trochlea → articulates w/ ulna
capitulum → articulates w/ radius
olecranon fossa → groove on back where ulna comes up into
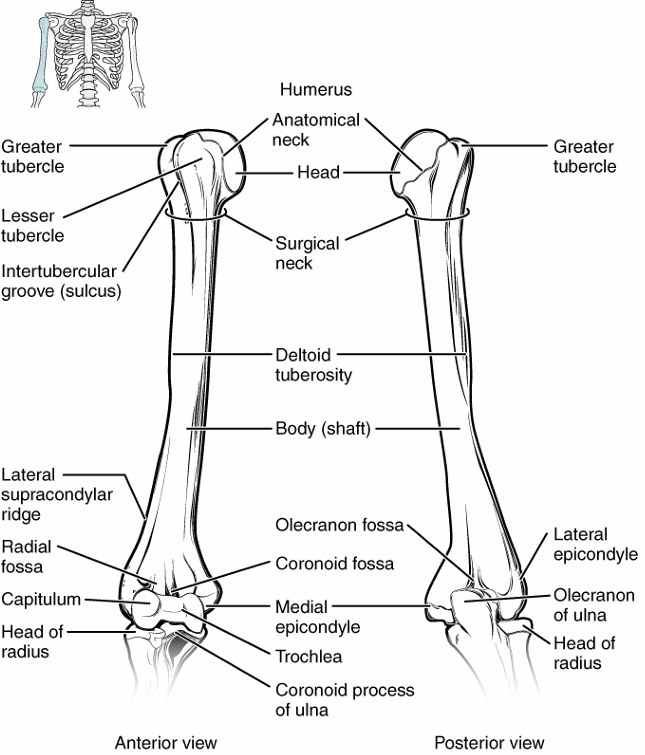
Ulna
lines up with pinkie finger
general shape- near elbow sticks out and up, gets narrower, bottom near wrist skinny
olecranon → sticks up from top of bone, grips humerus
trochlear notch → part of olecranon
coronoid process → sticks up from bone under olecranon, grips humerus
head → attaches to wrist
styloid process → tiny projection off head near wrist
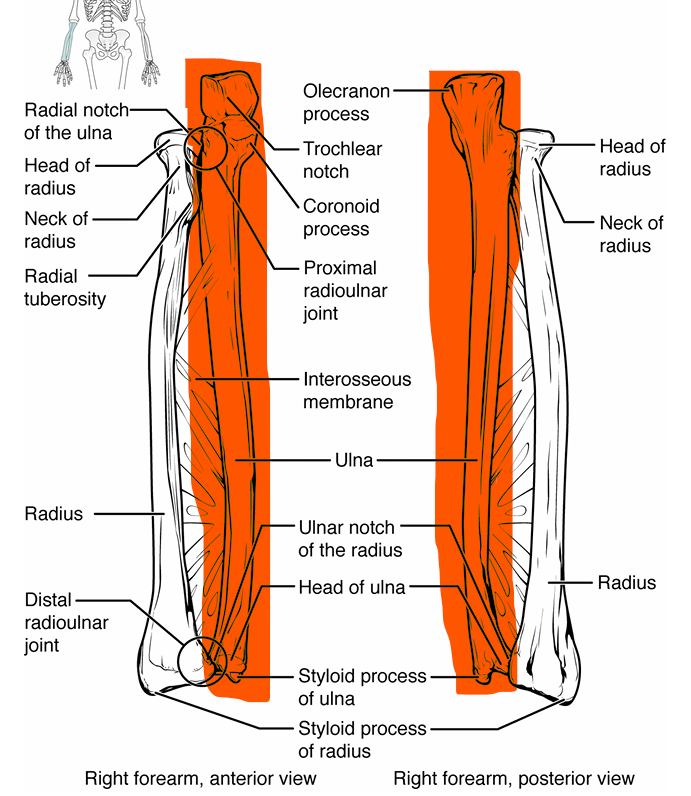
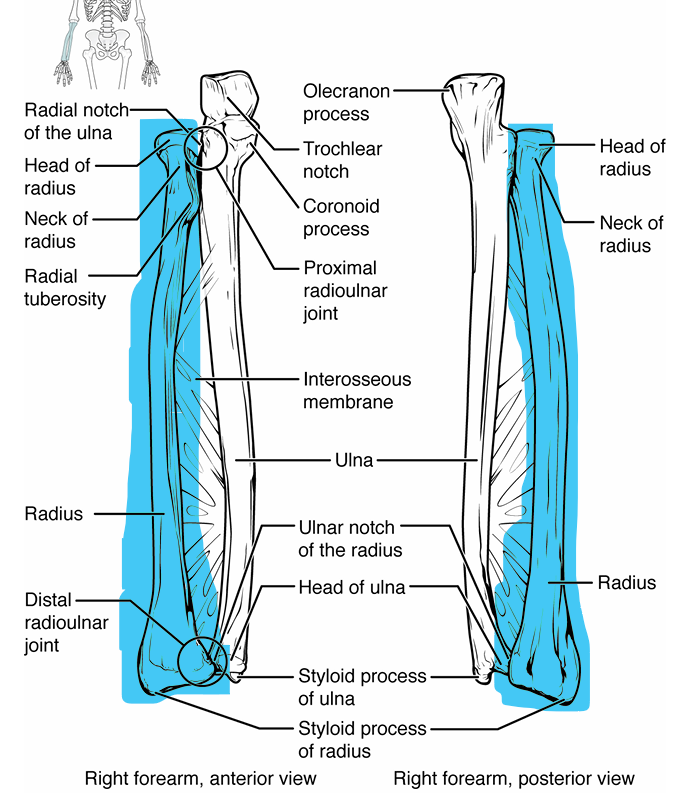
Radius
lines up with thumb
general shape- head near elbow looks like screw, slight curve in shaft, bottom gets wider near wrist
head → attaches w/ capitulum of humerus
radial tuberosity → attachment site for biceps brachii, protrudes into ulna
shaft- long portion of bone
styloid process- tiny point at bottom near wrist
Hand Bones
carpals → 8 small bones in wrist
metacarpals → 5 bones that connect carpals to phalanges of each finger → palm
phalanges → 2 in thumb, 3 in other fingers, make up digits
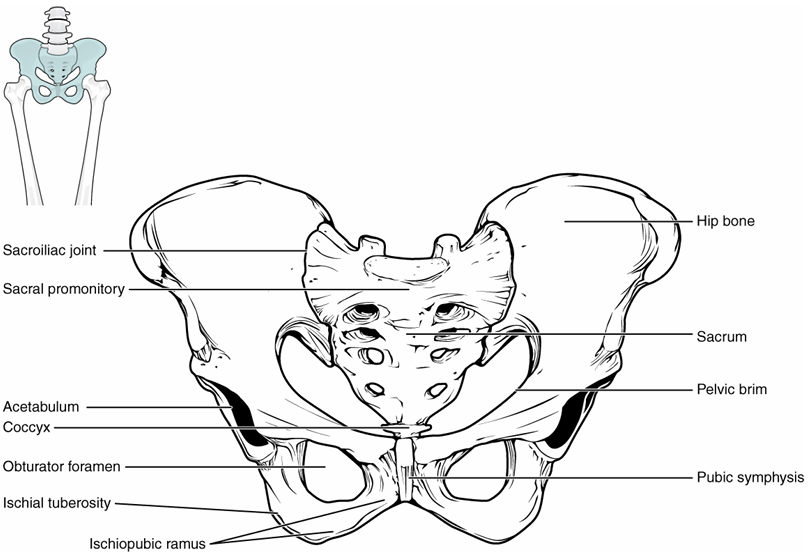
Pelvic Girdle
