Neuro 1.2 - meninges, ventricles, cisterns
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
dura, arachnoid, and pia
what are the three layers of meninges
leptomeninges
together, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater are called ____________
fibroblasts (different functions for each layer though)
Generally the layers of the meninges are made up of __________
dura
the _________ meningeal layer is close to the skull
arachnoid
the _________ meningeal layer is related to CSF
pia
the _________ meningeal layer is conformed to brain and spinal cord
S2
the subarachnoid space continues down the spine until about ______ level
superior sagittal sinus
the two layers of dura split and form a big sinus called _______ _______ ________
periosteal; meningeal
the dura mater has two layers, the _________ layer is the outer layer and the ________ layer is the inner layer
foramen magnum
the outer periosteal layer of the dura mater lines the cranium but stops at the ___________ ___________
connective
the two layers of dura mater are made of collagenous __________ tissue
sinus
__________ is a channel carrying venous blood
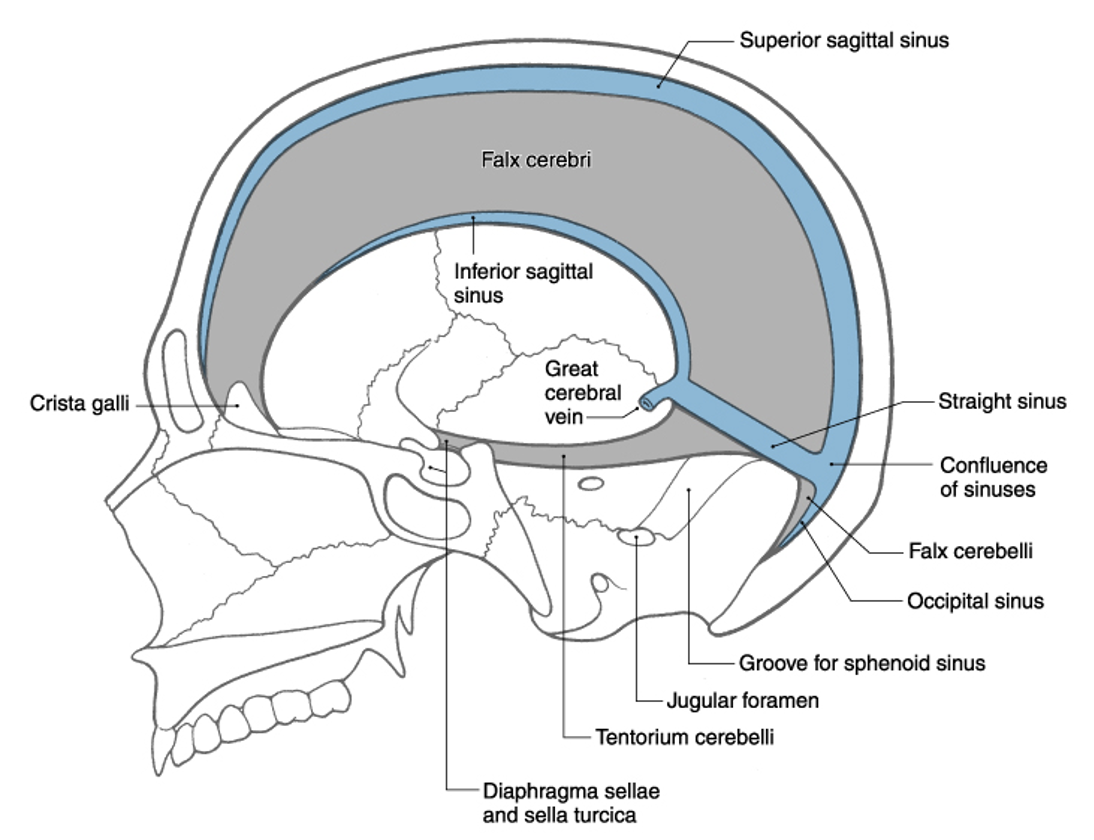
longitudinal cerebral; crista galli; internal occipital protuberance
the falx cerebri is suspended in the __________ _________ fissure and rostrally attached to the ________ ________ and caudally attached ot the __________ __________ _________
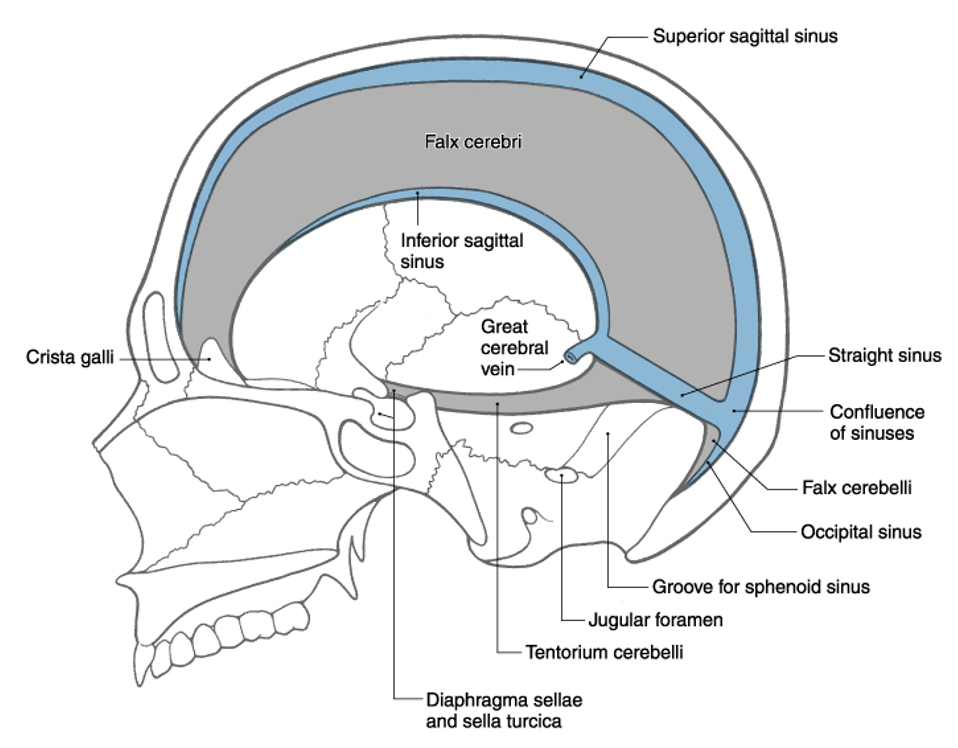
F
T/F: the great vertebral vein is considered a sinus
endothelial
the dural sinuses are lined with ____________ cells
falx cerebri
the dural sinuses border the _______ _______
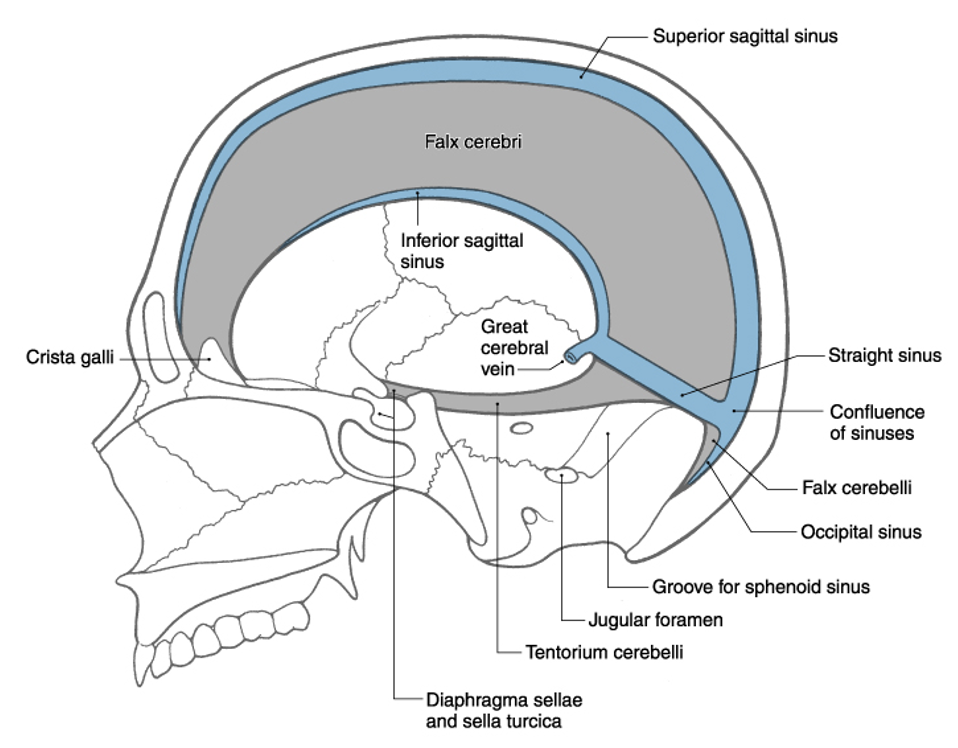
superior sagittal sinus
inferior sagittal sinus
confluence of sinuses
straight sinus
what are the 4 dural sinuses
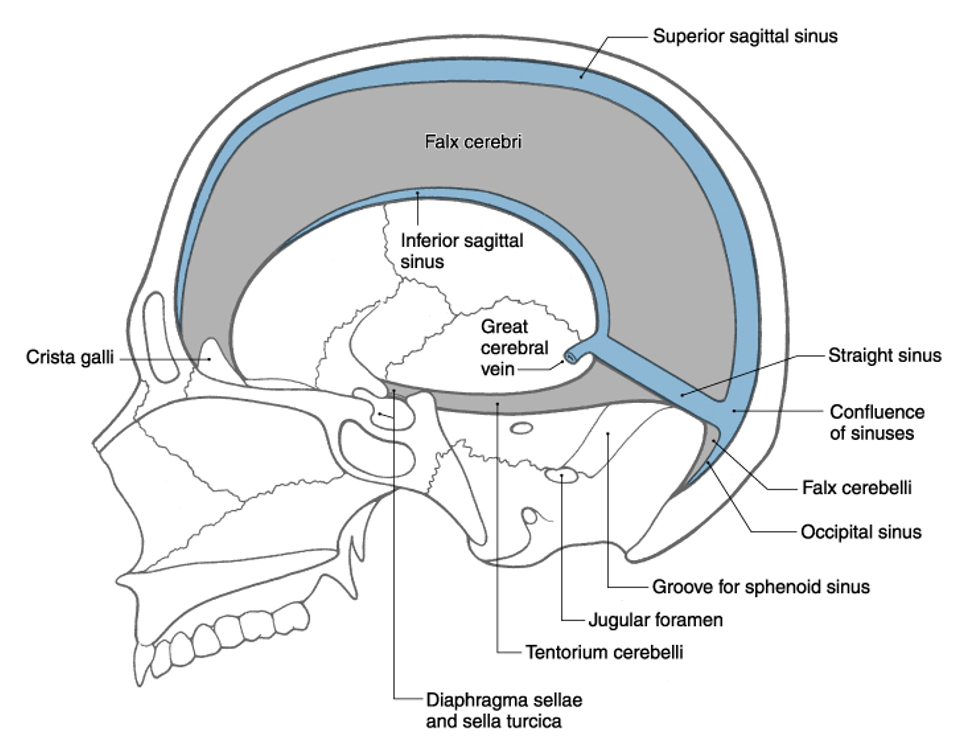
superior (or dorsal)
where is the falx relative to the corpus callosum?
