Period 6 (1865-1898) AP US History, apush unit 6
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
People's (Populist) Party
(1892-96) An agrarian political party; Drew support from angry farmers in the West and South; Highly critical of capitalism, especially banks and railroads; Allied itself with the labor movement.
populism
a philosophy supporting the rights and empowerment of the masses as opposed to elites
assimilation
the process by which a person or a group's language and/or culture come to resemble those of another group

"Gilded Age"
A sarcastic description of the late 19th century in the United States; Suggested both the extravagant wealth of the time and the terrible poverty that lay underneath; Coined by Mark Twain.
Social Darwinism
"survival of the fittest"; Provided a justification for the enormous wealth and power wielded by industrialists in the latter half of the 19th century.
trust
A set of companies managed by a small group known as trustees, who can prevent companies in the trust from competing with each other.
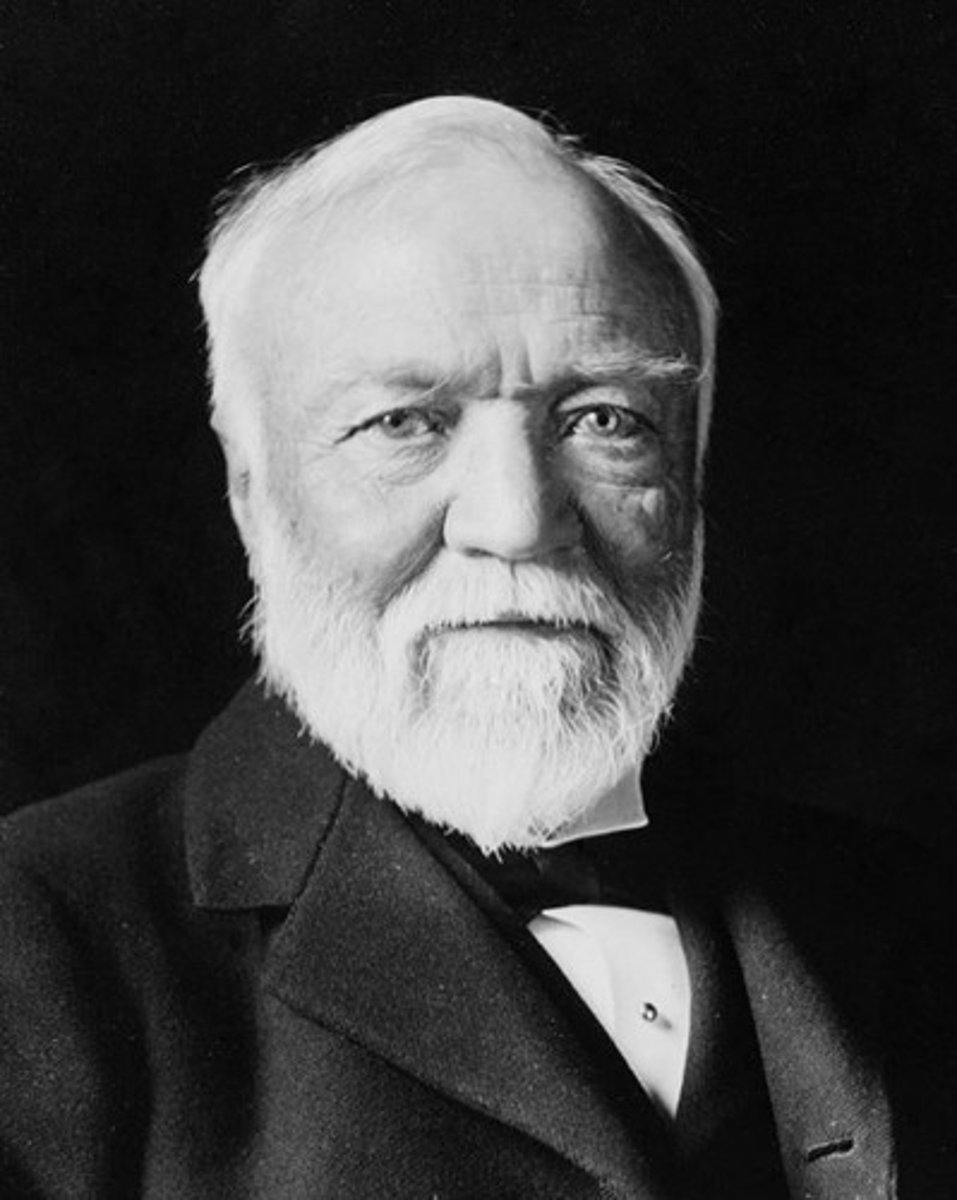
Gospel of Wealth
(1889) Andrew Carnegie and others; The idea that those who accumulated wealth to share their riches for the betterment of society.

