Quiz 4 Study Guide on Cellular Respiration and Cellular Reproduction
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from Chapter 7 on Cellular Respiration and Chapter 8 on Cellular Reproduction.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is necessary for the complete breakdown of glucose in cellular respiration?
Oxygen
What are the four phases of Cellular Respiration?
1) Glycolysis 2) Preparatory Reaction 3) Citric Acid Cycle 4) Electron Transport Chain.
GPCE
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytoplasm
How many ATP molecules are produced by cellular respiration?
36 to 38 ATP
What process occurs if oxygen is not present during cellular respiration?
Fermentation
What are the products of yeast fermentation?
Alcohol and carbon dioxide (CO2)
What is the breakdown of ATP into?
ADP and inorganic phosphate (P+).
What are the phases of the cell cycle during interphase?
G1 (Growth), S (DNA replication), and G2 (cell prepares to divide).
What happens in the G0 phase of the cell cycle?
Nerve cells go into this arrested stage and do not divide.
What is the order of phases in mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase.
What is cytokinesis?
Division of the cytoplasm.
What is pyruvte?
Two carbon 3 molecules produced from glycolysis.
What does glycolsysis do?
Breaks down glucose.
What is the preparatory reaction in cellular respiration?
Converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, producing NADH and releasing carbon dioxide.
What is the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration?
Known as the Krebs cycle, is a series of enzymatic reactions that further breaks down acetyl-CoA to produce ATP, NADH, and FADH2, along with releasing carbon dioxide.
What is the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
Series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, ultimately producing ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
What does ATP do for muscles?
It helps them contract.
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Mitochondria
What is the opposite of cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis
Cellular respiration uses OXYGEN to convert what into what?
Chemical energy into ATP.
What is glucose broken down into?
CO2 and H2O chemical energy
What happens to do CO2 and H2O?
They are released and converted into ATP.
What are the products of fermentation in animals?
Lactate, which is carried to the liver and converted into pyruvate
What happens in G1 of interphase?
Cell growth, organelles double
What happens in the S phase of interphase?
DNA replication occurs, resulting in two copies of each chromosome.
What happens in the G2 phase of interphase?
The cell continues to grow and prepares for mitosis by producing proteins and organelles, ensuring all DNA has been duplicated properly.
In short, what is mitosis?
The division of the nucleus
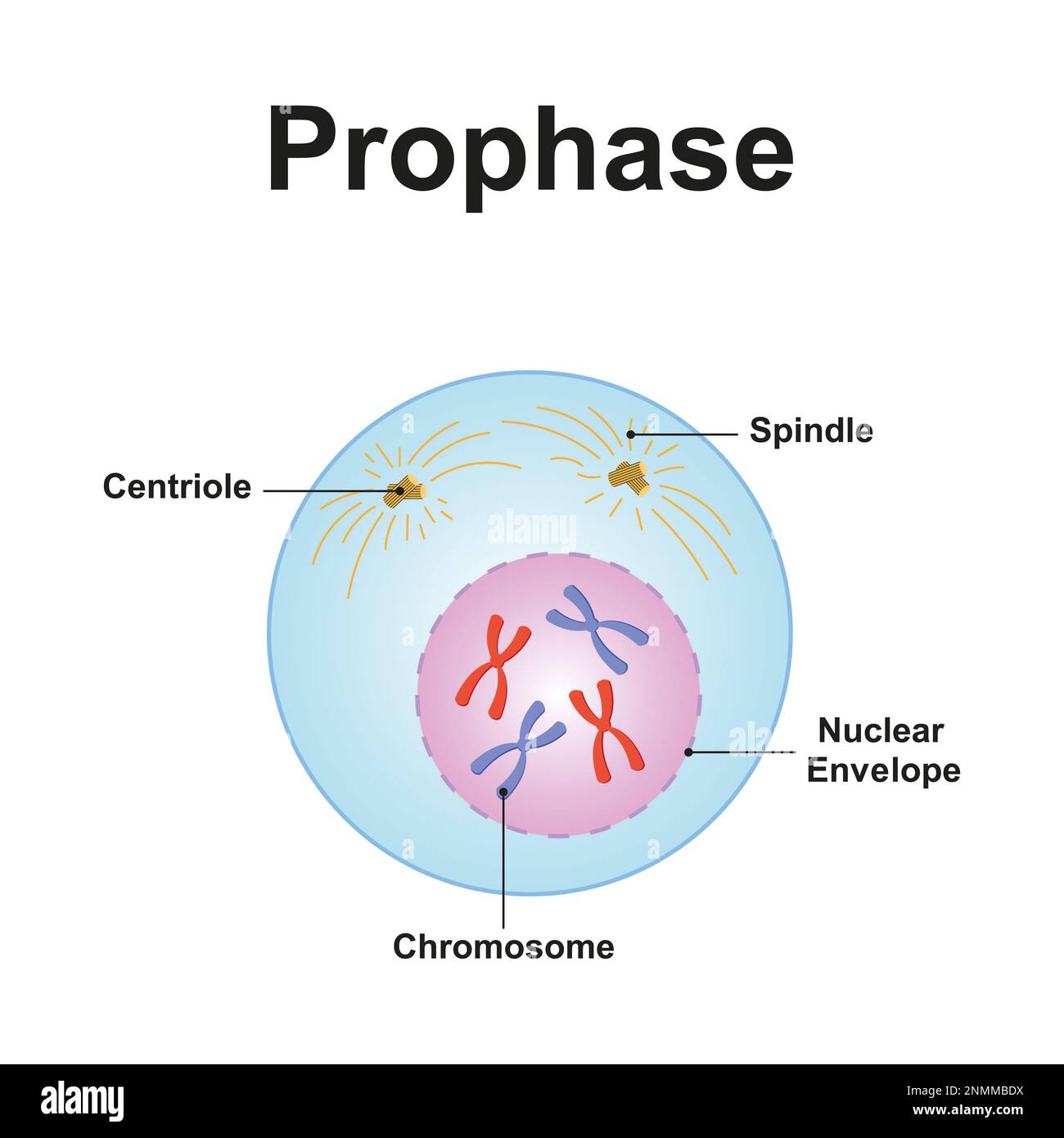
What is prophase?
Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the mitotic spindle begins to form.
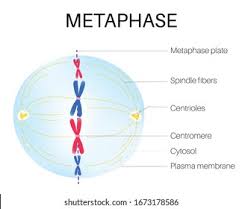
What is metaphase?
Chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, and spindle fibers attach to centromeres.

What is anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers.
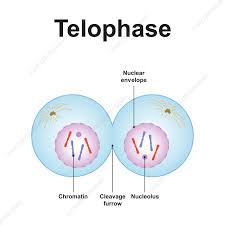
What is telophase?
The separated chromatids reach the opposite poles, the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set, and the chromosomes begin to de-condense back into chromatin.