ilium → superior portion of hip bone
iliac crest- curved superior portion
greater sciatic notch- allows sciatic nerve to enter thigh, U-shaped indent
ischium → inferior posterior part of hip bone
ischial spine- bony projection separating the greater and lesser sciatic notches
ischial tuberosity- bears weight when sitting, site of ligament/tendon attachment
pubis → inferior, anterior part of hip bone
general bone markings
acetabulum- articulates w/ head of femur
obturator foramen- blood vessel and nerve passage, lower smaller holes of butterfly

Femur
head → articulates w/ acetabulum of pelvic girdle
neck → bend in bone leading towards head
gluteal tuberosity → gluteus maximus attachment, on upper outside under neck
medial condyle → articulates with tibia on inside
lateral condyle → articulates with tibia on outside
medial epicondyle → roughened area of femur on medial side of medial condyle
lateral epicondyle → roughened area of femur on lateral side of lateral condyle
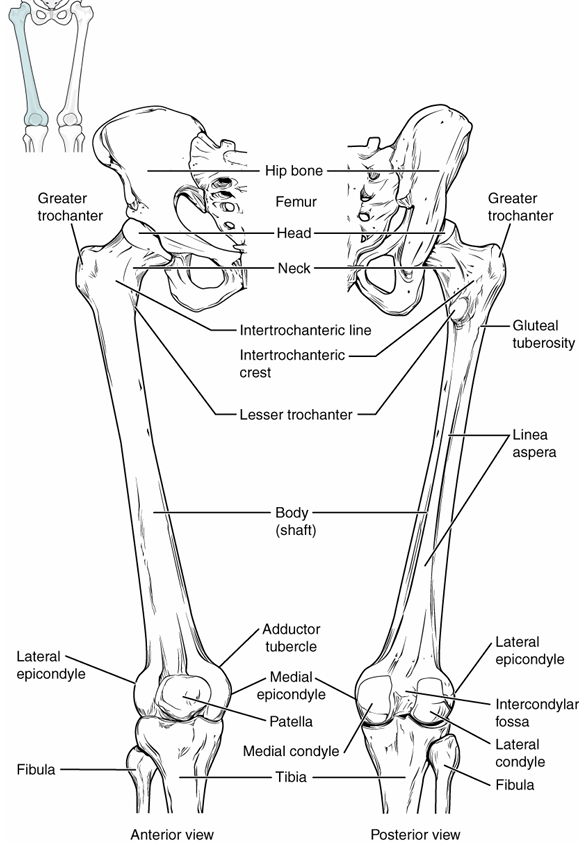
Patella
triangular sesamoid bone that sits in front of bottom femur
Tibia
innermost thicker bone of lower leg, thick head and thinner bottom with point