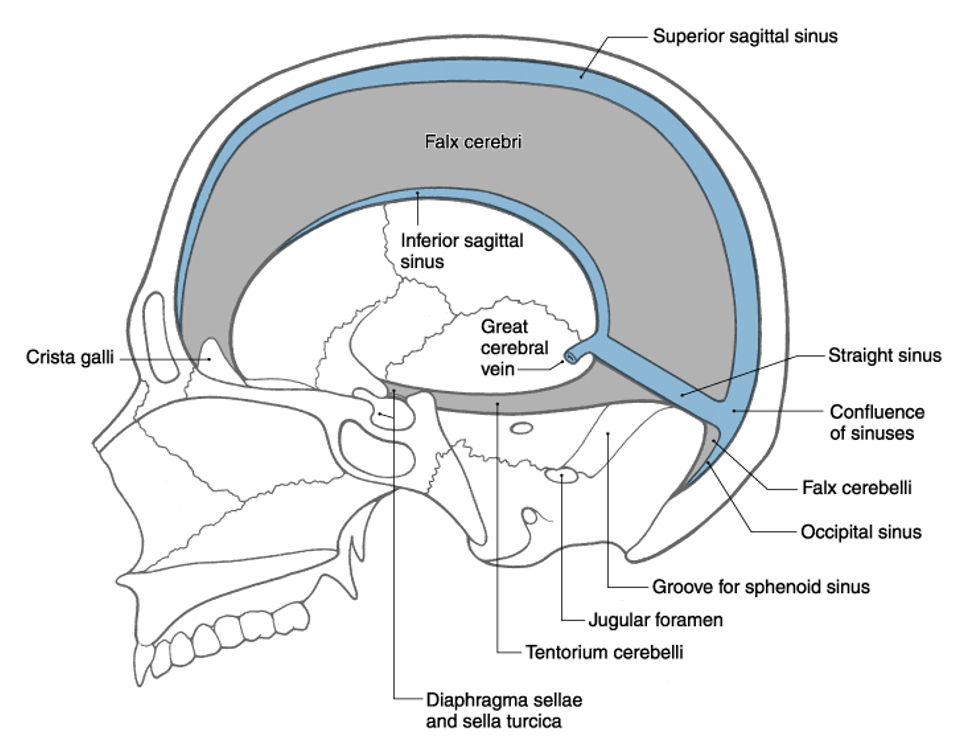
medial
where is the fax relative to the cerebral hemispheres
turkish saddle/sella turcica
where is the pituitary gland located
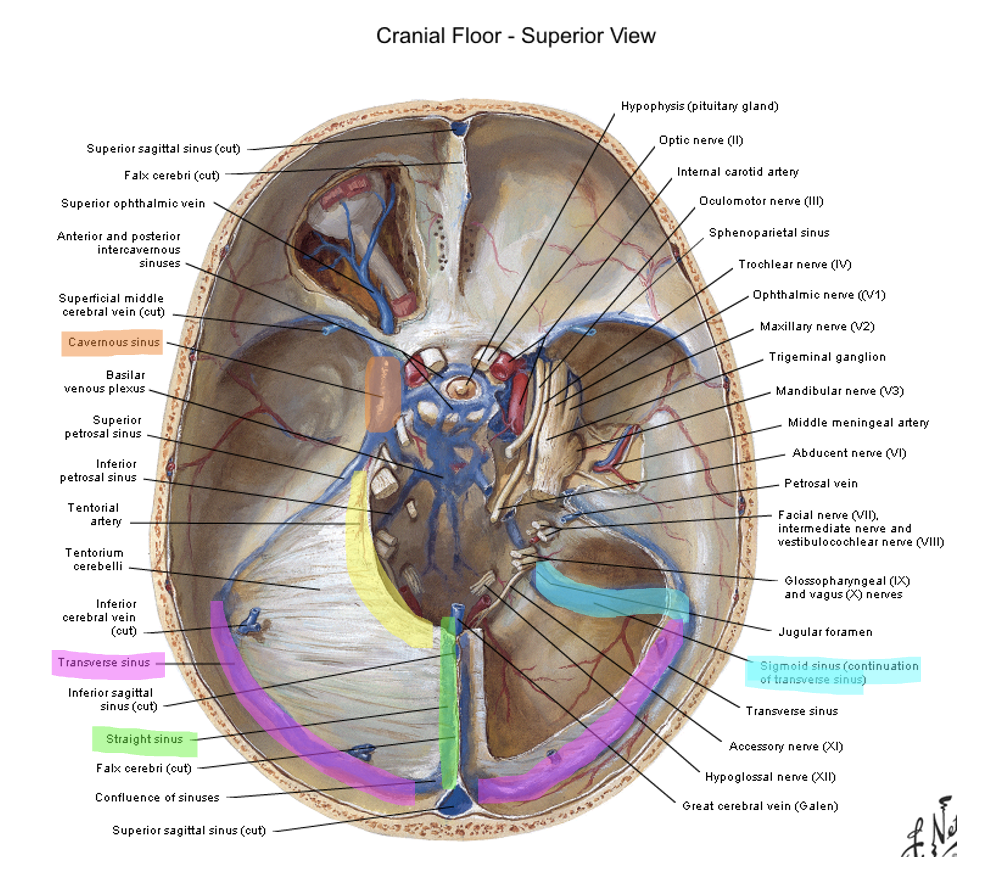
straight sinus (also where the great cerebral vein is draining) → confluence of sinuses (merges with superior sagittal sinus) → transverse sinus (also where superior petrosal sinuses drains from the cavernous sinus) → sigmoid sinus → internal jugular vein
what is the flow starting from the inferior sagittal sinus
pia
the _______ meningeal layer are on the gyri of the brain
vessels (can cause bleed)
a lot of ________ are located in the subarachnoid space
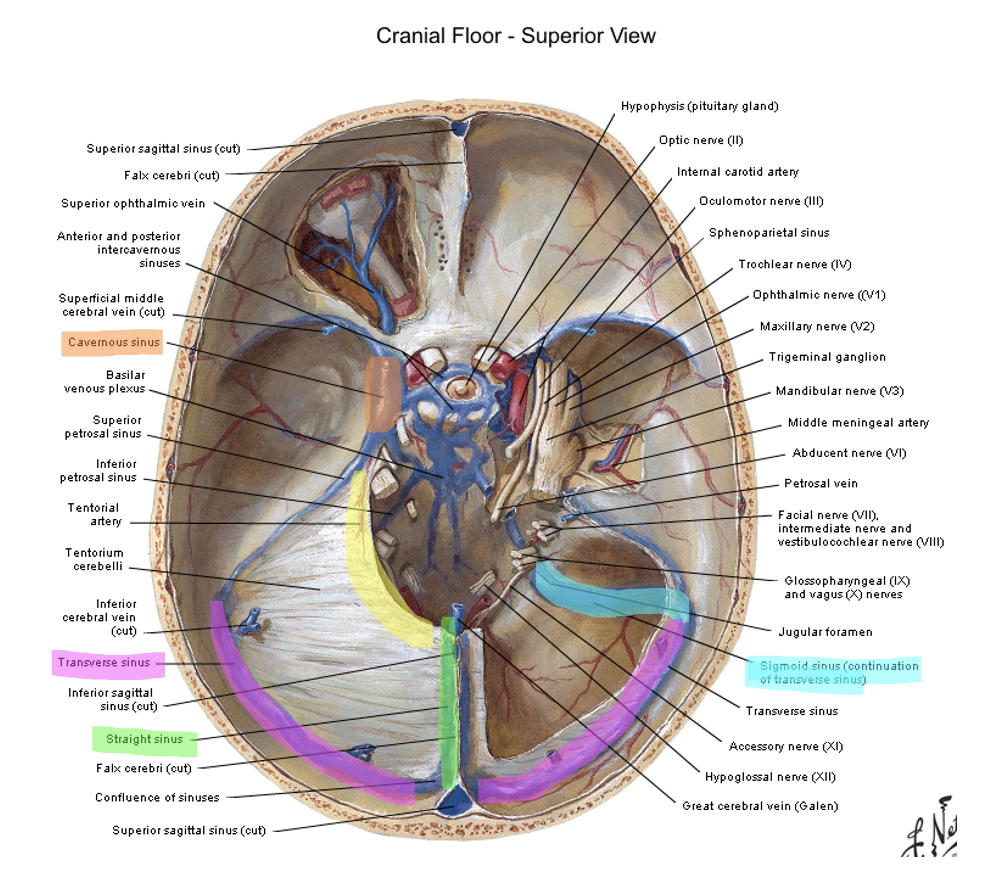
cavernous
the _________ sinus is on either side of the sella turcica/turkish saddle/pituitary gland
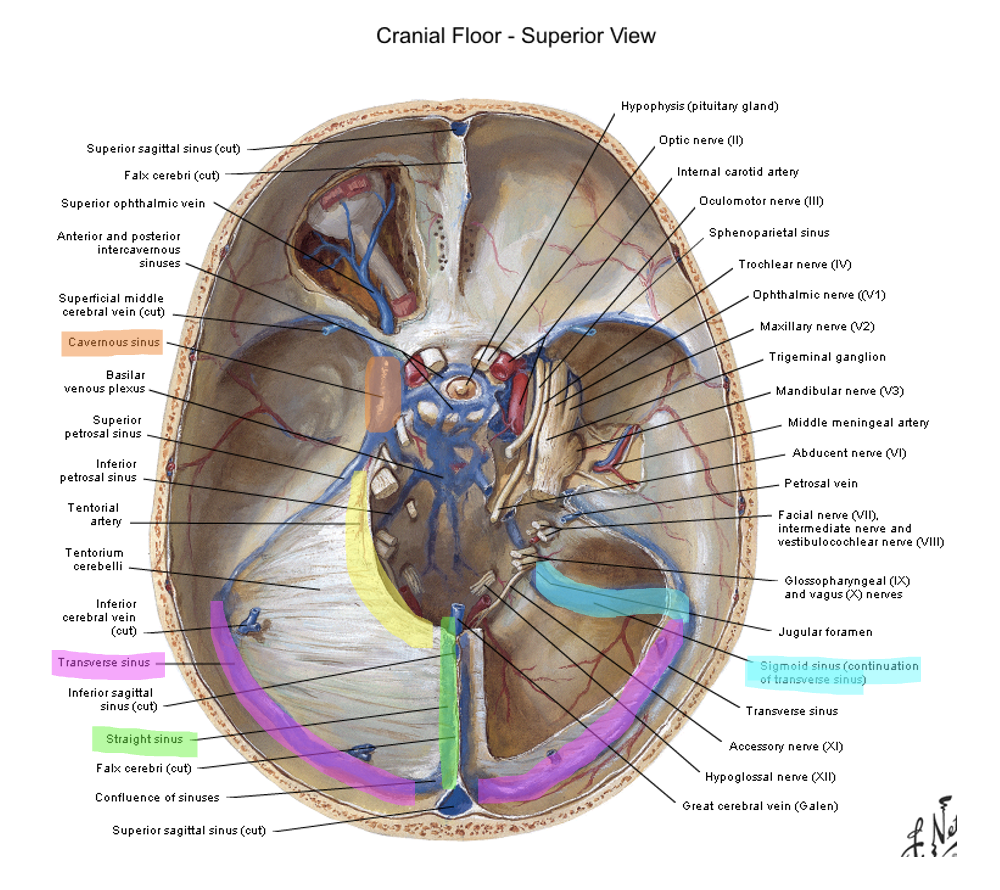
occipital; petrosal ridge (temporal bone); posterior clinoid process