Jane Addams
Reformer who helped poor immigrants; Established Hull House.

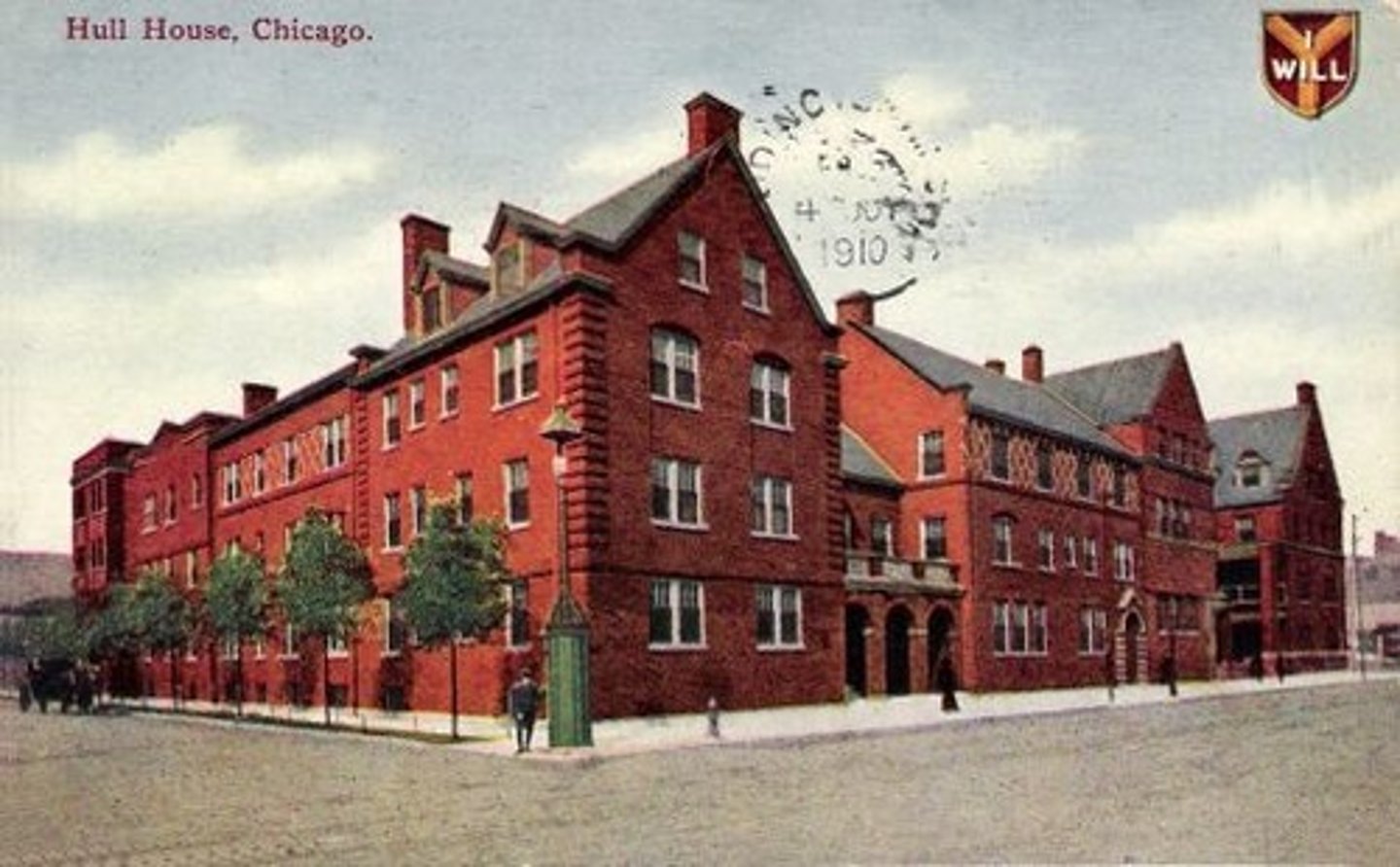
Hull House
settlement house founded by Progressive reformer Jane Addams in Chicago in 1889

