Digestive system
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Digestion
breakdown of large organic molecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed
Digestive system
performs the task of digestion
food is taken into it, where it is enzymatically broken down into smaller and smaller particles for absorption
consists of the digestive tract and specific associated organs
Digestive system functions
ingestion of solids and liquids
digestion of organic molecules
absorption of nutrient
elimination of waste
Digestive tract / gastrointestinal tract
one long tube from the mouth to the anus
Digestive tract components
oral cavity (mouth)
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestines
large intestines
rectum
anus
Associated organs
organs not directly in the digestive tract but have ducts that lead into the tract
salivary glands
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
Tunics
layers of tract wall
Layers of digestive tract wall
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis
serosa / adventitia
Mucosa
innermost
secretes mucus
Submucosa
above mucosa
contains blood vessels, nerves, small glands
Muscularis
above submucosa
longitudinal, circular, and oblique muscles
Serosa / adventitia
outermost layer
peritoneum is present - serosa
no peritoneum - adventitia
Peritoneum
layer of smooth epithelial tissue
Mesenteries
connective tissue organs in abdominal cavity
Lesser omentum
mesentery connecting lesser curvature of stomach to liver and diaphragm
Greater omentum
mesentery connecting greater curvature of stomach to transverse colon and posterior colon and posterior body wall
Oral cavity
first part of digestive system
contains stratified squamous epithelia
Salivary glands
produce saliva which contain enzymes to breakdown carbohydrates into glucose
cleanse mouth
dissolve and moisten food
Amylase
salivary enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates
Lysozyme
salivary enzymes that are active against bacteria
Tongue
house taste buds and mucus
Teeth
32 teeth in normal adult
incisors, canine, premolars, molars, wisdom
20 primary teeth (baby teeth)
each tooth has crown, cusp, neck, root
Pulp cavity
center of tooth
Enamel
hard covering protects against abrasions
Cavities
breakdown of enamel by acids from bacteria
Palate
roof of oral cavity
Hard palate
anterior part of palate
Soft palate
posterior part of palate
Salivary glands
includes submandibular, sublingual, parotid
produce saliva contains enzymes to breakdown food
Mumps
inflammation of parotid gland
Pharynx
throat
connects the mouth to the esophagus
has 3 parts:
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
Esophagus
tube that connects the pharynx to the stomach
transports food to the stomach
joins stomach at cardiac opening
Heartburn
occurs when gastric juices regurgitate into esophagus
caused by caffeine, smoking, or eating or drinking in excess
Swallowing
voluntary phase
pharyngeal phase
esophageal phase
peristalsis
Voluntary phase
bolus (mass of food) formed in the mouth and pushed into oropharynx
Pharyngeal phase
swallowing reflex initiated when bolus stimulates receptors in ororpharynx
Esophageal phase
moves food from pharynx to stomach
Peristalsis
wave-like contractions moves food through digestive tract
a wave of smooth muscle relaxation moves ahead of the bolus, allowing the digestive tract to expand
a wave of contraction of the smooth muscles behind the bolus propels it through the digestive tract

Stomach
located in abdomen
storage tank for food
can hold up to 2 liters of food
produces mucus, hydrochloric acid, protein digesting enzymes
contains thick mucus layer that lubricates and protects epithelial cells on stomach wall from acidic pH (3)
3 muscular layers of stomach
outer longitudinal, middle circular, and inner oblique to produce churning action
Rugae
large folds that allow stomach to stretch
Chyme
paste-like substance that forms when food begins to be broken down
Pyloric opening
opening between stomach and small intestine
Pyloric sphincter
thick, ring of smooth muscle around pyloric opening
Hunger pangs
stomach is stimulated to contract by low blood glucose levels usually 12-24 hours after a meal
Parasympathetic stimulation, gastrin, histamine
increase stomach secretions
regulation of stomach secretions
cephalic phase
gastric phase
intestinal phase
Cephalic phase
1st phase
stomach secretions are initiated by sight, smell, taste, or food thought
Gastric phase
2nd phase
partially digested proteins and distention of stomach promote secretion
Intestinal phase
3rd phase
acidic chyme stimulates neuronal reflexes and secretion of hormones that inhibit gastric secretions by negative feedback loops
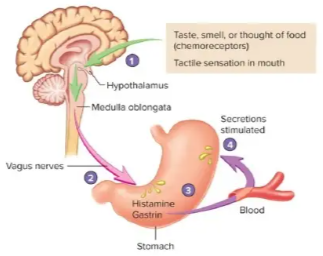
Cephalic phase of stomach control
the taste, smell, or though of food or tactile sensations of food in the mouth stimulate the medulla oblongata
vagus nerves carry parasympathetic action potentials to the stomach where enteric plexus neurons are activated
postganglionic neurons stimulate secretion by parietal and chief cells and stimulate gastrin and histamine secretion by endocrine cells
gastrin is carried through the blood back to the stomach where along with histamine it stimulates secretion
Gastric phase of stomach control
distention of the stomach stimulates mechanoreceptors (stretch receptors) and activates a parasympathetic reflex. action potentials generated by the mechanoreceptors are carried by the vagus nerves to the medulla oblongata
the medulla oblongata increases action potentials in the vagus nerves that stimulate secretion by parietal and chief calls and stimulate gastrin and histamine secretion by endocrine cells
distention of the stomach also activates local reflexes that increase stomach secretions
Gastrin is carried through the blood back to the stomach where along with histamine it stimulates secretion

