Lecture 2.4 - Metabolism and Enzymes
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary related to metabolism and enzymes as discussed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions performed by a cell or organism.
Anabolic pathways
Metabolic pathways that synthesize more complex compounds from simpler ones.
Catabolic pathways
Metabolic pathways that break down complex molecules into simpler ones.
Activation energy
The energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Exergonic reactions
Reactions that release energy, usually associated with catabolic processes.
Endergonic reactions
Reactions that require energy input, usually associated with anabolic processes.
Gibbs free energy (G)
The portion of energy stored in a system that can perform work, used to predict reaction spontaneity.
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions without being consumed.
Substrate
The initial reactant that an enzyme acts upon.
Co-factor
An inorganic molecule that assists with the chemical transformation of substrates → products
Co-enzyme
A small organic molecule that assists enzymes in chemical transformations.
Feedback inhibition
A regulatory mechanism where the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step.
Induced fit
The alteration of the active site shape of an enzyme to better fit the substrate.
Chemical chaos
The disorder that would occur if all metabolic pathways were active simultaneously.
Optimal temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme operates most efficiently.
Spontaneous reaction
A reaction that occurs naturally without the input of additional energy.
Hydrolysis of ATP
The reaction where ATP is broken down to ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy.
Individual reactions are…
Catalysed by specific enzymes
Connected into metabolic pathways, where the products of one pathway become the substrates for others
Two types of metabolic pathways
Anabolic and catabolic
Kinetic energy
Energy associated with the relative movement of objects
Thermal energy is…
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of atoms or molecules
Potential energy
Energy that an object possesses because of its location or structure
Chemical energy is…
The potential energy available for release in a chemical reaction
Gibbs free energy (G)
The portion of energy stored in a system that can perform work
The change in free energy ΔG can be measured for any reaction can be used to predict…
If a reaction will occur spontaneously or if it requires an input of energy to proceed
What goes a negative ΔG mean?
The reaction will be spontaneous
Catabolic reactions
Release energy
Exergonic
Spontaneous
Gproduct < Gsubstrate so ΔG<0
Anabolic reaction
Require energy
Endergonic
Non-spontaneous
Gproduct > Gsubstrate so ΔG>0
What does ΔG mean?
Change in system energy
The process of cellular respiration, which converts simple sugars such as glucose into CO2 and water, is an example of:
A catabolic pathway
Cells perform three kinds of work…
Chemical
Transport
Mechanical
Chemical work
Endergonic reactions
Transport work
Pumping across membranes against the concentration gradient
Mechanical work
Contraction of muscle cells, movement of chromosomes during cell division, beating of cilia
Energy for this work is paid by…
Harvesting the energy stored in adenosine triphosphate
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
ATP is composed of…
Nucleotide base adenine
Ribose sugar
3 linked phosphate groups
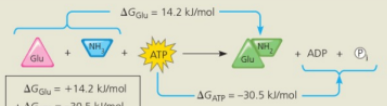
Glutamic acid conversion to glutamine
Glutamine synthesis from glutamic acid by itself is endergonic (ΔG is positive) so it is not spontaneous
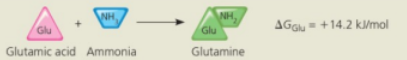
Glutamic acid conversion to glutamine
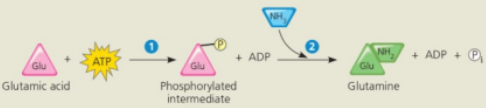
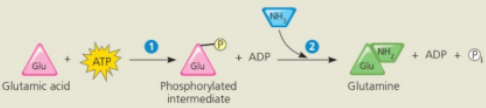
Conversion reaction coupled with ATP hydrolysis
In the cell glutamine synthesis occurs in two steps, coupled by a phosphorylated intermediate
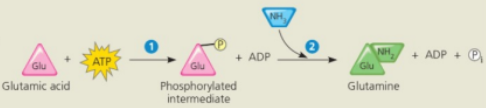
Conversion reaction coupled with ATP
Name 1
ATP phosphorylates glutamic acid, making it less stable, with more free energy
Name 2
Ammonia displaces the phosphate group, forming glutamine
Free-energy change for coupled reaction
ΔG for the glutamic acid conversion to glutamine (+14.2 kJ/mol) plus ΔG for ATP hydrolysis (-30.5 kJ/mol) gives the free-energy change for the overall reaction (-16.3 kJ/mol)
Free-energy change for coupled reaction
How to solve free-energy change for coupled reaction
ΔGglu + ΔG ATP = Net ΔG
Name
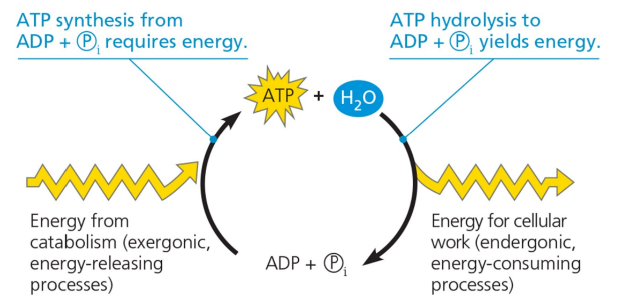
The ATP cycle
Where does the energy come from?
Energy comes from the breakdown of fuel molecules, primarily glucose, during cellular respiration, which is then stored in ATP.
Which of the following statements about ATP is correct?
1. The hydrolysis of ATP is an endergonic process
2. The hydrolysis of ATP can supply energy needed for catabolic pathways
3. Almost all the free energy released in the hydrolysis of ATP is released as heat
4. The cycling between ATP and ADP + Pi provides an energy coupling between catabolic and anabolic pathways
The cycling between ATP and ADP + Pi provides an energy coupling between catabolic and anabolic pathways
Enzymes are…
Proteins and catalysts
Exception of an enzyme being a protein
Some RNA-based (ribozyme)
What does enzymes do?
Speed up chemical reactions
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction
What do enzymes do?
Facilitate transformation of initial substances into different molecules
Enzyme names indicate…
Their function
Enzyme - Lipase
Breaks down lipids
Enzymes - Protease
Breaks down proteins
Enzymes - Synthase
Build larger molecules
Enzymes - Isomerase
Rearranges a molecule into its isomer
Types of enzymes
Lipase, protease, synthase, isomerase
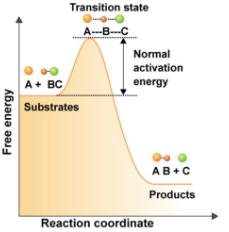
Chemical reaction order
Substrate → transition state → product(s)
Transition state is…
Highest energy state
Activation energy
Difference between energy levels of substrate and transition state
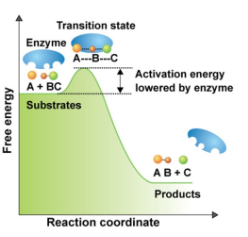
How does enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
By lowering energy barriers
Name
Uncatalyzed Reaction
Name
Enzyme-catalyzed Reaction
Why is it important to living systems that chemical reactions show have activation energies?
Activation energies prevent spontaneous reactions, allowing control over metabolic pathways and ensuring that reactions occur under specific physiological conditions.
How to pay the activation energy
by using enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy barrier.
How to enzymes work?
Enzymes work by binding substrates at their active sites, facilitating the formation of products while lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction.
Enzymatic reaction does not…
Permanently change the enzyme’s chemistry or structure
Enzymatic reactions changes…
Its shape during the reaction, but reverts to original conformation once the reaction is complete
Chemical chaos would occur if…
All the metabolic pathways of a cell were operating all the time!
Cells regulate enzymes by…
Turning them on and off
Enzymes are described as catalysts, which means that they…
Increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction