1.02 Medical Sciences
1/458
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
459 Terms
what is the main mechanism glucose and galactose are absorbed by?
secondary active transport
what is the first step in glucose/galactose absorption?
they compete for the sugar site on a sodium/glucose-linked transporter (SGLT1) in the brush border membrane of an enterocyte
what is the second step in glucose/galactose absorption?
either glucose or galactose bind to SGLT1 along with a sodium ion and both get transported into the cell against the electrochemical gradient
what happens to the sodium from the SGLT1 transporter?
transported out of the cell by the Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
what happens to the glucose/galactose from the SGLT1 transporter?
accumulate in the cell until they are removed by simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion by GLUT2 transporters on the basolateral membrane of the cell
why is glucose/galactose absorption called secondary active transport?
the SGLT1 transporters work against the electrochemical gradient, but using energy from the Na+/K+ ATPase
what is the mechanism that allows fructose absorption?
facilitated diffusion
which transporter allows facilitated diffusion of fructose into cells?
GLUT5 on the apical membrane
which transporter allows facilitated diffusion of fructose into bloodstream?
GLUT2 on basolateral membrane
can fructose be taken up against the electrochemical gradient?
no, because it is only absorbed by facilitated diffusion
what makes amino acid absorption difficult?
enterocytes have a high cytosolic concentration of free amino acids for protein synthesis
how is the difficulty of aa absorption overcome?
di- and tripeptidases are absorbed instead and then hydrolysed within the cell to maintain the concentration gradient of peptides
what is the main mechanism for aa/peptide absorption?
secondary active transport
what transporter takes up di- and tripeptides?
PepT1 - a H+ dependent cotransporter on the brush border
how is the H+ gradient created?
by an Na-H exchanger (active transport)
what type of transporter takes up AAs?
a sodium cotransporter
how do AAs enter the bloodstream?
through facilitated diffusion in basolateral membrane
what happens to the insoluble products of lipid digestion before being absorbed?
they are solubilised into mixed micelles by bile
what is the micelle composed of? (2)
- inner layer of lipid digestion products
- outer layer of bile salts
what is the only soluble lipid digestion product?
glycerol
how does glycerol get absorbed into capillaries?
they can diffuse directly into the cells via the luminal membrane and diffuse out via the basolateral membrane and into capillaries
how do micelles get absorbed into enterocytes?
they can diffuse through the apical membrane of enterocytes
how far along the small intestine are most lipid products absorbed by?
mid-jejunum
what happens to the lipid digestion products in the enterocytes? (2)
- re-esterified with fatty acids on the SER
- packaged with apoproteins to make chylomicrons
what happens to the chylomicrons?
- packaged into secretory vesicles on the golgi apparatus
- leave the basolateral membrane via exocytosis
where do the chylomicrons go after exocytosis?
too large to enter capillaries so they enter the lacteals
how do chylomicrons get into the bloodstream?
lymphatic circulation carries the chylomicrons to the thoracic duct which empties into the bloodstream
which vitamins are water-soluble?
B1
B2
B6
B12
C
biotin
folic acid
nicotinic acid
pantothenic acid
how are the water-soluble vitamins absorbed?
- passive diffusion or secondary active transport (sodium-dependent transport systems)
- apart from B12
how is vitamin B12 absorbed?
- binds to R protein, secreted in salivary juices
- in duodenum pancreatic proteases digest R protein so B12 moves onto instrinsic factor
- the vitamin B12-intrinsic factor complex is resistant to digestion so moves to the ileum where is it absorbed
which vitamins are fat-soluble?
A
D
E
K
how are fat-soluble vitamins absorbed? (2)
- they diffuse into the micelles that contain bile salts and lipid digestion products
- they then follow the pathway of lipid absorption
how is iron absorbed?
- as a free Fe2+ ion
- as haem iron bound to haemoglobin or myoglobin
how is calcium absorbed?
- depends on presence of active vitamin D
- needed for vitamin D-dependent Ca-binding protein (cabindin D-28K)
what are the 2 main types of muscle in abdomen?
- flat muscles
- verticle muscles
what are the 3 flat muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
- external oblique
- internal oblique
- transversus abdominis
what is the rectus sheath?
the aponeurosis of all 3 flat abdominal muscles
what is aponeurosis?
tendons (muscles joining) in the form of a sheet
what is the most superficial anterolateral flat abdominal muscle?
external oblique
which direction does the external oblique run?
inferomedially
what is the next most superficial anterolateral flat ab muscle?
internal oblique
which direction does the internal oblique run?
superomedially - perpindicular to external oblique
what is the deepest anterolateral flat ab muscle?
transversus abdominis
what are the 2 vertical muscles of the anteromedial ab wall?
