Lab 9 (Echinoderms and Chordates) Vocabulary
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
deuterostomes
Animals in which the blastopore becomes the anus during early embryonic development (anus develops before mouth)
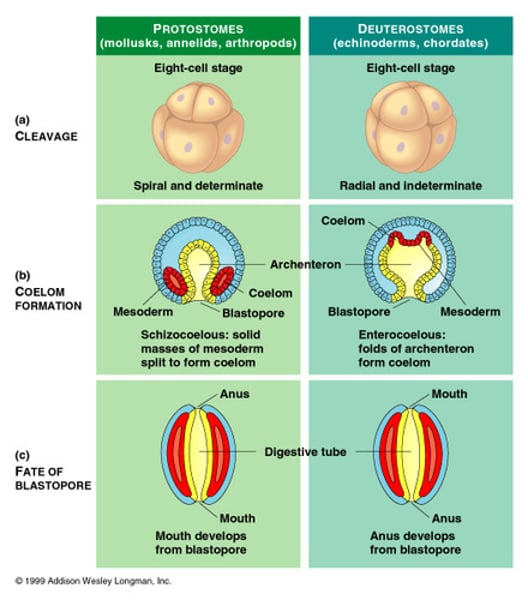
radial cleavage
A type of embryonic development in deuterostomes in that the planes of cell division that transform the zygote into a ball of cells are either parallel or perpendicular to the polar axis, thereby aligning tiers of cells one above the other.
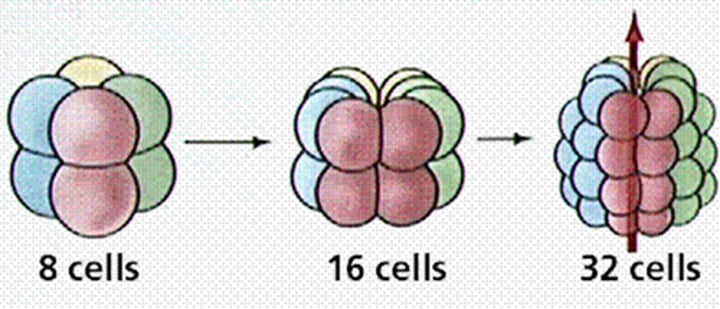
spiral cleavage
A type of embryonic development in protostomes, in which the planes of cell division that transform the zygote into a ball of cells occur obliquely to the polar axis, resulting in cells of each tier sitting in the grooves between cells of adjacent tiers.
Echinodermata
"prickly skin"; Phylum that includes sea stars, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars & sea cucumbers

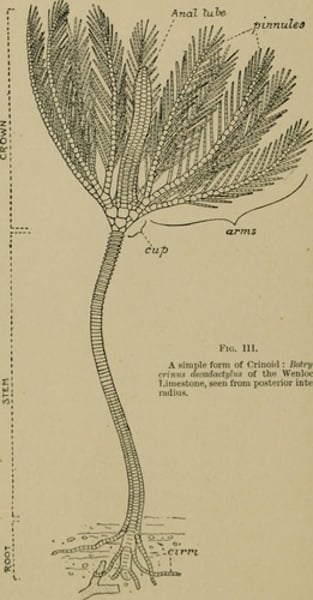
Crinoidea
Class including sea lilies and feather stars
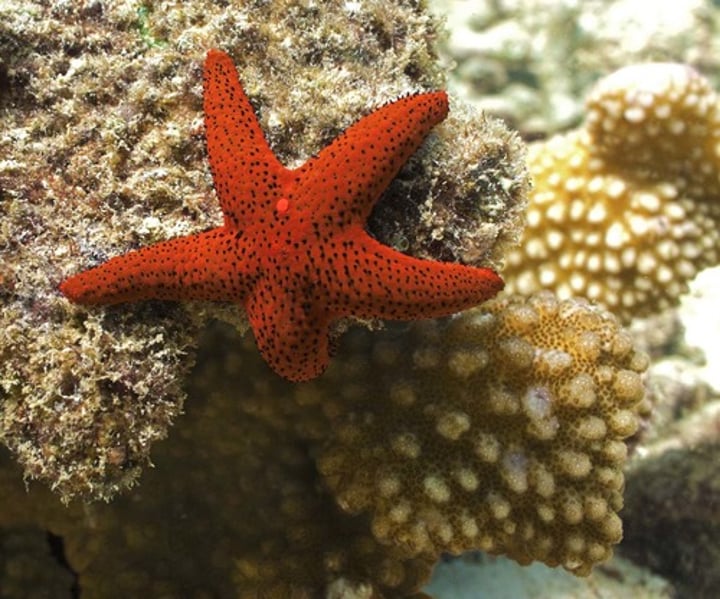
Asteroidia
Class of sea stars

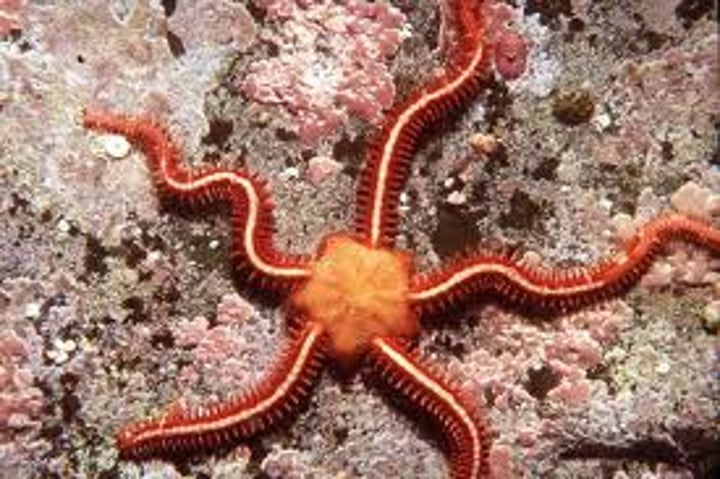
Ophiuroidea
Class including brittle stars and basket stars
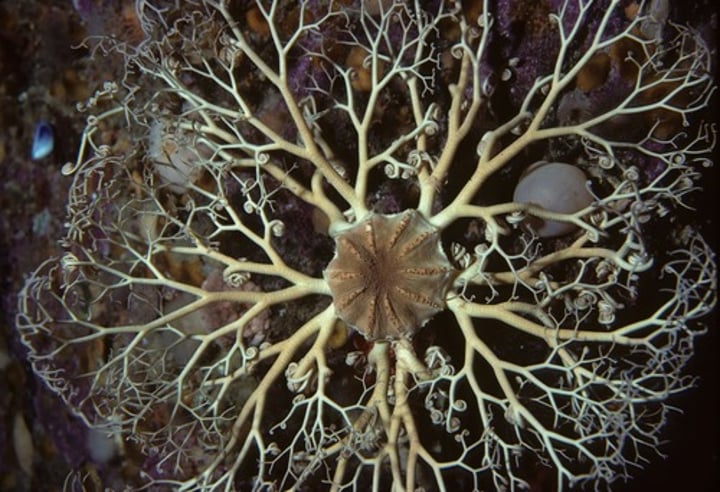
Echinoidea
Class of sea urchins and sand dollars

Holothuroidea
Class of echinoderms including the sea cucumbers

pentaradial symmetry
have 5 or multiples of 5 arms surrounding central disk

Calcite Ossicles
bone-like plates composed of calcium carbonate
pedicellariae
tiny pincers that are used for surface maintenance by sea stars and some sea urchins
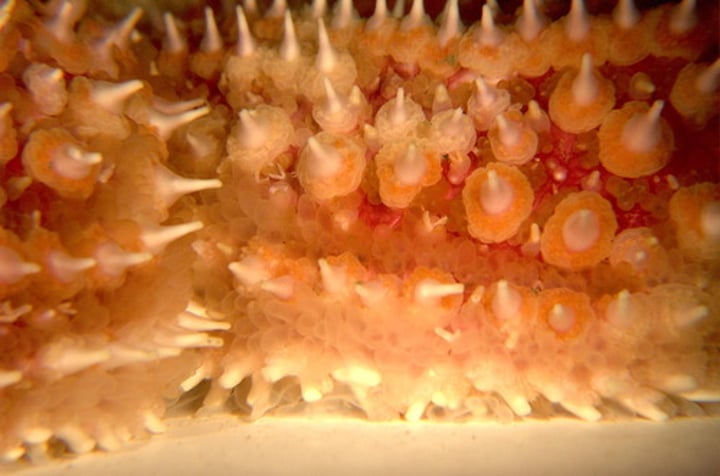
madreporite
sievelike structure through which the water vascular system of an echinoderm opens to the outside & regulates water pressure

