Economics 1 ( Sem 1 )
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
Dominant strategy
The strategy in a game that produces better results irrespective of the strategy chosen by one’s opponent
What does it mean for there to be a positive income effect?
When an increase in income leads to an increase in demand for the good
What does a negative substitution effect mean?
When a good’s price increases, making it less appealing compared to substitutes, causing consumers to buy less.
What does a positive substitution effect mean?
Occurs when a good’s price decreases, making it more affordable relative to other goods, leading consumers to buy more of it.
What does it mean for there to be a negative income effect?
When an increase in income leads to a decrease in demand for the good
Price discrimination
a practice where the monopolist chargers different prices to different buyers
First-degree price discrimination
extracting all consumer surplus e.g. two-part tariffs for student
Second-degree price discrimination
charging different prices for different units of a good e.g. two-part tariffs
Third-degree price discrimination
charging different prices to buyers in completely separate markets e.g. student discounts
What is an argument against A&R’s theory that institutions can explain why nations fail?
That education and human capital are relative.
What can be said about a function if f’(x) is greater than 0?
The function is strictly increasing over than interval
What can be said about a function if f’(x) is less than 0?
The function is strictly decreasing over that interval.
What can be said about a function if f’’(x) is greater than 0?
The function is at a local minimum.
What can be said about a function if f’’(x) is less than 0?
The function is at a local maximum.
What is signalling?
Signalling represents communication by the informed party which is meant to convey information about an agent’s true type. E.g. getting a good degree to signal that you are smart and hardworking or dressing well for an interview.
What is screening?
An attempt at eliciting information when initiated by the uninformed party such as asking potential applicants to solve difficult problems during a job interview.
What can be said about the second derivatives in partial differentiation?
The second derivatives indicates what will happen to the slope (first derivative) as we move away from the critical point. If they are both negative, that means the slope is decreasing and we are at a maximum. If they are both positive, that means we are increasing and we were likely to be at a minimum. If the slopes have different signs, we were likely at a saddle point. This would be checked using cross partial derivatives where if f(x,x,) x f(y,y) > f(x,y)² then you confirm that it is either maximum or minimum.
What can be said about supply elasticity in the long-run?
Supply for all goods is more elastic in the long run.
What can be said about the elasticity of demand in the short run for durable goods?
For durable goods such as TVs or refrigerators, the elasticity of demand is always more elastic in the short run than in the long run. This is because you can hold onto these goods before replacing them or finding alternatives.
In the Axelrod tournaments, what was the winning strategy?
Tit-for-tat which competed against other programmes such as random, grim-trigger …
What lessons can be learned from the Axelrod tournaments?
Don’t be envious: be fair with your partener
Be nice, cooperate, never be the first to defect
Be provocable: return defection for defection and cooperation for cooperation
Be clear and simple: don't try to be tricky (rules like JOSS which tried to
sneak one in when they could get away with it tended to be punished by
other less forgiving programmes).
Simply put, what is a quota on imports?
A quota on imports is a supply restriction. Graphically, at the quota supply will become vertical.
If a government is deciding between a quota or tariff on imports what is better for consumers?
Both politics are the same for consumers in terms of their effective price (however if the government raises lots of tax through the tariff then consumers overall taxes may be less).
