Bio 103 - Exam 3 JMU McMullen
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What are chromosomes and how are they created?
Coiled up lengths of DNA molecules; created when DNA wraps around the histone proteins and then folds to form a chromosome structure
What is the cell cycle?
process where cells divide by mitosis and restore their DNA to the original level
What are the phases of the cell cycle and what do they do?
G1 (cells grows in size, organelles double)
S (DNA replication)
G2 (cell grows, production of enzymes & other proteins)
M (karyokinesis & cytokinesis)
Interphase consists of what phases?
G1, S, G2
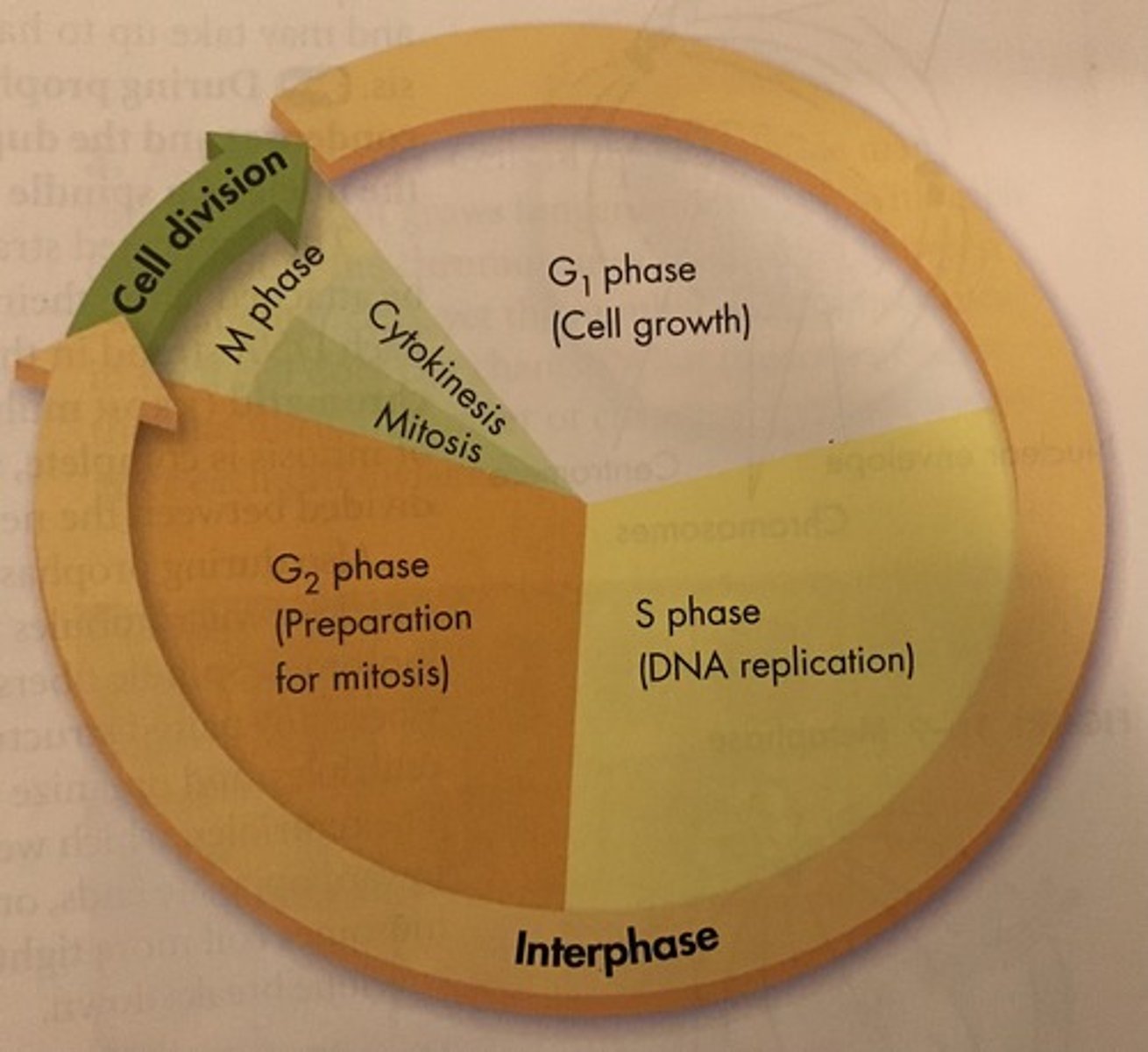
What is prophase in mitosis?
1st phase; Chromatin condenses into chromosomes, 2 pairs of centrioles visible outside the nucleus in the centrosomes; chromosomes move apart & polar spindle fibers form between them made up of microtubules; the nuclear membrane & nucleoli disappear & polar spindle fibers now reach from pole to pole with kinetochore fibers that attach to the protein structures called kinetochores
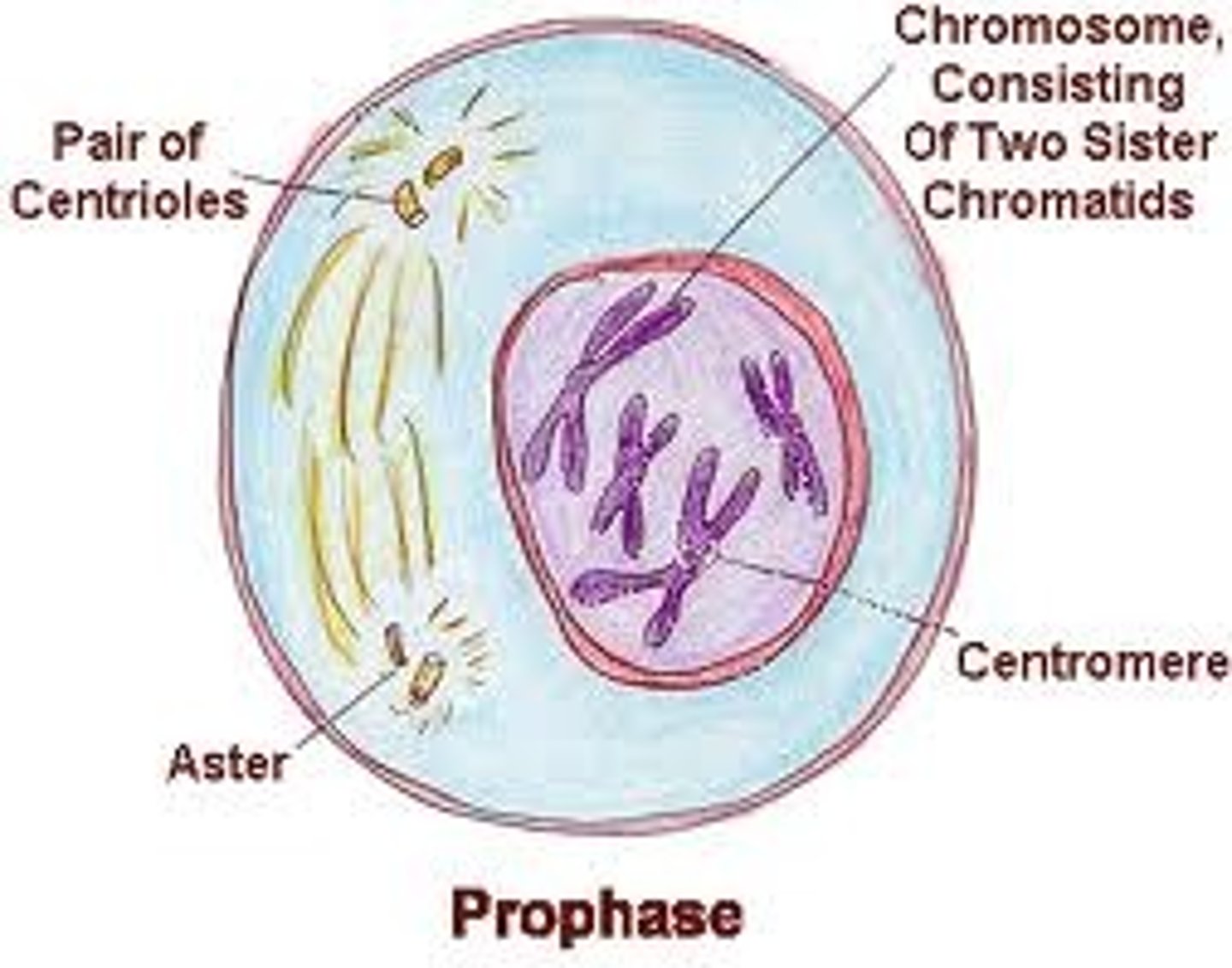
What is metaphase in mitosis?
2nd phase; kinetochore and its fibers move the chromosomes to the equatorial plate of the cell where they form a line
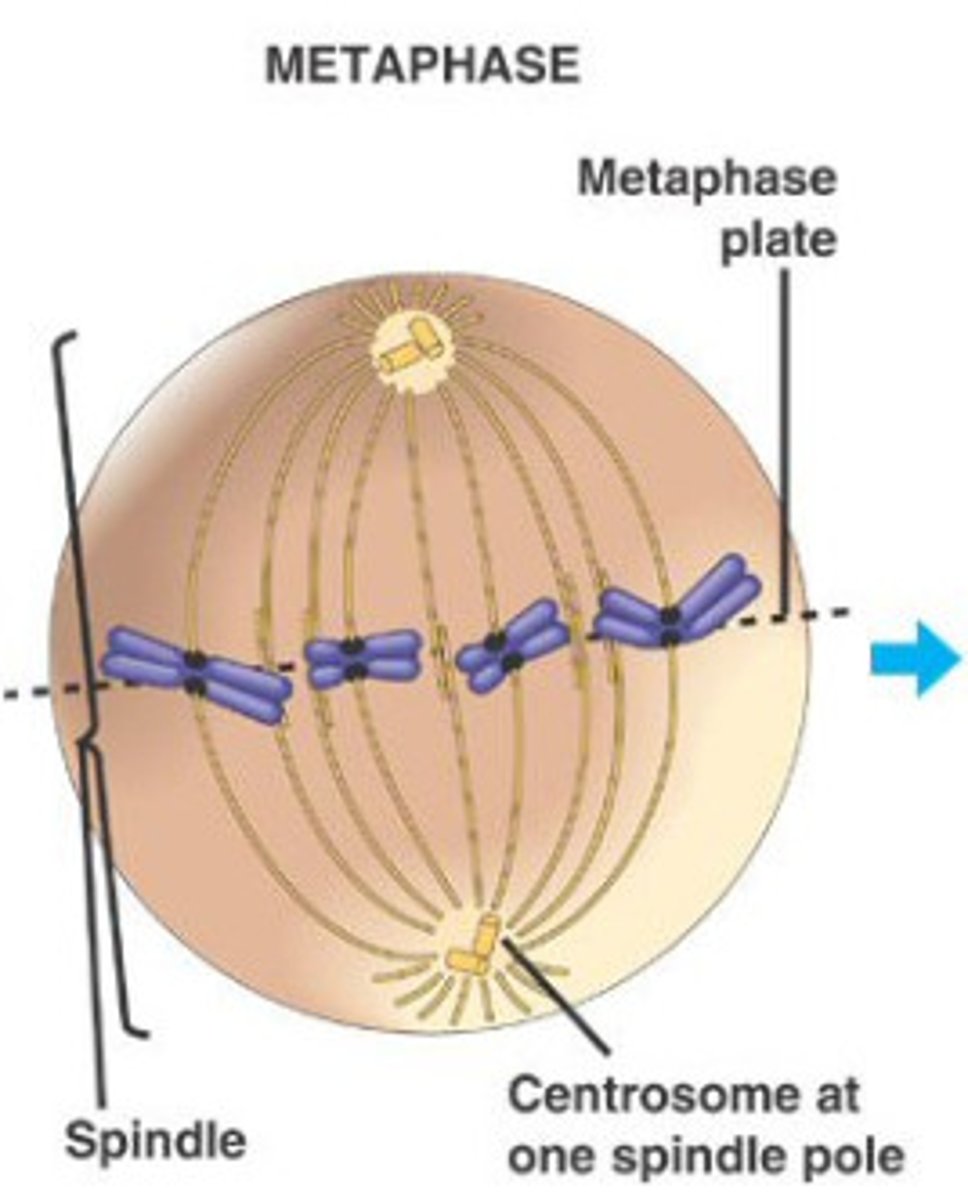
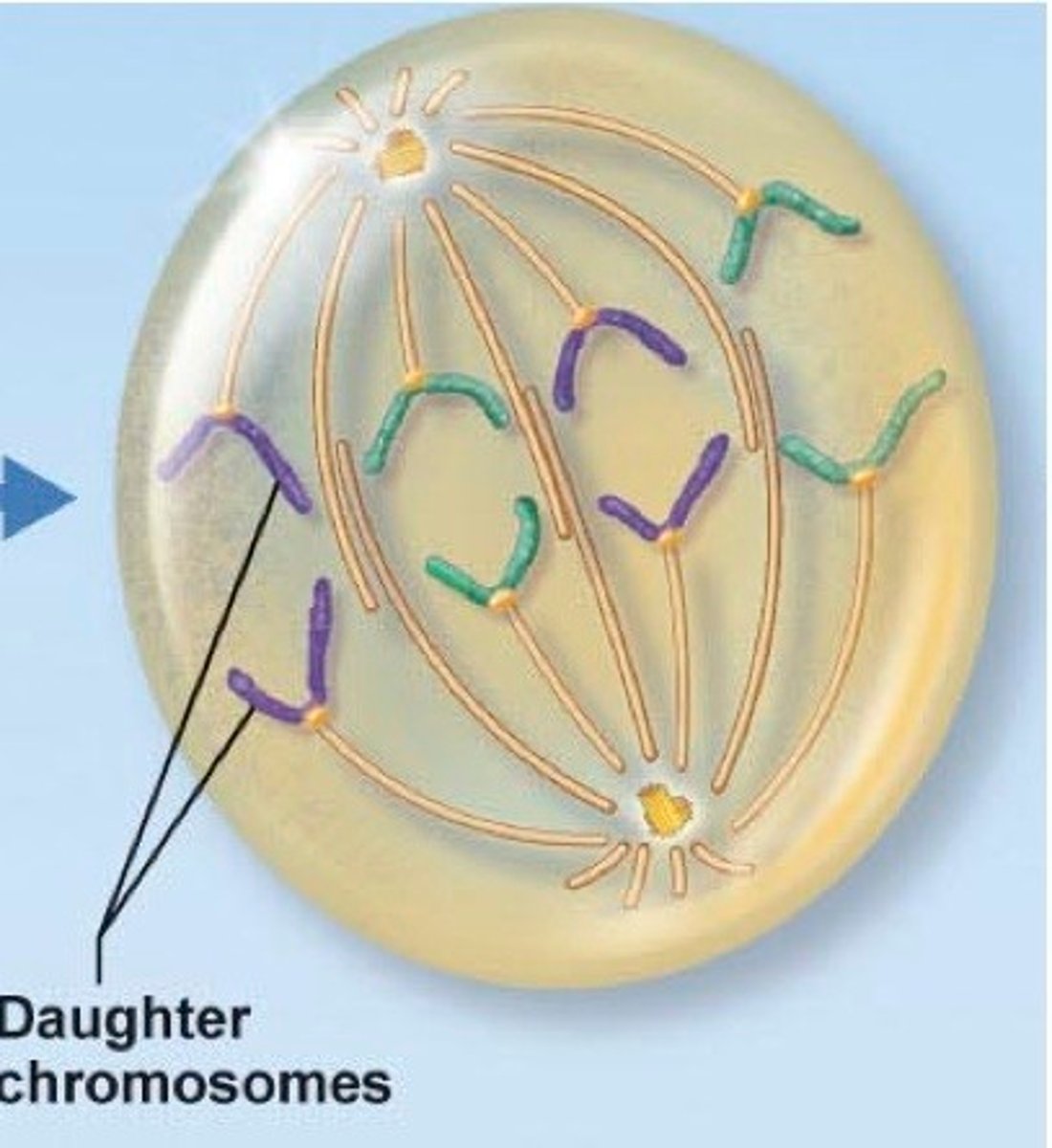
What is anaphase in mitosis?
3rd phase; the chromatids separate and move to opposite poles. Centromeres move first and drag the arms behind; the most rapid phase and one the chromatids separate they are called daughter chromosomes
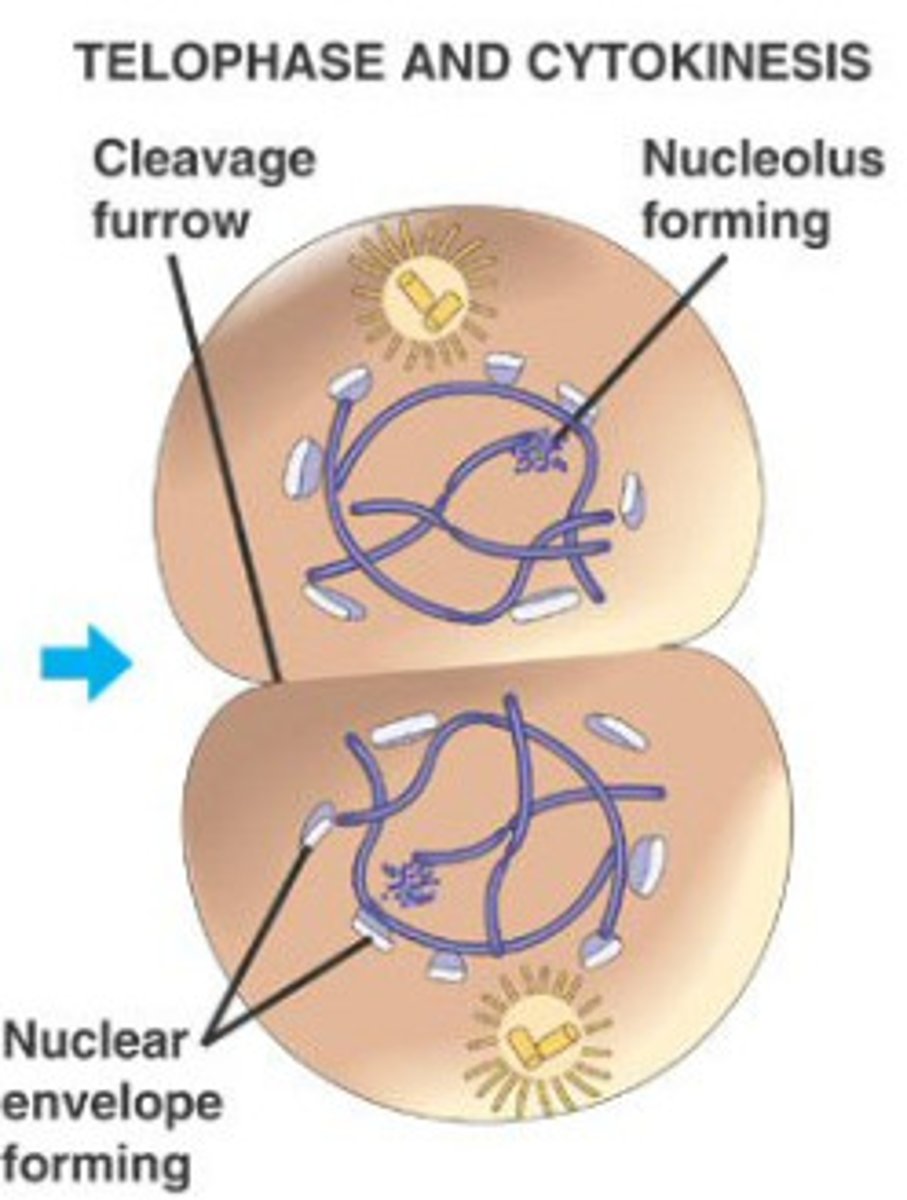
What is telophase in mitosis?
4th phase; spindle fibers break down during this phase. Nuclear membranes, nucleoli, and chromatin reappear. New centrioles may appear
A characteristic of all living things is that they reproduce either
A) sexually or asexually
B) Sexually
C) asexually
A) sexually or asexually
No matter how an organism reproduces, it will involve either
A) mitosis
B) Meiosis
C) Both
C) Both
What is mitosis?
A) a process where a single cell divides twice to produce four cells containing half the original amount of genetic information.
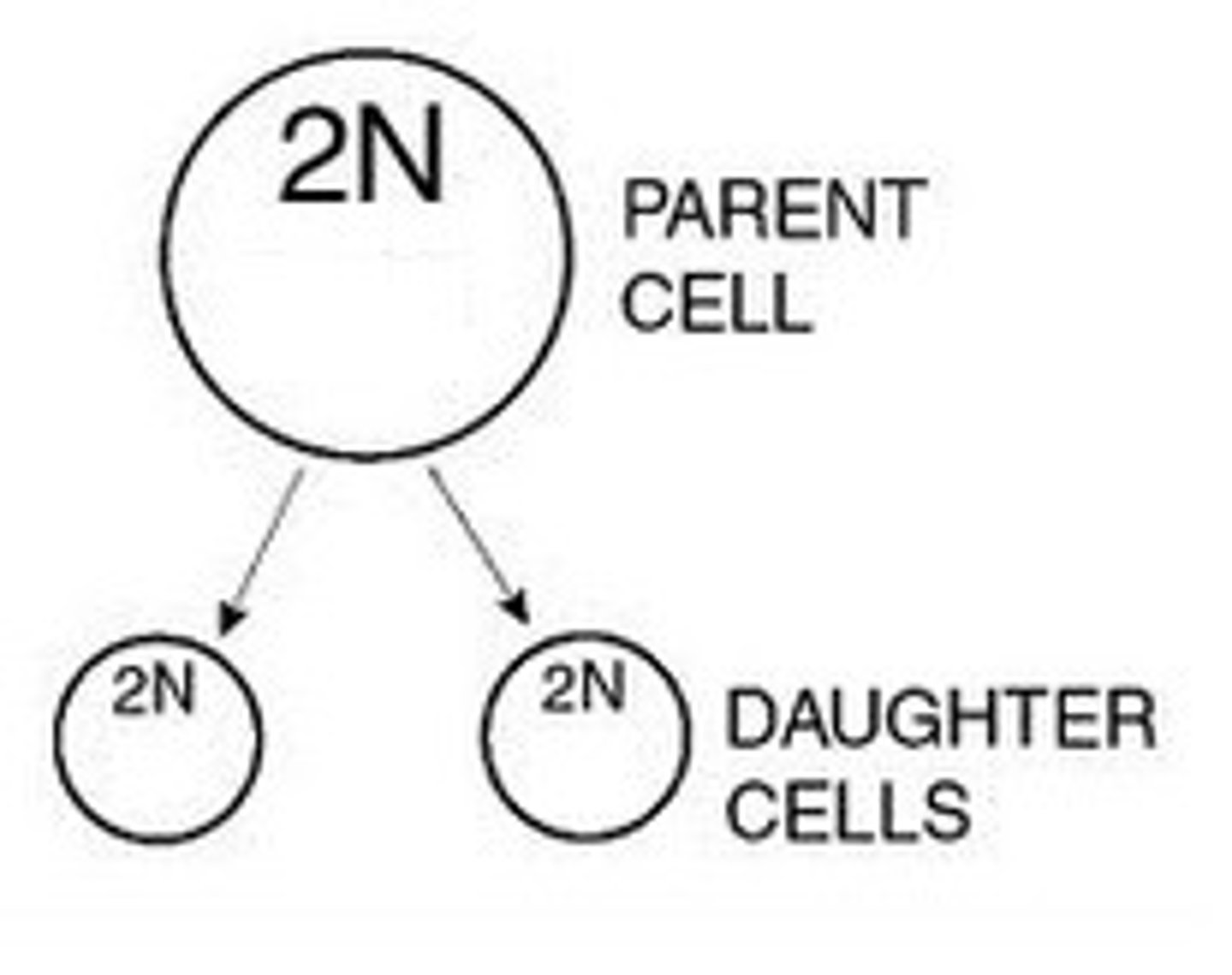
B) Cell division generates new cells for growth and repair. The division of one cell into two genetically identical daughter cells
B) Cell division generates new cells for growth and repair. The division of one cell into two genetically identical daughter cells
In mitosis, every eukaryotic cell possesses a true ________ bounded by a nuclear envelope
A) chromosome
B) nucleus
C) chromatin
B) nucleus
___________ is the name given to the unorganized mass of DNA and histone proteins seen within the nucleus
A) chromosome
B) rhizomes
C) chromatin
C) chromatin
Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes called the ___________ number, present in all ______ cells
diploid (2n); somatic
Eukaryotic cell division consists of 2 processes called ___________ & __________
karyokinesis (division of cell) & cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm)
Before division, each chromosome has a pair of __________ ___________ chromatids. They are attached at the centromere and are genetically ____________
identical sister; identical
Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells so sometimes it is called ___________ division
duplication
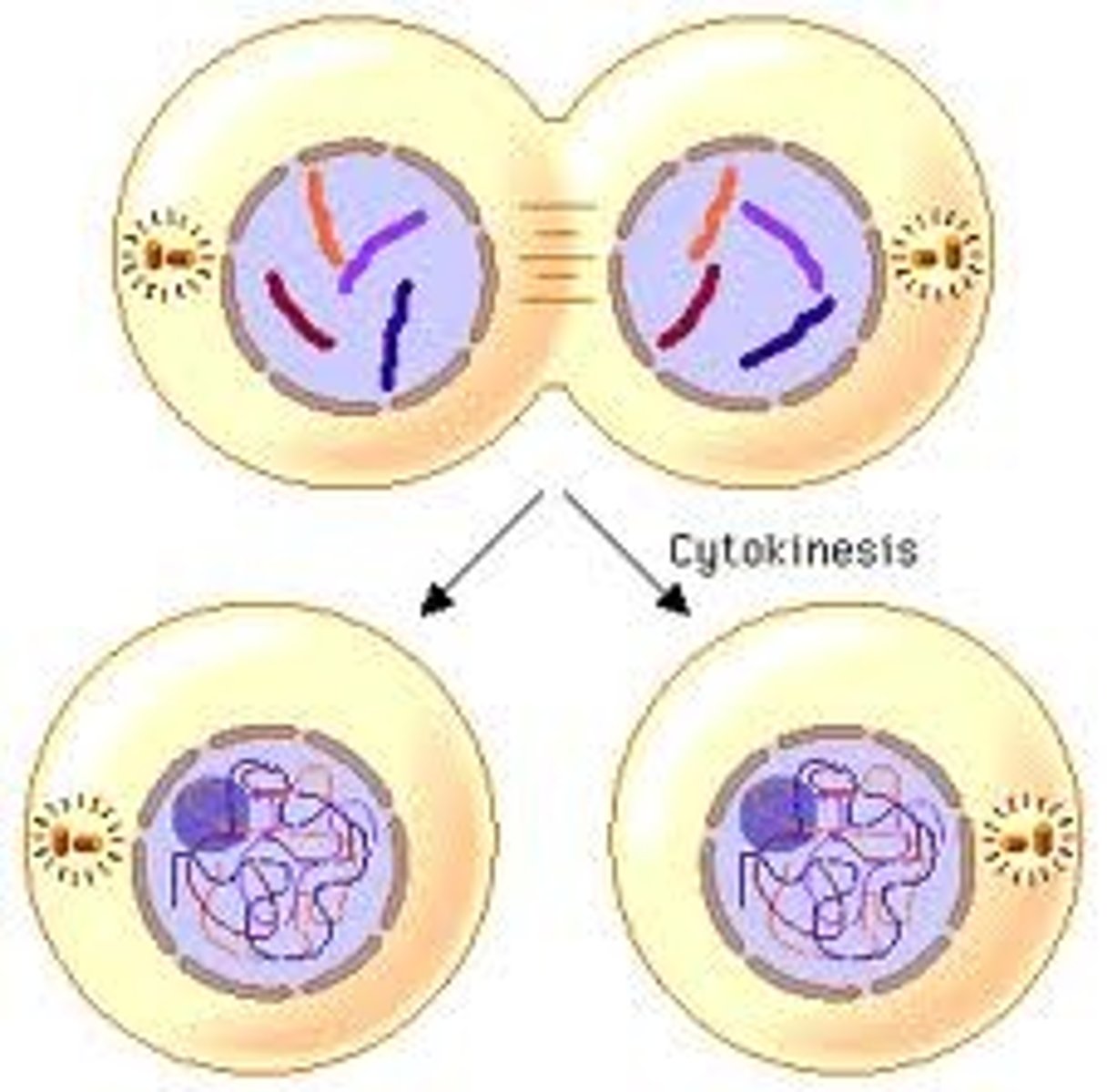
What is cytokinesis in mitosis?
typically begins during telophase, in animals it takes place by formation of cleavage furrow
In plants, a cell plate is formed from the inside out. It is formed from vesicles produced by dictyosomes. eventually it becomes the middle _________, and a cell _____ is formed
lamella; wall
What are the three asexual reproduction type plants?
rhizomes (horizontal underground stems, grasses, iris)
stolons (horizontal above ground stem (strawberry)
plantlets (formed at margins of leaves (air plants)
What is fragmentation?
Asexual reproduction in which a body part is lost and then regenerates into a new organism
ex) sponge (phylum porifera)
What is budding?
a new individual grows on the parent then separates
ex) sea anemone & hydra
What is fission?
separation of a parent into two or more individuals of about the same size
ex) sea anemone
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
create numerous offspring quickly, quickly colonize a new habitat, no need to find a mate, perpetuates successful combinations of genes (sexual reproduction breaks them up)
What are the main points of mitosis?
results in growth of multicellular organisms, results in replacement of cells in multicellular organisms, is a means of asexual reproduction in many unicellular organisms and some multicellular organisms
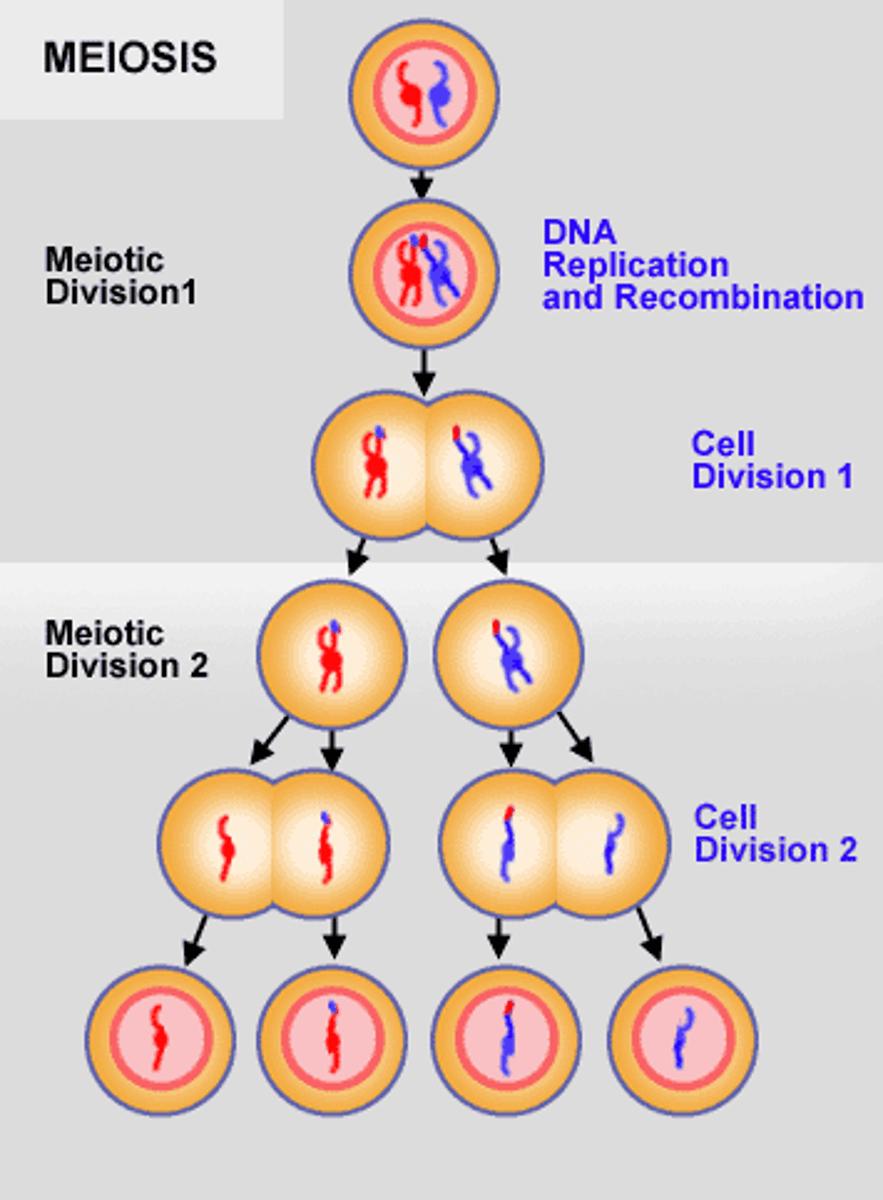
What is meiosis?
process of division in which the chromosome number is reduced from the diploid number (2n) to the haploid number (n)
What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
eukaryotes undergo sexual reproduction; involves gamete formation and syngamy
In meiosis, each daughter cell possesses the ________ number of chromosomes. Normally these latter cells are known as games.
haploid (n)
During meiosis, the nucleus of a diploid cell undergoes _____ divisions; where it results in the production of __ daughter cell (gametes), each with 1/2 the number of chromosomes of the original cell
2; 4
What is syngamy?
process by which the two gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote
What is interphase in meiosis?
chromosomes are replicated, thus, each consists of two identical chromatids held together at the centromere
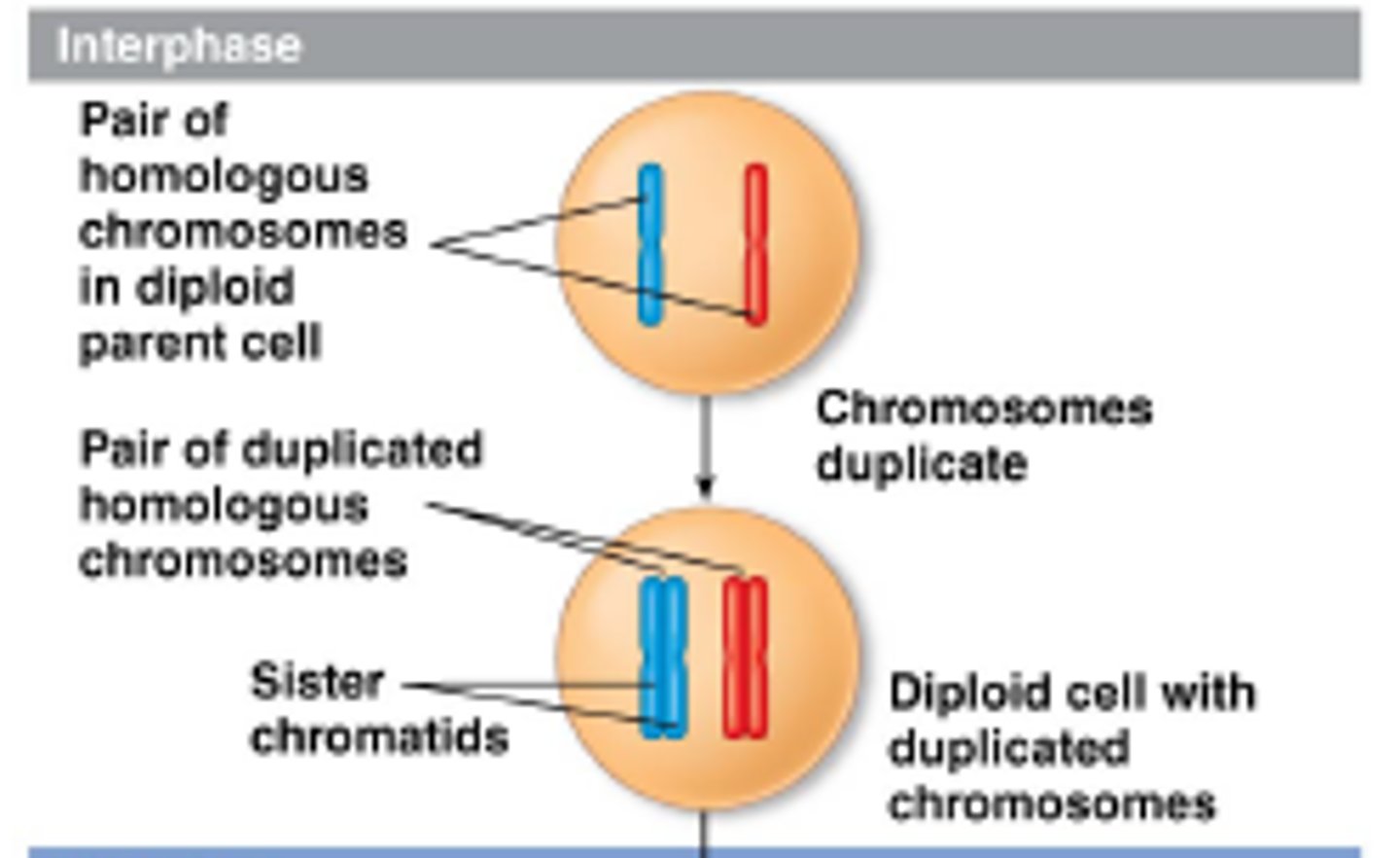
The phases of meiosis are?
Meiosis I & Meiosis II
What happens in meiosis I?
In meiosis I homologous chromosomes separate
What happens in Meiosis II?
sister chromatids separate
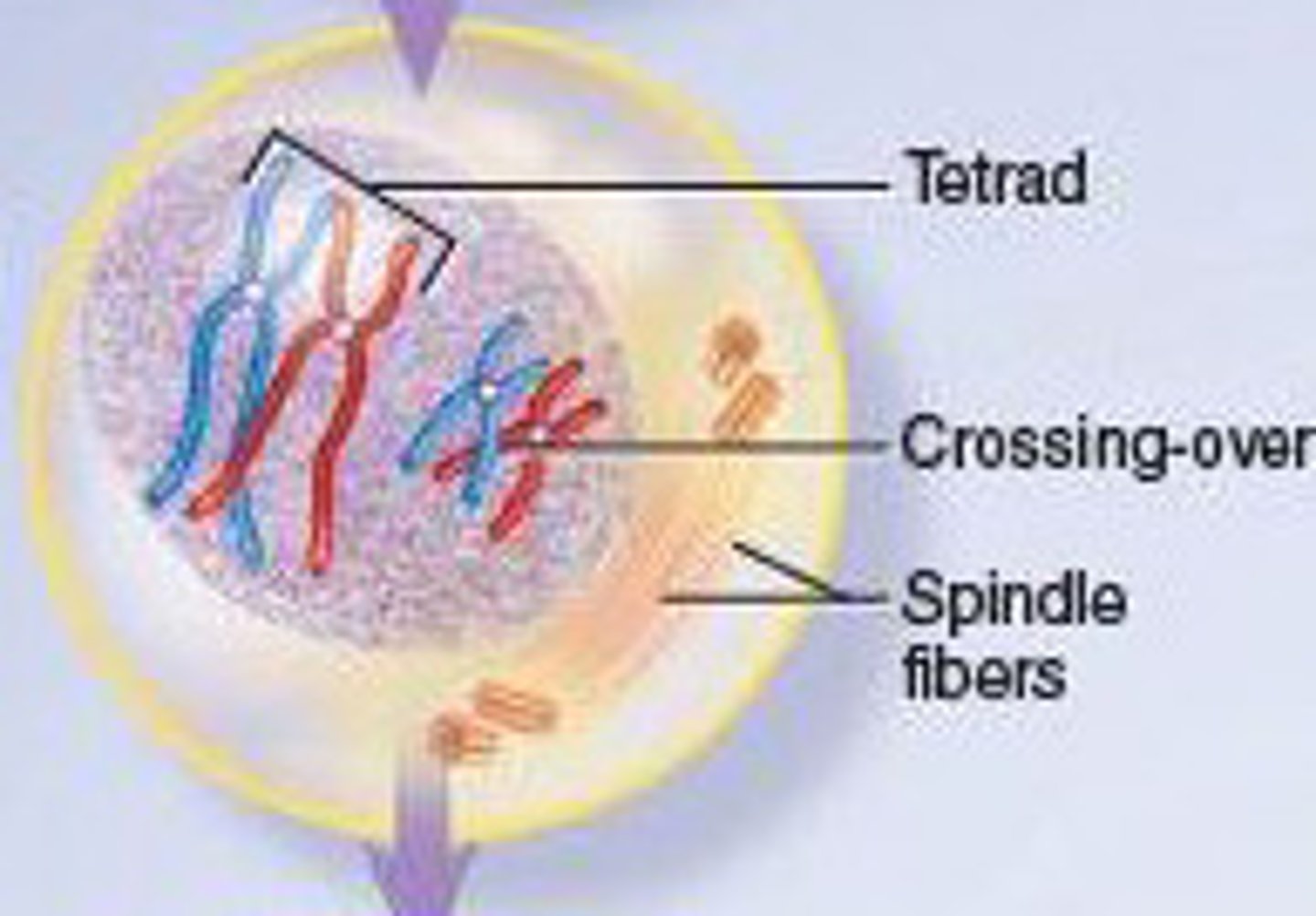
What happens in prophase I for meiosis?
chromosomes become visible and group in pairs. The pairs synapse and are called tetrads. recombination by crossing over during meiosis I
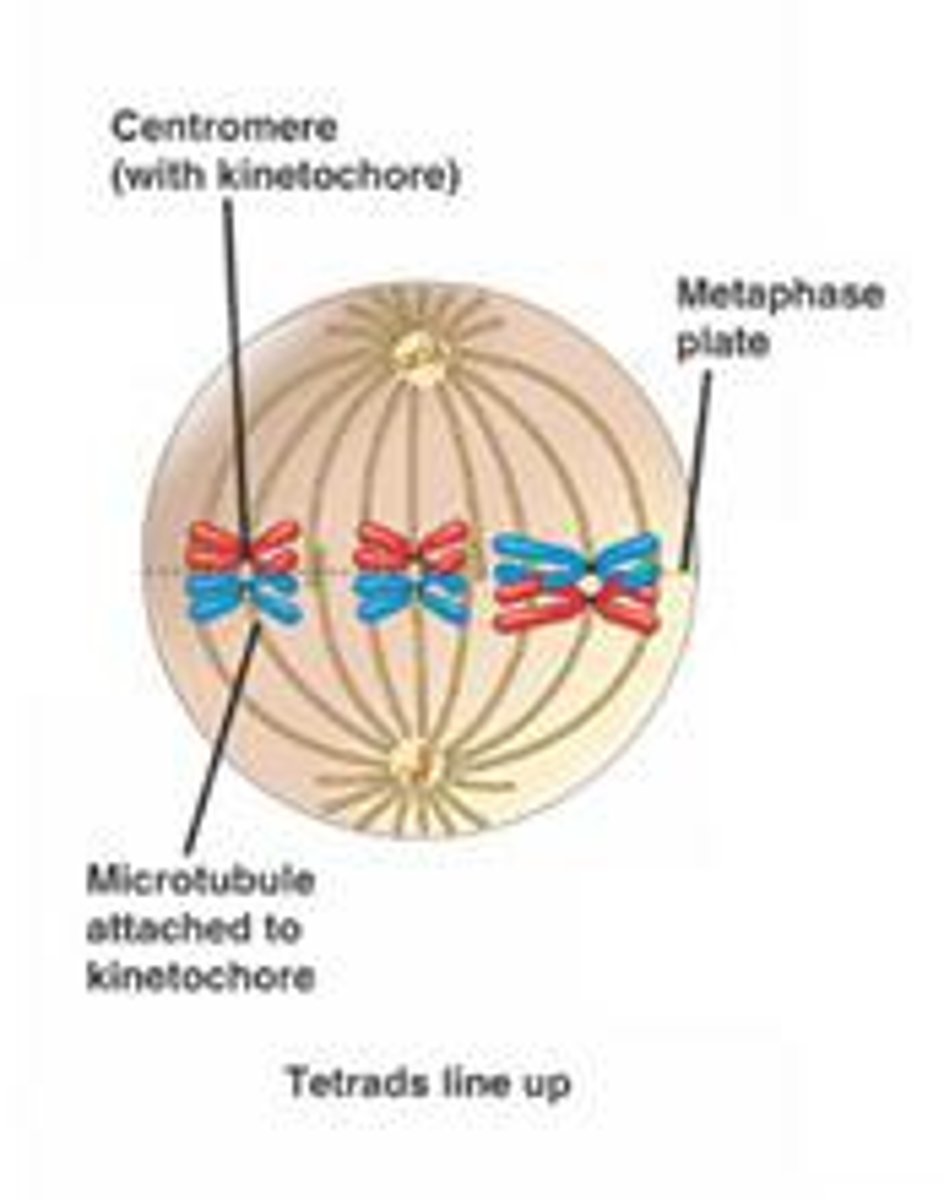
What happens during metaphase I in meiosis?
chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes and the pairs line up at the equatorial plate of the cell
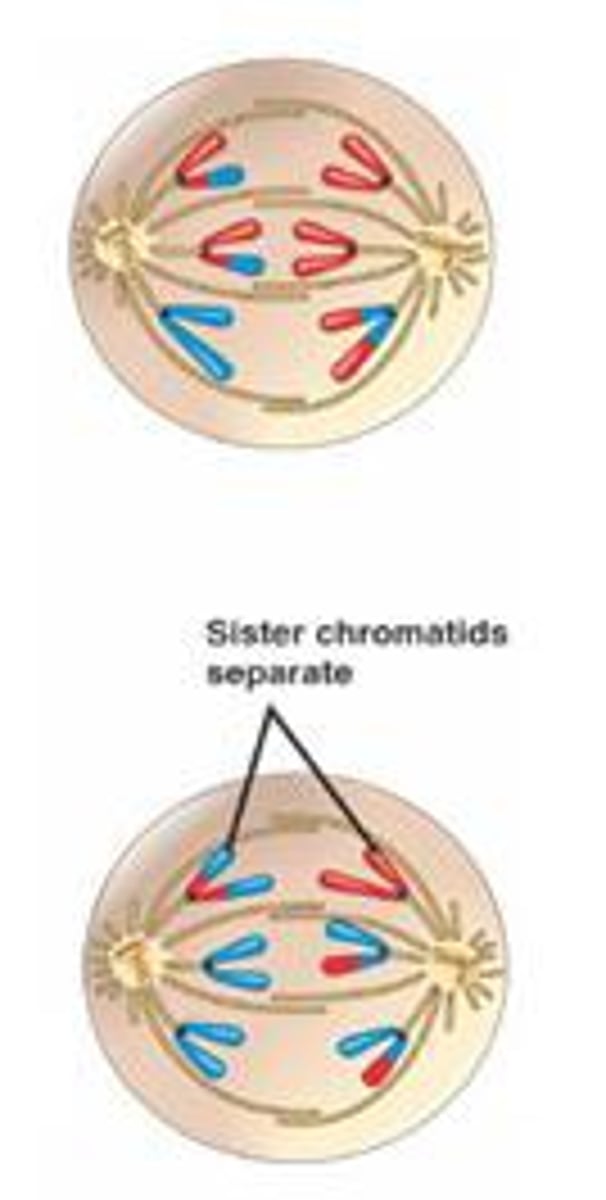
What happens during anaphase I in meiosis?
the homologous separate and move to opposite poles
What happens in telophase I in meiosis?
homologous chromosomes have reached the poles and depending on the organism, nuclear envelopes may or may not form, & cytokinesis may or may not occur
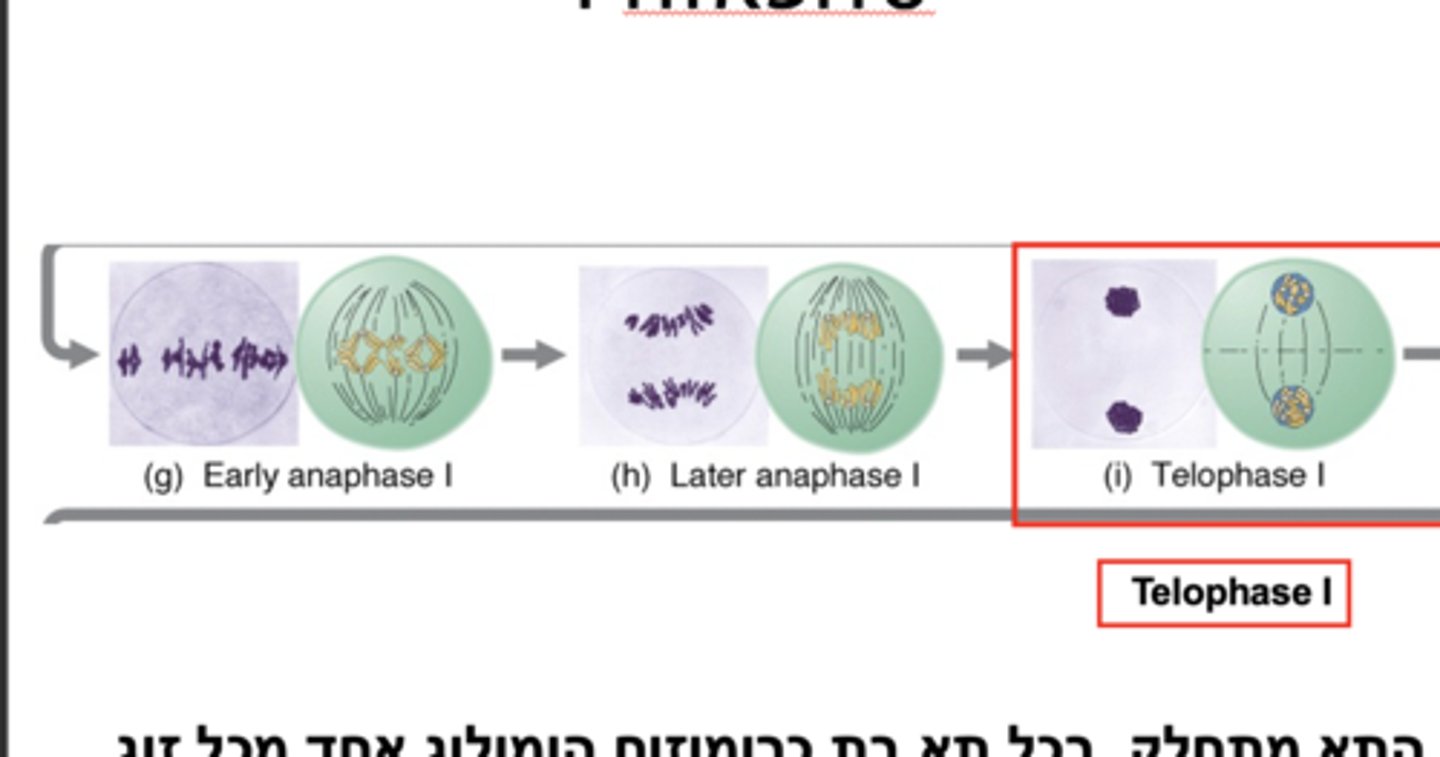
What is interkinesis?
Interphase after Meiosis 1 and before Meiosis 2 during which chromatin uncoils; no DNA replication occurs
What happens in prophase II in meiosis?
nuclear envelope, if present, breaks down again and spindle fibers reform
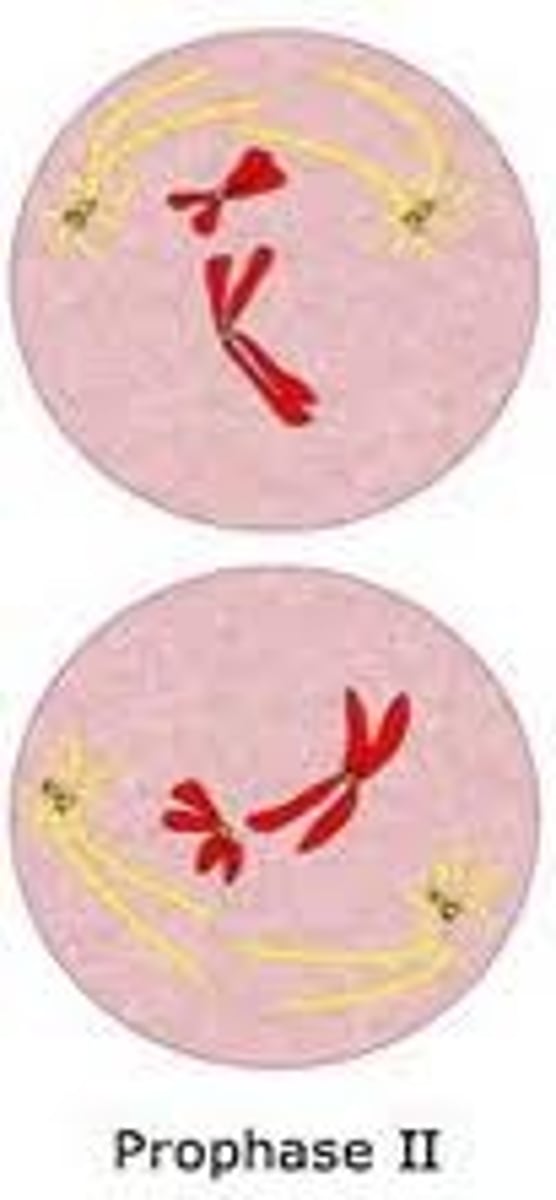
What happens in metaphase II in meiosis?
chromosomes in each cell line up on the equatorial plate
What happens in anaphase II in meiosis?
sister chromatids separate and each results in daughter chromosomes moving toward one of the poles
What happens in telophase II in meiosis?
spindles disappear and a nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes, cytokinesis takes place
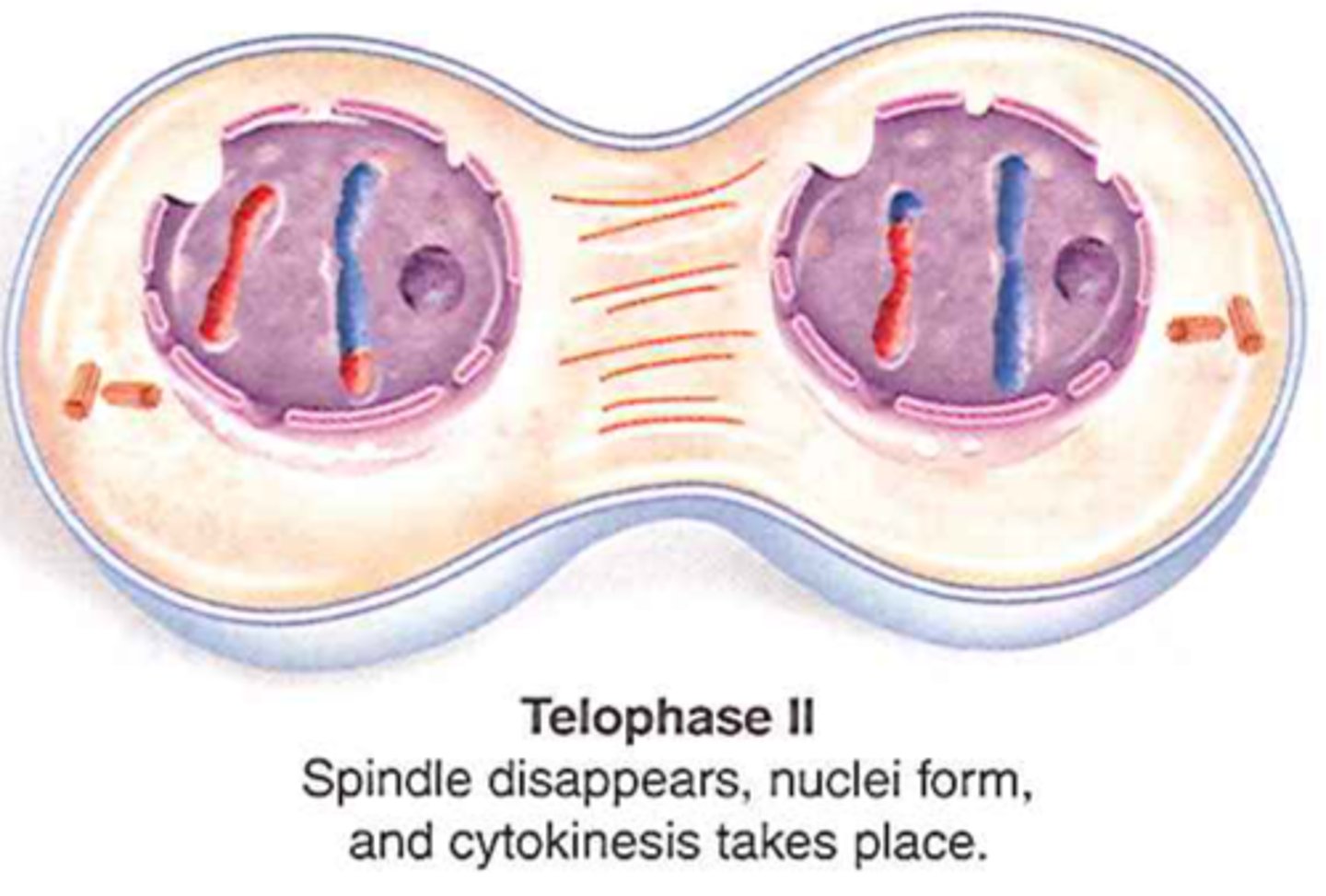
What is the importance of meiosis?
potential for genetic variability in sexually produced individuals is enormous. The number of different gametes that can be produced by meiosis is 2n
In humans, there are _____________ different combinations of chromosomes are possible
8,388,608
When fertilization occurs between 2 people, this means that there is a total of over ____ trillion different combinations of chromosomes possible.
64
What makes up green plants?
green algae and land plants
green plants include
green algae, nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms (seed vascular plants), angiosperms (seed vascular plants)
What are green plant synapomorphies?
chlorophyll b is the primary photo-synthetic pigment, thylakoids are stacked grana in chloroplasts, starch is food storage product, cellulose and hemicellulose are major cell wall components, plasmodesmata
What is green algae?
non-vascular, most primitive
What is the life cycle of green algae (ulva)?
During the first phase, adults produce spores by meiosis. The spores settle and grow to form male and female plants. During the second phase, the male and female plants produce gametes by mitosis. The gametes unite and develop into adult plants.