medial condyle → inner articulation to femur
lateral condyle → outer articulation to femur
tibial tuberosity → attachment site of patellar tendon on front of bone
medial malleolus → medial bulge of ankle, articulates with talus
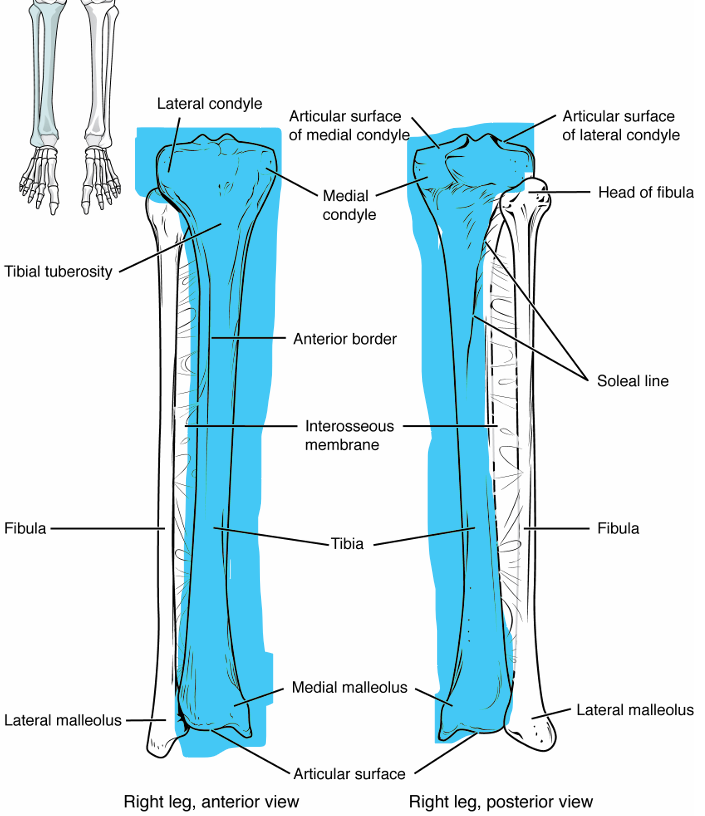
Fibula
outermost thinner bone of lower leg, thin head and shaft, pointed body to outside
head → top portion of bone near knee
lateral malleolus → lateral bulge of ankle, articulates with talus
Foot Bones
calcaneus and talus bear most of the weight
metatarsals connect tarsals to phalanges
phalanges are visible digits/toes
Basic Function of Joints
hold bones together
give flexibility + allow movement (not in synarthrosis joints)
Functional Classification of Joints
synarthrosis- no movement, immovable
amphiarthrosis- slightly movable
diarthrosis- freely movable, large range of motion
Structural Classification of Joints
fibrous joints
cartilaginous joints
synovial joints
Fibrous Joint Characteristics
bones are joined by fibrous CT
no joint cavity is present, no separation between bones without CT
amount of movement varies, but most are synarthrotic
Types of Fibrous Joints