Interstitial phase of stomach
chyme in the duodenum with pH less than 2 or containing fat digestion products (lipids) inhibits gastric secretions by three mechanisms
chemoreceptors in the duodenum are stimulated by H+ (low pH) or lipids. action potentials generated by the chemoreceptors are carried by the vagus nerves to the medulla oblongata where they inhibits
local reflexes activated by H+ or lipids inhibit gastric secretion
secretin and cholecystokinin produced by the duodenum decrease gastric secretions in the stomach

Movements in stomach
mixing waves
peristaltic waves
Mixing waves
weak contraction
thoroughly mix food to form chyme
Peristaltic waves
stronger contraction
force chyme toward and through pyloric sphincter
Hormonal and neural mechanisms
stimulate stomach secretions
Regular meal
stomach empties every 4 hours after this
High fatty meal
stomach empties every 6 - 8 hours after it
Movement in stomach

Small intestine
measures 6 metes in length
major absorptive organ
chyme tales 3 to 5 hours to pass through
contains enzymes to further breakdown food
contains secretions for protection against the acidity
Parts of small intestine
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
Duodenum
first part of small intestine
25 cm long
contains absorptive cells, goblet cells, granular cells, endocrine cells
contains microvilli and many folds
contains bile and pancreatic ducts
Jejunum
second part of small intestine
2.5 meters long and absorbs nutrients
Ileum
third part of small intestine
3.5 meters long
Mucosa of the small intestine
a simple columnar epithelium with 4 major cell types
absorptive cells
goblet cells
granular cells
endocrine cells
Absorptive cells
have microvilli
produce digestive enzymes
absorb digested food
Goblet cells
produce a protective mucus
Granular cells
may help protect the intestinal epithelium from bacteria
Endocrine cells
produce regulatory hormones
Crypts of Lieberkuhn / intestinal glands
epithelial cells are located within tubular glands of mucosa called,,, at the base of the villi
Glandular and endocrine cells
located in the bottom of the glands
Duodenal glands
mucous glands contained in the submucosa of the duodenum which open into the base of the intestinal glands
Free surfaces
epithelial cells in the walls of the small intestine have enzymes bound to their,,,
Peptidases
enzymatically breakdown proteins into amino acids for absorption
Disaccharidases
enzymatically breakdown disaccharides into monosaccharides for absorption
Mixing and propulsion of chyme
primary mechanical events that occur in the small intestine
Peristaltic contractions
proceed along the length of the intestine for variable distances and cause the chyme to move along the small intestine
Segmental contractions
propagated for only short distances and mix intestinal contents
Ileocecal sphincter (juncture of ileum) and large intestine
remains mildly contracted most of the time
Peristaltic contraction reaching the ileocecal sphincter from the small intestine
cause the sphincter to relax and allow chyme to move from the small intestine into the cecum
Ileocecal valve
prevents movement from the large intestine back into the ileum
Segmental contraction in small intestine

Liver
weighs about 3 lbs
located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen under the diaphragm
consists of right, left, caudate, and quadrate lobes
Porta
gate where blood vessels, ducts, nerves enter and exit
receives arterial blood from the hepatic artery
Lobules
divisions of liver with portal triads at corners
Portal triad
contain hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, hepatic duct
Hepatic cords
between center margins of each lobule
separated by hepatic sinusoids
Hepatic sinusoids
contain phagocytic cells that remove foreign particles from blood
Central vein
center of each lobule
where mixed blood flows towards
forms haptic veins
Hepatic duct
transport bile out of liver
Common hepatic duct
formed from left and right hepatic duct
Cystic duct
joins common hepatic duct
from gallbladder
Common bile duct
formed from common hepatic duct and cystic duct
Bile and pancreatic secretions

Functions of liver
digestive and excretory functions
stores and processes nutrients
detoxifies harmful chemicals
synthesizes new molecules
secretes 700 milliliters of bile each day
Bile
dilutes and neutralizes stomach acid and breaks down fats
Control of bile secretion and release

Pancreas
located to stomach in inferior part of left upper quadrant
head near midline of body
tail extends to the left and touches spleen
endocrine tissues have pancreatic islets that produce insulin and glucagon
exocrine tissues produce digestive enzymes that travel through ducts
Endocrine tissues
have pancreatic islets that produce insulin and glucagon