LECTURE 6 FISHERY INDUSTRY
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Aim of fisheries industry are
1. To ensure adequate supply
2. To guarantees the ability of the people to get fish as a source of protein in the diet
Subsector of Fisheries Industry
Food fish sector and non-food fish sector
Food fish sector includes
Marine capture Fisheries
Inland fisheries
Aquaculture fisheries
non-food fish sector includes
Ornamental fish
Marine capture fisheries can be categorized into two main types:
Coastal or inshore fisheries
Deep sea fisheries
Coastal or inshore fisheries
operate within 30 nautical miles from the coastline
The main focus of fishing activities
Reached their maximum level of exploitation
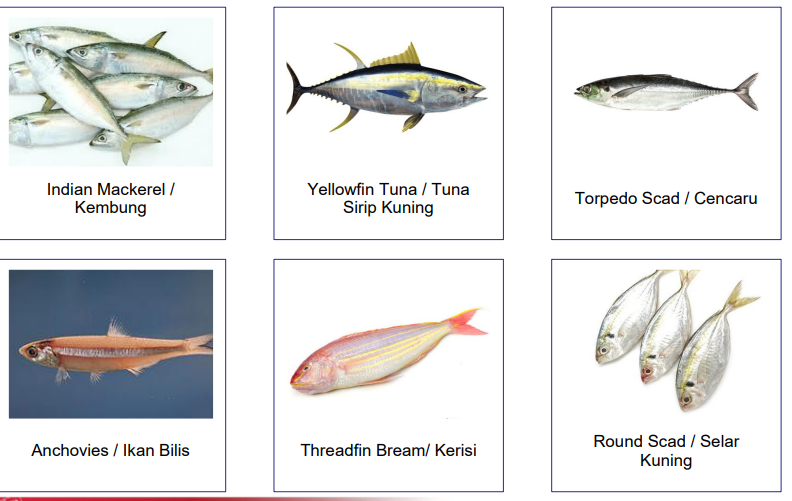
The main species are pelagic species
Eg : shrimp, indian mackerel, round scad, squid, Tuna, anchovies, ox-eye scad
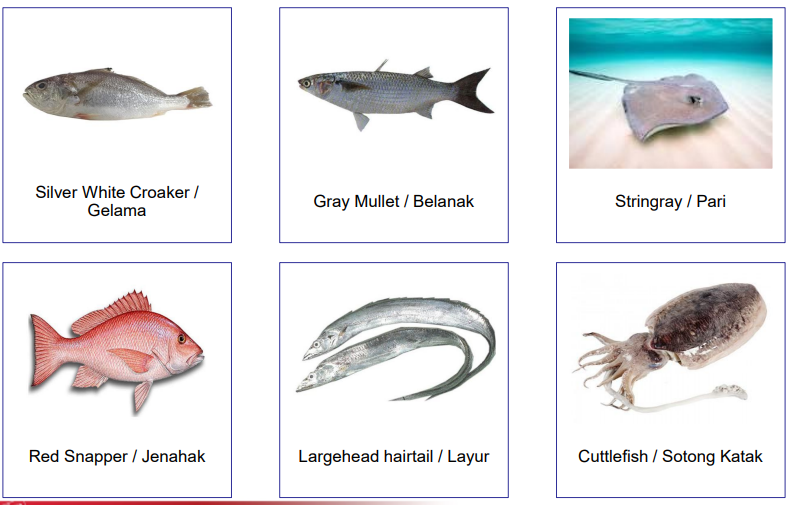
Deep sea fisheries
operate beyond 30 nautical miles from the shoreline
Target demersal/benthic species
Fishers have increasingly moved further offshore and into deep-sea regions
Advances in technology made it easier to exploit resources at great depths
Types of pelagic species

Types of Demersal species

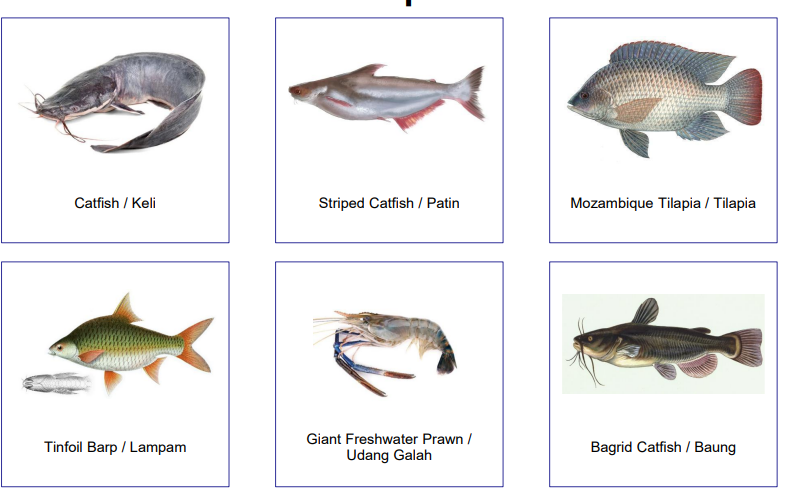
Inland fisheries
“Inland waters" => lakes, rivers, brooks, streams, ponds, inland canals, dams, and other land-locked (usually freshwater) waters
important role to play in the global challenge to sustainably feed this growing population in a manner of accessible and affordable.
important source of nutrition, food security, micronutrients.
Types of Inland Species

What is invasive species?
an organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area.
How invasive species has been introduced?
by human activity (deliberately or accidentally) to geographic areas outside its native range
caused ecological or economic impacts in that location
Impact of Invasive Species
new and spread outbreaks of diseases.
Disrupt biodiversity balance of natural habitat
Will be dominant and reproduce in natural aquatic habitats
Great economic losses to farmers
Examples of Invasive Species (Prohibited for import into Malaysia)

What is aquaculture?
Aquaculture is the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of fish, shellfish, plants, algae, and other organisms in all types of water environments.
Main Purpose of Aquaculture in Malaysia
To increase fish production for food security
To support economic growth and export earnings.
Restoration of threatened and endangered species population.
Wild stock population enhancement
Habitat restoration
Why aquaculture can increase fish production for food security?
✔ Meet the growing domestic demand for fish and seafood.
✔ Reduce dependence on capture fisheries.
Why aquaculture can help support economic growth and export earnings?
✔ contributes significantly to Malaysia’s agriculture GDP.
✔ shrimp, grouper, tilapia, and catfish have potential export to other countries.
Why aquaculture can help the Restoration of threatened and endangered species population?
✔ Supports the preservation of genetic diversity through broodstock banks.
✔ Breed endangered species in controlled environments.
How aquaculture can enhance Wild stock population?
✔ Juvenile fish or larvae are raised in hatcheries and then released into natural ecosystems.
How aquaculture can help restore habitat?
✔ Some aquaculture projects are linked with habitat restoration like:
⮚ Mangrove replanting
⮚ Artificial reef
There are a few types of aquaculture
Mariculture
Freshwater
Barckish water
Seaweed farming
Mariculture
the farming of aquatic plants and animals in salt water.
Freshwater aquaculture
culture of aquatic species within a freshwater environment
Brackish Water
a mixture of fresh and salty water which usually occurs in estuaries
CULTURE SYSTEM
open system
semi-closed systerm
closed system
Integrated system
Characteristics of Open System Farming
The oldest aquaculture systems.
Use of environment as fish farm
Does not require water to be pumped out of a sea or a lake
The organism to be cultured are kept in the sea or lake
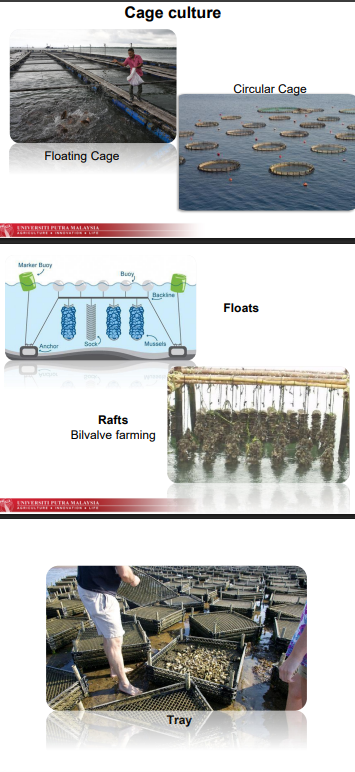
Eg: clams tray, oyster rafts and fish cages
Advantages of Open System Farming
Capital expenses are low – land can be leased from some government agency.
Less management
Less time to spent to monitor.
organisms – natural and uncrowded culture environment.
Disadvantage of open system farming
Predation and poaching of culture organism.
Rate of growth and uniformity of the yields are variable.
cage culture in open system farming