Earth Sciences (Sedimentary Rock 2)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
composition
the type and abundance of minerals and rock fragments present in the sedimentary rock
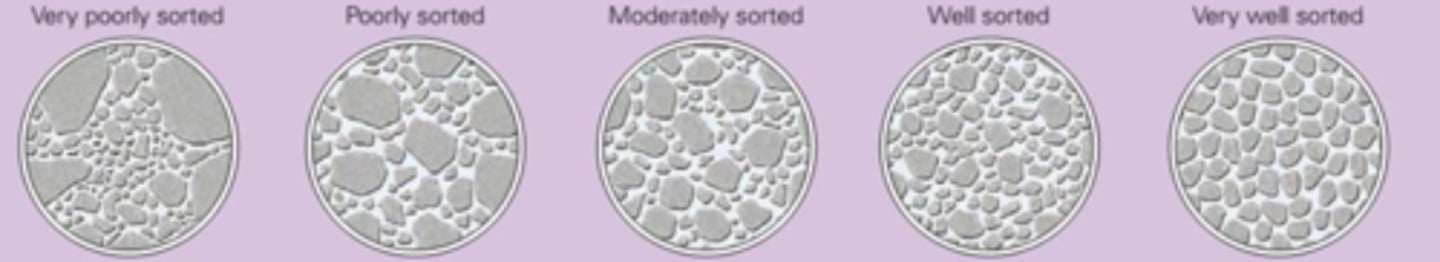
Sorting
the degree of similarity in particle size in a sedimentary rock
Rounding
How round the sedimentary rock is

poorly sorted
grains vary widely in size
well sorted
grains are nearly all the same size
When does well sorted deposits occur
occur when consistent energy selectively separates rocks into sizes by currents or reworked by waves
When does poorly sorted deposits occur
Rapid drop in energy of the transportation medium
Fluctating energy levels in the environment
Maturity
refers to the amount of weathering, erosion and transportation experienced bygrains
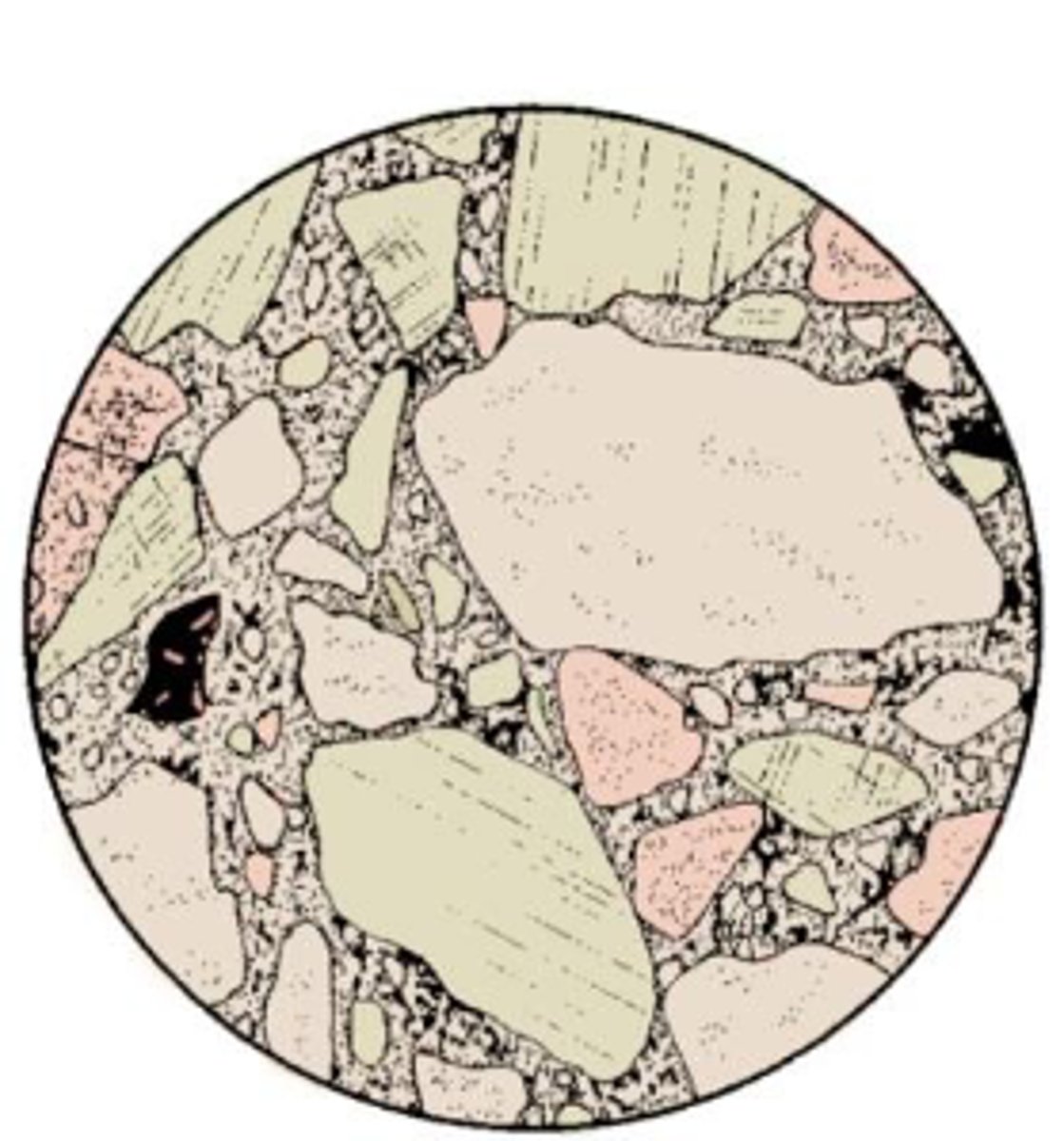
Immature
abundance of feldspar,ferromagnesian minerals and rock fragments
less quartz
angular grains
poorly-sorted
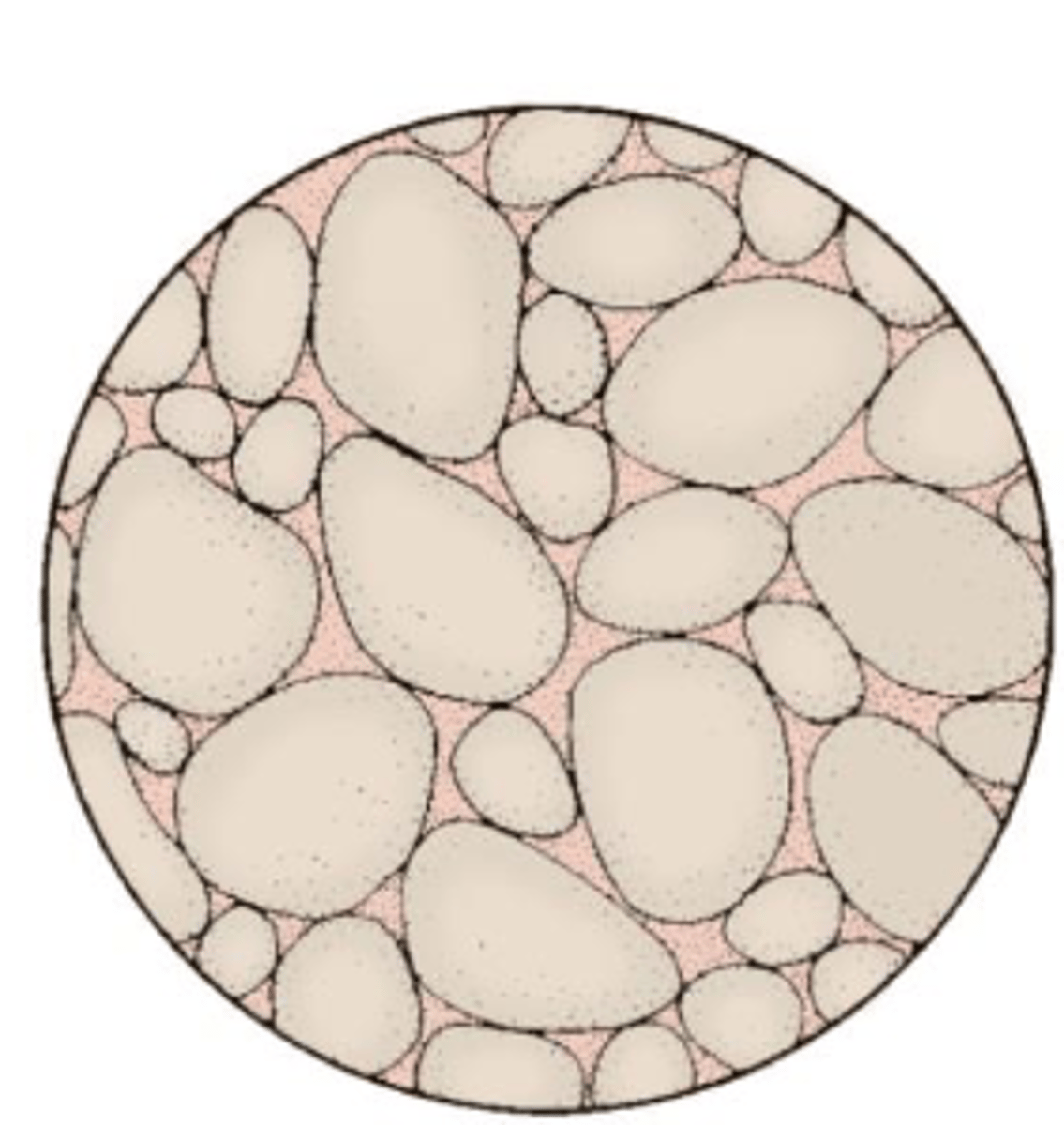
Mature
quartz-rich
well rounded
well-sorted
What leads to the gradual destruction of less stable minerals and rock fragments?
Substantial weathering, long transport, and reworking.
Which minerals are gradually destroyed due to weathering?
Feldspars and ferromagnesian silicates.
What is the result of weathering in terms of mineral abundance?
Increased abundance of quartz.
Why does quartz become more abundant during weathering?
Because it is stable in the weathering environment.
depositional environment
a geographic setting where sediment is accumulating(and in which organisms maylive and die)
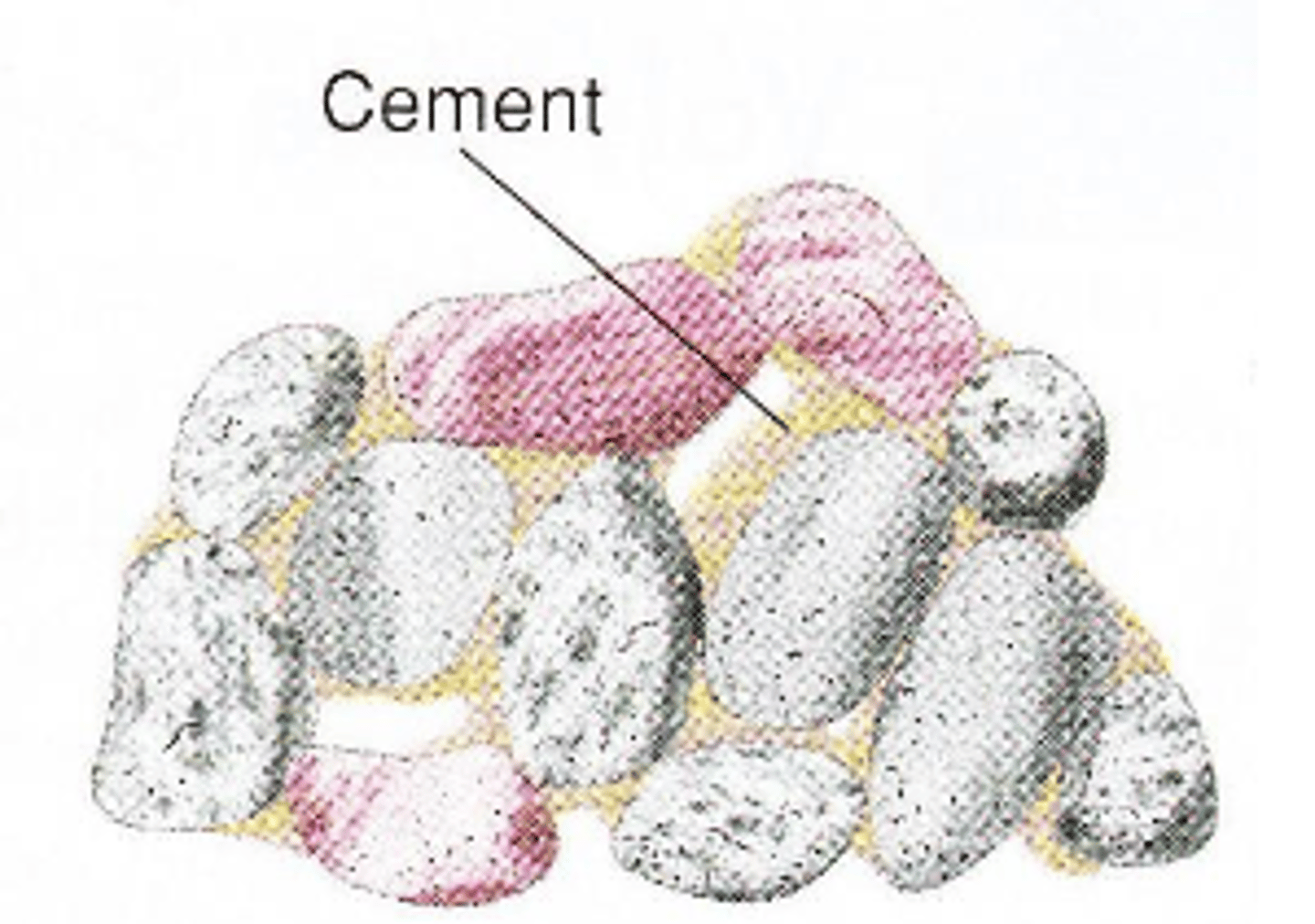
Cementation
minerals inorganically precipitate from water that percolates in the pore space between sediment particles
Compaction
weight of the overlying sediment compresses and consolidates more deeply buried sediment
Rivers
Whenever a streams velocity slows, particles of sediment that were transported at higher velocity are deposited—beginning with the coarsest (largest) particles.
What is an alluvial fan?
A fan-shaped deposit of stream sediment formed on a gently sloping or flat valley floor at the base of a mountain where a stream's slope and velocity are abruptly reduced.
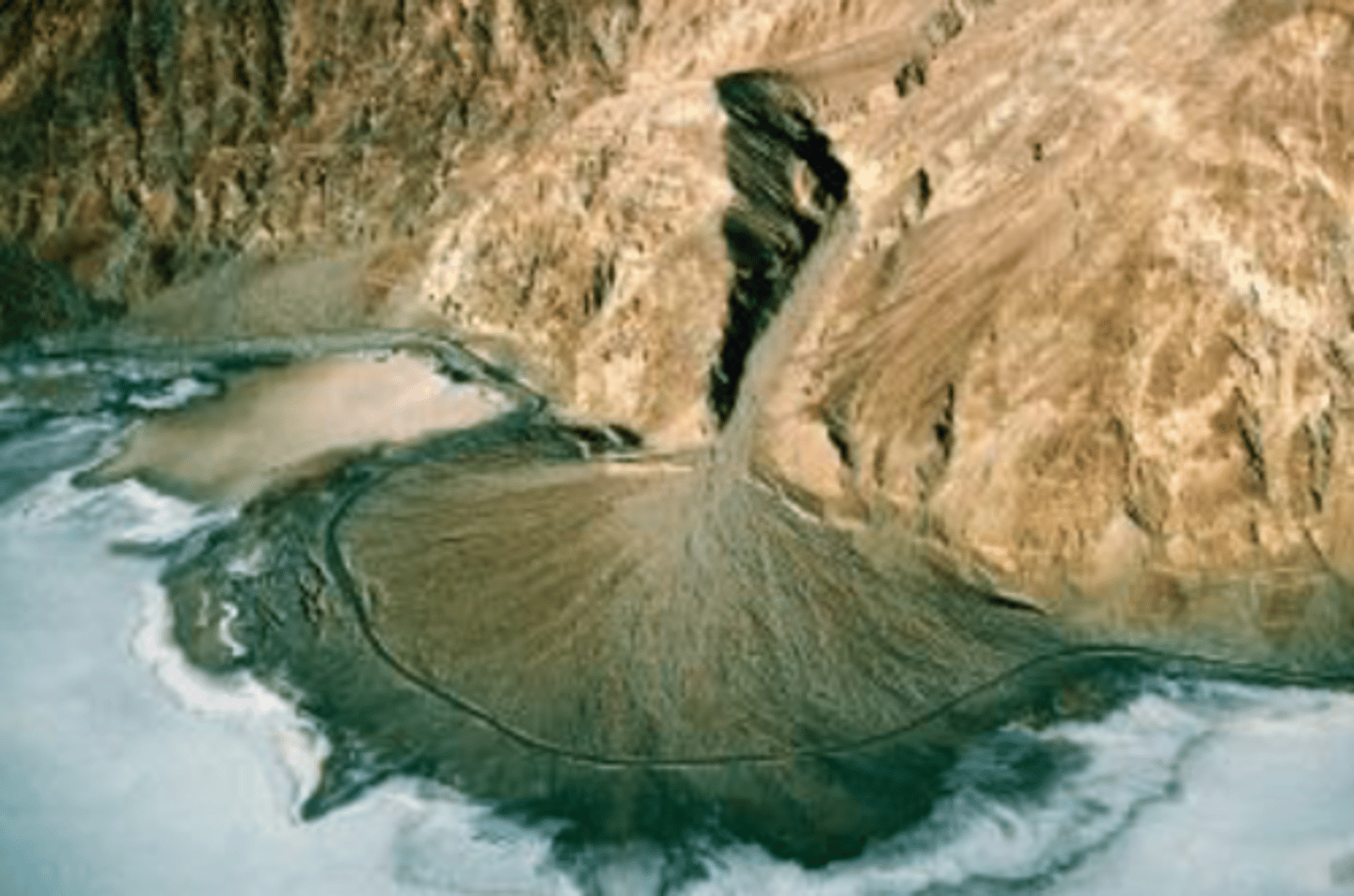

What is the typical grain size of deposits in an alluvial fan?
Deposits are generally coarse grained, consisting of gravel and coarse sand.
Composition and texture of alluvial fan deposits
They are compositionally and texturally immature, being angular and poorly sorted.
What type of deposits accumulate in lakes?
Clastic, chemical (e.g., evaporites), and biogenic sediments.
What types of sediments are commonly found in lake/lacustrine deposits?
Silt and clay, although a variety is possible depending on size, depth, and climate.
What geological features form along the lakeshore?
Small deltas and beaches.
Where do finer sediments come to rest in a lake?
On the lake floor.
Desert deposits (Aeolian or wind deposits
Where winds are strong and the surface is not anchored by vegetation, sand accumulates in dunes
Composition and texture of desert deposits
Compositionally and textually mature quartz-rich, well-rounded and well sorted sand
Glacial Deposits
Glaciers (moving ice) pluck and transport clasts ranging in size from clay to boulders the size of houses. Sediment deposited directly from a glacier is called till
Till
unstratified (not layered) and poorly sorted (ranging from clay to boulders)
Delta deposits
Deposits of clay, silt, and sand.
Where do deltas form?
Where a stream flows into a standing body of water, such as a lake or the ocean which has an abrupt decrease in velocity of the stream.
Beaches
Exposed to moderate to high energy waves
Deposit a range of grain sizes depending onthe energy
Continental shelf deposits
Limestone (CaCO3) form in ocean water that is light, warm, clear and shallow
Shallow water
consist of skeletal debris of carbonate secreting shells and coral reefs
Deep marine ocean
consists principally of the skeletons of microscopic plankton
Strata/beds
Layers in the sedimentary rock