- rectus abdominis
- pyramidalis
where is the rectus abdominis found?
in pairs either side of the midline in the abdominal wall
what is the vertical midline of the abdomen called?
linea alba
what segments the rectus abdominis?
tendinous intersections
where is the pyramidalis located?
- superficially and inferiorly to rectus abdominis
- base is on pubis bone
what is the pyramidalis attached to?
the apex is attached to the linea alba
above the umbilicus where do the 3 flat muscles run in relation to the rectus abdominis?
external oblique - anteriorly only
internal oblique - anteriorly and posteriorly
transeversus abdominis - posteriorly only
below the umbilicus where do the 3 flat muscles run in relation to the rectus abdominis?
external oblique - anteriorly only
internal oblique - anteriorly only
transversus abdominis - anteriorly only
where do the internal oblique and transversus abdominis travel from posterior to anterior to the rectus abdominis?
at the arcuate line
what are the 5 muscles of the posterior abdominal wall?
- quadratus lumborum
- psoas major
- psoas minor
- iliacus
- diaphragm
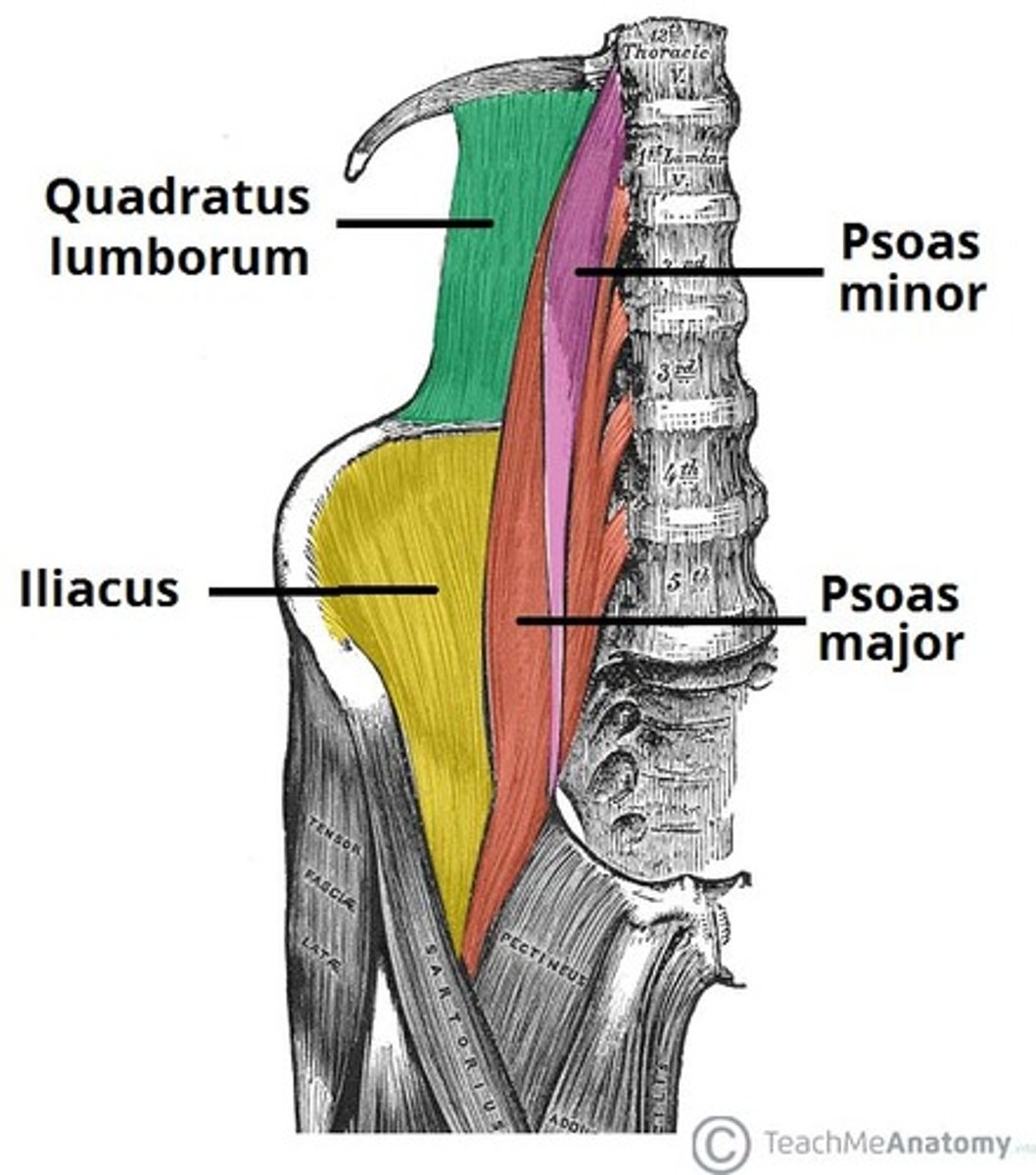
where does quadratus lumborum originate?