suture
gomphosis
syndesmosis
Suture
united by very short CT fibers
ex: most skull joints
Gomphosis
tooth secured into bony socket by ligament
Syndesmosis
bones connected by short ligaments
amphiarthrotic
ex: distal articulation of tibia and fibula
Cartilaginous Joint Characteristics
articulating bones are connected by plate or pad
no joint cavity is present
most are amphiarthrotic
Types of Cartilaginous Joints
synchondrosis
symphysis
Synchondrosis
bones joined together by hyaline cartilage
ex: ribs to sternum via costal cartilage
Symphysis
bones connected by fibrocartilage disc
ex: intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis
Synovial Joint Characteristics
articulating bones separated by joint cavity containing synovial fluid
ALL ARE DIARTHROTIC
joint surfaces are enclosed by a two-layered joint
General Structure of Synovial Joints
joint cavity contains synovial fluid
articular cartilage caps bones
articular capsule
inner layer of synovial membrane, secretes fluid
outer layer of fibrous membrane
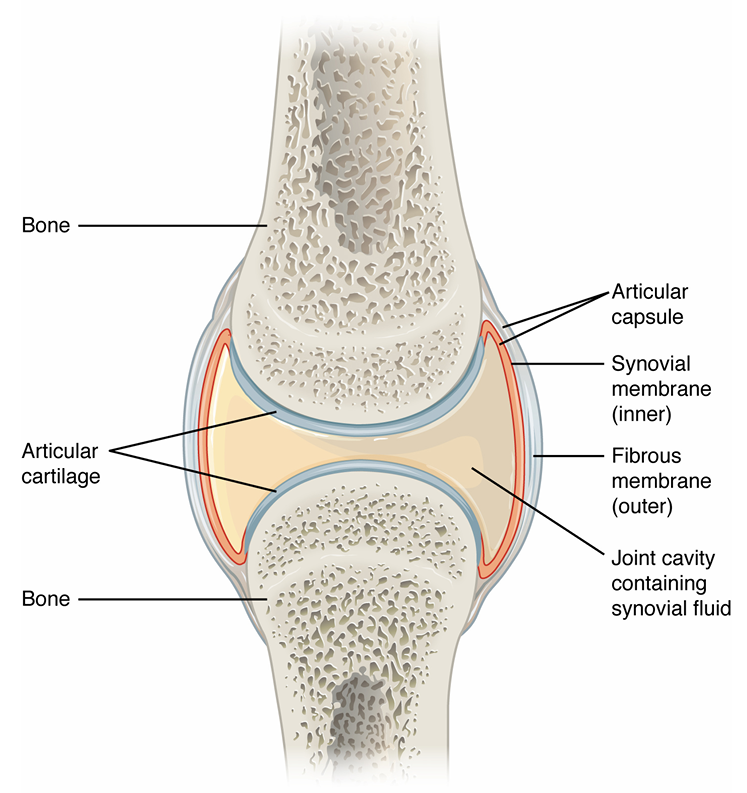
Movements at Synovial Joint
gliding
angular
rotational
special
Gliding Movements
