Biochem423 - Gluconeogenesis
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Gluconeogenesis
Creating glucose from endogenous sources
Occurs primarily in the liver (and a little in the kidneys)
Glycolysis net production
+2 ATP
+2 NADH
2 Pyruvate
catabolic reaction
Gluconeogenesis net production
1 Glucose
-4 ATP
-2 GTP
-2 NADH
anabolic reaction
Different enzymes between Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Glycolysis: Hexokinase (IV or II), PFK-1, Pyruvate Kinase
Gluconeogenesis: Pyruvate carboxylase, PEPCK, FBPase-1, G6Pase
Pyruvate Carboxylase
Anaplerotic reaction for TCA (creating OAA)
Converts Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate
Uses bicarbonate (HCO3-) and ATP (has Mg2+)
Upregulated by Acetyl-CoA
Phosphoenolpryuvate (PEPCK)
Oxaloacetate —> PEP
Uses GTP —> GDP + CO2 (has Mg2+)
Transport of Pyruvate —> OAA —> PEP
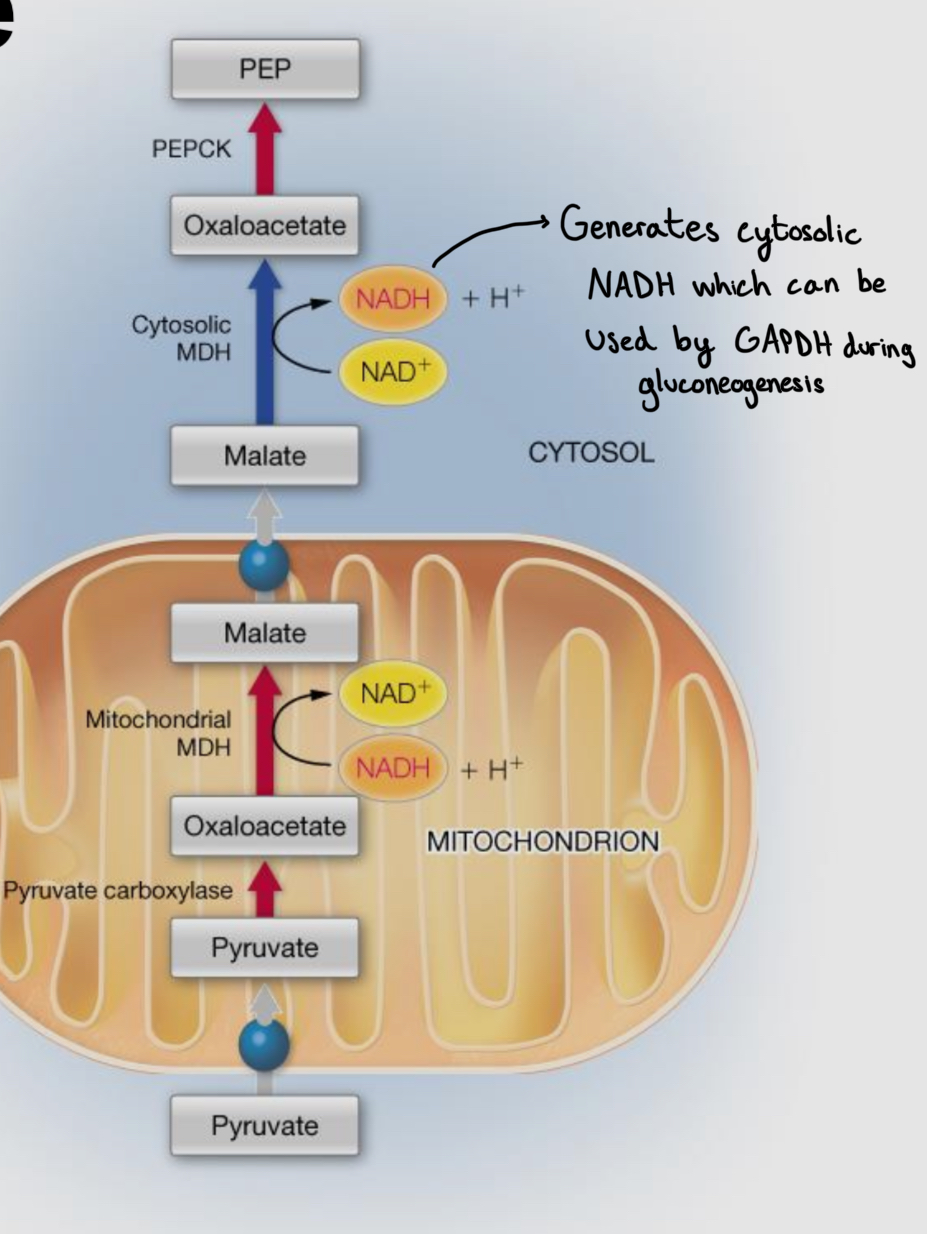
Pyruvate carboxylase is only located in the mitochondrion
Starting material for gluconeogenesis
Oxaloacetate
All amino acids except ___ and ____ can be converted to OAA to make new glucose via gluconeogenesis (in the liver)
Leucine and Lysine — as both amino acids are ketogenic
Leucine is used to make acetyl-CoA
Lysine is used to make acetoacetyl-CoA
Cori Cycle
Using lactate produced by anaerobic respiration to make glucose
When in anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted into lactate (especially in skeletal muscle cells)
This lactate is sent released into the blood and collected by the liver
The liver then performs gluconeogenesis, and sends the glucose back into the bloodstream.
Redox reactions are matched up (Glucose —> Pyruvate makes NADH, and Pyruvate —> Lactate uses NADH to make NAD+)
Substrate cycles

Primary sites for reciprocal regulation of these pathways
All of these are allosteric enzymes which will be either inhibited or promoted by certain effectors
This allows substrate cycles to amplify metabolic signals for key steps
Fructose-2,6-biphosphate
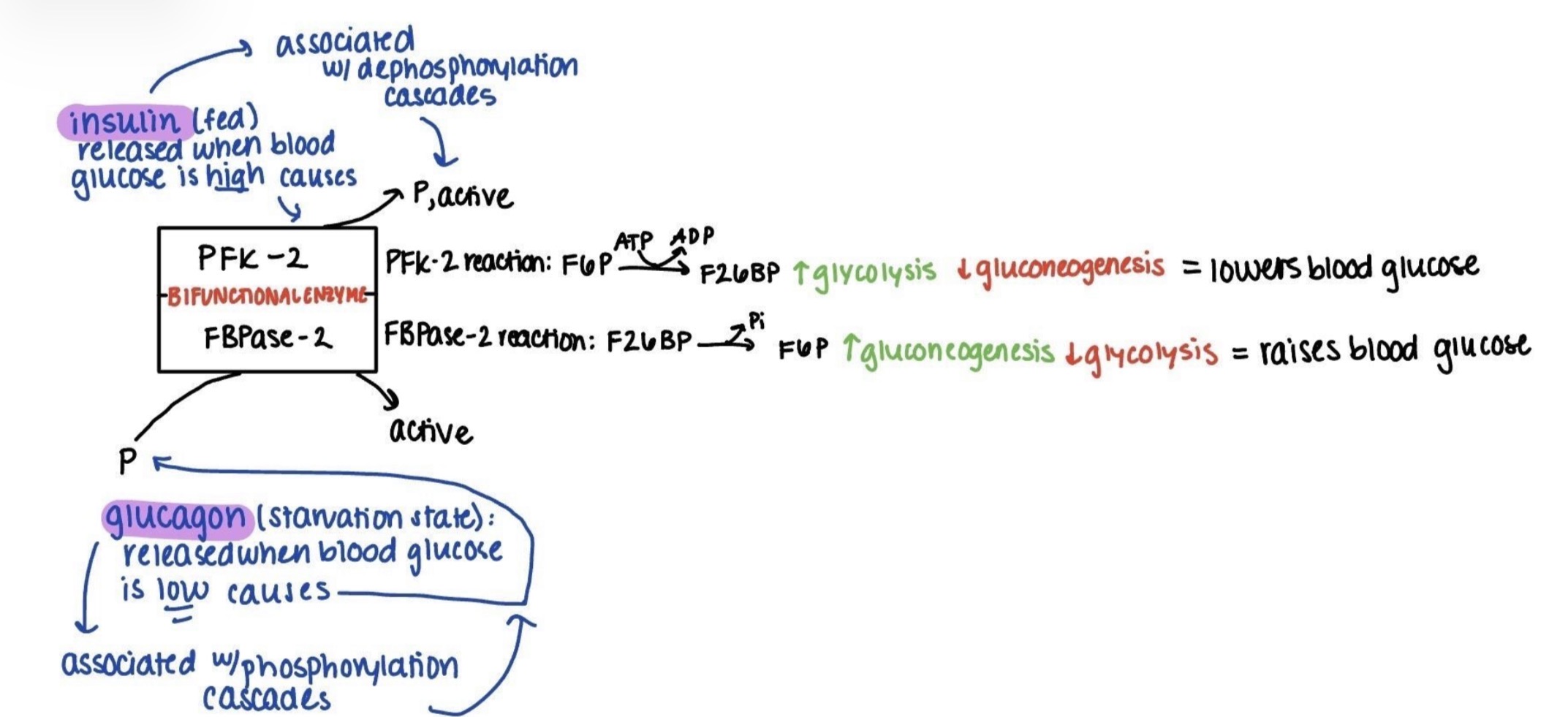
F2,6BP will activate PFK-1 and inhibit FBPase-1
Bifunctional enzyme is not a part of glycolysis or gluconeogenesis, but it affects both pathways
PFK-2 activity promoted when dephosphorylated - insulin
FBAase-2 activity promoted when phosphorylated - glucagon