What are land plants?
have an outer, waxy covering called a cuticle; gametandia, each with an outer, sterile layer of protective cells; diploid embryo grows into multicellular, sporophyte generation
Land plants include
nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, gymnosperms (seed vascular plants), angiosperms (seed vascular plants)
What are some examples of nonvascular plants?
mosses, liverworts, hornworts
Sexual reproduction in land plants is called
sporic meiosis; haploid generation = gametophyte & diploid generation = sporophyte
What is sporic meiosis?
Gametes are the only produced by meiosis.
Is water necessary for fertilization in moss?
yes
Is the sporophyte or the gametophyte dominant in moss?
gametophyte
How many types of spores are produced in the moss life cycle?
1 (homospory)
Where does meiosis occur in moss?
sporangia
Are the spores released in the moss life cycle?
yes
Vascular plants are different from other land plants by having
organs (roots, stems, leaves), vascular tissue (xylem, phloem), dominant sporophyte generation, and lignin (comprises secondary cell wall of certain cells)
What are seedless vascular plants?
A plant that has tissues that conduct water and other materials, but does not reproduce by seeds; sporophytes
What are vascular plants?
Plants that have tissue organized so that food and water can be circulated throughout the plant.
What is Cooksonia?
oldest known vascular plant, round sporangia, extinct by mid-Devonian period ca. 390 mya.

