grav fields
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
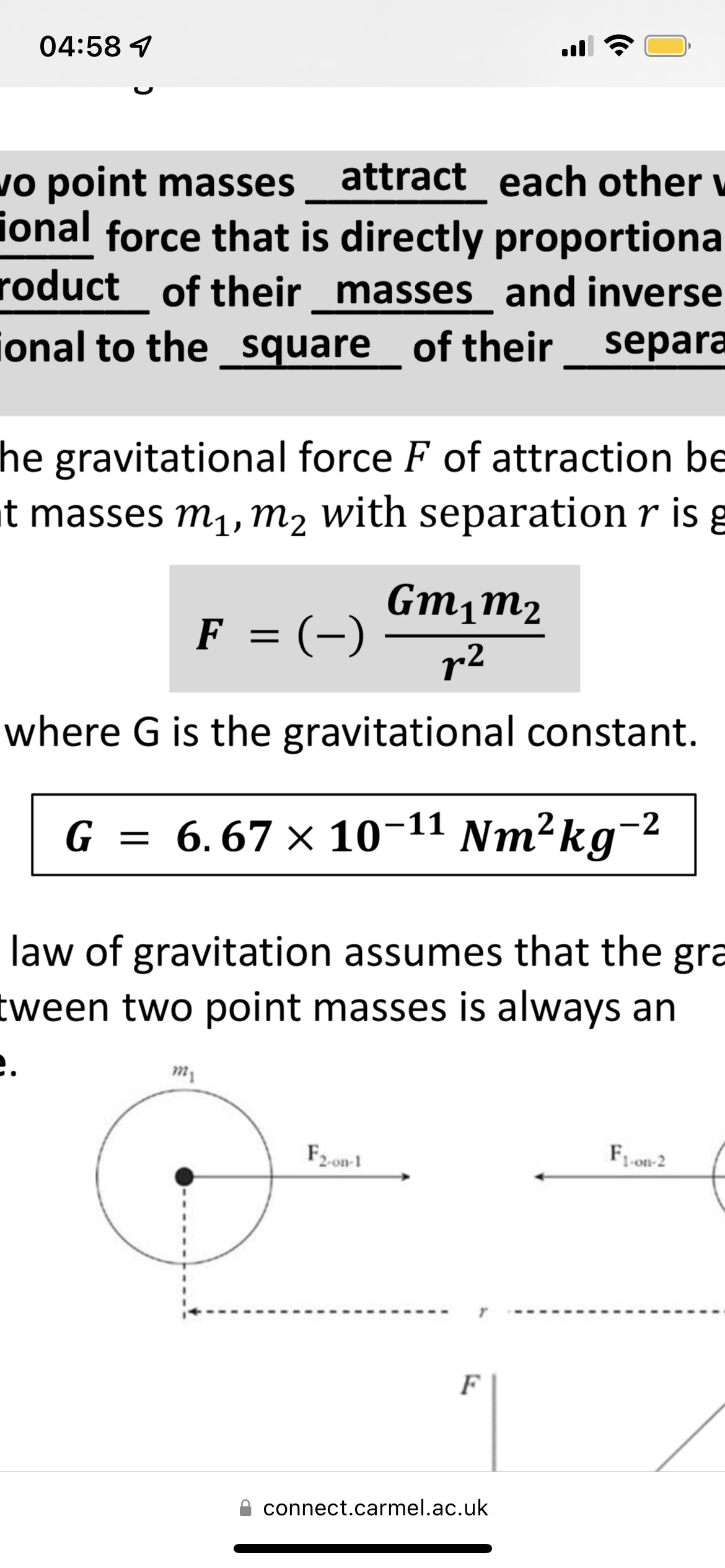
Newtons law of gravitation
Any two point masses separated by a distance r attract each other with a gravitational force that’s proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation
Field line rules
Represent magnitude and direction of force per unit mass at that point in the field
Always towards centre of mass