iliac crest
where does quadratus lumborum travel and insert?
superomedially and inserts onto L1-L4
where does the psoas major originate?
T12-L5
where does the psoas major travel and attach?
inferolaterally and attaches to femur
where does the psoas minor originate?
T12 and L1
where does the psoas minor run and attach?
inferiorly and attaches to pubic bone
where does the iliacus originate?
iliac fossa
where does the iliacus attach?
femur
what is the order of posterior abdominal wall muscles from posterior to anterior
- quadratum lumborum
- diaphragm/iliacus
- psoas major
- psoas minor
does everyone have the psoas minor muscle?
no, only 60% population have it
what are the layers of the abdomen from external to internal? (9)
1) skin
2) fatty layer of superficial fascia - Camper's fascia
3) membranous layer of superficial fascia - Scarpa's fascia
4) external oblique
5) internal oblique
6) transversus abdominis
7) fascia transversalis
8) extraperitoneal tissue
9) parietal layer of peritoneum
what are the 2 main types of muscle in abdomen?
- flat muscles
- verticle muscles
what are the 3 flat muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall?
- external oblique
- internal oblique
- transversus abdominis
what is the rectus sheath?
the aponeurosis of all 3 flat abdominal muscles
what is aponeurosis?
tendons (muscles joining) in the form of a sheet
what is the most superficial anterolateral flat abdominal muscle?
external oblique
which direction does the external oblique run?
inferomedially
what is the next most superficial anterolateral flat ab muscle?
internal oblique
which direction does the internal oblique run?
superomedially - perpindicular to external oblique
what is the deepest anterolateral flat ab muscle?
transversus abdominis
what are the 2 vertical muscles of the anteromedial ab wall?
- rectus abdominis
- pyramidalis
where is the rectus abdominis found?
in pairs either side of the midline in the abdominal wall
what is the vertical midline of the abdomen called?
linea alba
what segments the rectus abdominis?
tendinous intersections
where is the pyramidalis located?
- superficially and inferiorly to rectus abdominis
- base is on pubis bone
what is the pyramidalis attached to?
the apex is attached to the linea alba
above the umbilicus where do the 3 flat muscles run in relation to the rectus abdominis?
external oblique - anteriorly only
internal oblique - anteriorly and posteriorly
transeversus abdominis - posteriorly only
below the umbilicus where do the 3 flat muscles run in relation to the rectus abdominis?
external oblique - anteriorly only
internal oblique - anteriorly only
transversus abdominis - anteriorly only
where do the internal oblique and transversus abdominis travel from posterior to anterior to the rectus abdominis?
at the arcuate line
what are the 5 muscles of the posterior abdominal wall?
- quadratus lumborum
- psoas major
- psoas minor
- iliacus
- diaphragm
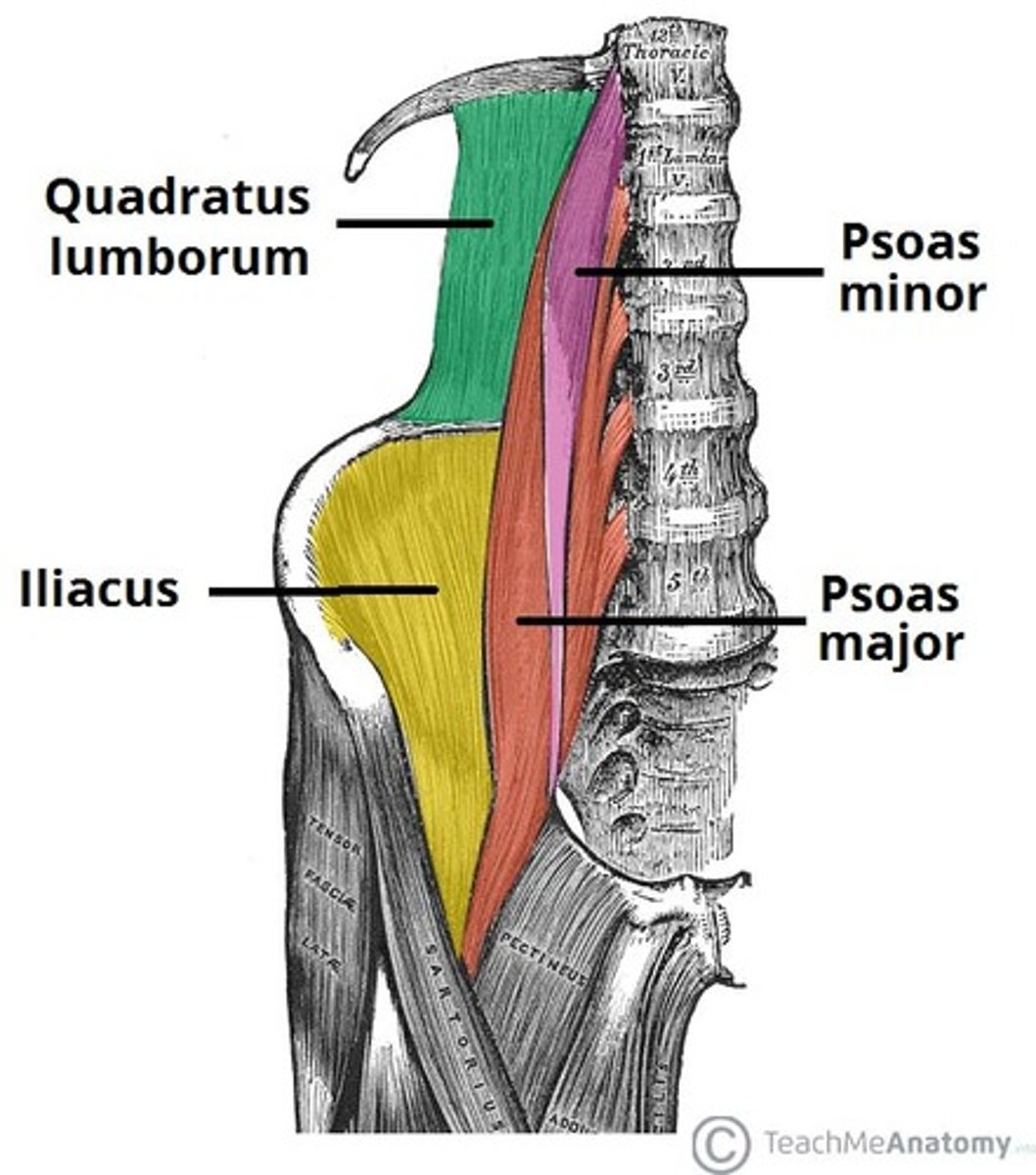
where does quadratus lumborum originate?
iliac crest
where does quadratus lumborum travel and insert?
superomedially and inserts onto L1-L4
where does the psoas major originate?
T12-L5
where does the psoas major travel and attach?
inferolaterally and attaches to femur
where does the psoas minor originate?
T12 and L1
where does the psoas minor run and attach?
inferiorly and attaches to pubic bone
where does the iliacus originate?
iliac fossa
where does the iliacus attach?
femur
what is the order of posterior abdominal wall muscles from posterior to anterior
- quadratum lumborum
- diaphragm/iliacus
- psoas major
- psoas minor
does everyone have the psoas minor muscle?
no, only 60% population have it
what are the layers of the abdomen from external to internal? (9)
1) skin
2) fatty layer of superficial fascia - Camper's fascia
3) membranous layer of superficial fascia - Scarpa's fascia
4) external oblique
5) internal oblique
6) transversus abdominis
7) fascia transversalis
8) extraperitoneal tissue
9) parietal layer of peritoneum
what are the 7 classifications of pathogens?
- bacteria
- fungi
- viruses
- protozoa
- helminth
- athropods
- prions
what is an example of a fungi?
yeast
what are protozoa?
single-celled animals that can cause infection
what is the difference between a protist and a parasite?
not all protists are parasitic
what is an example of a protist?
cysts
what is an example of a helminth?
parasitic worms