autotomy
in Echinoderms, refers to ability to detach arms in order to get away from predators
fragmentation
A means of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals
aboral surface
in starfish & other Echinoderms, the side away from the mouth; top surface
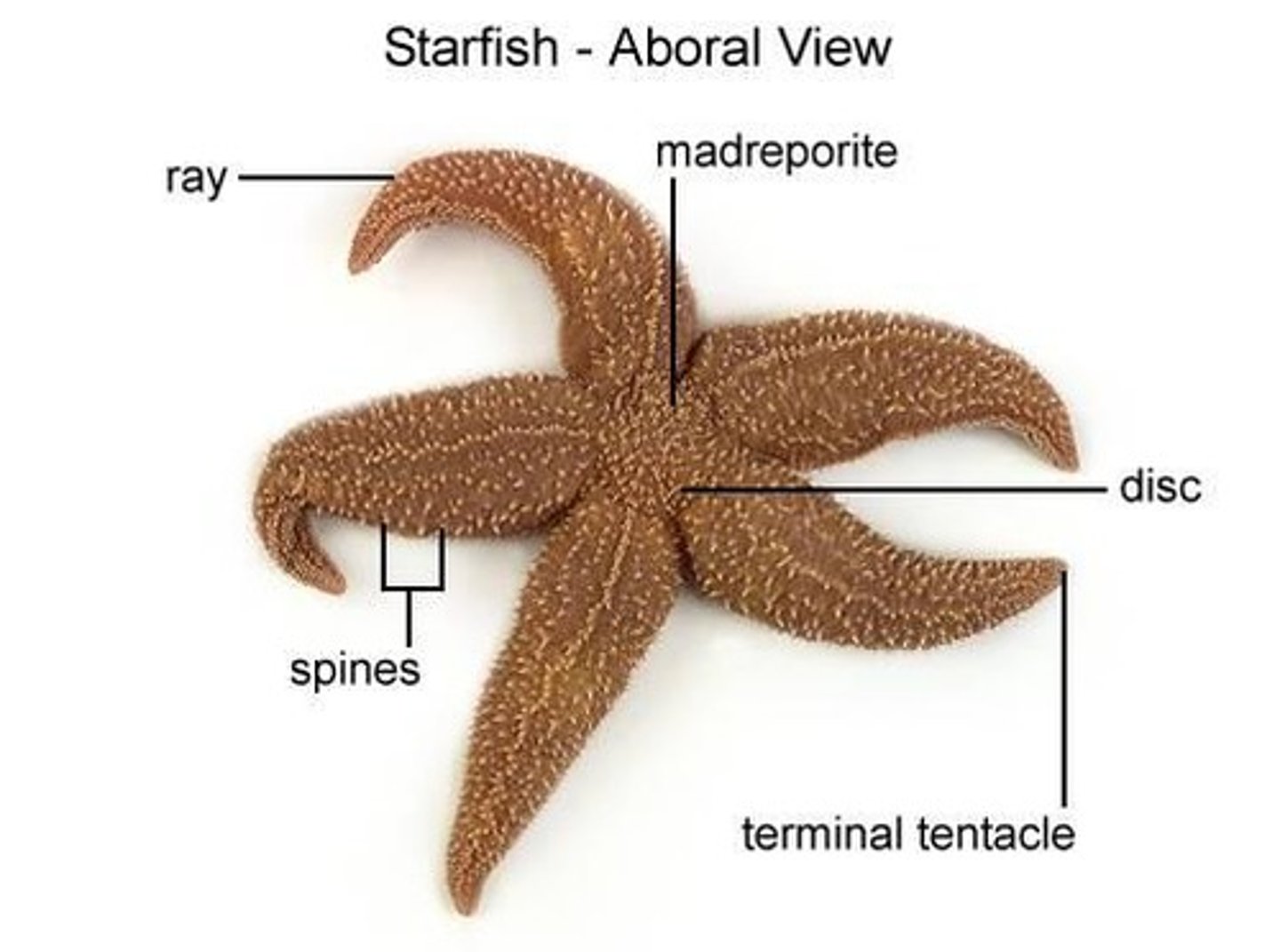

tube feet
Extensions of an echinoderm's water vascular system that stick out from the body and function in movement and obtaining food.
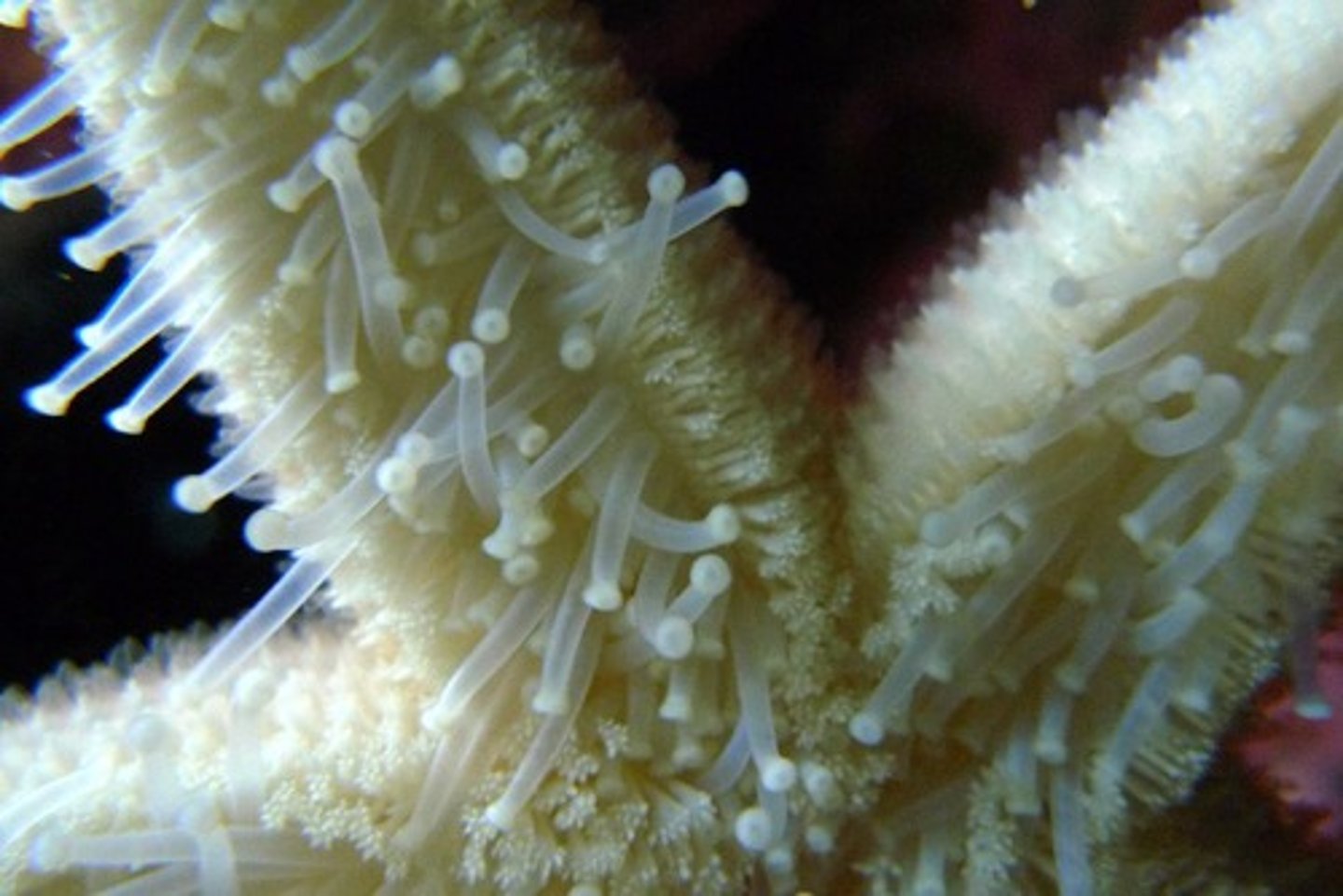