What is Psilotum nudum (whisk fern)?
have enations that look like small bulbs that look like trying to be leaves; most primitive vascular plant
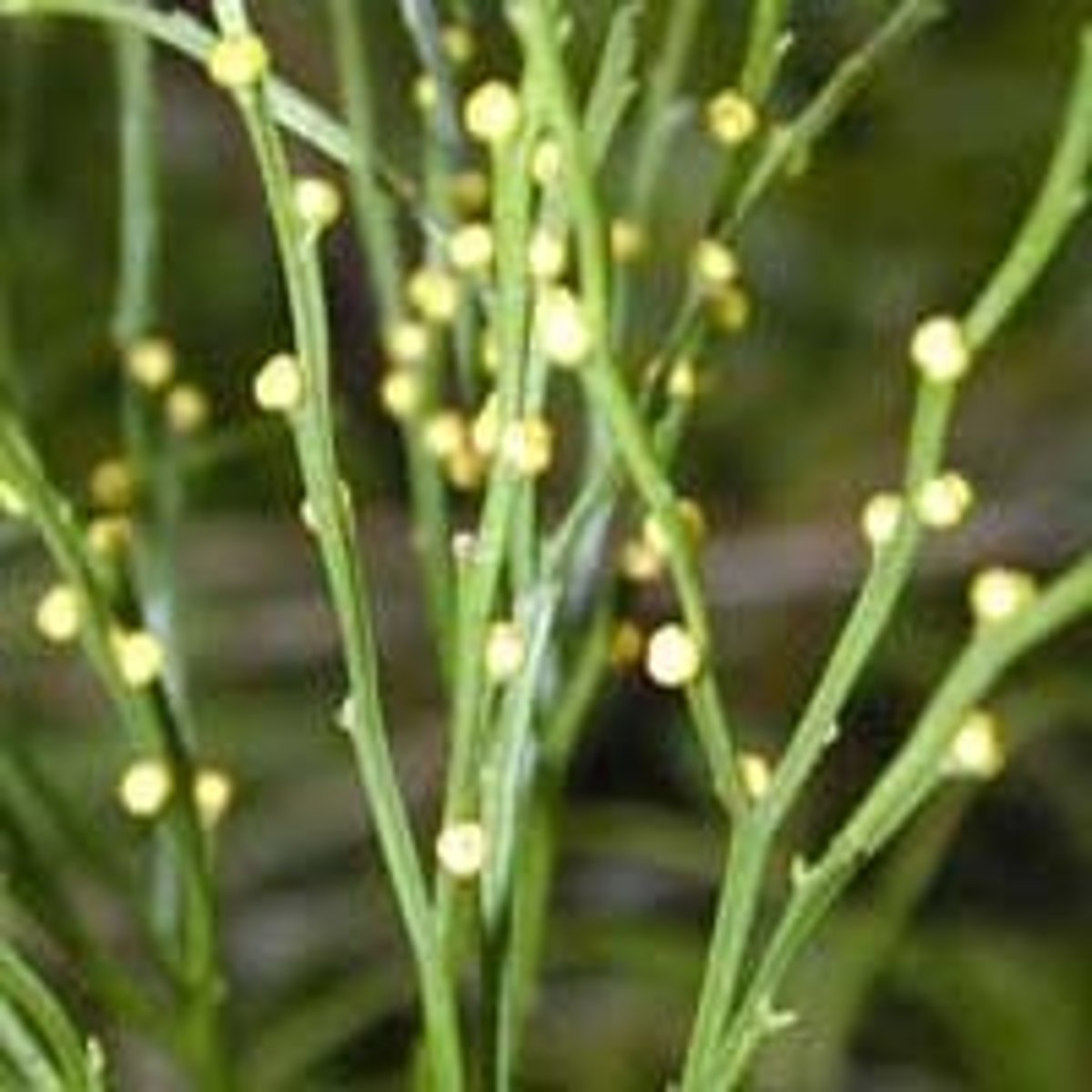

