Neuroanatomy and Gross Structure of the Human Nervous System
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Function & organizational principles of the brain
1. interconnectivity in the brain
2. centrality of the central nervous system
2a. hierarchy of neuroaxial organization
3. Laterality of brain organization
4. structural and functional specilization
5. topographical organization in cortical pathways
6. brain plasticity
7. nonmythical brain
Brain interconnectivity
Constant interactivity for information integration through association fibers, commissural fibers, and projection fibers.
association fibers
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
commissural fibers
connect one hemisphere to the other
projection fibers
connect the hemispheres with lower brain or spinal cord
centrality of CNS
CNS as the Decision Maker for:
Integration of incoming/outgoing information
Analyzes and synthesizes a variety of information
Generation of appropriate response
CNS
central nervous system
CNS contains
brain and spinal cord
PNS
peripheral nervous system
PNS contains
cranial and spinal nerves
incoming
sensory
outgoing
motor
Hierarchic organization
each level reflecting organizational complexity (complexity increases with ascending levels)
lowest level: simpliest level
highest level: more complex
lowest level
spinal cord reflexes
highest level
Cerebral cortex- sensory motor integration and higher mental functions
laterality organization
-bilateral anatomic symmetry
-unilateral functional differences
-contralateral sensorimotor control
Bilateral Anatomic Symmetry
The two sides of the brain look alike. Same basic structure.
unilateral functional differences
- Left hemispheric dominance for language
- Right hemispheric dominance for emotions, visual spatial skills, musical skills, paralinguistic functions, and attention
Contralateral Sensorimotor control
The right cerebral cortex controls and feels the left body. The left cerebral cortex controls and feels the right body
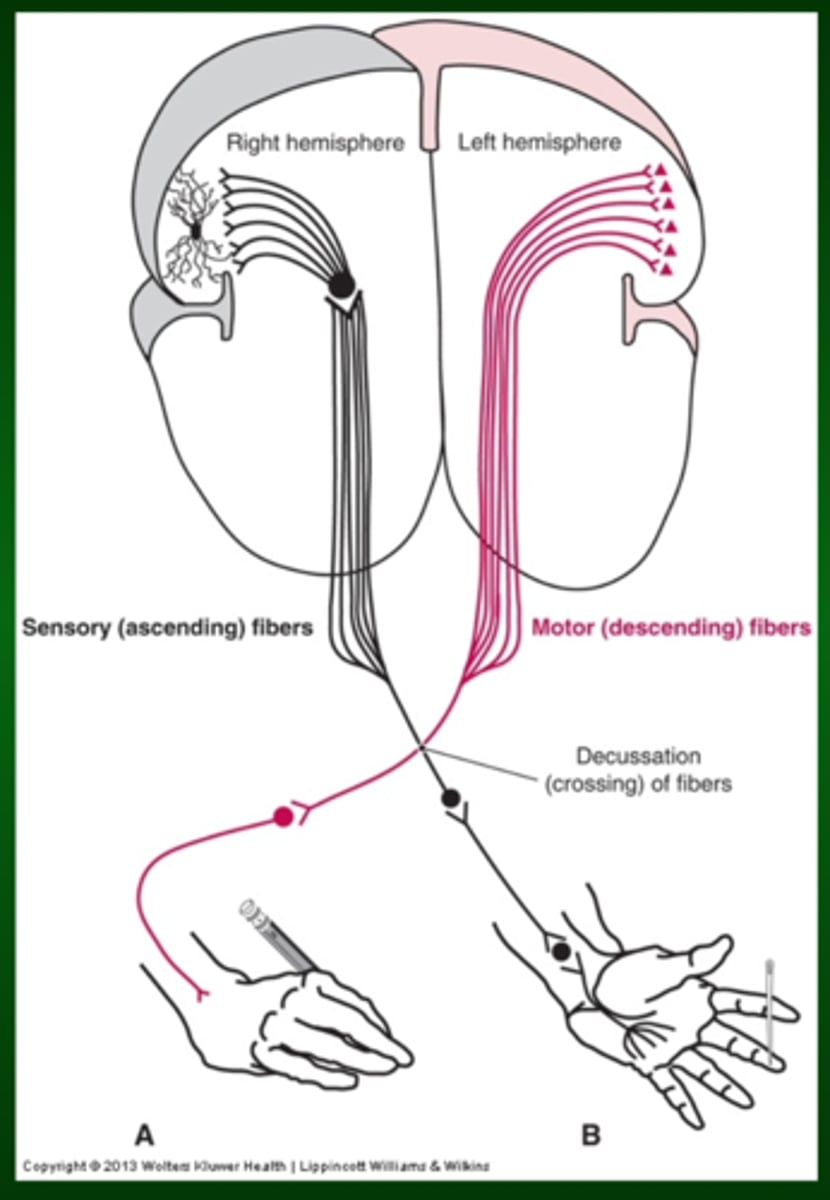
Functional Networking
Networking
Distinct parallel pathways conducting different types of information
Sensory fibers
Touch
Discriminative touch
Motor efferents
Pathways to various limbs
topographical organization
-Selectivity of Organization
*Spatial organization of neurons, tracts, and terminals serving the same function
*Discrete representation of body surfaces and muscles in the brain
*Discrete pathway passage
*Somatosensory homunculus: each part of your body is represent in the brain
Plasticity in the brain
- Reorganizational Capacity
- Implications for learning and recovery
Plasticity
the ability to change or org as a result of experience and ability to reorganize or modify tissue function when injured
Reorganizational Capacity
- Brain's ability to reorganize & modify tissue functions when faced with pathology
- Adaptation to internal/external changes
Implications for learning and recovery
- Greater plasticity at a young age: learn and adapt, brain is spongy
- Importance of critical period for experience
- Tissue-function reorganization with CVA
CVA
cerebrovascular accident (stroke)
The mature brain is ____
age 25
Nonmythical Brain
-Brain potential-independent of gender, color, or cultural variations
-Notable variations in brain size, shape, or weight
-Functionally unimportant normal variations
brain orientation: cerebrum
Rostral, caudal, dorsal and ventral
rostral
near front of the head
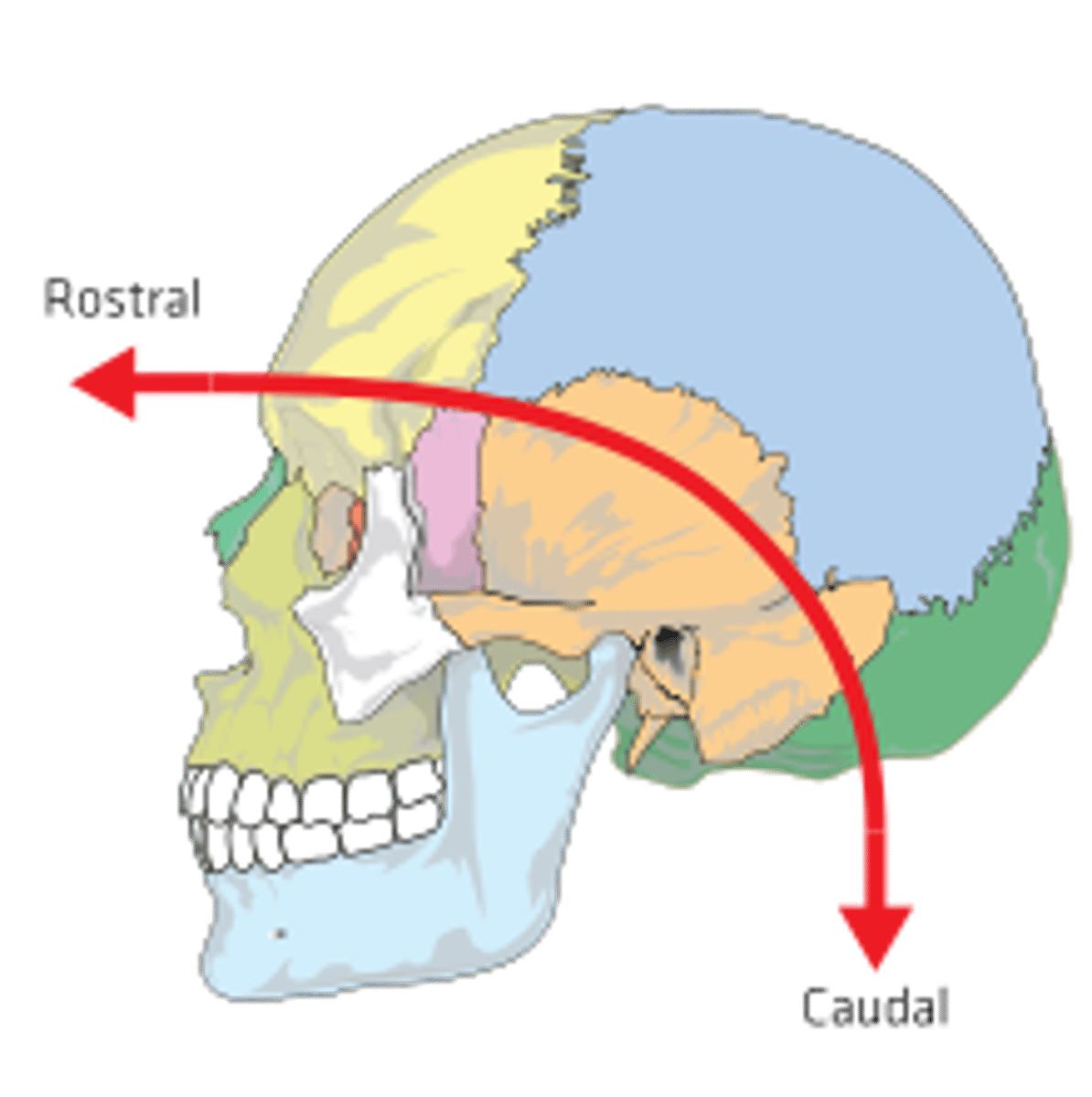
caudal
back of brain or head
dorsal
top of brain
Ventral
bottom of brain
plans of brain section
sagittal, midsagittal, coronal, horizontal
Sagitall
divides body into left and right
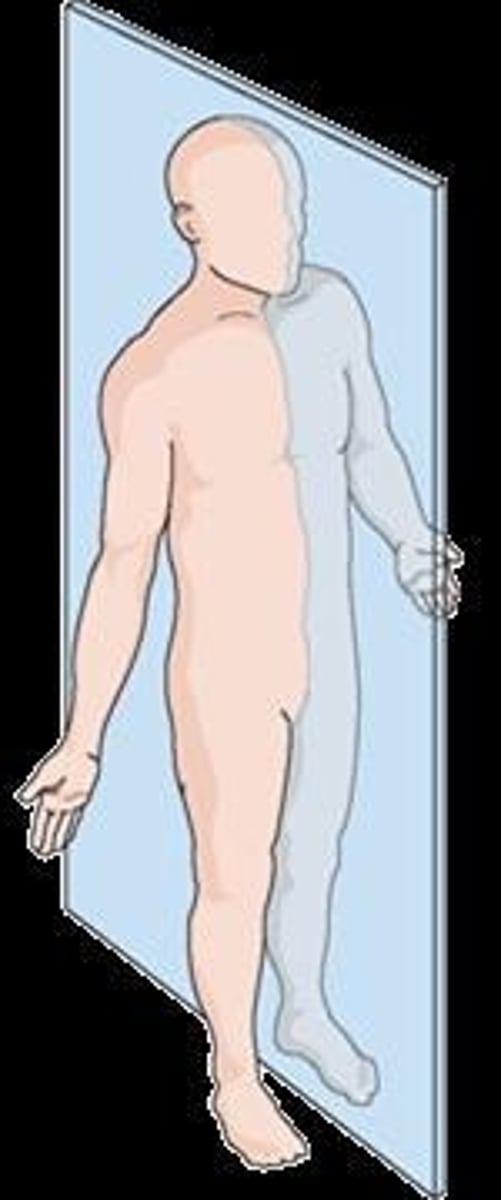
Midsagittal
the plane dividing the body into equal right and left halves
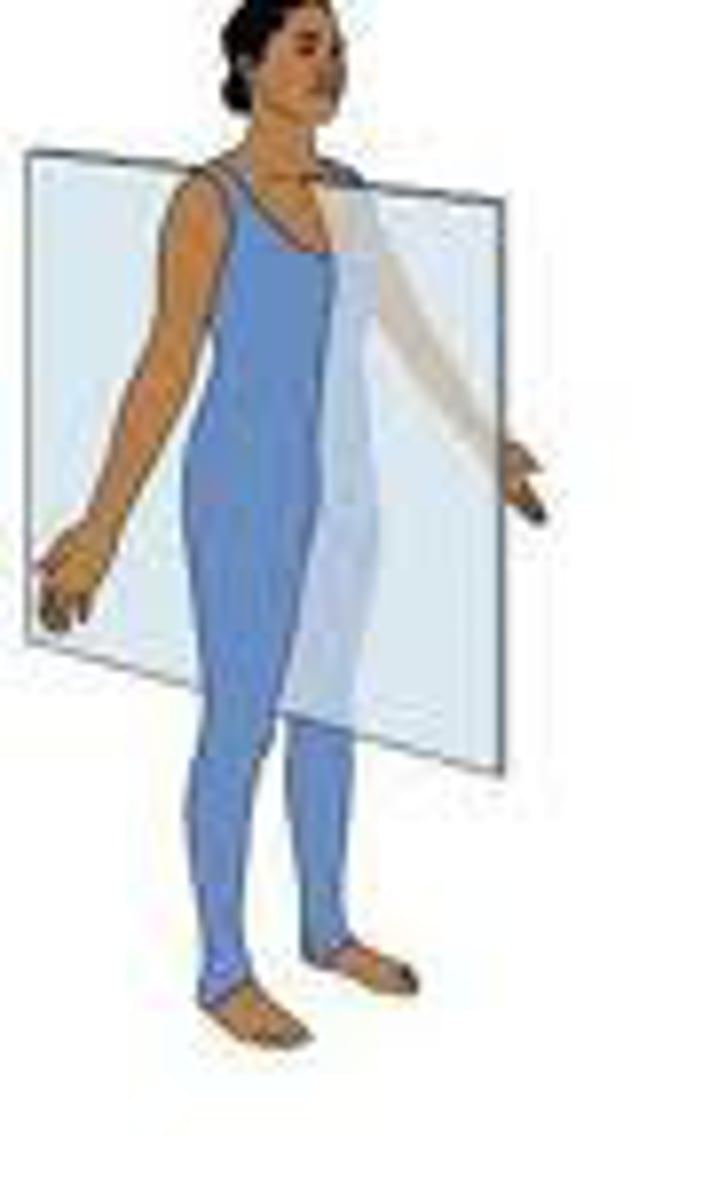
coronal
divides the body into slices from front to back
horizontal
divides into top and bottom
lateral
more to outside
medial
more middle, inside
Proximal
close
distal
far
gyrus (gyri)
convolution or the hill
sulcus (sucli)
fissure or the valley
Commissure
band of fiber together
gray matter
nerve cells that are not myelinated, not extra coating
white matter
nerve cells that are myelinated, they are wrapped
neuron
basic building block of the brain; transmits info
glial cell
cells that provide support, don't process info; it goes to damage areas to fill in ex: cheerleader
PNS (peripheral nervous system)
Ganglion and nerve; AMS: anamonic nervous system
ganglion
collection of neurons ex: ganglion cyst
ganglion of the dorsal root
The ______ _____ __________ is located in the intervertebral foramen.
nerve
bundle of axons ex: facial nerve
facial nerve is what number
VII
CNS (central nervous system)
Nucleus, tract and fascicules
nucleus
mass of neurons
caudate nucleus
mass of neurons in basal ganglia
tract
bundle of axons in the CNS
corticospinal tract
connections between brain and spine, motor traveling down
fascisulus
several parallel running tracts, bundle of axons traveling to same place
The CNS consists of the
brain and spinal cord
Brain consists of
cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem
Brainstem consists of
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
spinal cord
reflexing controlling center; connects brain to peripheral structures
Primary Brain Divisions
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
Prosencephalon (forebrain)
telencephalon and diencephalon
telencephalon
cerebral hemispheres, basal ganglion and limic lobe
Diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
metencephalon and myelencephalon
Metencephalon
pons and cerebellum
Myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
Cerebrum
two hemispheres: cerebral cortex and basal ganglia
cerebral cortex
gray matter: nerve cells are arranges in six layers
serves all symbolic functions-language, orientation, memory and attention
basal ganglia
masses of gray matter in depth of each hemisphere
important for regulating motor functions and muscle tone
Diencephalon: central core of the brain
thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
collection of subcortical nuclei, sensory relay station: coming in from the body to brain and then to thalamus
Hypothalamus
central structure for control of various metabolic activities
body temperature, water balance and sugar
Midbrain
links brain with brainstem, tiny and critical
- CN nuclei
Pons
regulates facial movement and sensation
-respiration
- CN nuclei
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
- CN Nuclei
cerebellum
dorsal-caudal to the brain
regulates skilled movement
contributes to maintenance of equilibrium and coordination of motor activity
attached to but not part of the brainstem