Uniform at surface : parralel to each other , perpendicular to surface , equidistant space between them
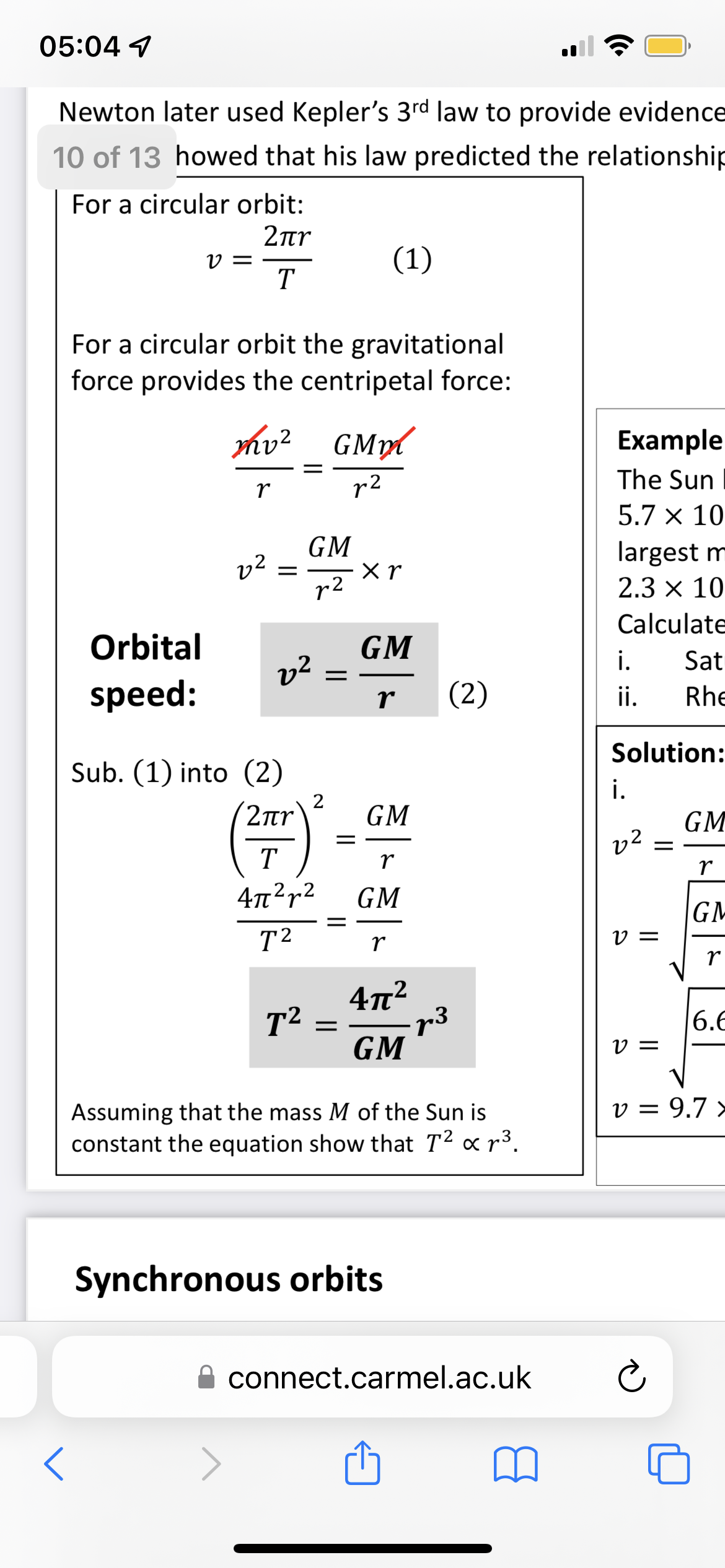
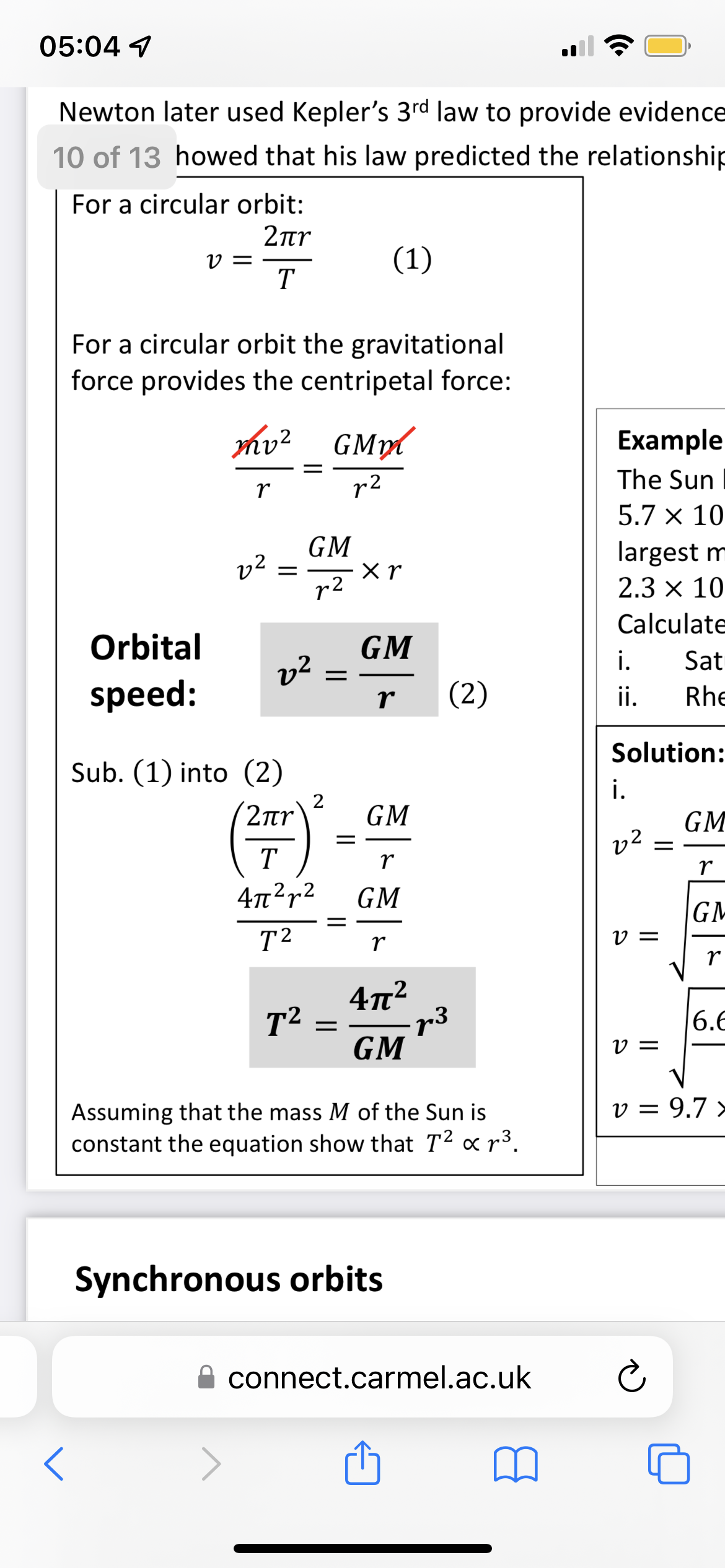
Keplers 3rd law
T ² is proportional to r³
Resultant field
Neutral point is closer to object if heavier mass
Synchronous orbits
Equal time period to rotational time period of planet being orbited
Geostationary orbit definition
Remains vertically above the the same point of the equator at all times