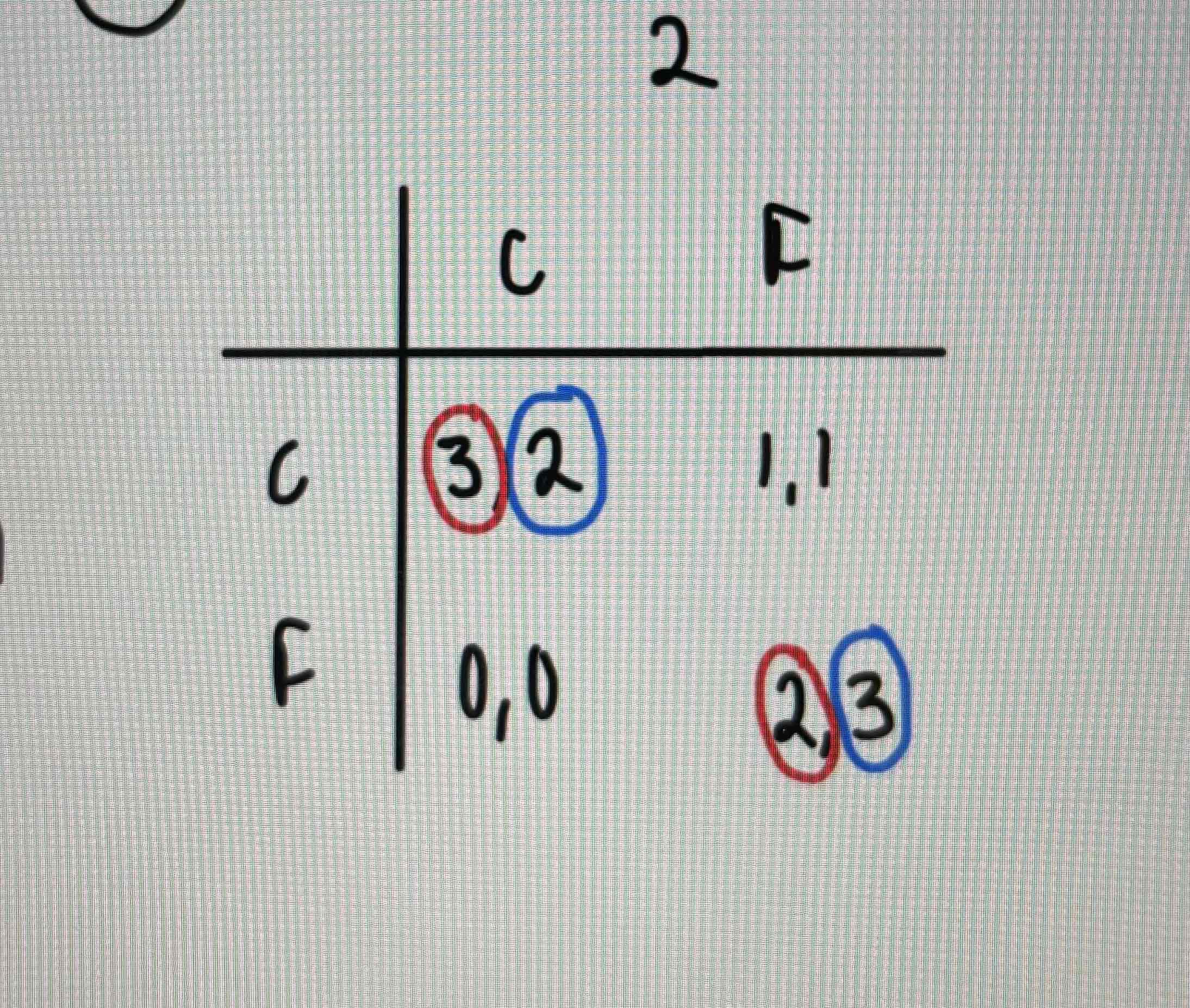
What type of game is this?
A battle of the sexes game with two nash equilibrium and no dominant strategies.