What is lycopodium (club moss)?
strobilus on top of plant is made up of sporangia

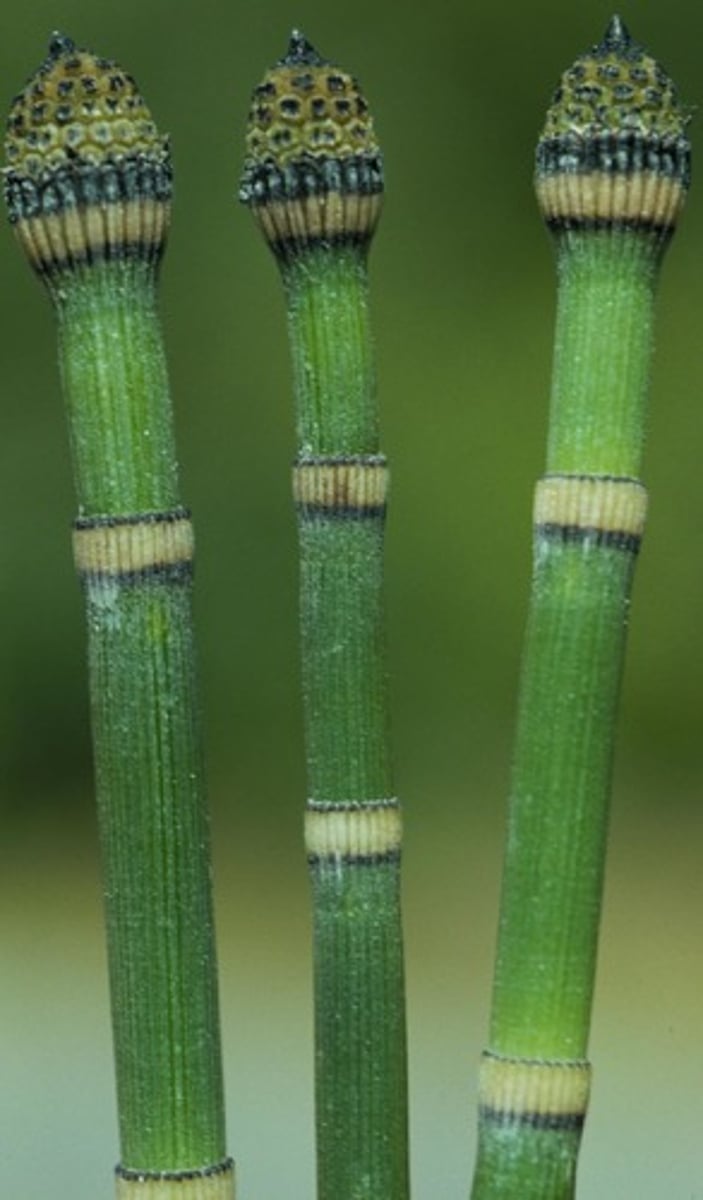
What is equisetum (scouring rushes & horsetails)?
have elaters that will wrap around spore when moist and when dry out, it will shoot out and elaters will shoot out spores

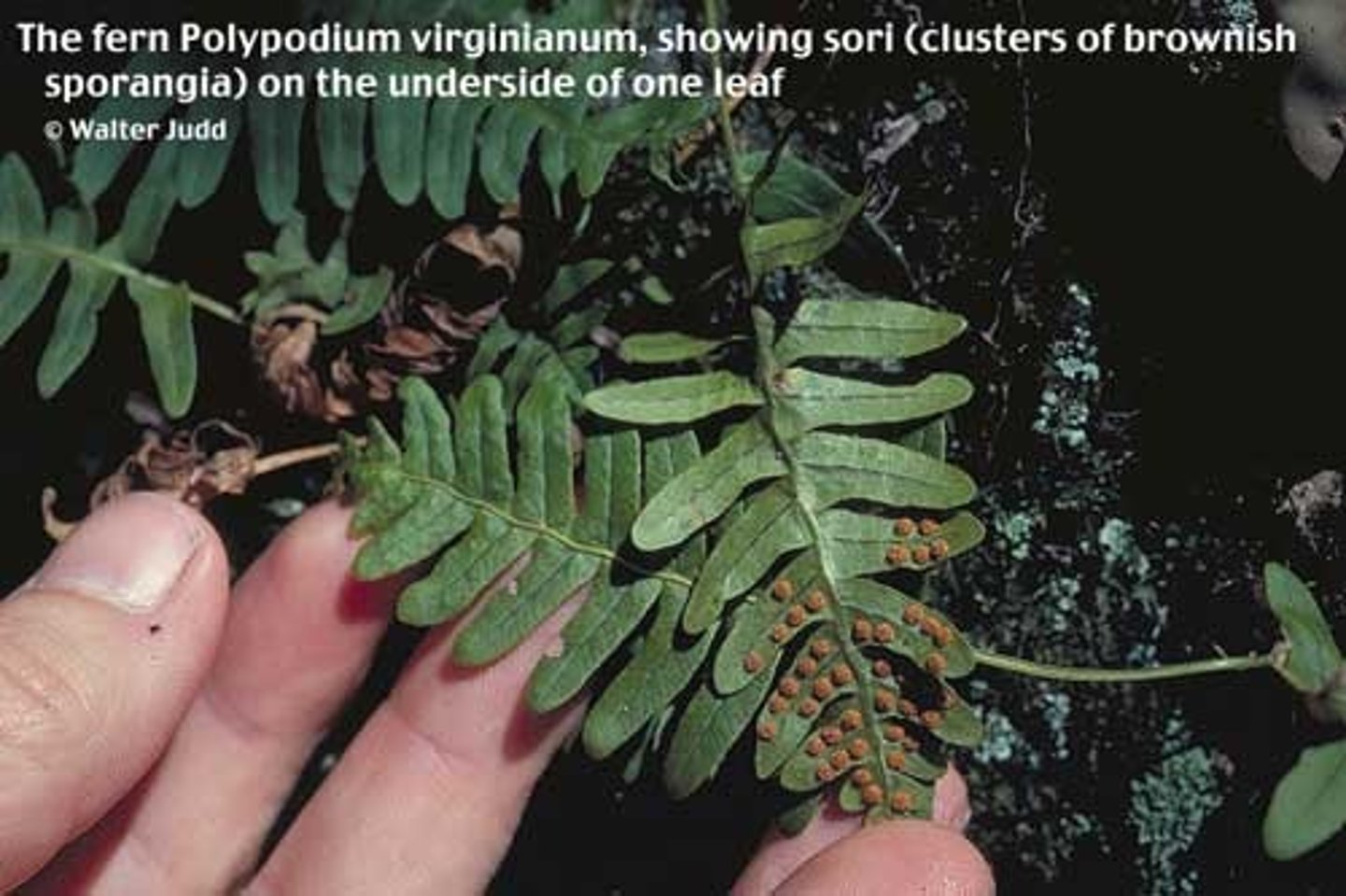
What is polypodium (fern)?
leaves are called fronds, Sori are a bunch of sporangia on back of fronds and eventually wind will disperse them, clump of sporangia is called sorus

What is the life cycle of a fern?
water is necessary for fertilization, sporophyte is dominant, 1 type of spore produced (homospory), meiosis occurs in the sporangium, spores are released, gametophyte not dependent on sporophyte and vice versa for nutrients
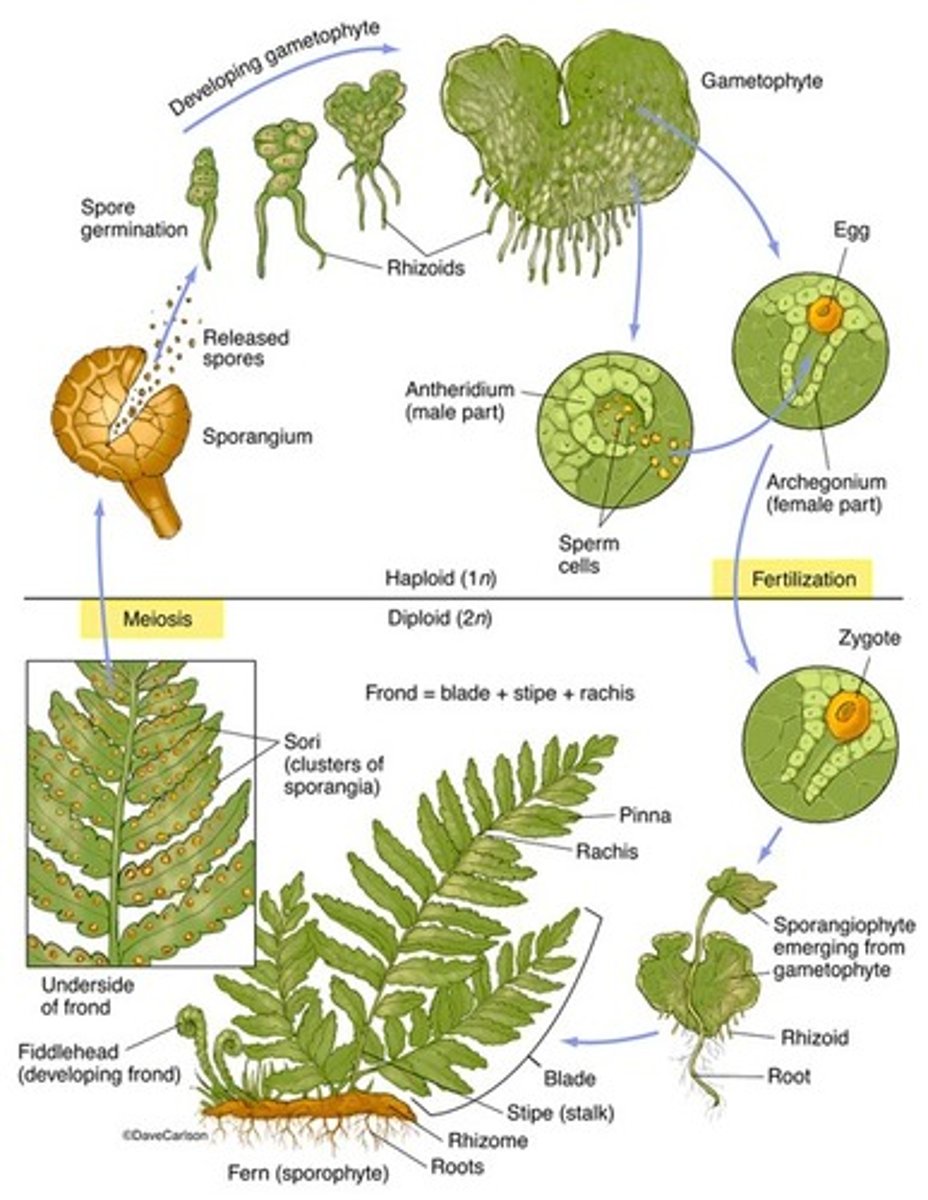
Seed plants are different from other vascular plants in having
seeds (embryo + nutritive tissue + seed coat)
What is a seed?
A seed is a structure formed by the maturation of an ovule following fertilization
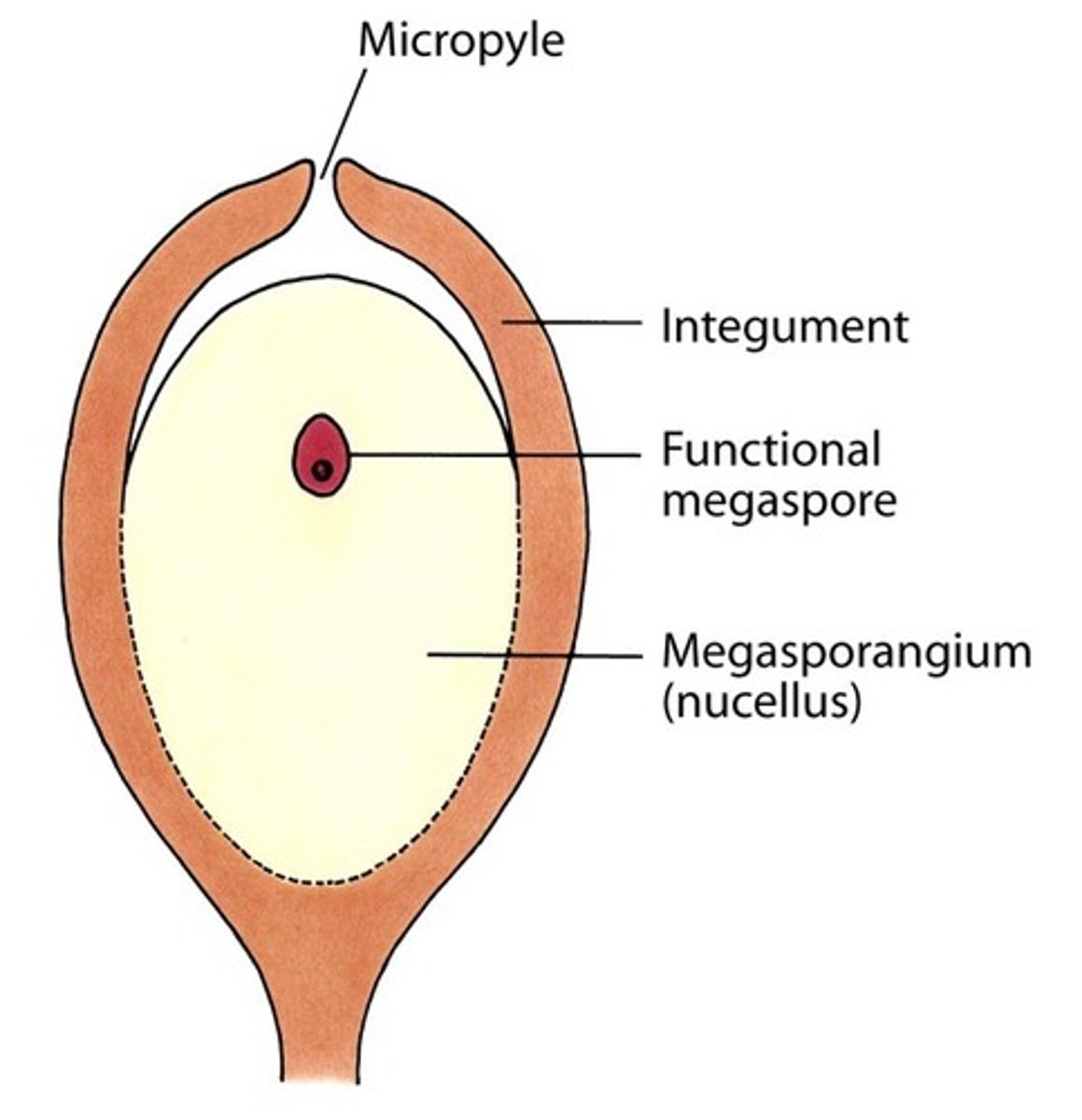
What is a gymnosperm?
a seed plant that produces naked seeds
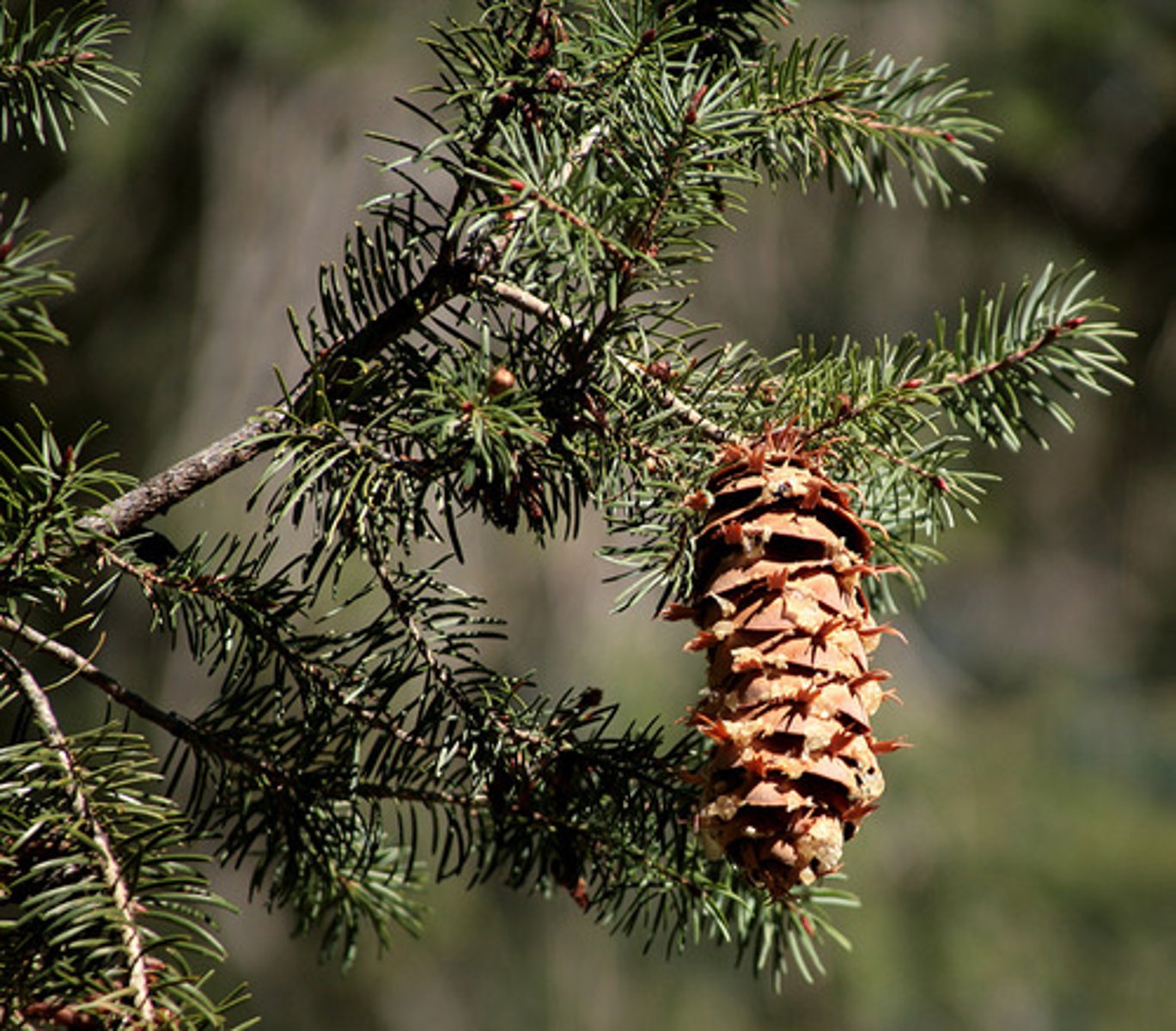
What is phylum coniferophyta?
conifers, appeared during late carboniferous period (use cones for reproduction)

What tree is known as a living fossil?
ginko tree
What are male cones (pinus)?
Heterosporous, inside the microsporangia haploid spores are created and become micro gymnosperms (pollen), the spores are not released and no antheridia is produced

What are female cones (pinus)?
large cones, made of ovules, has seed coat (integument), inside megasporangia haploid megaspores are created that become megagametophytes (embryo sac), creates archegonium (contains egg), anthroidium not produced, has seed scale complex (ovuliferous scale + ovule + sterile bract)
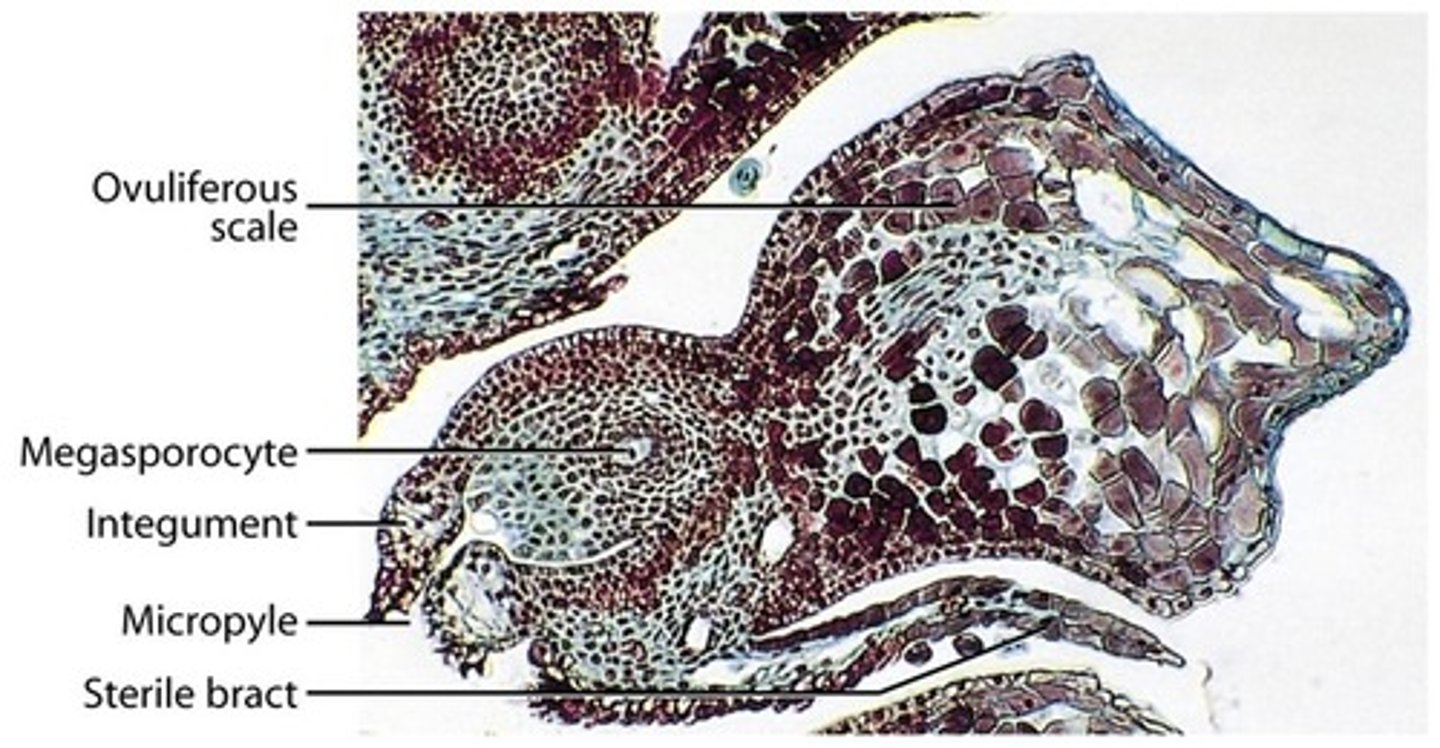
What is the pine life cycle?
water not necessary for fertilization, meiosis occurs in micro & mega sporangeum, sporophyte generation is dominant, sporophyte not dependent & gametophyte is dependent, 2 types of spores & not released
4 haploid spores created by sporic meiosis but only 1 is functional