the tentorium cerebelli is attached caudally to the __________ bone, laterally to the _______ _______ and anteriorly to the _______ ________ _______
cerebellum; occipital
the tentorium cerebelli is on top of the _________ and under the __________ lobe
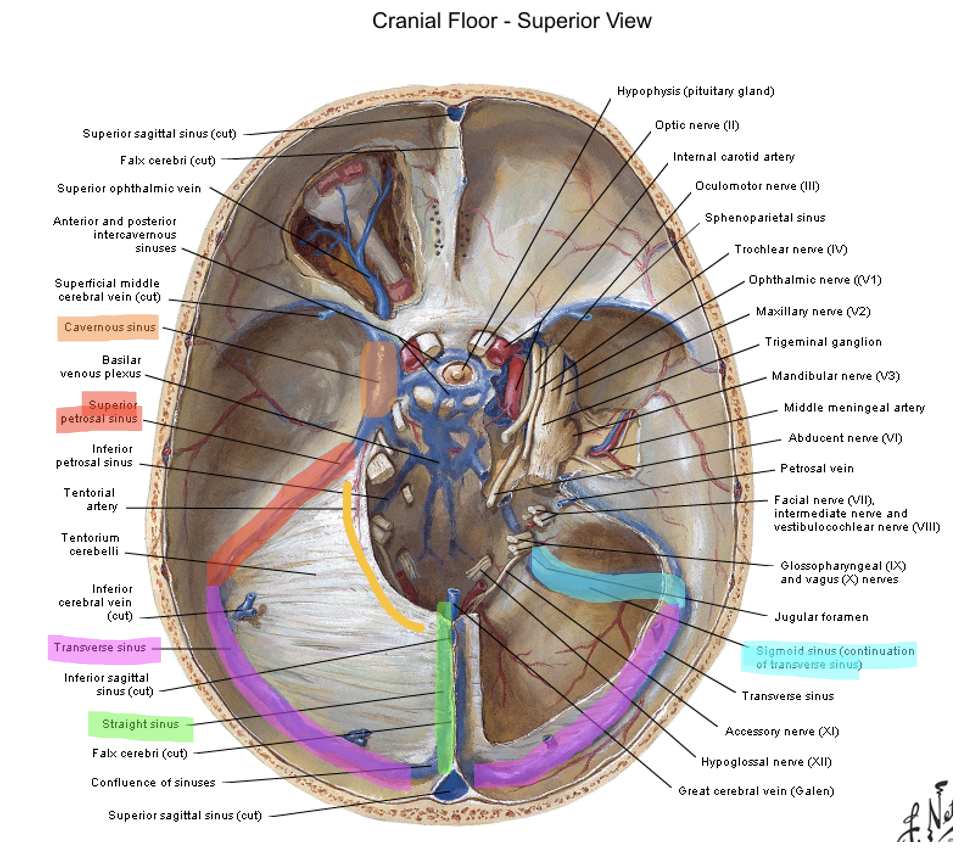
superior petrosal ridge → transverse sinus → sigmoid sinus → internal jugular vein
how does content from the cavernous sinus get to the internal jugular vein
brainstem
the tentorial notch creates space for the ___________
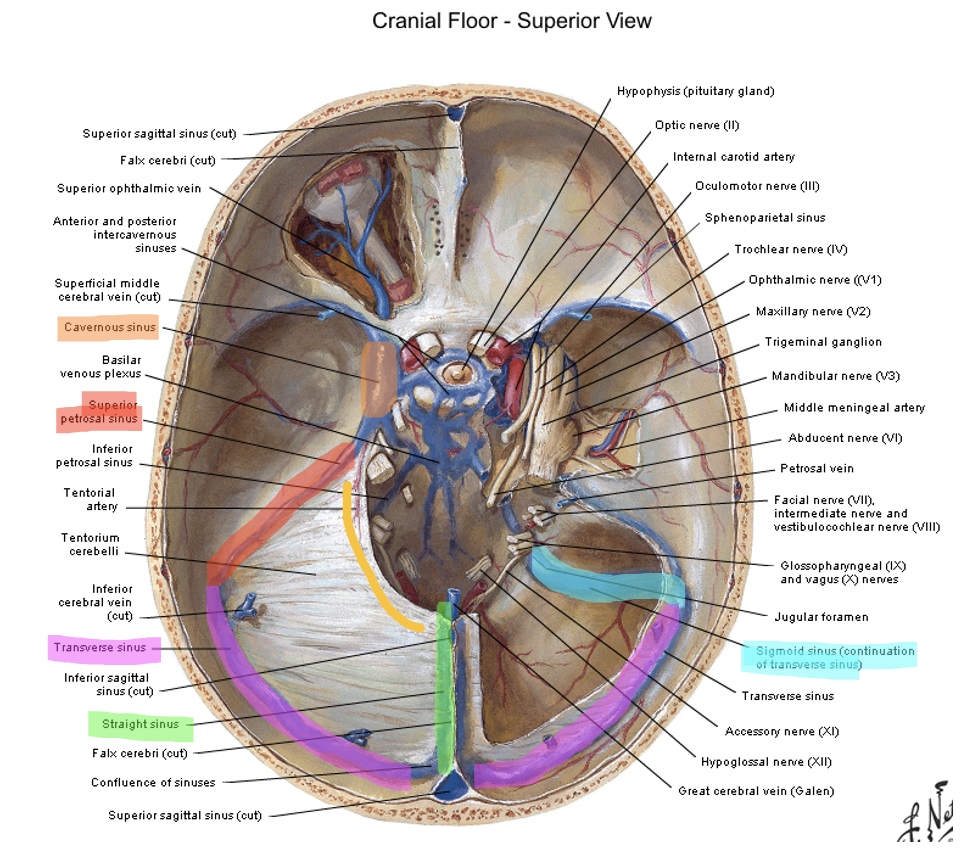
lateral and caudal
where is the tentorium cerebelli located in relation to the tentorial notch
lobes of the cerebrum
diencephalon
what are the 2 neural structures located in the supratentorial compartment
cerebrum
medulla
pons
what are the 3 neural structures located in the infratentorial compartment
sella turcica (over the pituitary gland); posterior clinoid processes (what else attaches here? the tentorium cerebelli)