Chordata
The phylum of the animal kingdom that includes vertebrates (chordata - "cord")
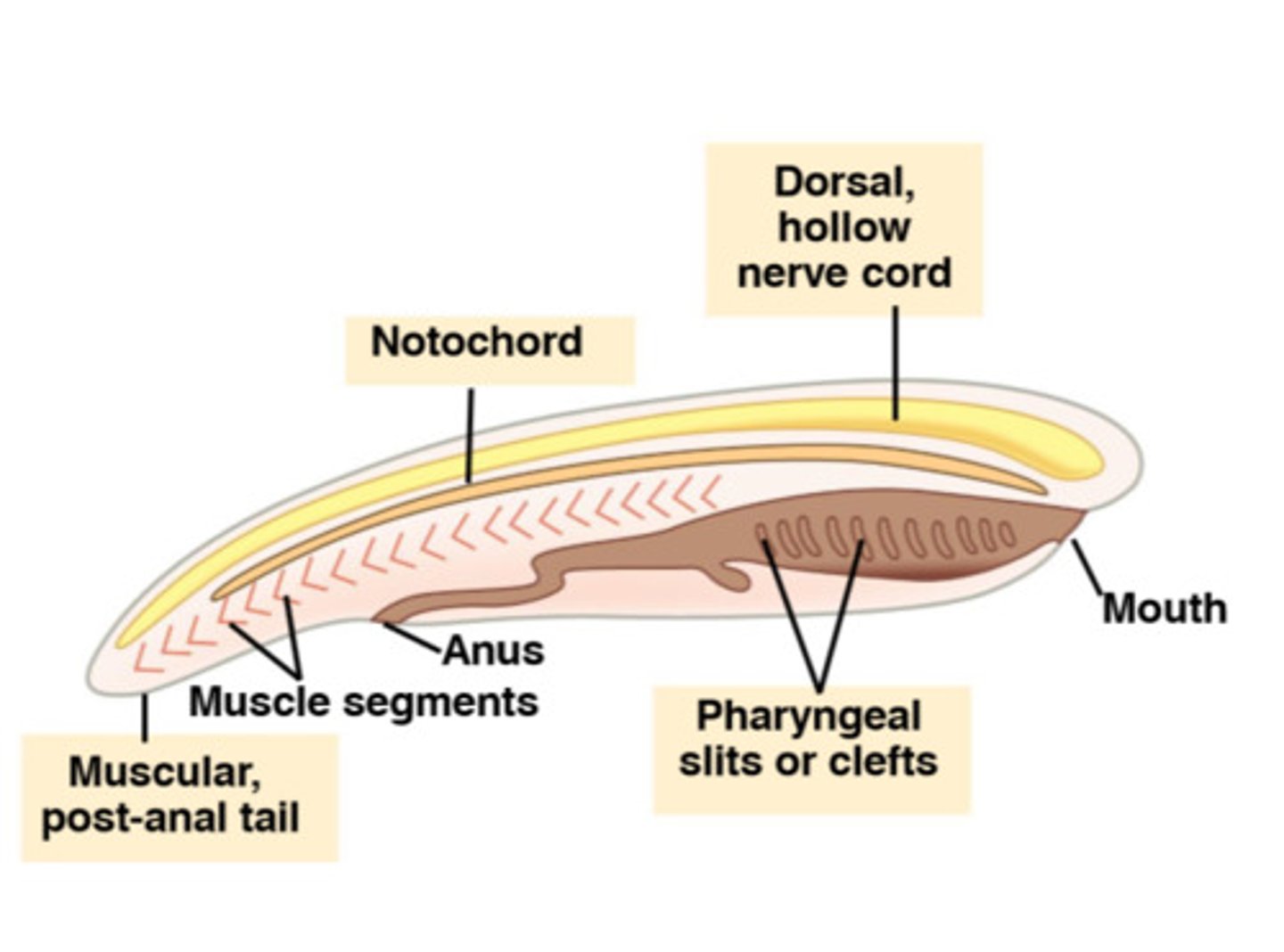
notochord
long supporting rod that runs through a chordate's body just below the nerve cord
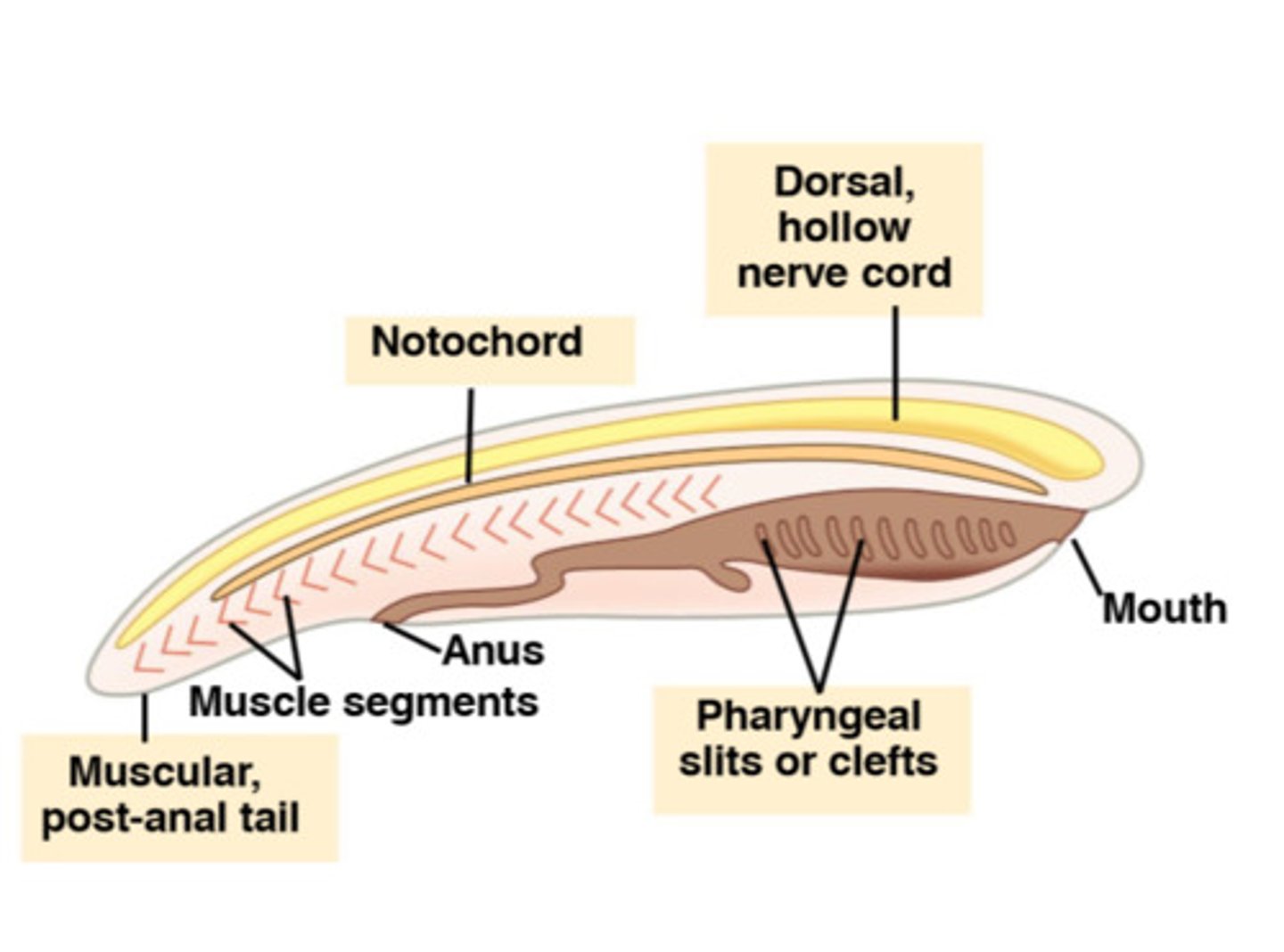
endostyle
tissue that secretes mucus and traps food on the pharyngeal floor
pharyngeal gill slits
all chordates share this at some point in life cycle; appear in the pharynx at some stage in their development, evolved to aid in respiration and filter feeding
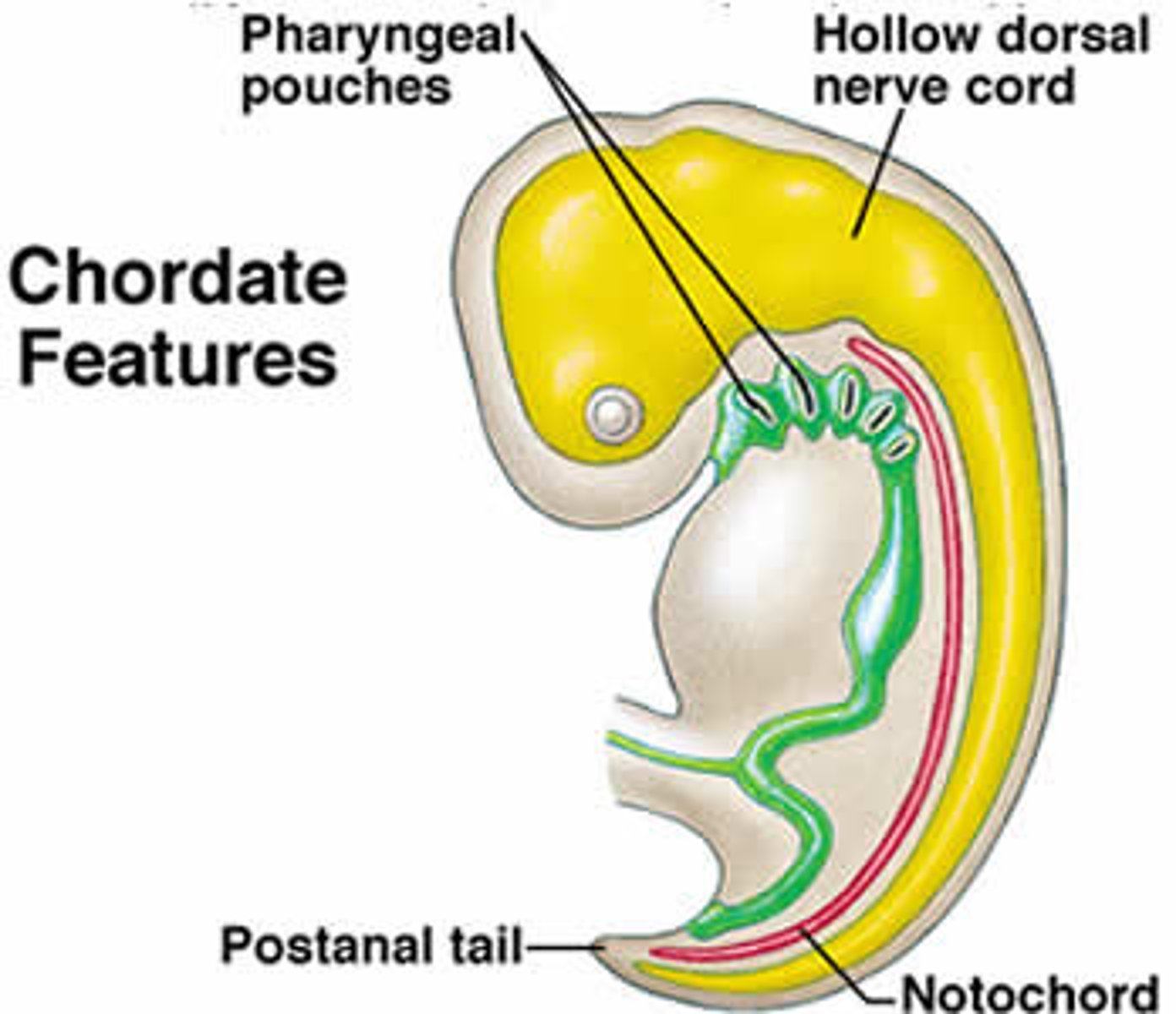
dorsal hollow nerve cord
a hollow, tubular structure derived from ectoderm, develops into CNS, brain & spinal cord; located dorsal to the notochord in chordates
epidermis
outermost layer of skin
parthenogenesis
Asexual reproduction in which females produce offspring from unfertilized eggs
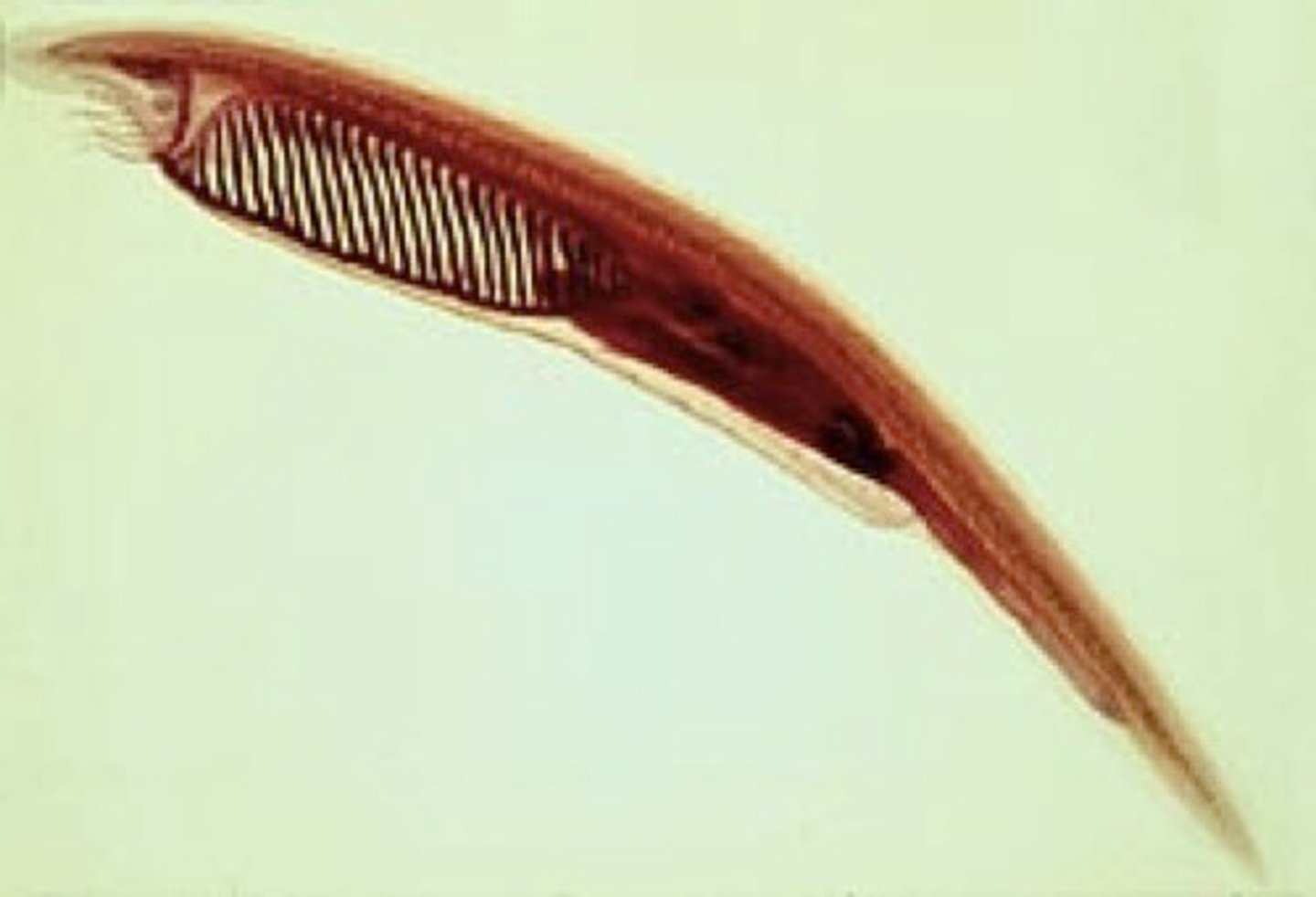
Cephalochordata
subphylum of lancelets
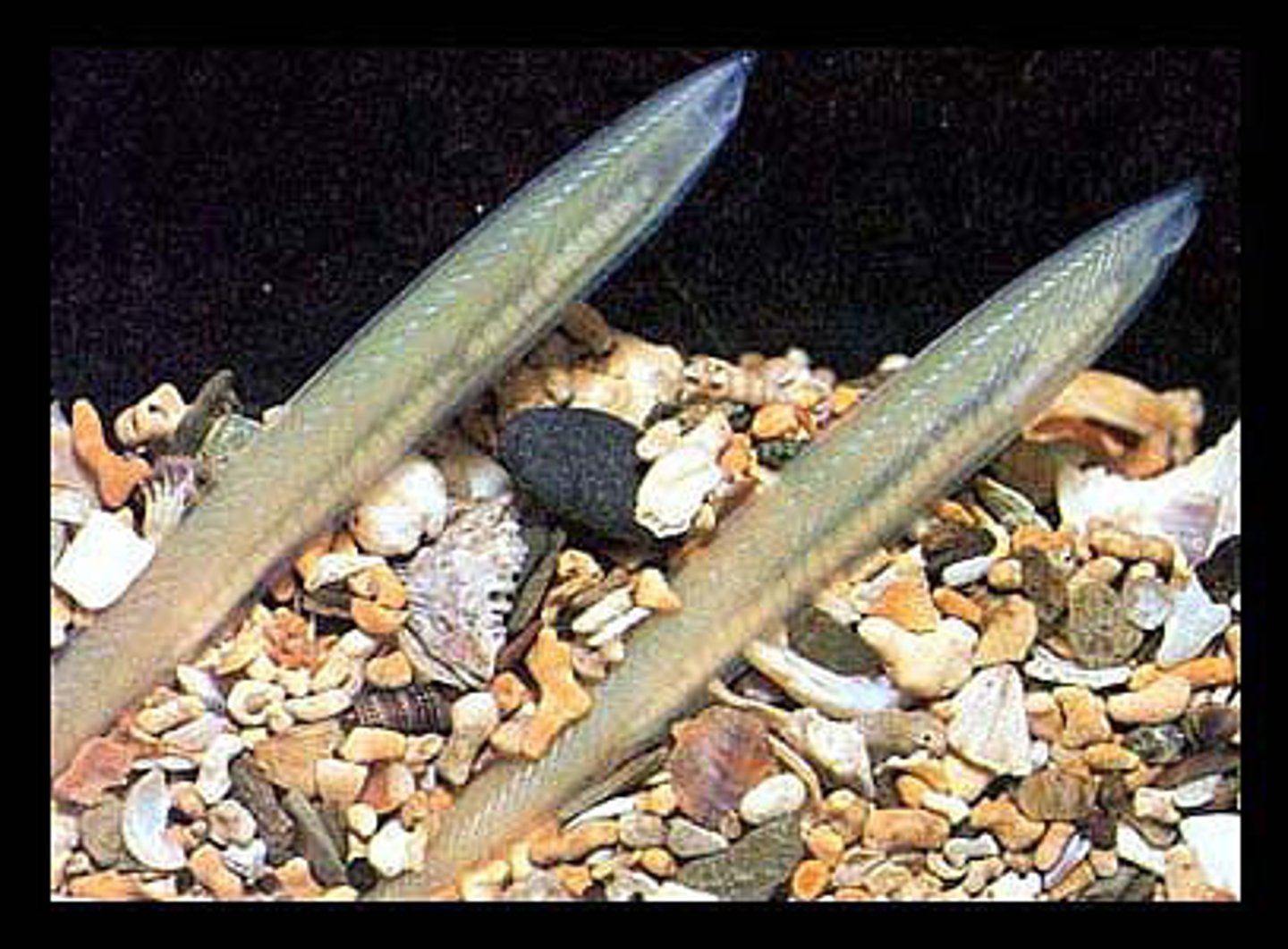