Geostationary orbit Features
Same time period as earths rotation (24hrs)
Orbit in equatorial plane
Move in the same direction as earths rotation
Geostationary orbit Uses
satellite television broadcasting
telecommunications transmissions
Geostationary orbit advantages
Maintain continuous contact with satellite and area
Geostationary orbit Disadvantages
Restricted area covered by each satellite - would need many to cover whole earth
Low polar orbits
Passes above north and south poles during each complete orbit
Low polar orbits advantages
Can scan Earth in just a few days
Closer to earth
Greater speed , multiple orbits per day
Low polar orbits disadvantage
Affected by atmosphere so speed can be reduced by air resistance
Low polar orbit uses
Mapping land features
Tracking cloud coverage
Military surveillance
Monitoring ocean currents
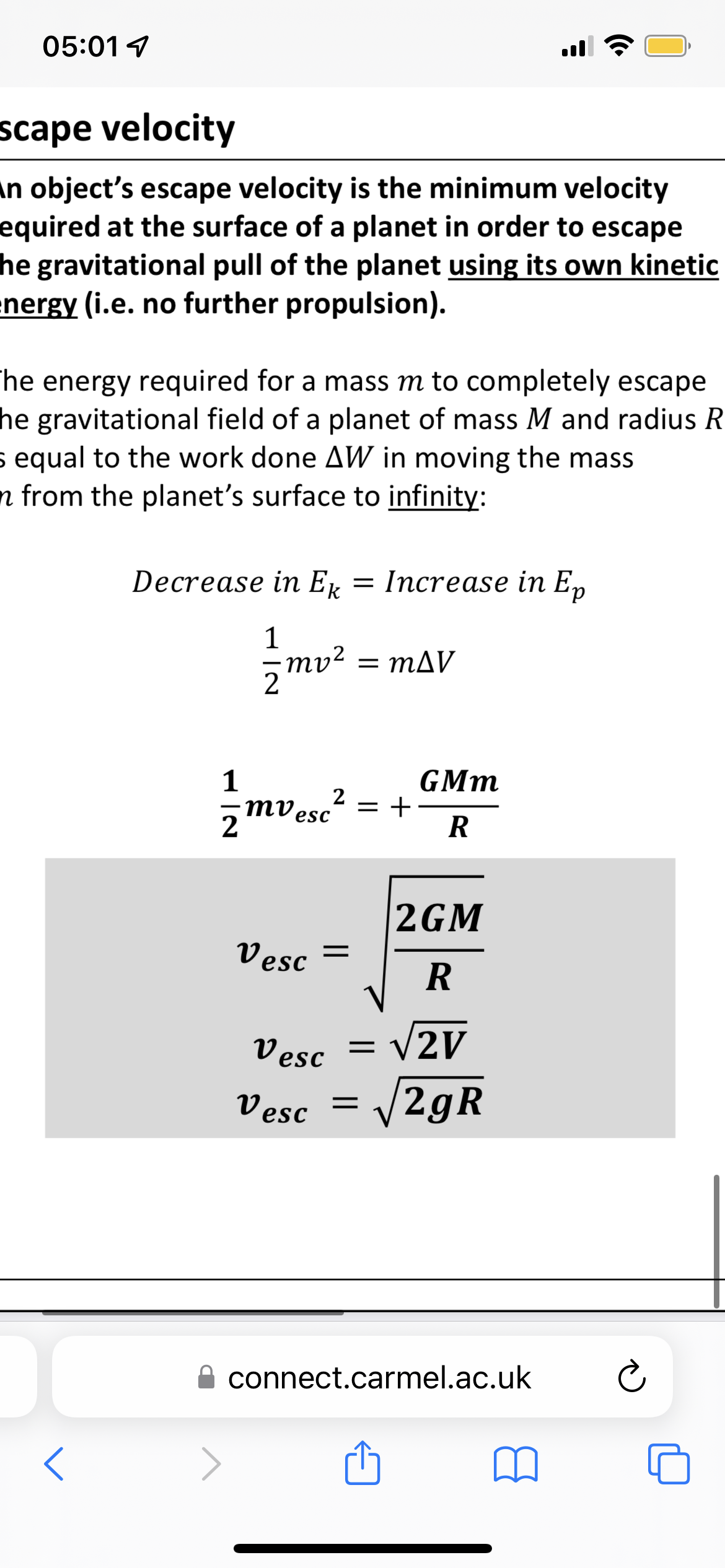
Escape velocity
Minimum velocity required to at the surface of a planet in order to escape the gravitational pull of the planet using its own kinetic energy
what is g
gravitational field strength , force on a unit mass at the earths surface
What is G
gravitational constant , relates to the force of attraction between two masses & their separation
Total energy of an orbiting satellite equation