two flat surfaces sliding relative to one another
Angular Movements
flexion
extension
hyperextension
abduction
adduction
circumduction
Flexion
decreasing of the joint angle
ex: when you do bicep curls, your arm angle goes from 180 to 45
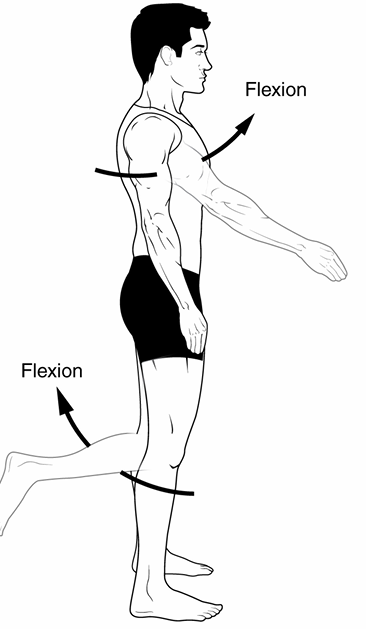
Extension
increasing of the joint angle
ex: when you go down from a bicep curl, your arm angle goes from 45 to 180

Hyperextension
increasing joint angle beyond resting/anatomical position
ex: arm going backwards
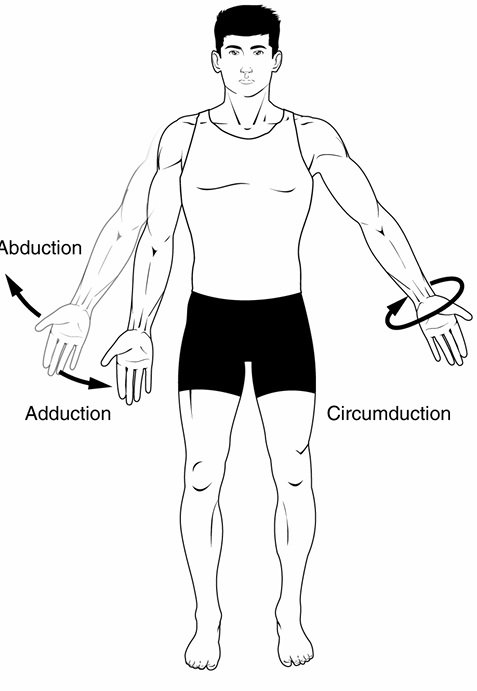
Abduction
movement of a limb away from the midline
ex: moving arm away from body
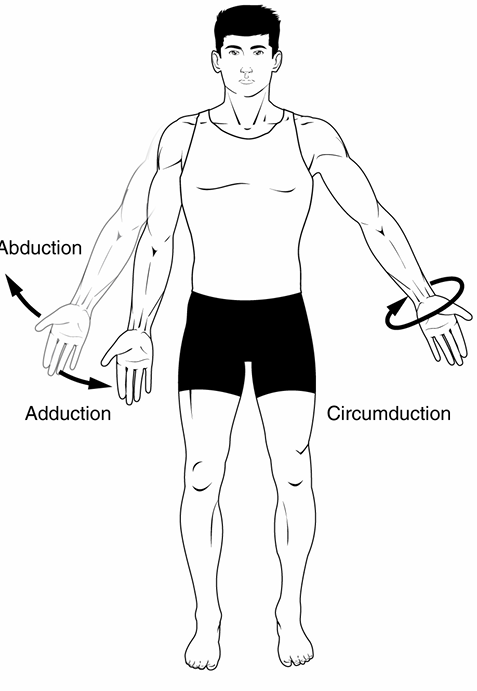
Adduction
movement of a limb towards the midline
ex: moving arm back towards torso
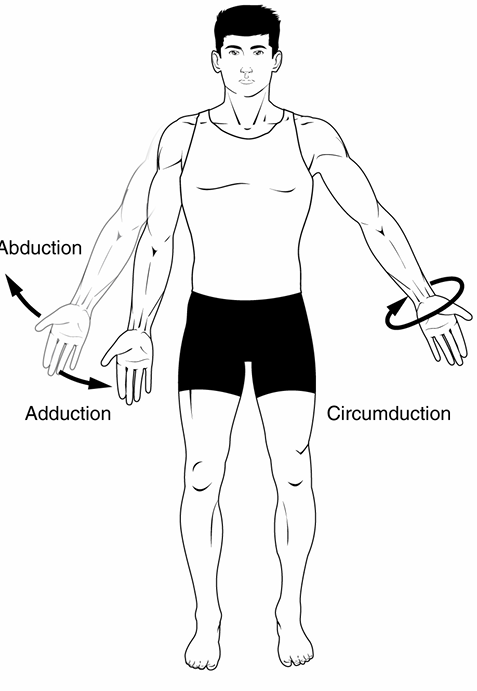
Circumduction
simultaneous combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
ex: circling arm
Rotational Movements
internal/medial rotation
external/lateral rotation
Internal/Medial Rotation
rotation towards the midline
ex: turning head from facing right to facing forward
External/Lateral Rotation
rotation away from midline
ex: turning head from forward to facing the side
