CHEM 272 Exam 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Experiment 6: Intro to Titrations
two scenarios in which titrations are used
titrant is unknown (conc), analyte is know
titrant is known, analyte is unknow
what is it called when an analyte is known?
primary standard
using titration to calculate molarity
M: moles solute/L solution (volume delivered)
need to figure out what you don’t know from moles that you do know
2 strategies to monitor progress of titration:
pH monitoring with pH probe (potentiometric titration)
color change with pH indicator (endpoint titration)
what happens when there’s a 1:1 buffer
pH=pka
moles A- = moles HA
equivalence point
moles titrant=moles analyte
point of max slope on graph of volume of titrant v.s. pH
½ equivalence point
pH=pka
first derivative
total pH/ total volume
endpoint
where color change occurs
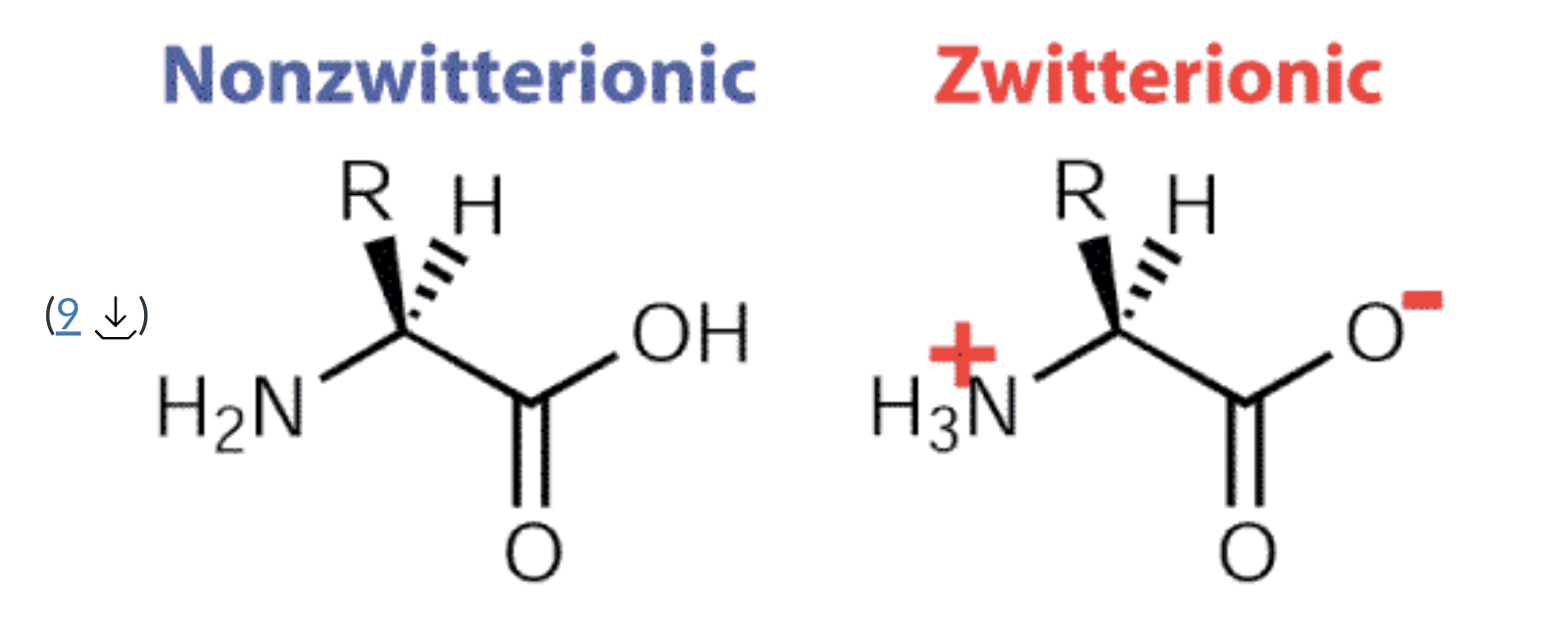
zwitterionic
has both a positive and negative charge that has a net neutral charge
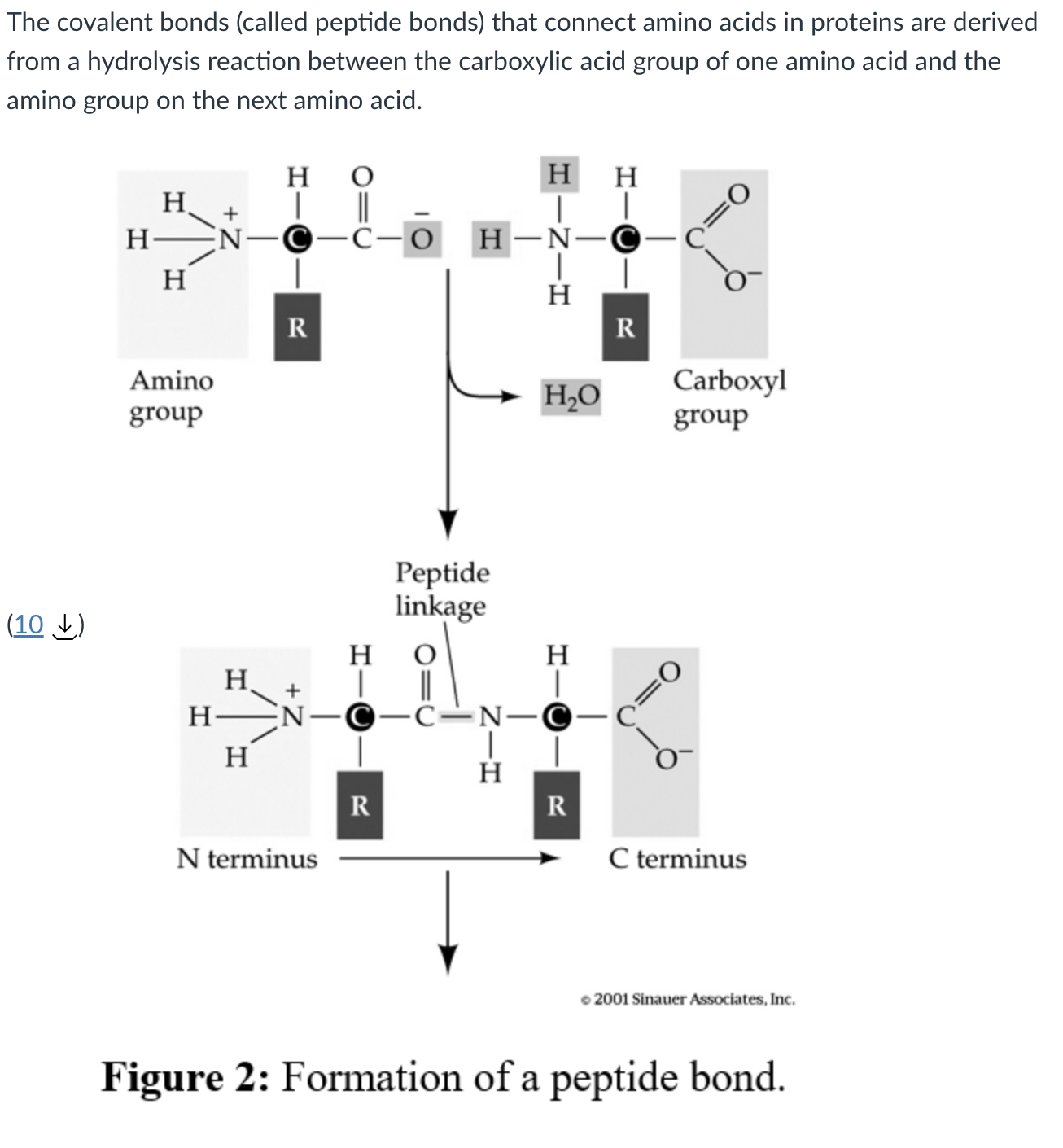
how are peptide bonds formed?
hydrolysis reaction between the carboxylic acid of one r group and the amino acid group of the other
pKas in an amino acid
carboxylic acids are 2
amino groups are 9
R groups vary
You will be analyzing a series of amino acid titration curves resulting from a new protein supplement. The goal is to determine whether the supplement is safe for those who are diagnosed with phenylketonuria. Which amino acid will you be looking for in your samples?
phenylalanine
Experiment 7
standard reduction potential
a reducing agent’s ability to donate electrons
signs of oxidation
gain bonds to oxygen
lose bonds to hydrogen
gain a double bond
lose electrons
signs of reduction
gain hydrogen
lose bonds to oxygen
gain electrons
lose double bonds