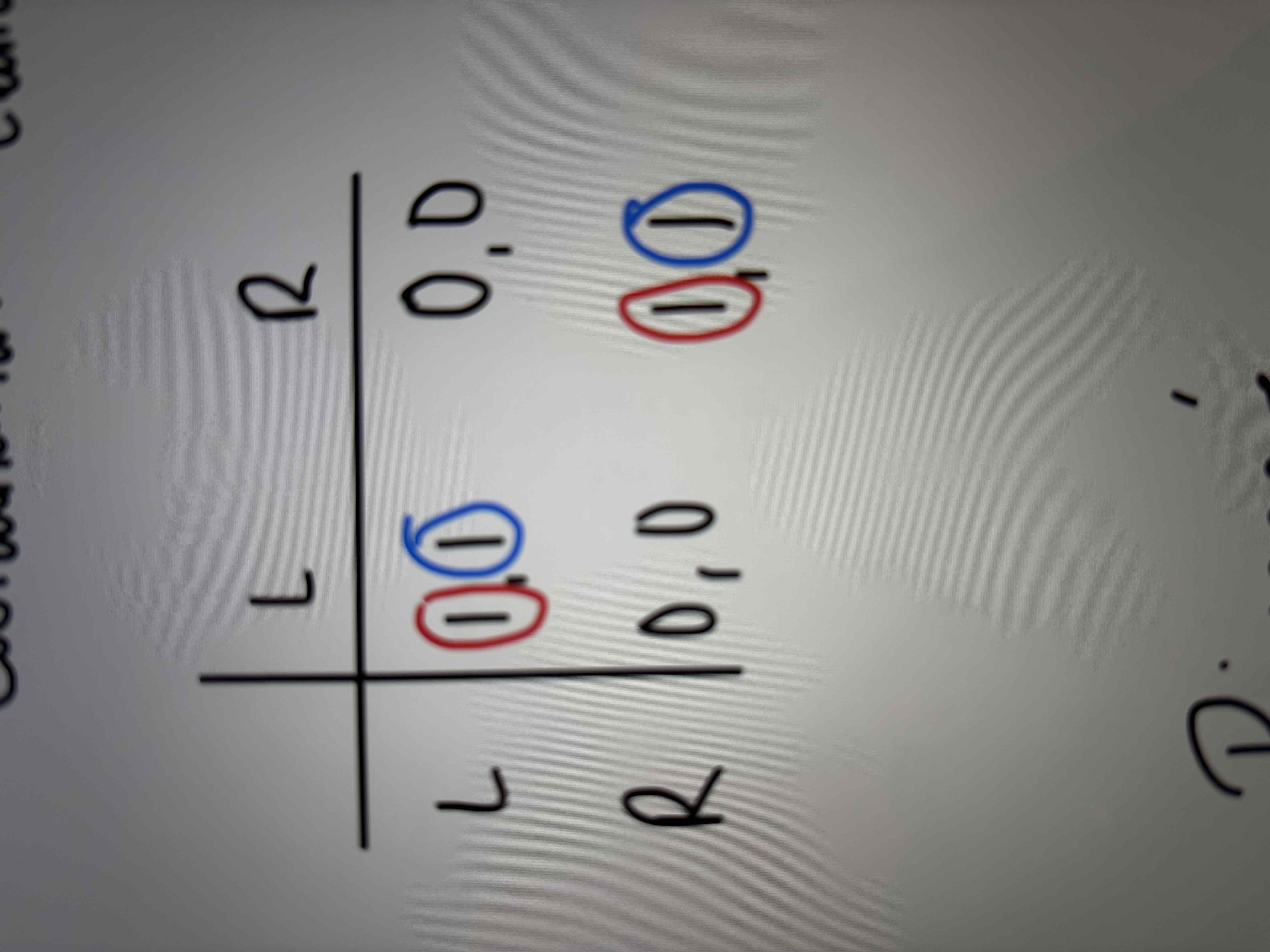
What kind of game is this?
A coordination game with two nash equilibrium and no dominant strategies.
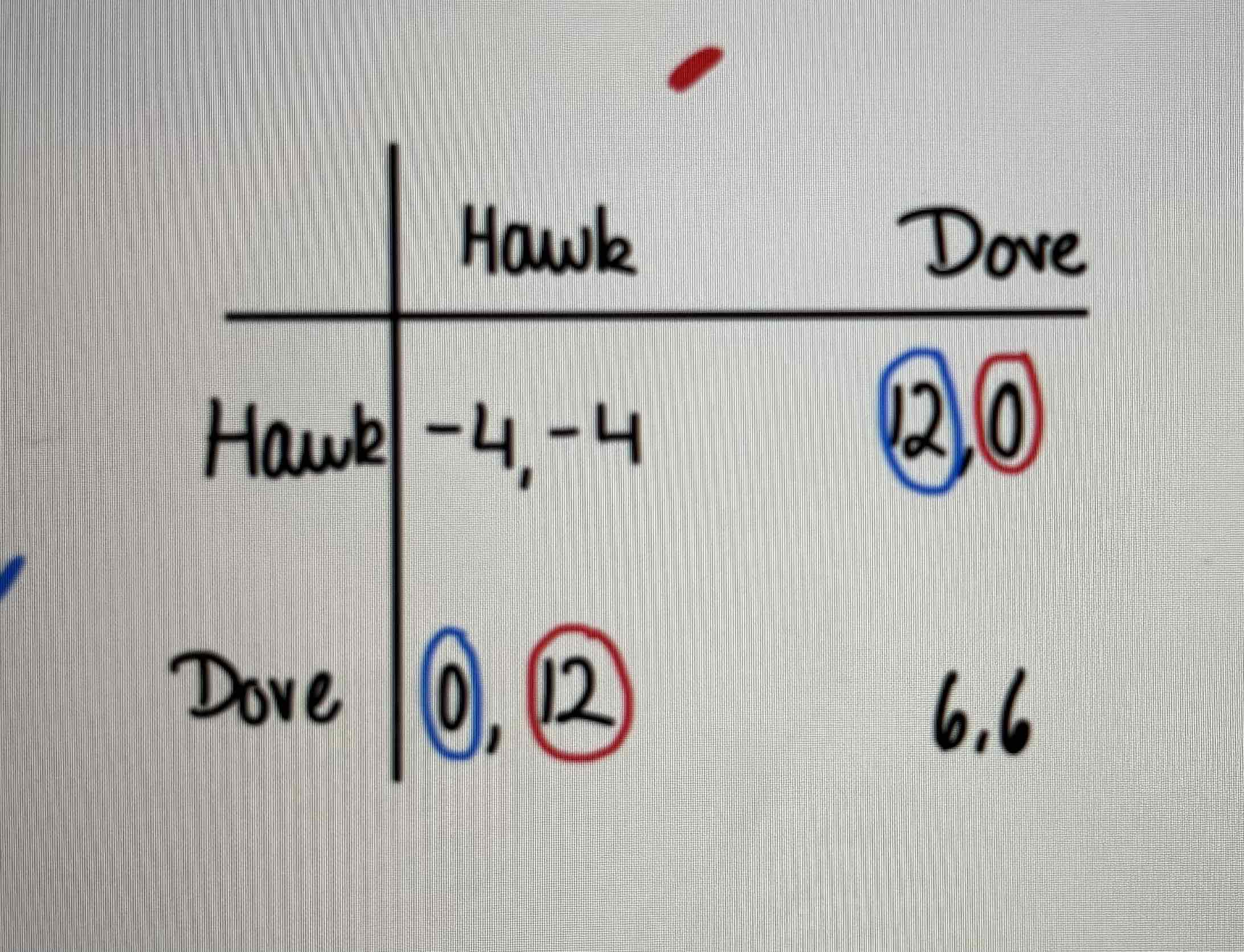
What kind of game is this?
A hawk-dove game with two nash equilibrium and no dominant strategies.
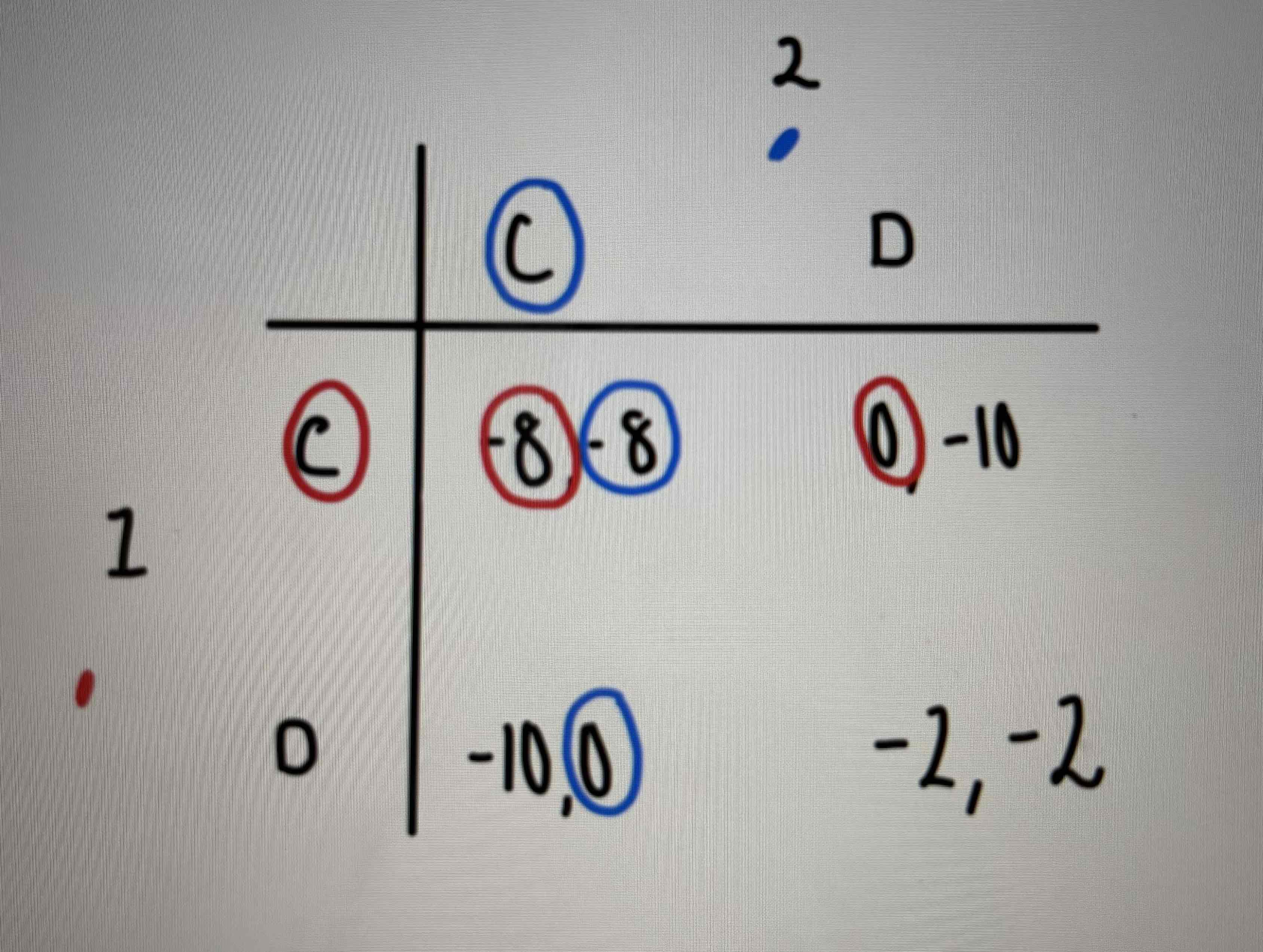
What kind of game is this?
Prisoner’s dilemma with a dominant strategy to confess and an equilibrium (which is a bad one for the prisoner’s)
For a normal good the willingness to accept the loss of a good will be greater than the willingness to pay, just as the compensating variation of a price rise is greater than the equivalent variation. The difference should, however, only be large if there are significant income effects.
Willingness to pay and Willingness to accept
Is WTP - WTA larger the more expensive a good is?
Yes, because the income effect will be larger.
Representativeness heuristic