Special Movements
pronation
supination
dorsi flexion
plantar flexion
inversion
eversion
Pronation
turning palm to face backwards
Supination
turning palm to face forwards
Dorsi Flexion
pointing toe towards ceiling, resting weight on heels
Plantar Flexion
pointing toe towards ground, resting weight on toes
Inversion
turning the bottom of your foot in to face other leg
Eversion
turning the bottom of your foot out to face laterally
Types of Synovial Joints
plane
hinge
pivot
condyloid
saddle
ball and socket
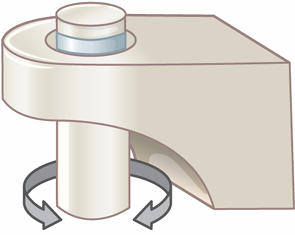
Plane Synovial Joint
description: flat articular surfaces
movement: gliding
example: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, intercarpal, intertarsal, patellofemoral, proximal tibiofibular joint, tarsometatarsal joint, sacroiliac joint
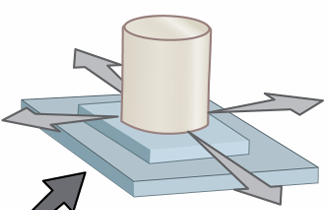
Hinge Synovial Joint
description: 1 bone is convex; 2nd bone is concave
movement: flexion and extension
example: elbow, knee, interphalangeal, ankle
Pivot Synovial Joint
description: 1 bone has projection; 2nd bone has ring-like structure
movement: rotation
example: C1 and C2 vertebra, proximal and distal radioulnar joints