What are angiosperms?
plants that produce flowers as reproductive organs (most evolved)
Angiosperms are different from other seed plants in having
flowers, fruits, double fertilization (endosperm), 3 nucleate microgametophytes, 8 - nucleate megagametophytes
The _________ tree is the largest angiosperm
eucalyptus

_________ is the smallest angiosperm
duckweed (wolffia)

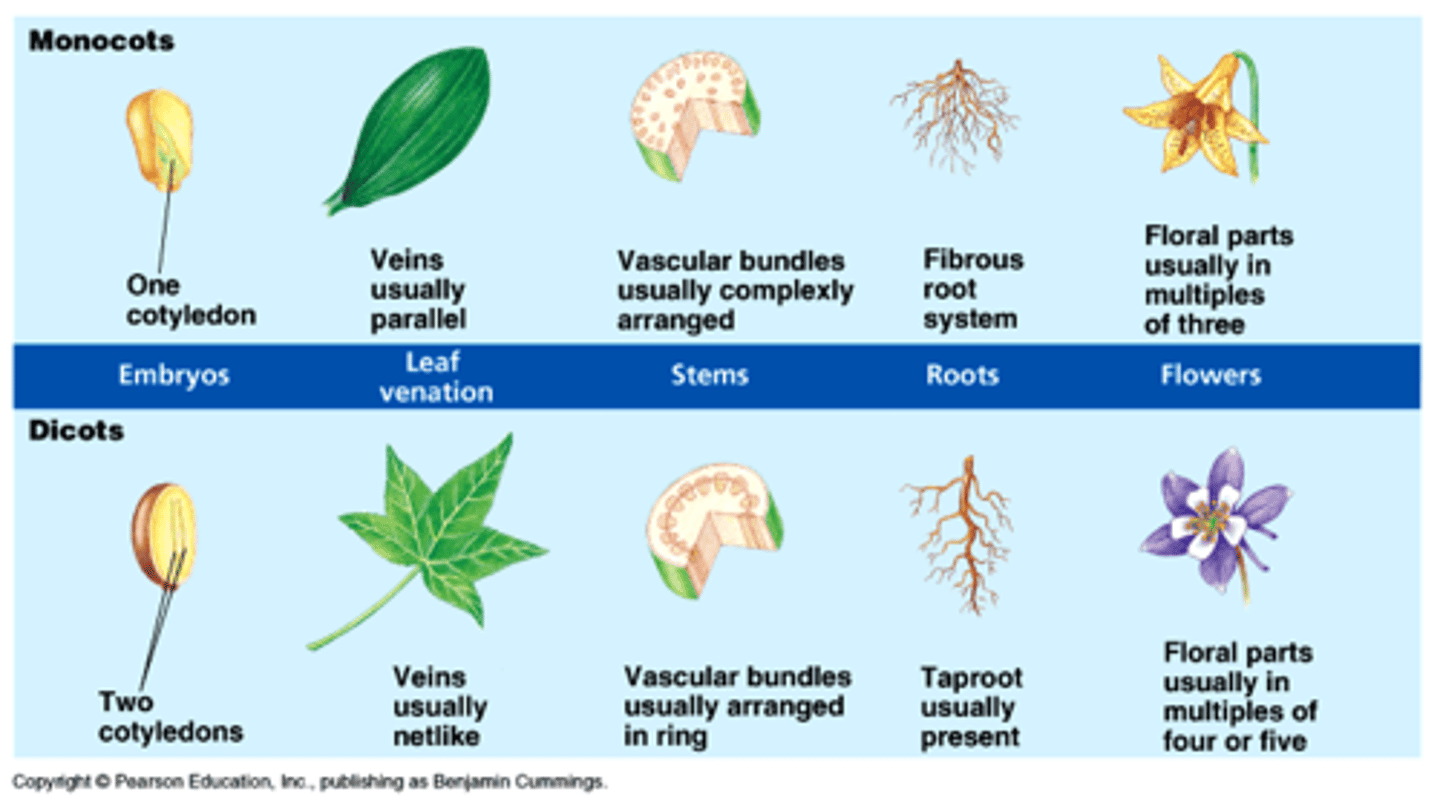
What is the class monocotyledones in flowers?
1 cotyledon, flowers in parts of 3s or multiples of 3s, parallel leaf variation, stem vascular bundles scattered, root xylem & phloem in a ring
example: coconut palm, rice
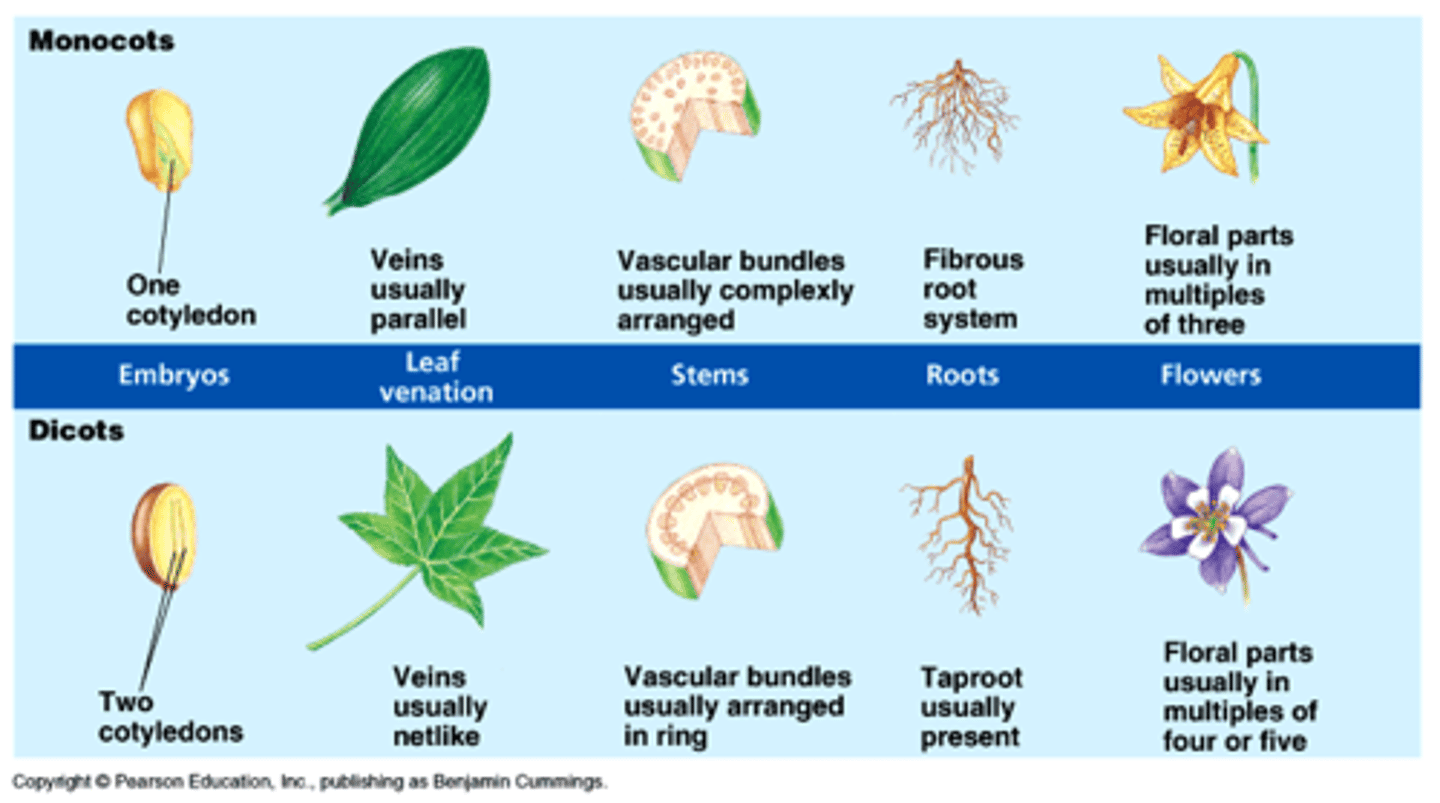
What is the class eudicotyledones in flowers?
2 cotyledons, flowers in parts of 4s or 5s or multiples of these, net leaf variation, stem vascular bundles in a distinct ring
ex) daisy, strawberry, poppy
The stem where the flower is produced is called a _________
receptacle
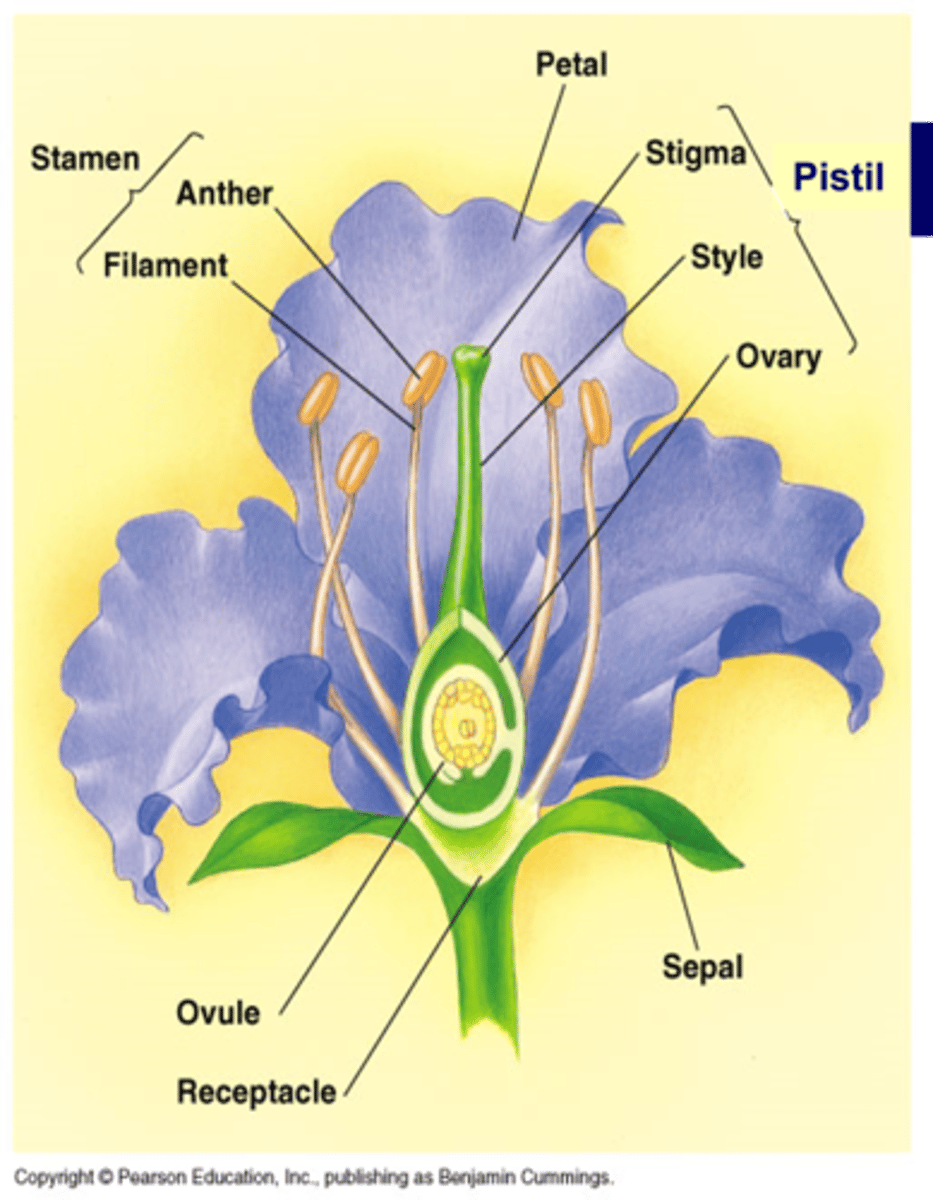
The ________ of a flower protects the inner part of the flower until is opens
sepal (calyx is made up of individual sepals)
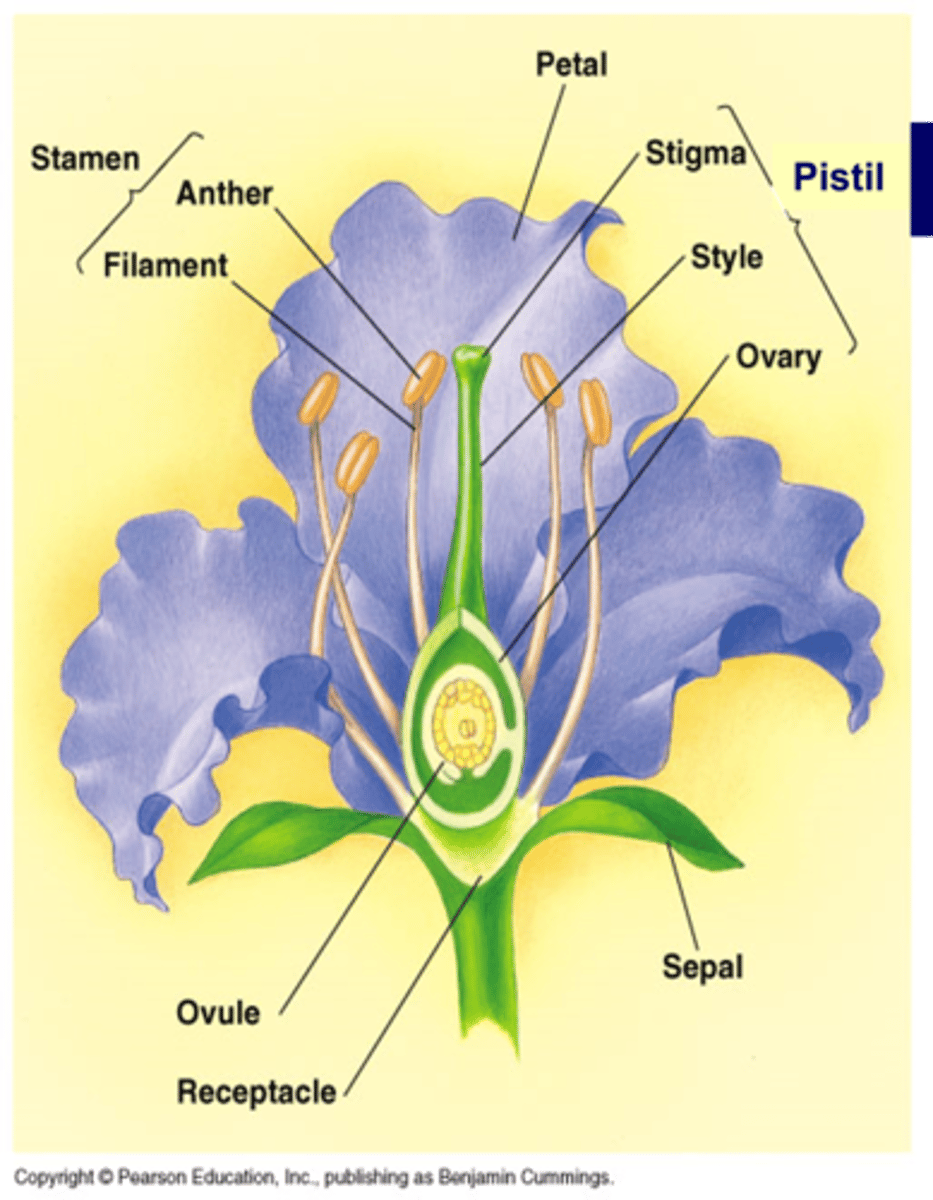
The ________ also called corolla attracts pollinators
petal
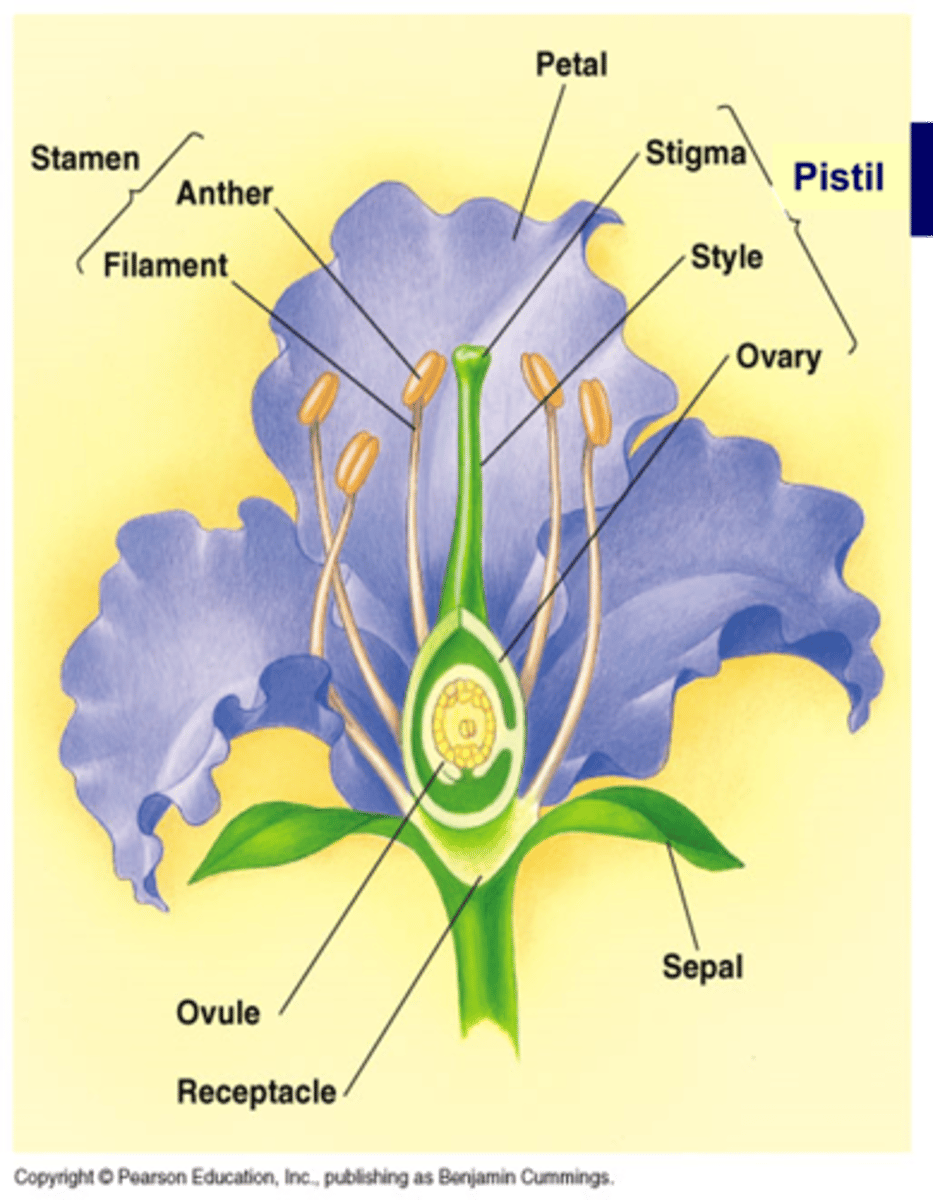
The _________ made up of _________ & ___________ make up the male parts of the flower
stamen, anther (microsporangia, pollen released from here), filament
The _________ is made up of _____, ________, & ________. These make up the female parts of the flower
Pistil, stigma (where pollen lands), style, & ovary (becomes fruit, contains 1 or more ovules that become seeds)
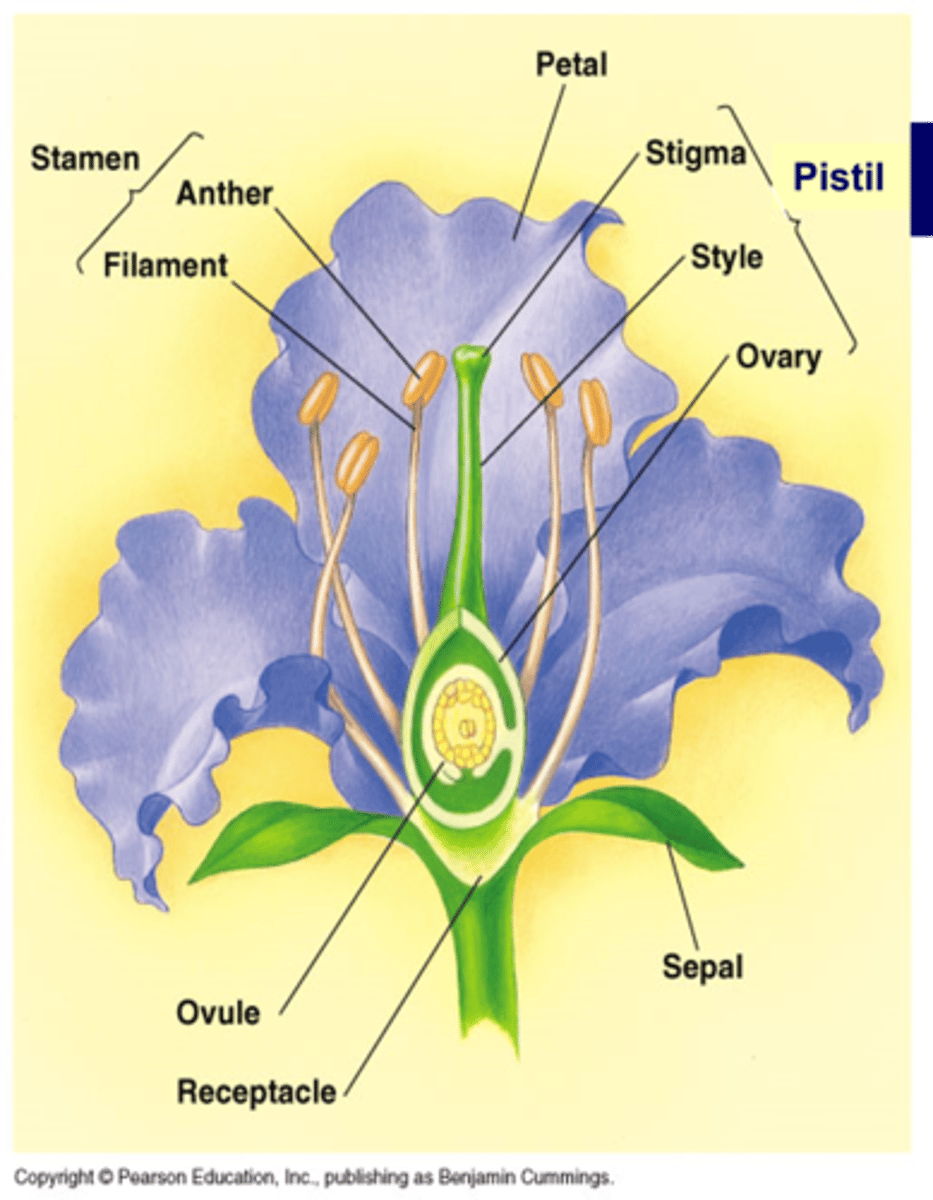
Flowers on a plant may be grouped into an ____________
inflorescence
What is a spike inflorescence?

What is a raceme inflorescence?
What is panicle inflorescence?

What is a head inflorescence?

What is catkin inflorescence?

What is the reproductive cycle of flower?
sporophyte is dominant (diploid), 4 microsporangia inside anther with diploid cells that produce 4 haploid microspores by sporic meiosis. Then becomes microgametophyte (pollen), then it lands on the stigma where pollen tube grows toward ovary. No archegonium produced, sperm cells released from micro sporophyte to fertilize egg. 1 sperm fertilizes the egg and the others joins to make endosperm (3n) that feeds the growing embryo in seed
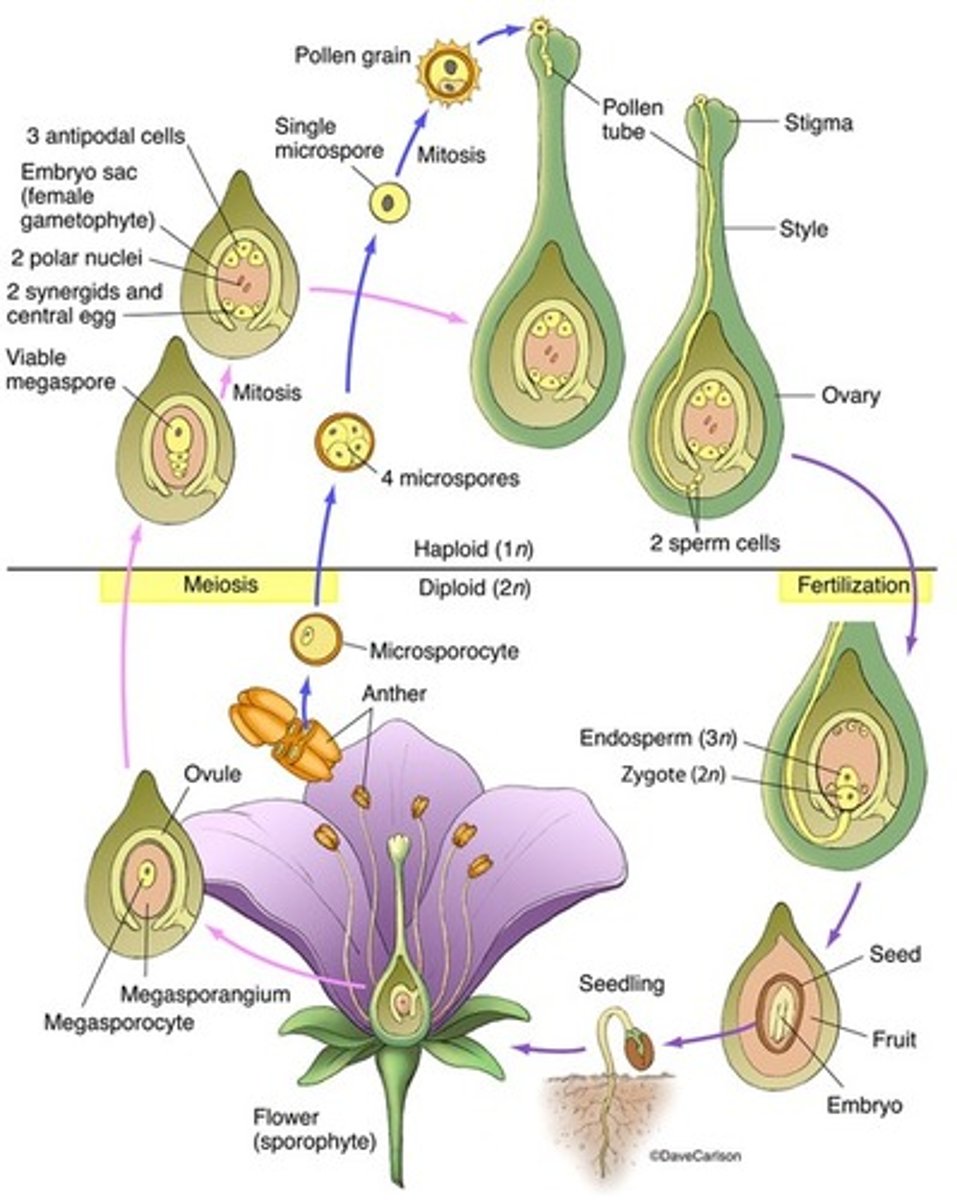
What is the life cycle of a flower?
water is not necessary for fertilization, sporophyte generation is dominant, meiosis occurs in micro and mega sporangia (heterospory), sporophyte is not dependent, spores not released
Flowers and pollinators _______
coevolve
What is beetle pollination?
flowers are primitive, large, beetle will eat pollen so the ovules are buried deep in flower to prevent beetle from eating it
ex) magnolia
What is bee pollination?
bees prefer yellow or white flowers & pleasant odor, adults eat nectar & flowers have little nectar guides on flowers, larve eat pollen brought back by adult bee, some orchids resemble adult female bees to make males copulate with them and spread pollen