active ingredient versus excipients
active ingredient: therapeutic affect
excipients: inert (bulking, color, preservatives)
back titration
indirectly quantifying analyte
what color does I-3 produce?
blue black
what color does I- produce?
colorless
Which of the following species is the primary standard?
ascorbic acid
iodate
thiosulfate
iodate
Which of the following species is the titrant in the standardization titration?
Group of answer choices
ascorbic acid
iodate
thiosulfate
triiodide
thiosulfate
Which of the following species is the analyte in the ascorbic acid titration?
Group of answer choices
ascorbic acid
iodate
thiosulfate
triiodide
triiodide because it is a back titration
experiment 9
cell potential equation
Ecell=Ecathode-Eanode
If E is +:
If E is -:
spontaneous, nonspontaneous
voltaic (galvanic) cell
spontaneous, generates voltage
electrolytic cell
nonspontaneous, needs voltage

experiment 10: thermodynamics
total system + total surrounding= 0
system: reactions
surroundings: everything else (universe)
1st law of thermodynamics
energy of universe is constant
2nd law of thermodynamics
dispersal of energy (entropy) in universe is always increasing
if delta G is negative
if delta G is positive
reactant have more energy than products, rxn is spontaneous, exergonic
reactants have less energy than products, rxn is nonspontaneous (endergonic), energy required
K>Q
rxn shifts towards products
K<Q
rxn shifts towards reactants
K and Q
product/reactant
Reaction Coupling
nonspontaneous rxn paired with spontaneous rxn
chemical processes
redox processes→ electron flow → generate electrons
biochemical standard state
temperature of 298K
initial pressure of gaseous species is 1atm
initial concentration of aqueous species is 1M EXCEPT for:
water (55.5M)
H+ (10-7M)