amphioxus
small marine animals - invertebrates- doesn't lose notochord
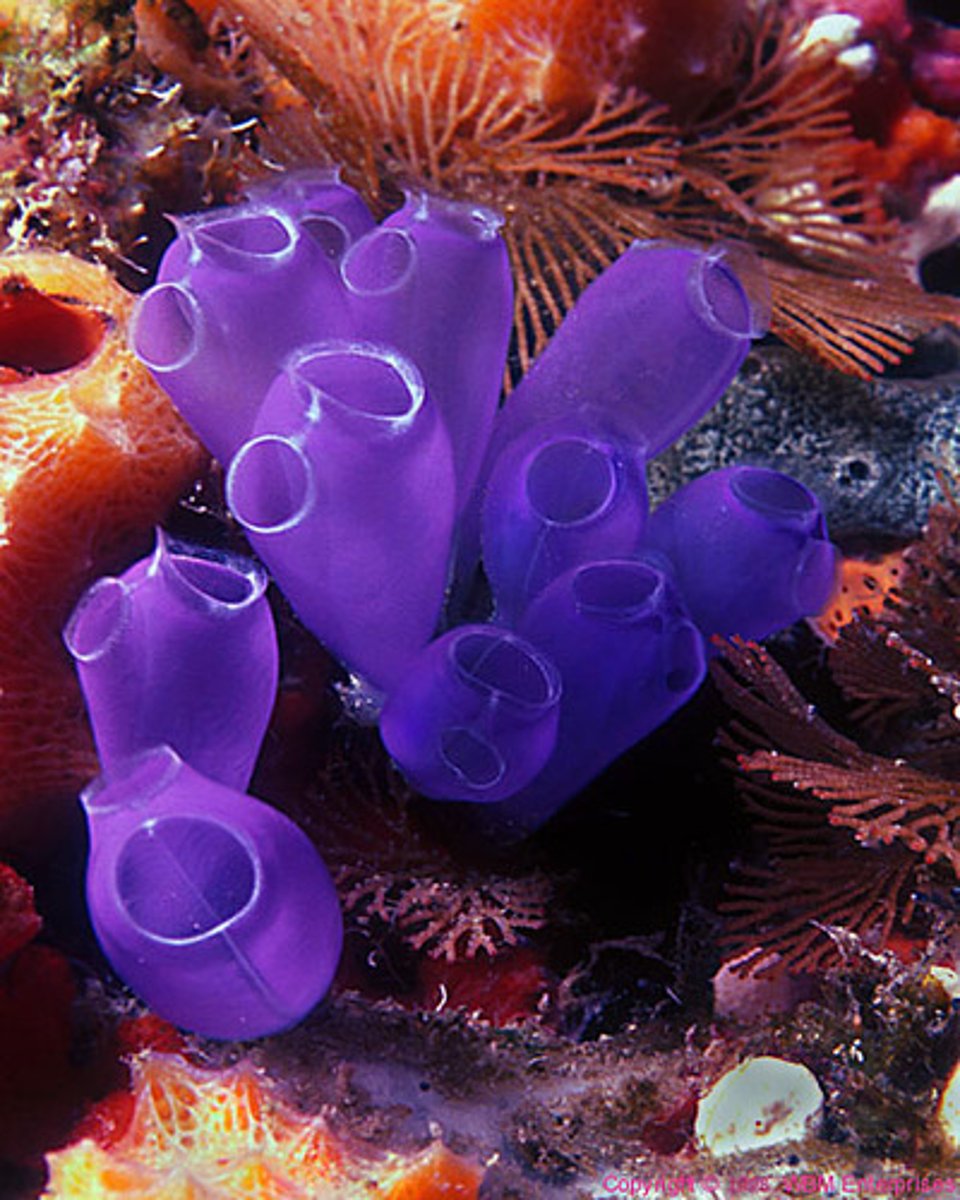
Tunicata
Subphylum of sea squirts (tunicates)

Vertebrata
Subphylum of Chordata which includes lampreys, sharks, fish, frogs, turtles, birds, humans, etc.
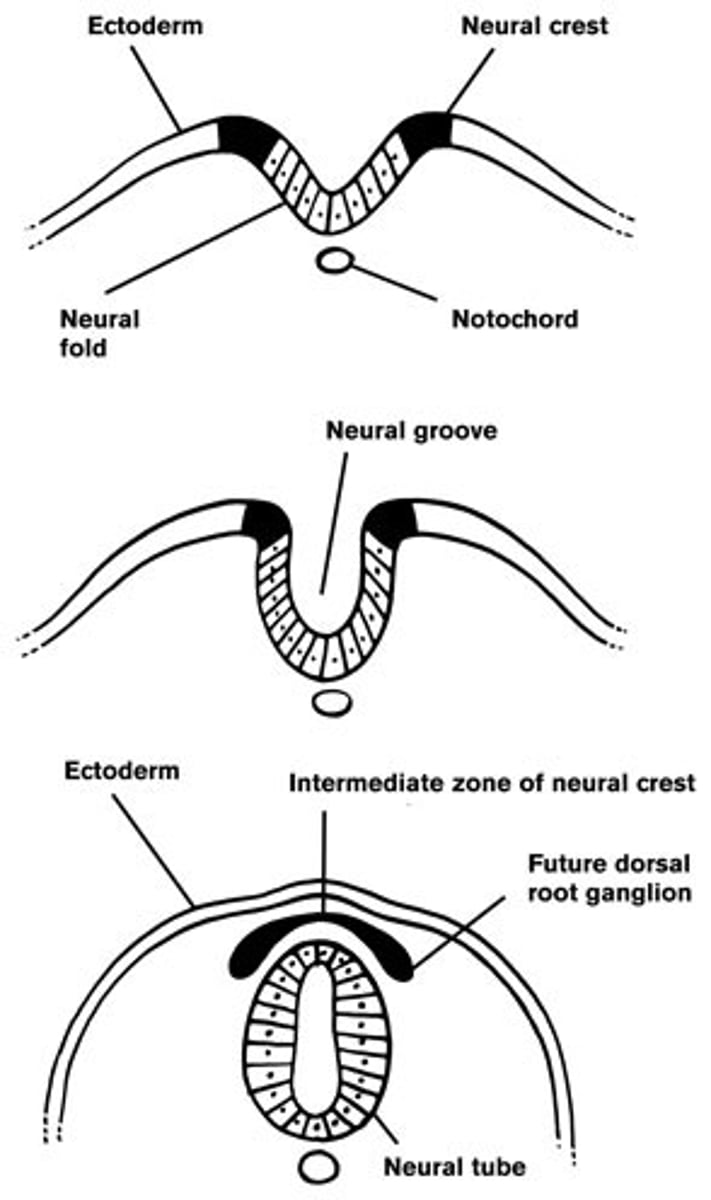
neural crest
group of cells that develops from the embryo's ectoderm and contributes to the development of many vertebrate structures such as formation of some skeletal elements (bones and cartilage of cranium), as well as to specialized cells in nervous system (neurons and glia)
cranium
the portion of the skull that encloses the brain
vertebral column
series of irregularly shaped bones called vertebrae that houses the spinal cord
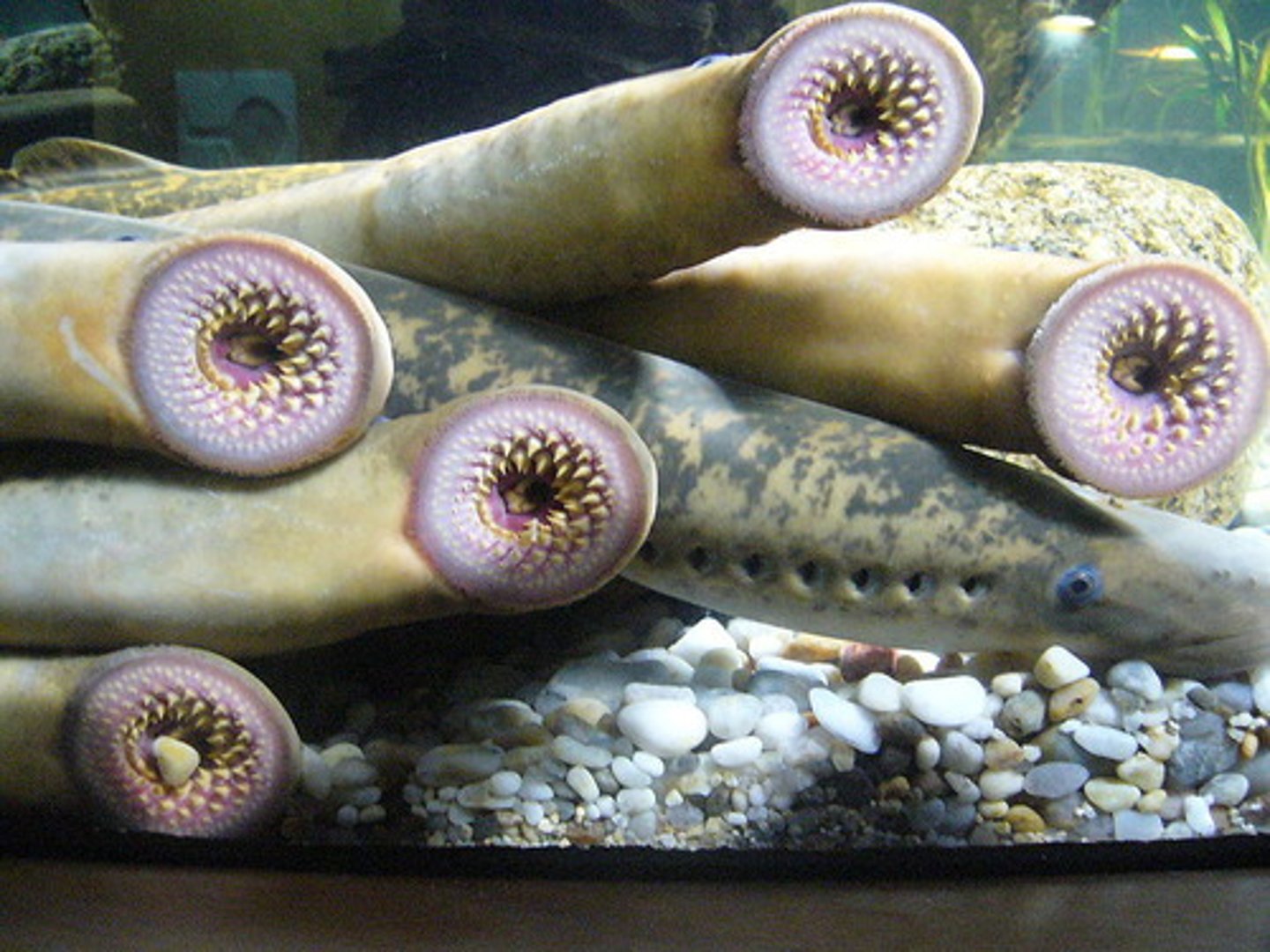
Petromyzontida
lampreys, jawless vertebrates

Chondrichthyes
Chordates including cartilaginous fishes such as sharks, rays & skates (jawed vertebrates)
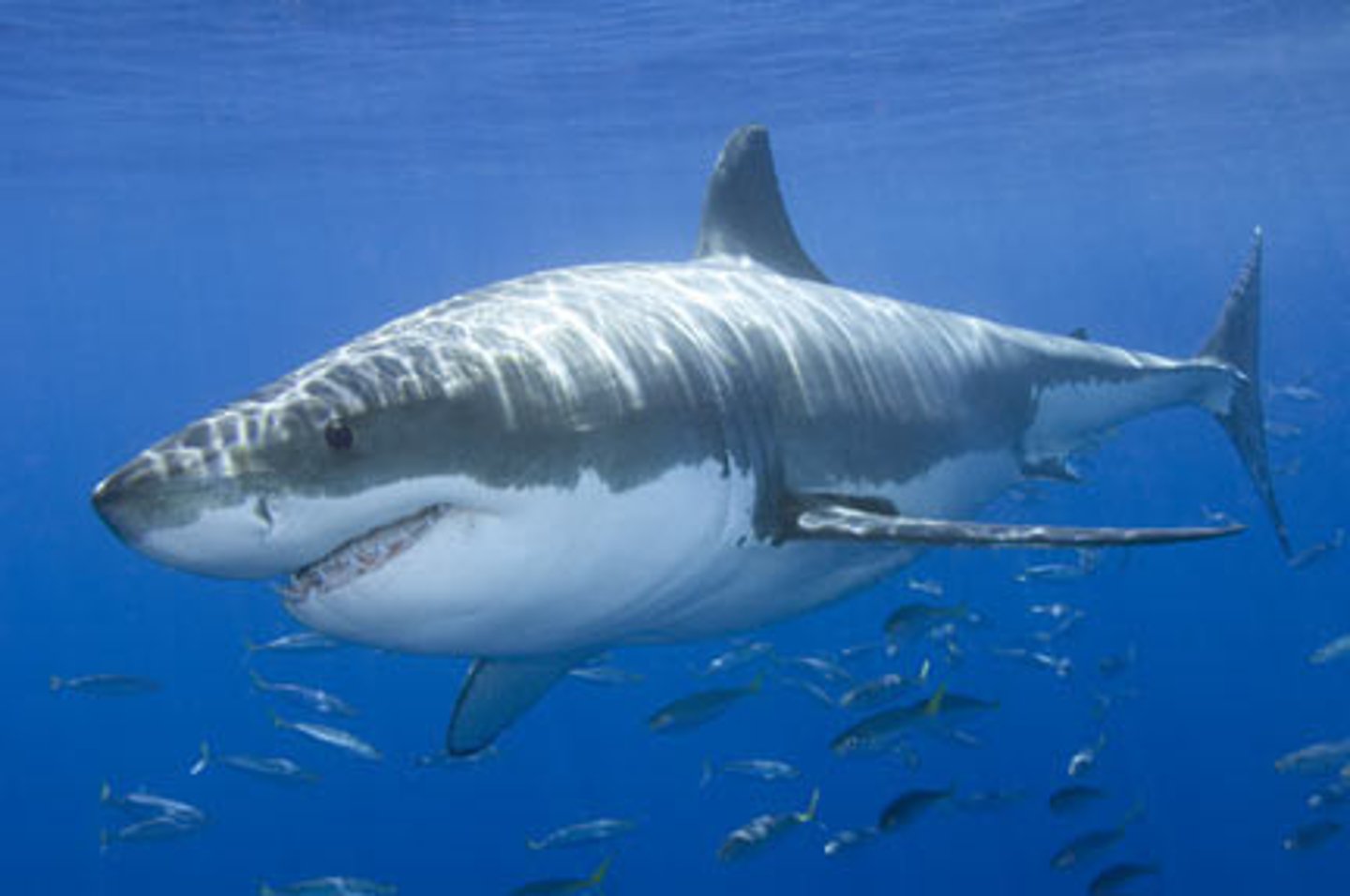

lateral line system
sensory receptors that enable fishes to detect vibrations or sound waves in water
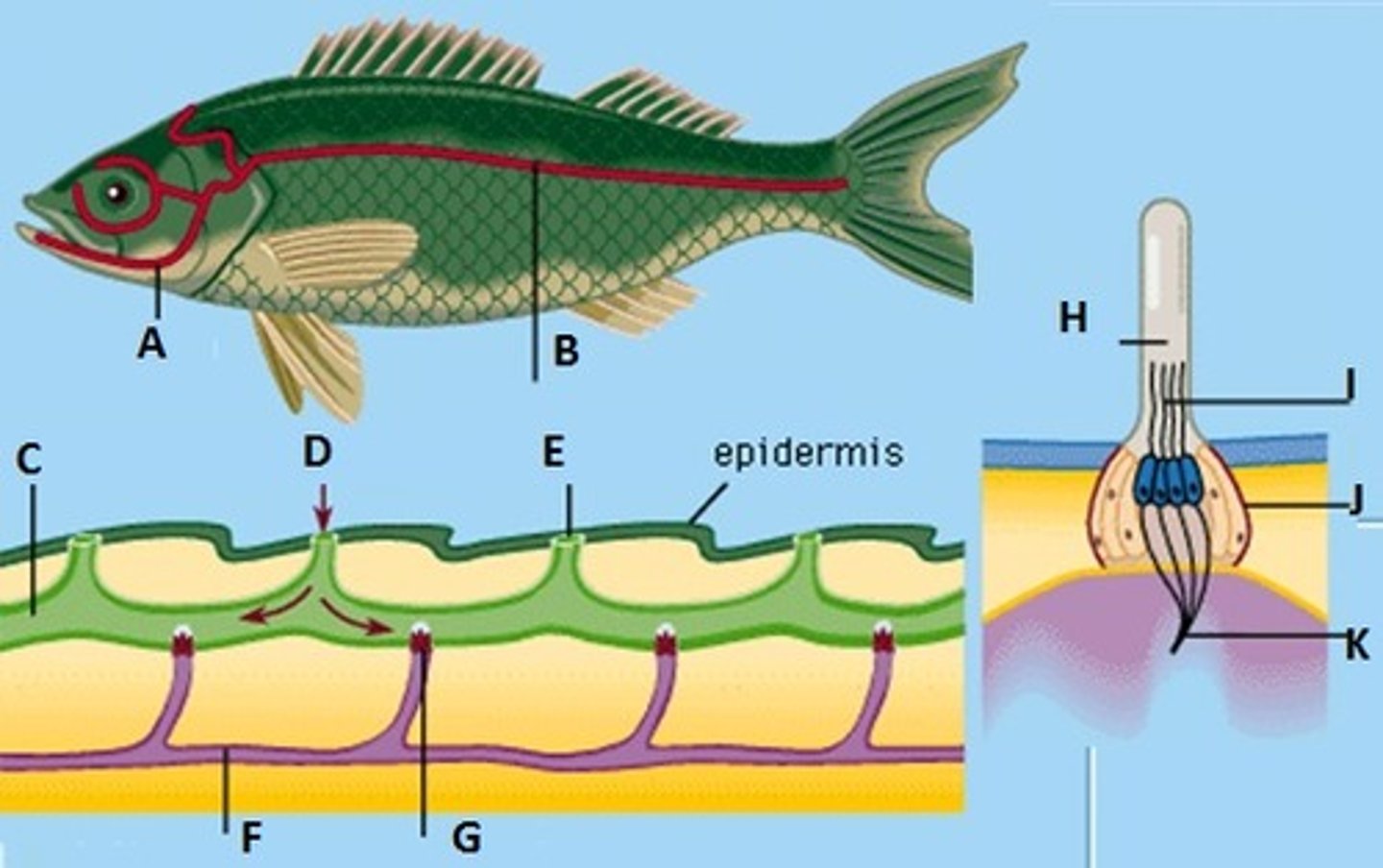
Ovoviviparous
term used to refer to animals whose young are born alive after developing in eggs inside the mother's body
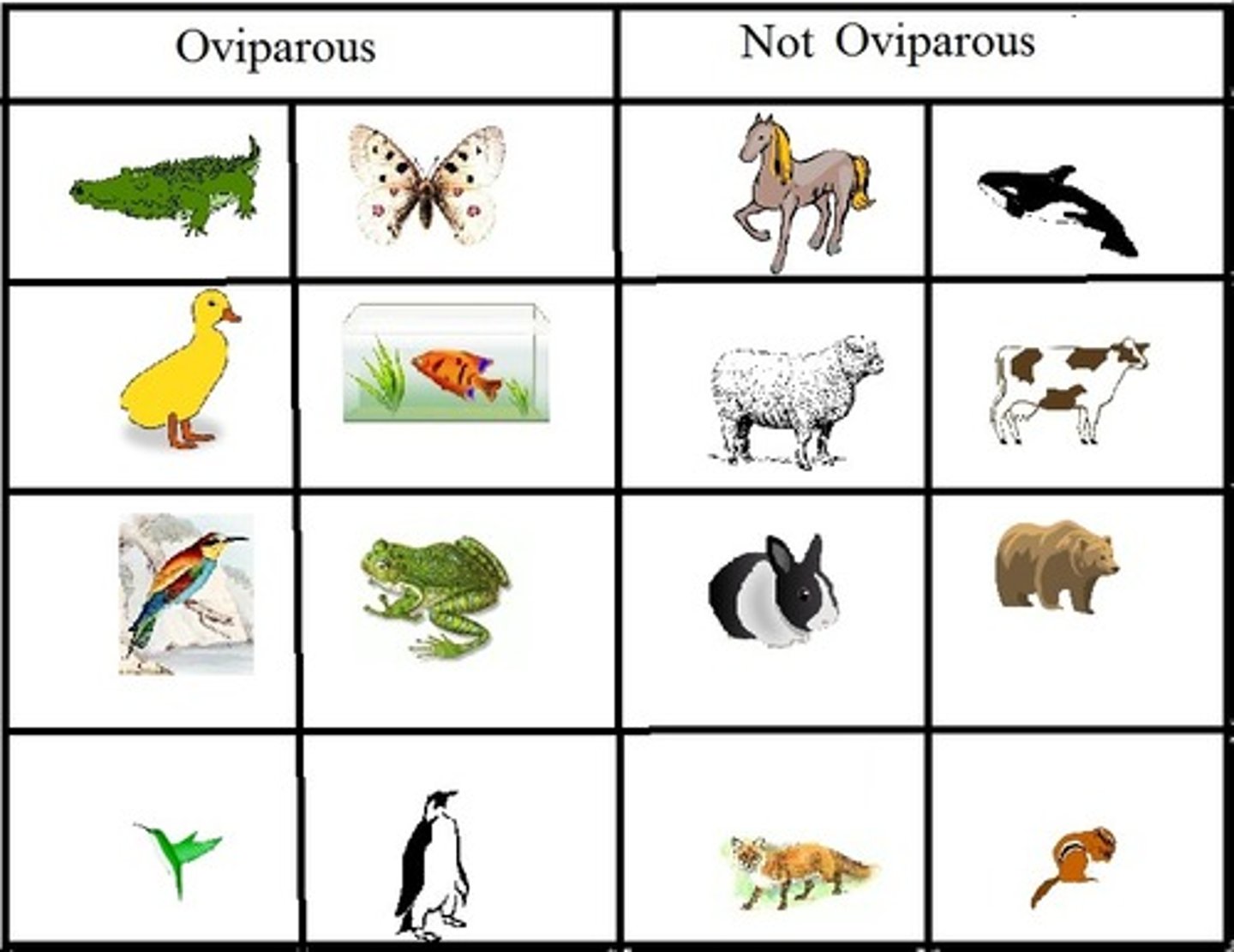
Oviparous
Eggs hatch outside the mother's body (think: ovi=over and out)
Actinopterygii
ray-finned fishes; Class of vertebrates
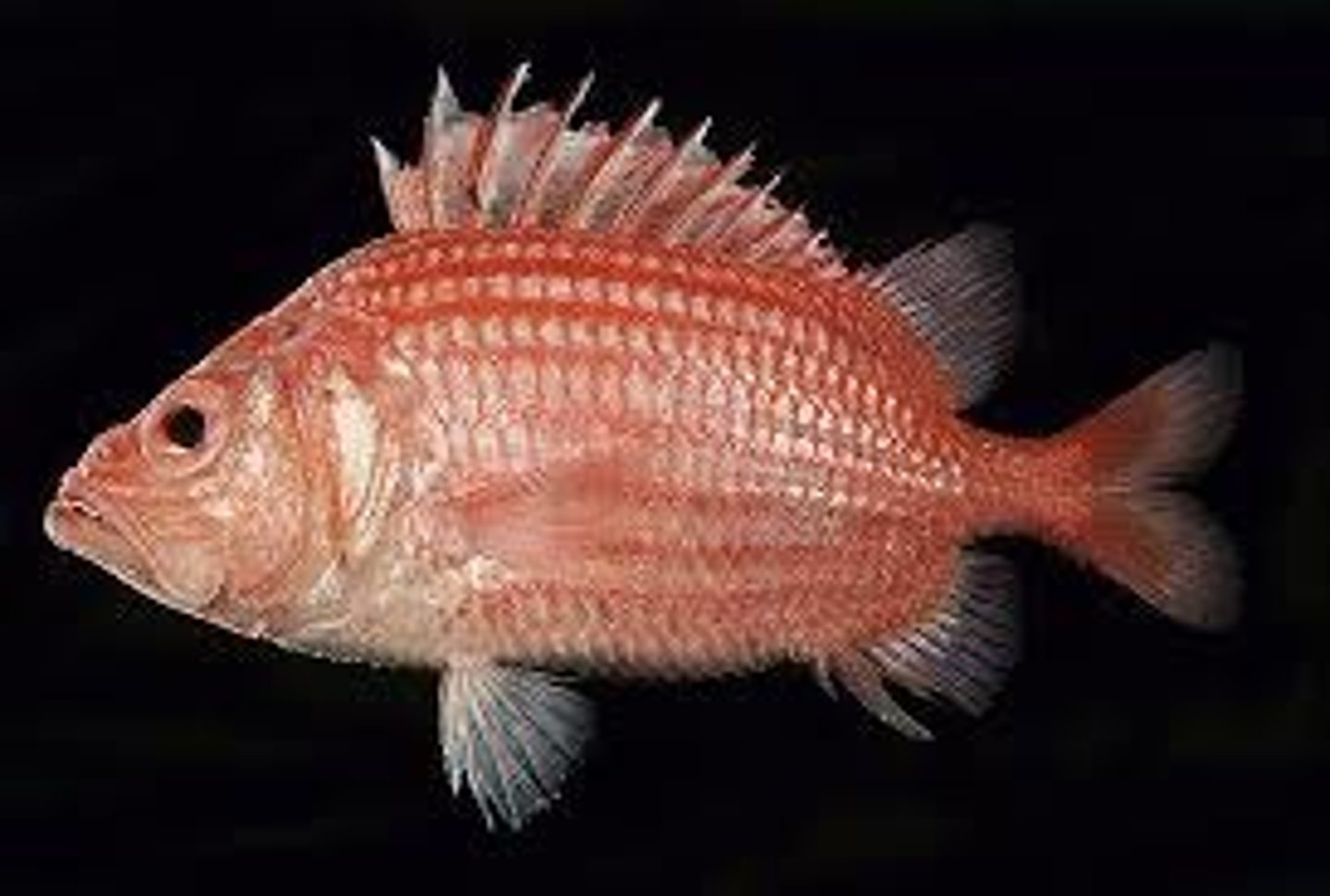

operculum
protective flap that covers the gills of fishes
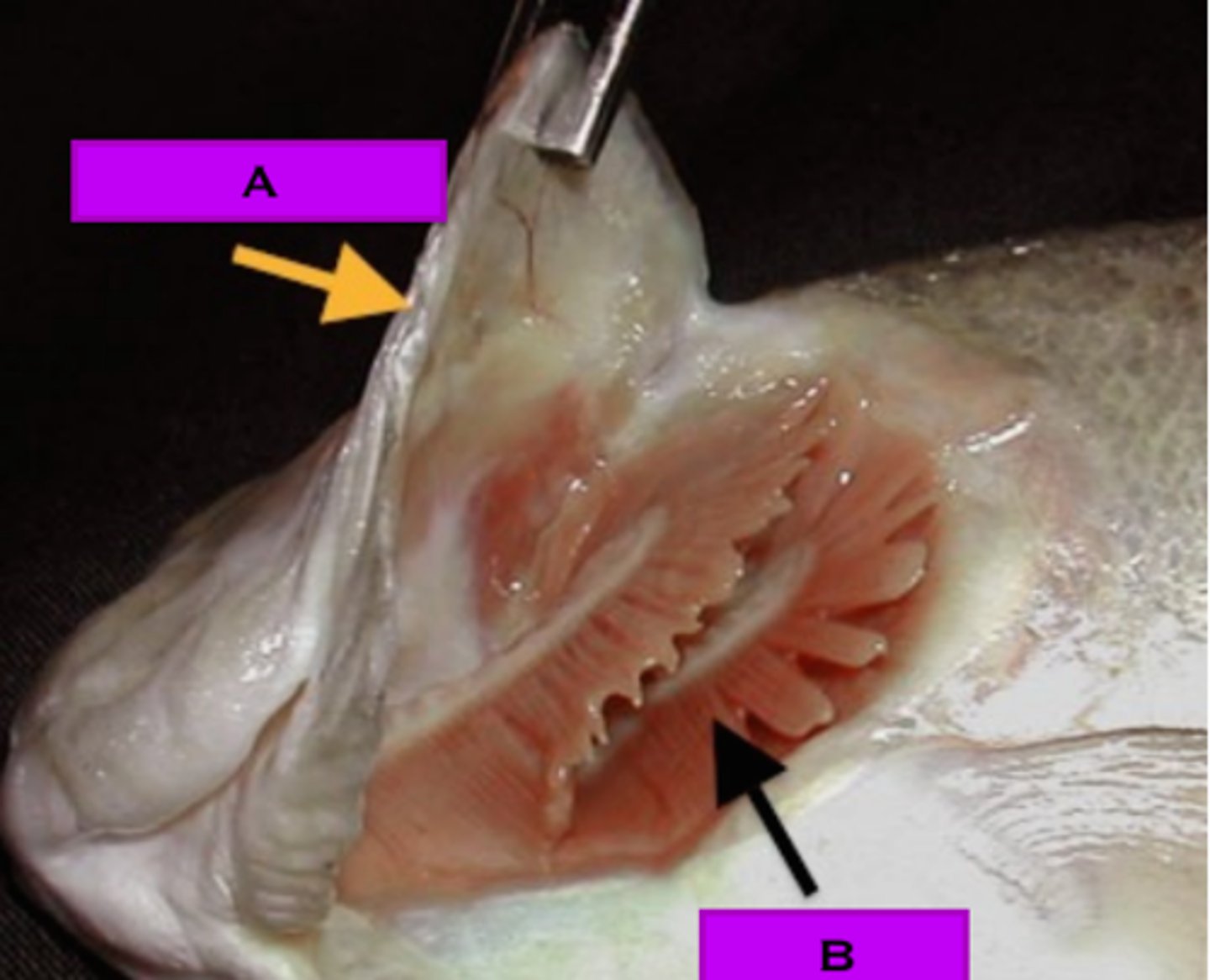
swim bladder
an air-filled sac near the spinal column in many fishes that helps maintain buoyancy
Sarcopterygii
lobe-finned fishes; Class of vertebrates
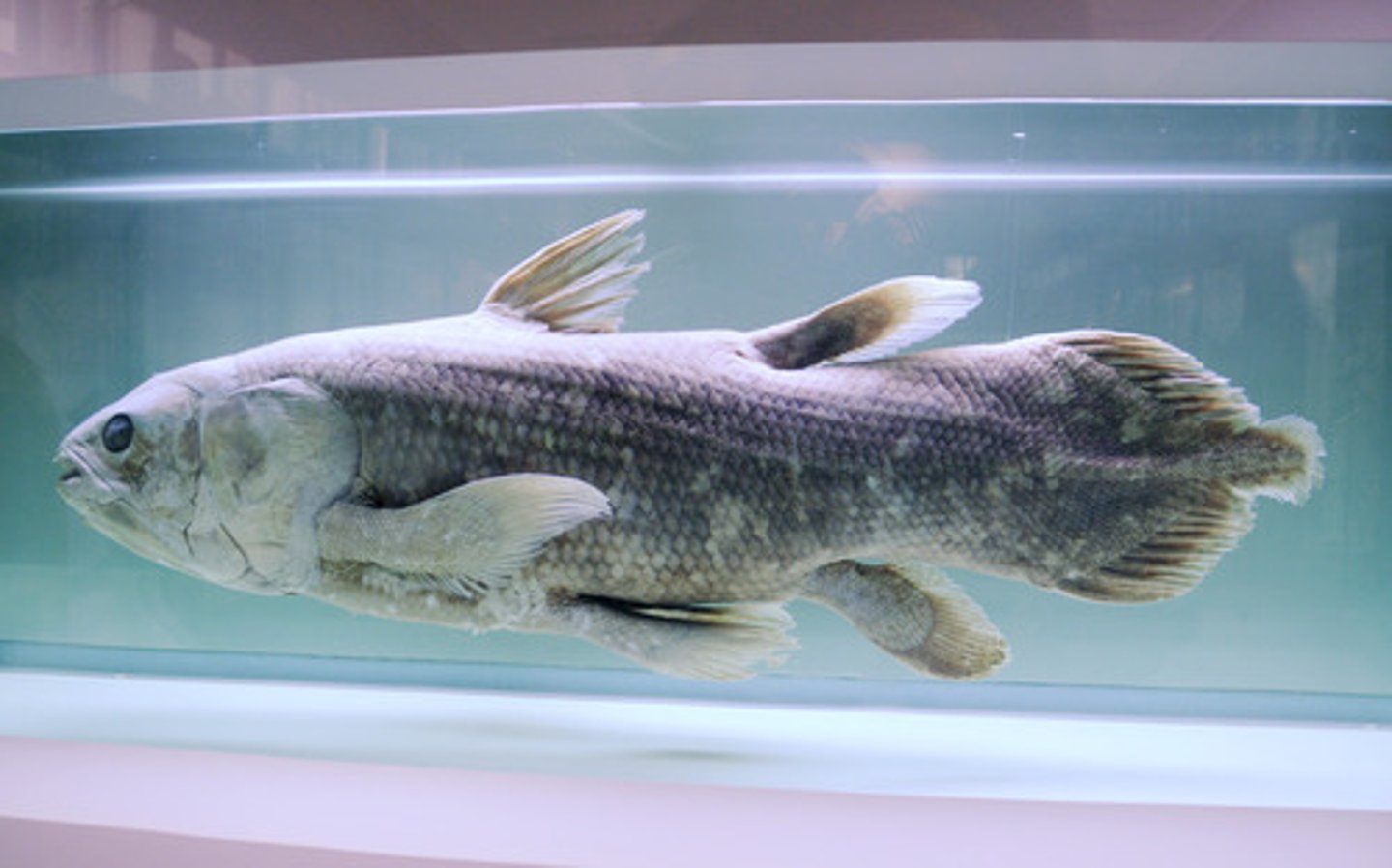

Amphibia
Class of vertebrates including frogs, toads, salamanders
ectothermic
organisms that lack an internal mechanism for regulating body heat
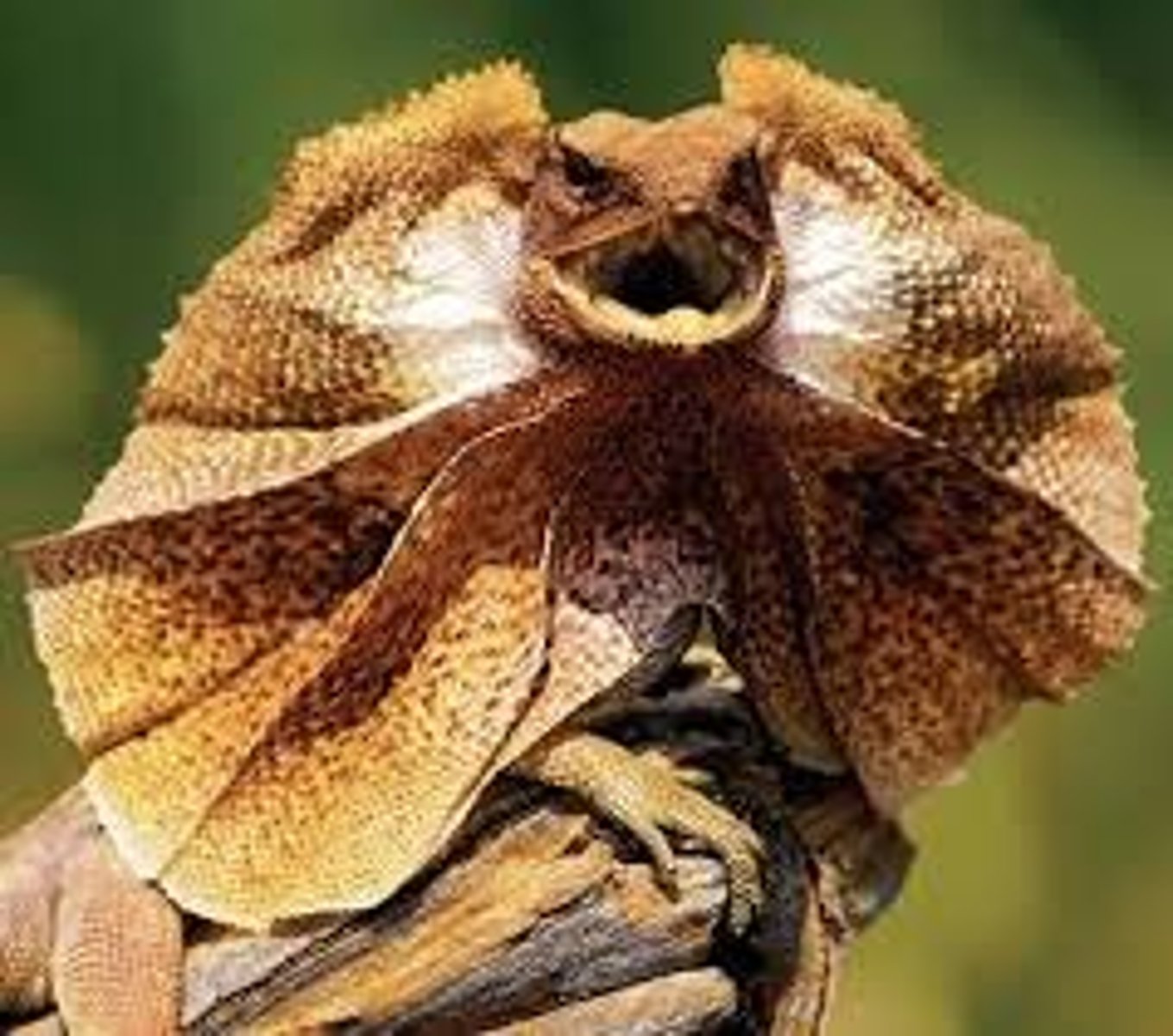

Reptilia
Class of chordates including reptiles; lizards, snakes & birds

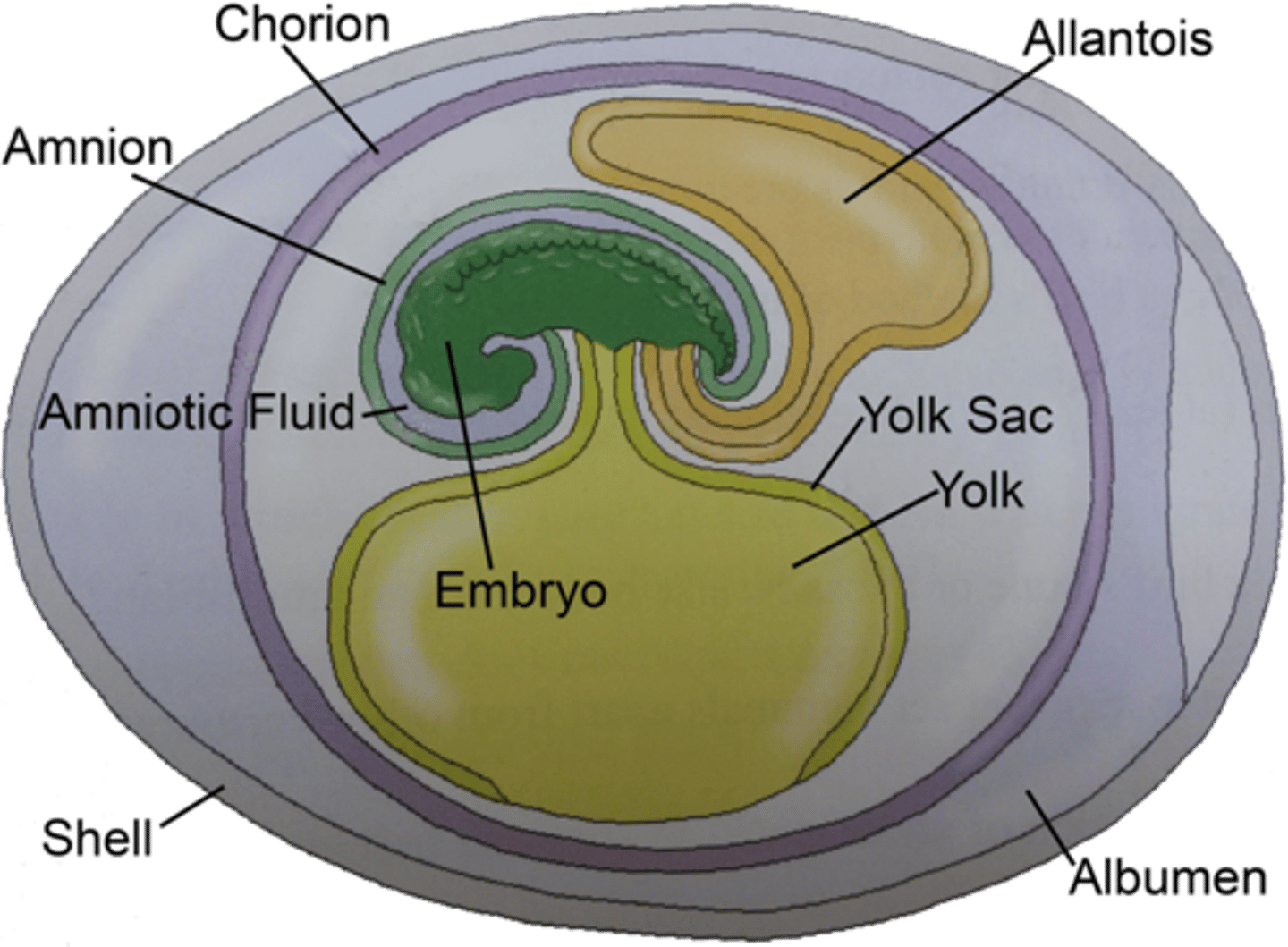
amniotes
have an amniotic egg containing specialized membranes that protect the embryo; mammals, birds & reptiles
feathers
modified scales that serve two primary functions: providing lift for flight and regulating body temperature

endotherms
Animals (such as birds or mammals) that can regulate their body temperature.

Mammalia
Class of chordates (Phylum Vertebrata) who carry out internal gestation, have hair, mammary glands, four-chambered hearts, a large brain with a neocortex and 3 middle ear ossicles

mammary glands
Specialized organs in mammals that produce milk to nourish their young
post-anal tail
a tail that extends beyond the anus; exhibited by all chordates at some stage of development
vertebrae
series of bones that surround and protect nerve cord and support main trunk of an organism's body. The vertebrate skeleton is bone, cartilage, or a combination of the two, and is internal and therefore grows with the animal. Additional skeletal elements include the axial skeleton (helps make the large body size strong and fast), rib cage (for protection of internal organs and points of muscle attachment), and the appendicular skeleton (support for paired appendages).
water vascular system
A network of hydraulic canals unique to echinoderms; branches into extensions called tube feet, which function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange