Wk One - Cardiac A&P, The Clinical Approach
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Year 2 Clinical Approach
Standard Pres > Gloves, Goggles, etc..
Rapid assessment triangle - WOB, appearance and circulation to skin. (> SICK/NOT
DRSABCDE (+AEIOUTIPS)
METHANE if major, SITREP if not
REST, REASSURANCE AND RAPPORT
Brief history
POETS + BGL
AMPLE
DOLORS
VSS
Secondary survey
Treatment
Transport & Refferal options
HANDOVER - IMISTAMBO
AEIOUTIPS

What is the pathway blood travels in through the heart?
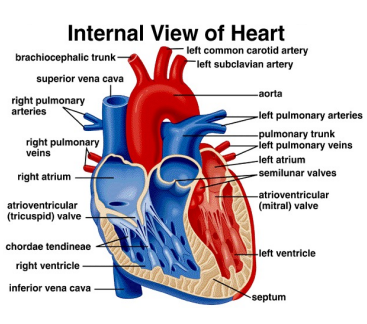
Deoxygenated blood enters through the SVC or IVC or coronary sinus into the right atrium, through the right atrioventricular valves to the ventricle, where it is then pushed up through the semilunar valves to the pulmonary arteries & trunk, where it will be oxygenated at the lungs. Oxygenated blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins, and into the left atrium. This is pumped up through the mitral valve (bicuspid), to the left ventricle, and then through the semilunar valve to the aorta & systemic arteries. Whatever doesn’t make it out of the atrium, funnels back through the coronary arteries to provide O2 to the heart muscle.
What is the wall between the two ventricles called?
The muscular interventricular septum
Heart Anatomy
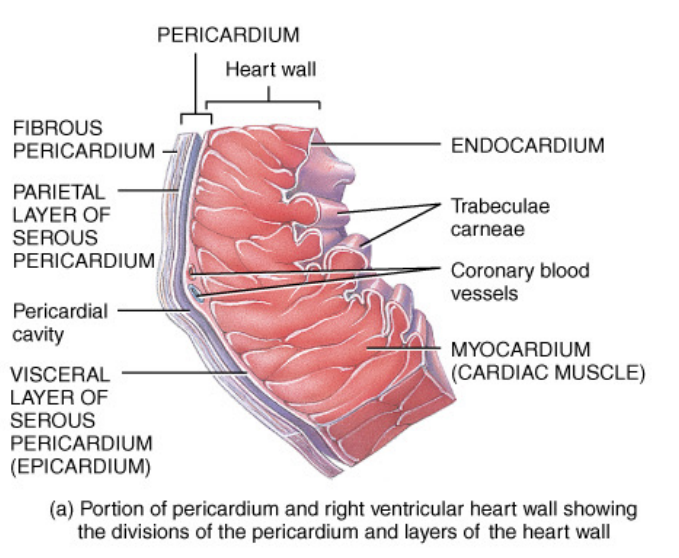
What is the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
Dense connective tissue rings that surround the valves of the heart and merge with the interventricular septum. It forms the point of insertion for cardiac muscle bundles and is where the valves attach to prevent stretching. Electrical insulator that prevents spread of action from the atrtai to the ventricles.
Bicuspid valve (/mitral/left atroventricular)
an aortic valve that contains only two cusps (or flaps) instead of three, controlled by the chordae tendinae & papilliary muscles. Prevents backflow into the atria.
Semilunar valve
Aortic & Pulmonic, consisting of three cusps or flaps which prevent the flow of blood back into the heart
%’s of blood in vessels
60% systemic veins and venules (blood reservoirs
Systemic arteries and arterioles 15%
Pulmonary vessels 12%
Heart 8%
Systemic capilliaries 5%
What does the circumflex artery supply blood to?
Posterolateral LV, sometimes inferior LV, may also supply posterior left bundle and A-V node.
What does the LAD artery supply blood to?
Anterior and anterolateral LV, 2/3 septum, medial anterior RV, lower 1/3 posterior RV
What does the RCA artery supply blood to?
Anterior RV, upper ½ (basal) posterior wall, posterior 1/3 septum, posterior left bundle, inferior LV, usually AV and proximal HIS bundle via AV nodal branch.
Where does the left coronary circulation originate from, and what pathway does this blood take?
Aortic root sinus - goes through left main (LM) and then the circumflex (Cx) and then the left anterior descending (LAD) and then diagnoal & septal (D & S)
Left main artery occulsion ECG sign
ST elevation in the AVR lead
Where does the right coronary circulation originate from, and what pathway does this blood take?
Aortic root sinus - through the right coronary artery (RCA) and then the Marginal (Mx) and then the Posterior Interventricular Artery (PIV) and then the SA (RCA 55 Cx 45) & AV nodes (Mx).
AV Node
Controls conduction, allows for ventricular filling "gatekeeper" between the atria and ventricles, ensuring coordinated heartbeats by introducing a slight delay in electrical impulses
SA node
the heart's natural pacemaker, a specialized cluster of cells in the upper wall of the right atrium that initiates electrical impulses, setting the heart's rhythm and rate (60-100)
Purkinje Fibers
electrical conduction and propagation of impulse to the ventricular muscle
Bundle of HIS
a specialized pathway of muscle fibers that transmits electrical signals from the atrioventricular node (AV node) to the ventricles, facilitating coordinated heart contractions
Time spent on heart contractions
Atrial systole - 0.1s, AV valve closes, Ventricular systole - 0.3s, all valves close, complete diastole - 0.4s
3 layers of a vein
Tunica intima/interna Endothelium (simple squamous) Elastic tissue In contact with the blood
Tunica media (thickest layer) Smooth muscle (innervated by SNS) Sheets of elastin
Tunica adventitia/externa Elastic and collagen fibres
Pressures in different vessels
Aorta = 100mmHg
Arteries = 100-40 mmHg
Arterioles = 40-25 mmHg
Capillaries = 25-12mmHg
Venules = 12-8mmHg
Veins = 10-5 mmHg
Vena cave = 2mmHg
R. Atrium = 0mmHg
Which ventricle is thicker?
Left
AV node
Acts as a gatekeeper between the atria & ventricles, and conducts between this + and backup pacemaker for the heart. (40-60)
Stupid acronyms for lymph flow
BHP - Blood hydrostatic pressure
IFHP - Interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
BCOP - blood colloid osmotic pressure
IFOP - interstitial fluid osmotic pressure
NFP - net filtration pressure
Where does excess interstitial fluid go?
To the cariovascular system and back into the blood plasma