Adding additional detail should make an outcome less problem however, we tend to treat more detailed scenarios as if they’re more probable e.g. dice rolling
What can be said about an ordinary demand curve and an income compensated demand curve for an inferior good?
The ordinary demand curve will always be steeper than the income compensated demand curve.
Confirmation bias
The tendency of investors to seek out and accept information that confirms their existing beliefs about an investment.
Choice-supportive bias
Belief that our choices are better than they actually are.
Availability heuristic
When something is more available, you estimate is as being more likely e.g. if you see a recent car crash you estimate car crashes as being more likely or where letters are in a word
When is a country likely to grow rapidly?
After a war a country is likely to grow rapidly, but this does not mean they are destined to be a rich country.
What kind of countries should grow fast?
Countries that have recently abandoned bad policies.
What kind of countries should be rich?
Countries that have good policies and lots of capital.
What do Acemoglu and Robinson say effects technology and capital?
Institutions
What are some typical explanations as to why nations fail?
Traditional - geography, climate, culture, religion or political leaders.
What are two basic types of institutions?
Inclusive (good) and extractive (bad).
What are some examples of inclusive economic and political institutions?
Secure property rights, consumer protection, open markets, voting rights, free media …
What are some examples of exclusive economic and political institutions?
Weak property rights, crony capitalism, forced or extractive labour, suppression of freedoms and single-party rule …
Why are inclusive institutions good?
They are secure, stable places for investment and security in the government allows for investors to have reliable work forces etc.
What are some historical examples of extractive institutions?
Colonial Spanish governments in latin America extracting resources and not returning anything.
What is the correlation between high expropriate risk (unlikely to exploit) and GDP?
There is a positive association between them.
What are two contrasting post-colonial countries that are different institutionally?
Canada was set up to be inclusive (bringing farmers over from the UK) whereas Jamaica was extractive in order to export sugar.
How did European settler mortality rates determine whether a country was colonised or not (from a 2021 paper)?
High mortality rates for settlers often resulted in extractive institutions so that money could be made, and returned home to their original country. Example, countries which had higher mortality rates for European settlers in 1800’s have lower GDP per capita today. This is an example of what might have effected the quality of institutions and how this has effected the countries today.
Is there a correlation between high urbanisation and high GDP per capita?
Yes, as institutions are long-lived within a society. However, there is a negative correlation between urbanisation in 1500’s and their GDP per capita now. High urbanisation rates in countries in 1500’s have low GDP per capita now.
Did Sachs agree with A&R about institutions being the reason why some countries and rich and some countries are poor?
No, he believed the data was weak, the idea too simple and that it ignores a countries geography.
Is education and human capital a good example?
Using data of education in a country from decades ago, predicts their GDP per capita today very well. However, Human Capital Index might be better which uses standardised tests to determine how much people are learning and how many years of schooling they get.
What are the three types of rich countries today?
Old west (USA, Australia), Petrostates (Saudia Arabia) and Asian tigers (Singapore, Hong Kong …)
How many asian tigers are there?
Four - Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan - all high growth economies.
What were three characteristics the four asian tigers had in common?
Threat of communism and densely populated in the 1950’s
All typically pursuing ISI (import substitution industrialisation) replacing foreign inputs with domestic production through taxation of foreign countries like India or Latin America
Struggle to pursue ISI due to their small size
What are the two kinds of asian tigers?
City states e.g. Hong Kong who were the richest and Japanese-style e.g. Japan and Taiwan who were liberated by the USA and involved on the US side during the cold war.
Features of the asian tigers today
high population density
none rich in mineral resources
low inequality for emerging economies
taxes and GDP low
high savings rates
free economically
What two countries might have hope?
Serbia and Vietnam as they are recovering from communism.
What are two countries today that illustrate the institutions argument?
North Korea and South Korea.
Examples of pancake style cities
Pitare in Latin America where houses are built on hilltops but the buildings are very low, Kibera (Kenya).
Examples of pyramid style cities
New York or Chicago
What is a key feature of Chinese cities?
They are administratively designated with wide boundaries to include parts of farmland. American cities are typically very narrow and have small official parts of the city, even though what people would class as the city is much larger.
What are three ways a city can expand?
Horizontal - expanding outward, new development
Vertical - replacing short buildings with tall buildings
Infill - adding buildings that are the same height and density as before into existing spaces such as car parks
Is density the problem?
No, Example → Dharavi Mumbai vs Midtown New York. Both have the same density, one has a much larger income per person than the other but we cannot argue then that density is the problem in Mumbai. Therefore, income?
How do you achieve a pyramidal structure and is it good?
Pyramidal structure for a city will result from good growth and good policies, but they are not desirable ends in themselves, and there are bad ways to get the same results. In the absence of government control, cities typically end up taking a pyramidal form of growth.
What is the percentage of built-up area on Earth?
0.2% of Earths land is built up. Proportionally, the share of expansion has been largest in east Asia during 1990 - 2015 and smallest in middle east and north Africa.
Where is horizontal urban expansion common?
In low-income countries, nearly all built-up area growth is through horizontal spread outside the existing urban extent. In high-income countries 1/3 was due to infill construction and 2/3 due to horizontal spread.
What is necessary to turn pancakes into pyramids?
Increasing incomes are necessary. In low-income cities, buildings in the centre are a little bit taller than the average of the whole city, but on the whole, the city is flat. As you increase from low-income cities, to high-income cities, the centre of the cities have taller buildings which are very different from the buildings in the outer parts of the city. Richer cities are more pyramid shaped, with peaked skylines.
Do dysfunctional land markets inhibit pyramidal growth?
In developing cities, a lack of legal clarity often deters investors from building.
Developers cannot readily buy downtown land. Formal land transactions are long, costly and complicated. E.g. Cairo had a policy at one point where if a property was unfinished you paid less or no tax on it so for a while buildings could be seen with scaffolding and TV satellite dishes.
Blank slate for cities → private cities. However, private companies often mange public entities and charge high compensation and in many cases, quality is poor.
Does improved transport, facilitate healthy pyramidal growth?
Glaeser summarised as “ Bus good. Train bad” as they have similar commute times at a reduction of the time and cost to implement. Much cheaper than a metro system.
What country is urbanising rapidly?
Africa is urbanising rapidly even though their GDP per capita is less than countries which had similar urbanisation milestones 30 years ago.
What has african urbanisation occurred alongside?
Low productivity gains in agriculture, low wages and limited industrialisation.
What kind of employment is high in african cities?
Agriculture employment
What is a primate city?
The largest city in a country.
What can be said about the population in African primate cities?
The concentration of the population in african primate cities are high by global standards.
Why do people leave cities in africa?
Expanding schools, healthcare and other services
Employment opportunities for household members
What is a matching pennies game?
Matching pennies game is a zero-sum two-player game played simultaneously.
What are common pitfalls in decision making (the ways that people fail to think rationally)?
Failure to understand the average-marginal distinction
Measuring costs and benefits as proportions rather than absolute monetary amounts
Failing to ignore sunk costs
Ignoring implicit costs
When will the incidence of tax fall entirely on the producer of a good?
If demand is totally elastic at a given price or when supply is totally fixed.
Is the prisoners dilemma and the matching pennies games, coordination games?
No, as one player wants to anti-coordinate in the matching pennies game and both players have a dominant strategy in the prisoners dilemma.
The Kahneman-Tversky value function is …
much steeper in losses than in gains.
What is the set up of a two-player ultimatum game?
Person A is give a sum of money £M and must make a one-time-only offer to split the money with person B ranging from a large portion to a small portion of £M. If person B refuses, then they both get £0 .
Is it better to get a brand new car as a gift or a cash gift equivalent to the price of the car?
The cash
Is a giffen good a normal good or an inferior good?
An inferior good
What is the income effect for inferior goods?
The income effect for inferior goods is negative i.e. when income rises, demand falls
Does a giffen good have a larger income effect than a substitution effect?
Yes, the definition of a giffen good is an inferior good for which the income effect is bigger than the substitution effect.
What does a diminishing marginal rate of substitution imply about an indifference curves shape?
That it is convex
If a corner solution exists…
the marginal rate of substitution will differ from the slope of the budget constraint
What is overoptimism?
Overestimating positive outcomes (in terms of frequency or magnitude).
What is overprecision?
Beliefs may be accurate on average, but the variance of outcomes is underestimated.
What should companies do to maximise profit if they think potential customers will underestimate their usage of the product?
When consumers guess wrong about how much they will use the service, firms should distort marginal prices to exploit. Therefore, they should charge low up-front costs, and a high marginal cost e.g. phone companies. It would be the other way around for overestimation e.g. gym memberships with high up front cost and low marginal cost.
Consumer price index overestimates inflation because …
it fails to take into account the substitution of costly goods with cheaper goods.
Present aim
Present aim standard takes individual interests as given even if these interests appear to be irrational. (As long as you attain your goals, you are considered rational).
Self-interest standard
Argues that people are purely egoistic, which is not true.
Social dilemma
Type of game where individual incentives conflict with efficiency
Commitment device
A device that commits a person to behave in a certain way in the future, even though he may wish to behave otherwise when the time comes
Tit-for-tat
Strategy to cooperate at first and then do whatever the other player did in the previous interaction
Grim-trigger
Strategy to cooperate unless the other player defects but defect for ever more if the other player defects.
Nash equilibrium
The combination of strategies in a game such that neither player has any incentive to change strategies given the strategy of his opponent
Game of incomplete information
A game where some players have private information about, say, their payoffs or possible moves in the game (CV’s for a job)
“Battle of the sexes”
Coordination game where both players have a preferred outcome
Pareto coordination game
Coordination game where one of the payoff options are clearly worse for both but we can still end up with it (choice of units)