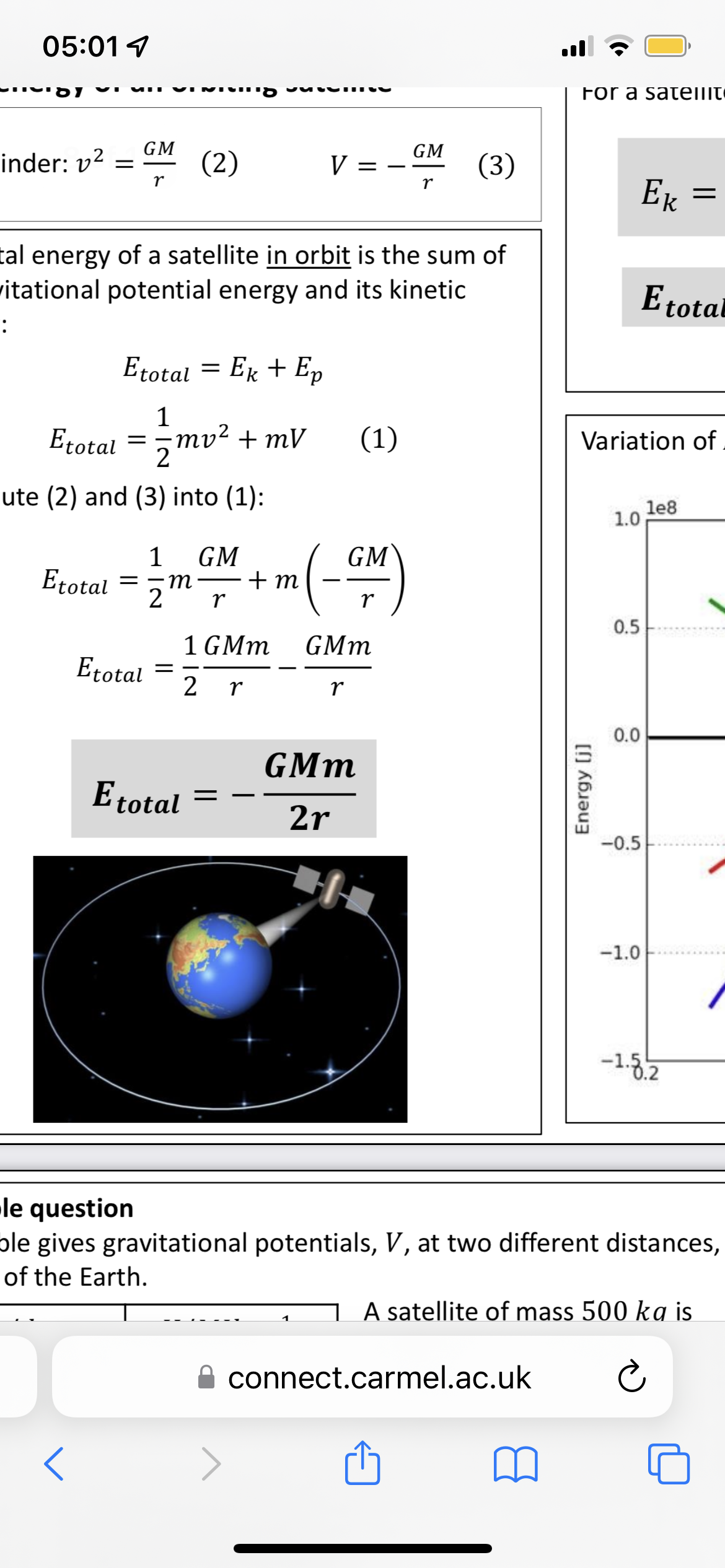
Escape velocity equation
Orbital time period equation
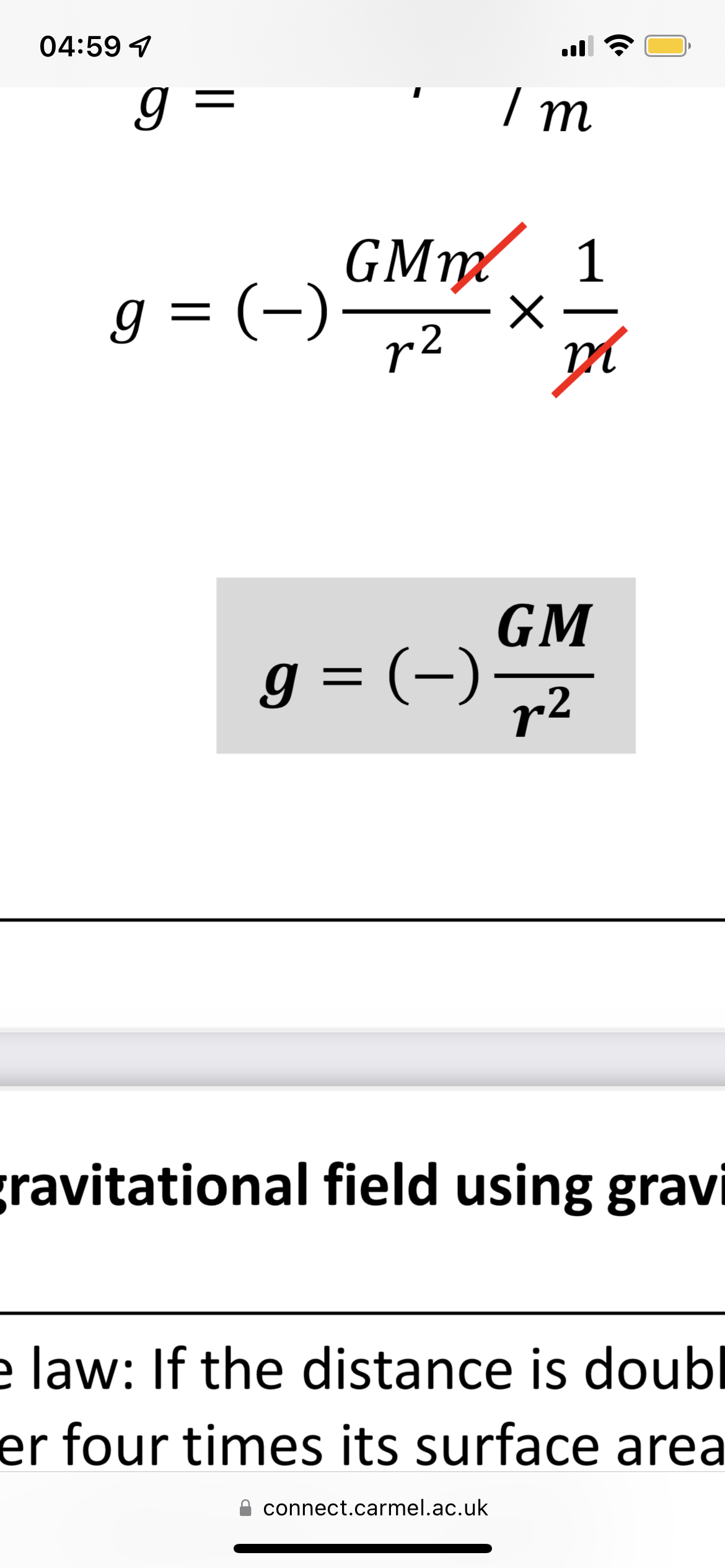
Gravitational force equation
Gravitational field strength equation
Orbital speed equation
Gravitational potential equation

Properties of a radial gravitational field
Field strength is inversely proportional to the distance squared
Region where mass experiences force due to another mass
Non contact force