the diaphragma sellae passes over the _______ ______ going from anterior to posterior and attaches to the _______ _______ ________ posteriorly
cavernous sinuses
the _____________ ________ forms the walls of the diaphragma sellae as it passes over the sella turcica
internal carotid artery
CN III (oculomotor)
CN IV (trochlear)
CN Vi (ophthalmic division of trigeminal n.)
CN Vii (maxillary division of trigeminal n.)
CN VI (abducens)
what runs through the cavernous sinus
middle meningeal
___________ is the primary artery to the dura
maxillary → external artery
the middle meningeal artery is a branch off of the ___________ artery which is a branch off of the __________ artery
trigeminal CN; CN 2 and 3
the ________________ is the main nerve supply of the dura in the anterior and middle fossae
the _______________ is the main nerve supply for the posterior cranial fossa
middle meningeal
extra-dural bleed is usually caused by rupture to the _______________ artery
arachnoid villi
the __________ __________ allow CSF to go from the subarachnoid space to the venous sinus by protruding through the dura mater and into the sinus
granulations
the arachnoid villi are also called
subarachnoid space
valves of the arachnoid villi will open when there is more pressure in the subarachnoid space or superior sagitaal sinus
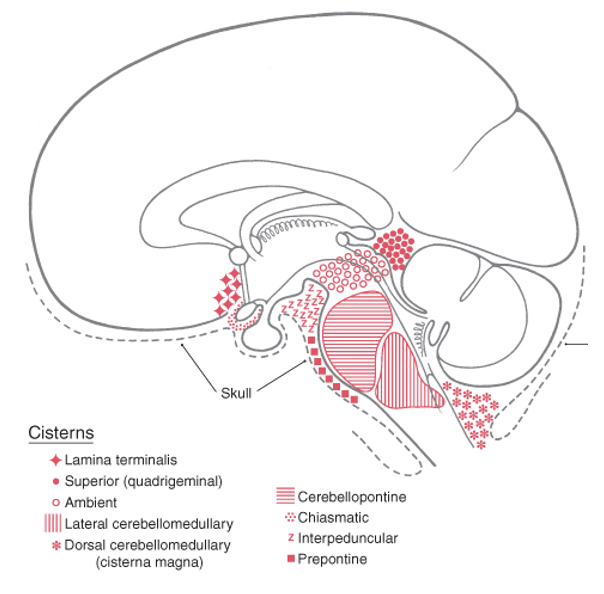
cisterns
_________ are bigger areas of subarachnoid space
cisterns
___________ occur where the brain moves away from the skull due to the shape of neural structures
CSF
arteries
veins
cranial nerves (sometimes)
what are the 4 things that cisterns usually contain
L2
at what level does the spinal cord end
T (it is not because it is part of the ventricular system)
T/F: the third ventricle is not a cistern
trochlear (CN IV)
What cranial nerve emerges dorsally and travels through the Ambient cistern?
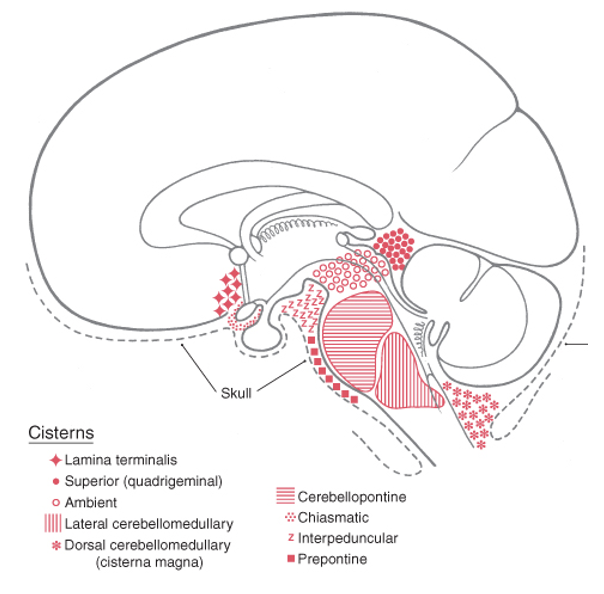
superior and inferior colliculi
The Superior (Quadrigeminal) cistern is anterior to the tentorium cerebelli and posterior to what?
cerebral peduncles
Interpeduncular cistern (fossa) is found between what midbrain structures?
oculomotor
What other cranial nerve emerges from the midbrain?
pons
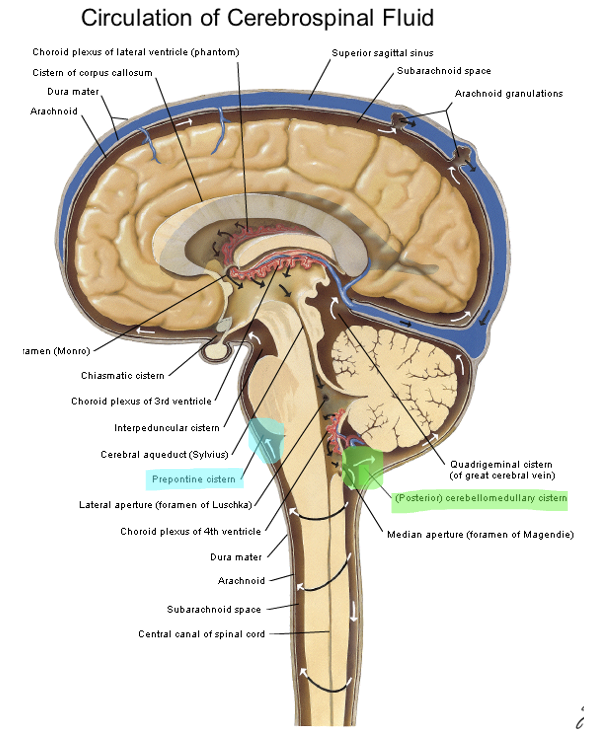
Prepontine cistern is anterior to what part of the brainstem?
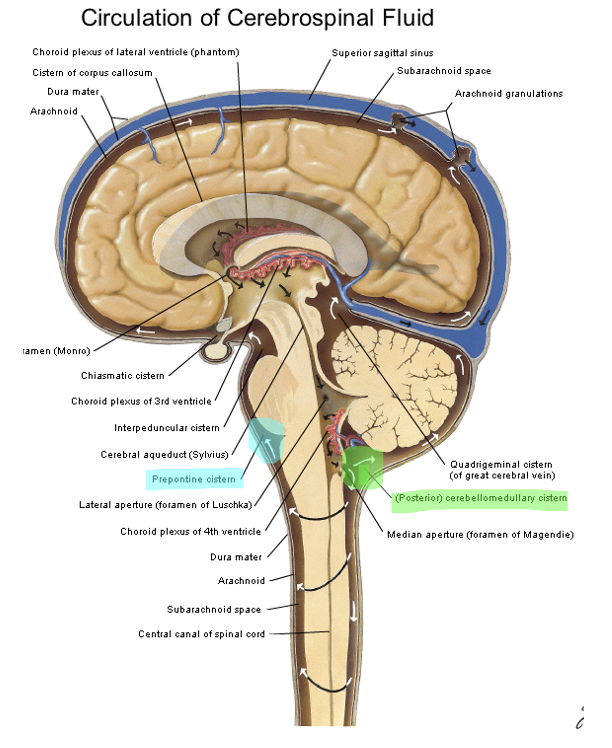
cerebellum
medulla
foramen magnum
largest cistern
the dorsal cerebellomedullary cistern (cisterna magna) is bordered by what 4 structures
cauda equina; filum terminale internus; filum terminale externus
contents in the lumbar cistern
_______ _______: spinal nerves
_______ _______ ______: anchoring the conus medullaris (end of spinal cord) to the end of the dural sac
_______ _______ ______: anchors the dural sac to the coccyx (coccygeal ligament)
pia (anchors the middle of the conus medullaris to the end of dural sac)
filum terminale internus is made of _______ mater
dural
filum terminale externus is made of _______ mater
Denticulate ligaments
_________ __________ are thickened pia running longitudinally along SC attaching to arachnoid-lined dural sac
pia
__________ mater hugs the gyri and follows every sulcus of brain and SC
blood vessels; endothelial
pia mater surrounds the _______ ________ in the subarachnoid space and then fuses with ________ cells
epidural
epidural or spinal anesthesia:
can be done at any level of the spine
spinal anesthesia (L2 is where the spinal cord stops)
epidural or spinal anesthesia:
can only be done below low
spinal anesthesia
epidural or spinal anesthesia:
lasts for one to two hours
epidural
epidural or spinal anesthesia:
catheter so it can continue as needed (drip method)
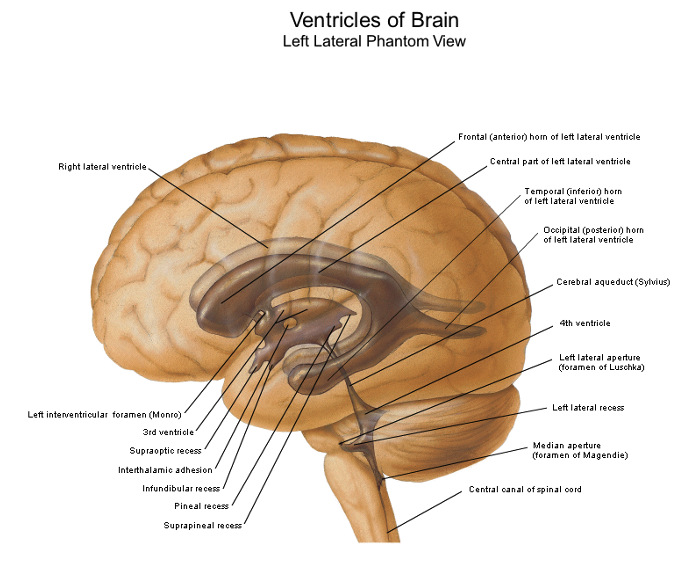
lateral
the ___________ ventricles are in the cerebral hemispheres
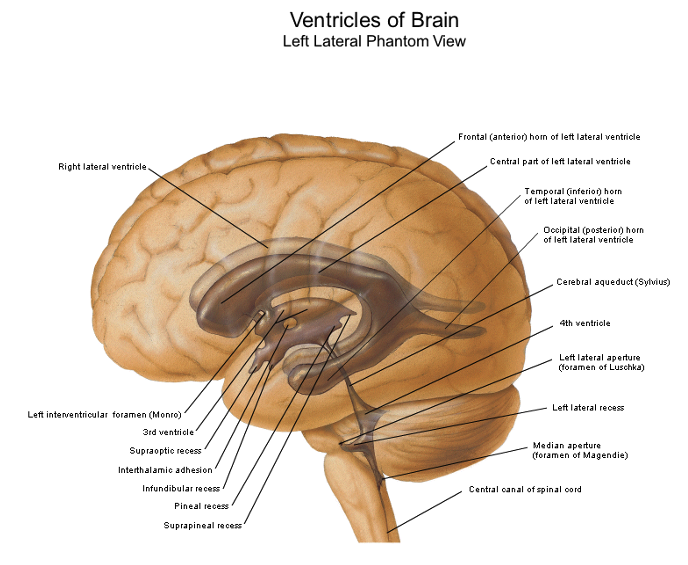
third
the _________ ventricle is located midline, vertical, diencephalon
fourth
the ___________ ventricle is pyramid shaped, pons and medulla, cerebellum
3 and 4
the cerebral aqueduct is between what two ventricles
frontal horn
body
atrium
posterior (occipital) horn
inferior (temporal) horn
temporal horn
what are the five parts of the lateral ventricle?
which one is closest to the hippocampus?
interventricular foramen
CSF from the lateral ventricle enters the third ventricle through the __________ __________
cerebral aqueduct
the third ventricle communicates caudally with the ________ _________
supraoptic
infundibular
suprapineal
lamina terminalis
anterior and posterior commissures
what are the five recesses (small outpocketings) in the 3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
the ___________ ___________ is an extension of the 3rd ventricle through the midbrain to the 4th ventricle
T (the space is very narrow)
T/F: there is no choroid plexus in the cerebral aqueduct
gray; periaqueductal
the cerebral aqueduct is surrounded by a sleeve of ________ mater, which is also called _________
fourth
the _________ ventricle is the apex of the cerebellum
central canal
foramen of magendie
rhomboid
the fourth ventricles pathways:
caudally tapers into the _______ _________ of the spinal cord
lateral recesses empty into cerebellopontine angle thru the _________ _________ which is the roof
the flood is the __________ fossa
foramen of luschka and magendie; fourth
what are the only two openings between the ventricles of the brain and the subarachnoid space? what ventricle are the found in?
luschka
in the fourth ventricle, the foramen of ____________ in the fourth ventricle leads to the subarachnoid space
magendie
in the fourth ventricle, the foramen of _________ is a central foramen and leads to the subarachnoid cisterna magna
tight; endothelial
the blood brain barrier is made of _________ junctions and __________ cells
ependymal; simple cuboidal epithelium
the ventricles are lined with ____________ cells, also known as _________ ________ _________
choroid plexus; lateral
CSF is produced by the _________ ________ mostly in the _________ ventricle
fenestrated; connective; cuboidal
structure of the choroid plexus:
__________ capillaries
_________ tissue core
__________ epithelium with microvilli
blood capillary → connective tissue → cuboidal epithelium (gets filtered, tight junctions) → ventricular space → subarachnoid space
what is the flow of things in the choroid plexus starting from the blood capillary
450-750; 400
the choroid plexus filters about ______-______ mL of CSF/day and resorbs about _____ mL
normal = 15-45
abnormal = 100
normal and abnormal values of protein in CSF
protein
abnormal levels of ______ is the CSF could indicate tumor, bleed, infection
< 10; 200-300; 1,000-20,000
normal values of neutrophils in CSF
abnormal values of _____-____ could indicate syphilitic meningitis
abnormal values of ______-______ could indicate bacterial meningitis
60; < 40
normal and abnormal values of glucose in CSF
glucose
abnormal values of ___________ could indicate CNS infection
CSF
________ reduces momentum and acceleration of the brain
CSF
____________ acts as a lymphatic system for the brain by removing waste products
cerebral aqueduct (connection from third ventricle to fourth ventricle, very thin)
where is the CSF flow most vulnerable to direct obstruction or indirect pressure
magendie
the foramen _________ drains into the cisterna magna
luschka
the foramen ____________ drains into the subarachnoid space on the sides of the medulla and pons
open
if the CSF pressure is more than the blood pressure the arachnoid granulation valve (open or closes)
closes
if the CSF pressure is less than the blood pressure the arachnoid granulation valve (opens or closes)
10-20
CSF pressure is ____-_____ cm H2O depending on body position
headache (due to compression on skull or irritation of meninges)
____________ is the most common symptom of an intracranial mass lesion
papilledma
____________ is dilation of the optic disc which may occur with an increase in intracranial pressure
skull and dura mater
an epidural hematoma is between the ________ and the ___________