30: Skull, CT, and MRI
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Common indication for intraoral rads (where they may actually be useful)
Dental radiographs
Auricular structure that may be evaluated on radiographs
Tympanic bullae
Radiographic view done to evaluate nasal disease
Open mouth maxillary VD
Radiographic view done to evaluate the frontal sinus
Rostral → caudal skyline view
Radiographic view done to evaluate the TMJ
Double obliqued lateral view: rotate the head away from you and tip the nose
Common fracture of the scull
Depression fracture
How do radiographs estimate skull damage as compared to CT
Radiographs will underestimate skull fractures
Proliferative skull conditions we CAN evaluate on radiographs
Calvarial hyperostosis
Craniomandibular osteopathy
Multilobular osteochondrosarcoma
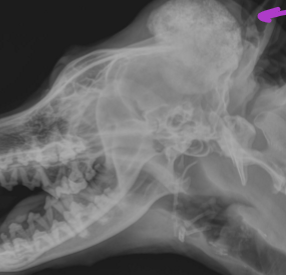
Calvarial hyperostosis
Increased deposition of new bone along the calvarium in puppies
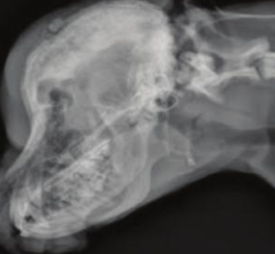
Craniomandibular osteopathy
Increased deposition of new bone along the mandible in puppies
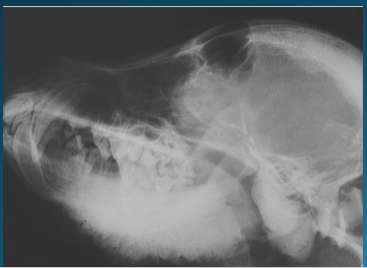
Multilobular osteochondrosarcoma
Slow-growing neoplasia in older dogs that looks like a popcorn ball
Imaging techniques that remove superimposition of the skull
CT and MRI
Other name for MRI
NMR
Energy used by CT
Still x-rays
Energy used by MRI
Magnetic and radiofrequencies
Tissue type better visualized on a CT
Bone
Tissue type better visualized on an MRI
Soft tissue
Which imaging modality (CT or MRI) is faster
CT
Which imaging modality (CT or MRI) is radiographically safer
MRI; no radiation!
How much more radiation does a CT give off than an X-ray
200x
Contrast used in CT
Iohexol
What indications are best for CT
Honestly most things
Polytraumas
Orthopedic disease
Masses
Vascular anomalies
Head bones
Exotics we don’t want to sedate
Basic physics of how MRI works
Strong superconducting magnet makes all the H atoms line up, then they are blasted with radiofrequency pulses to add energy, and the H atoms emit energy at different rates
Unit for measuring magnet strength
Tesla
Why do we have to be so careful about metal in MRI machines
The magnet can pull violently at things, and the radiofrequency can cause tissues and implants to heat up
How do we keep the MRI magnet cold
Liquid helium
Which imaging modality (CT or MRI) can evaluate different tissues in one take
CT; MRI you need to run different sequences to highlight different tissues
Contrast used for MRI
Gadolinium-based contrast
Tissue that does not take up gadolinium contrast well on MRI
Vasculature
Tissues that are best imaged by MRI
Brain, spinal cord, and distal ST in limbs