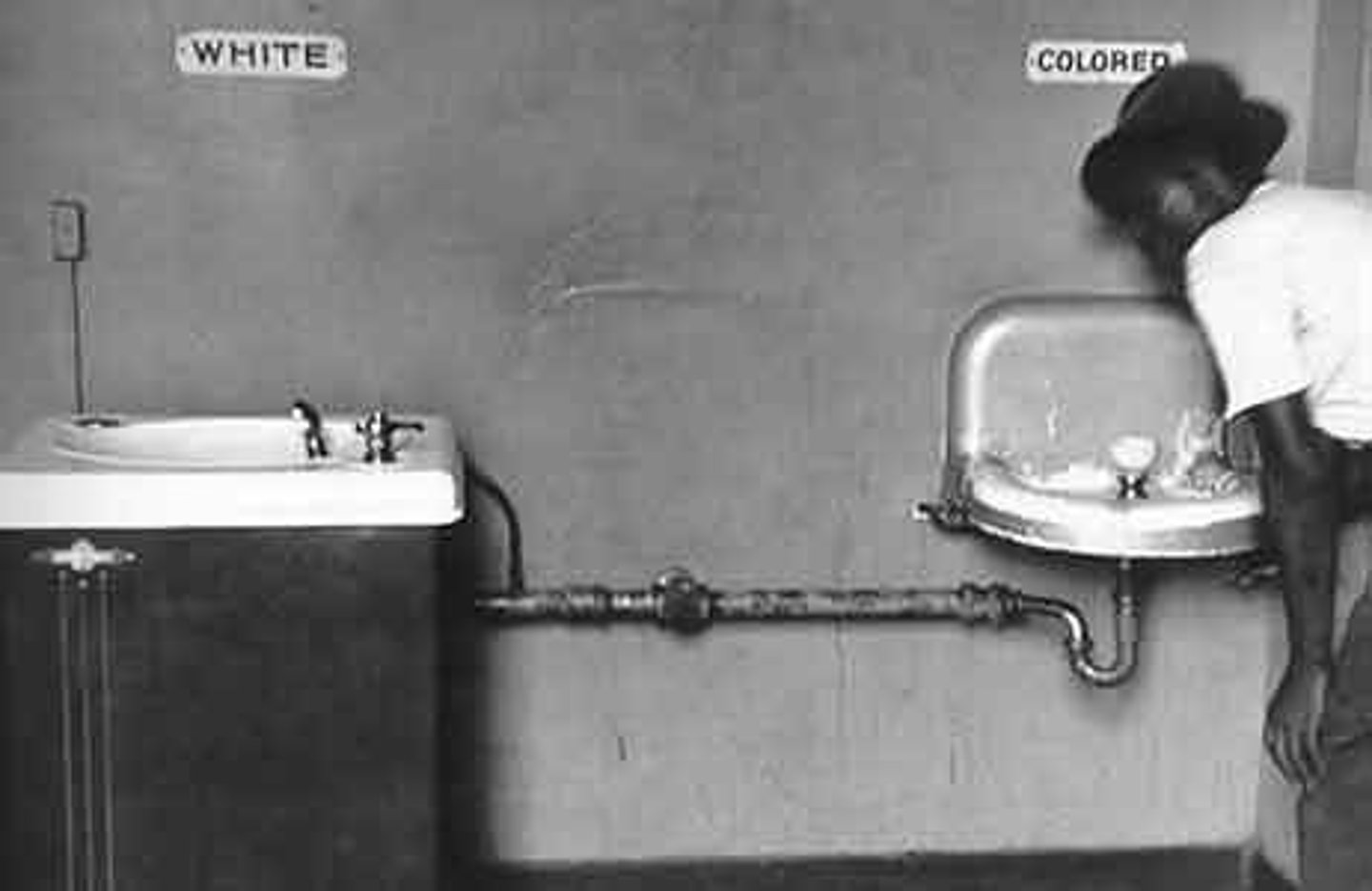
Plessy v. Ferguson
(1896) Legalized segregation in publicly owned facilities on the basis of "separate but equal."

segregation
The separation into ethnic or racial groups in daily life: Restaurants, water fountains, public toilet, school, entertainment venues, transportation, residential neighborhoods.

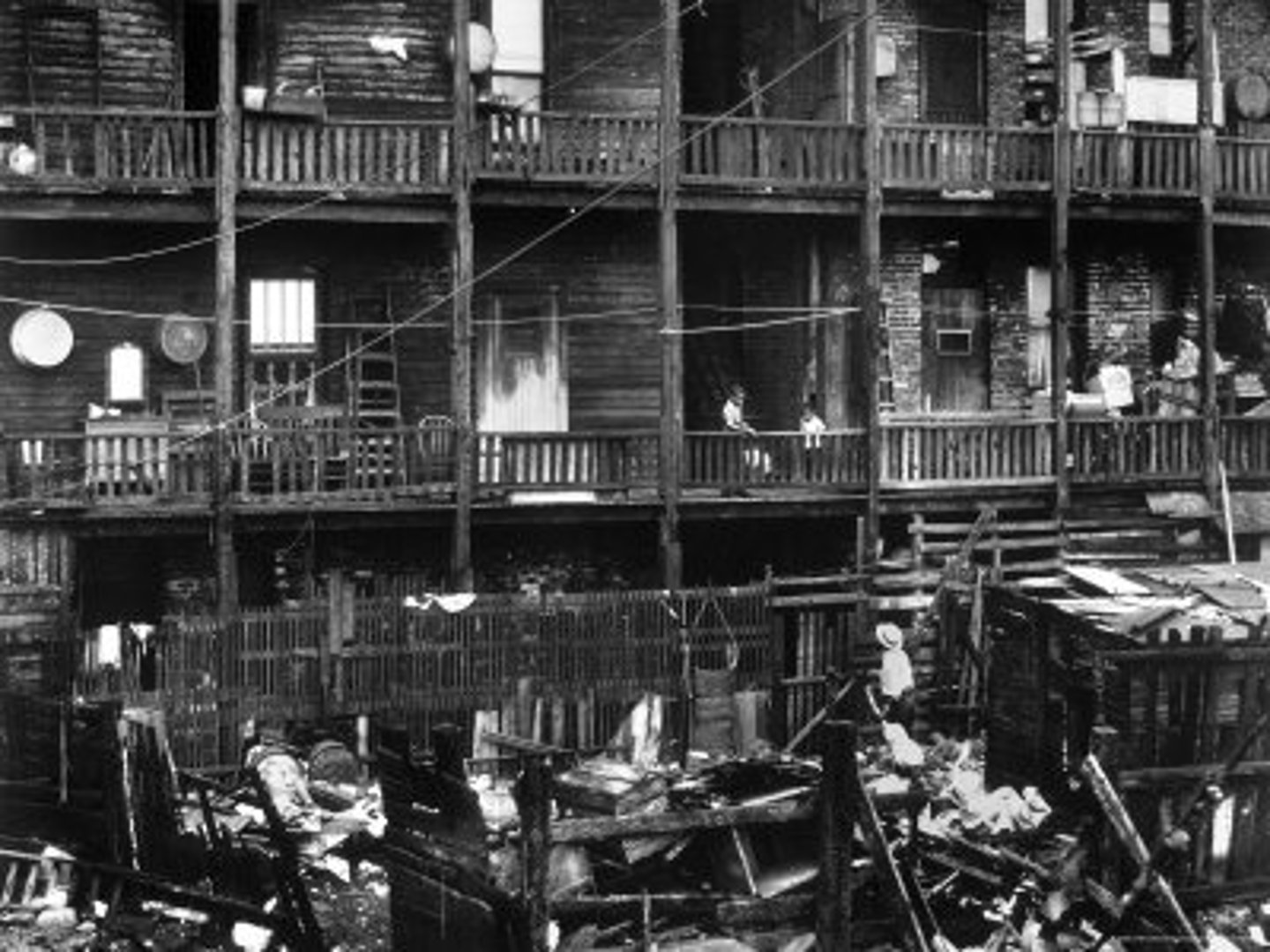
tenement
a multi-dwelling building, often poor or overcrowded

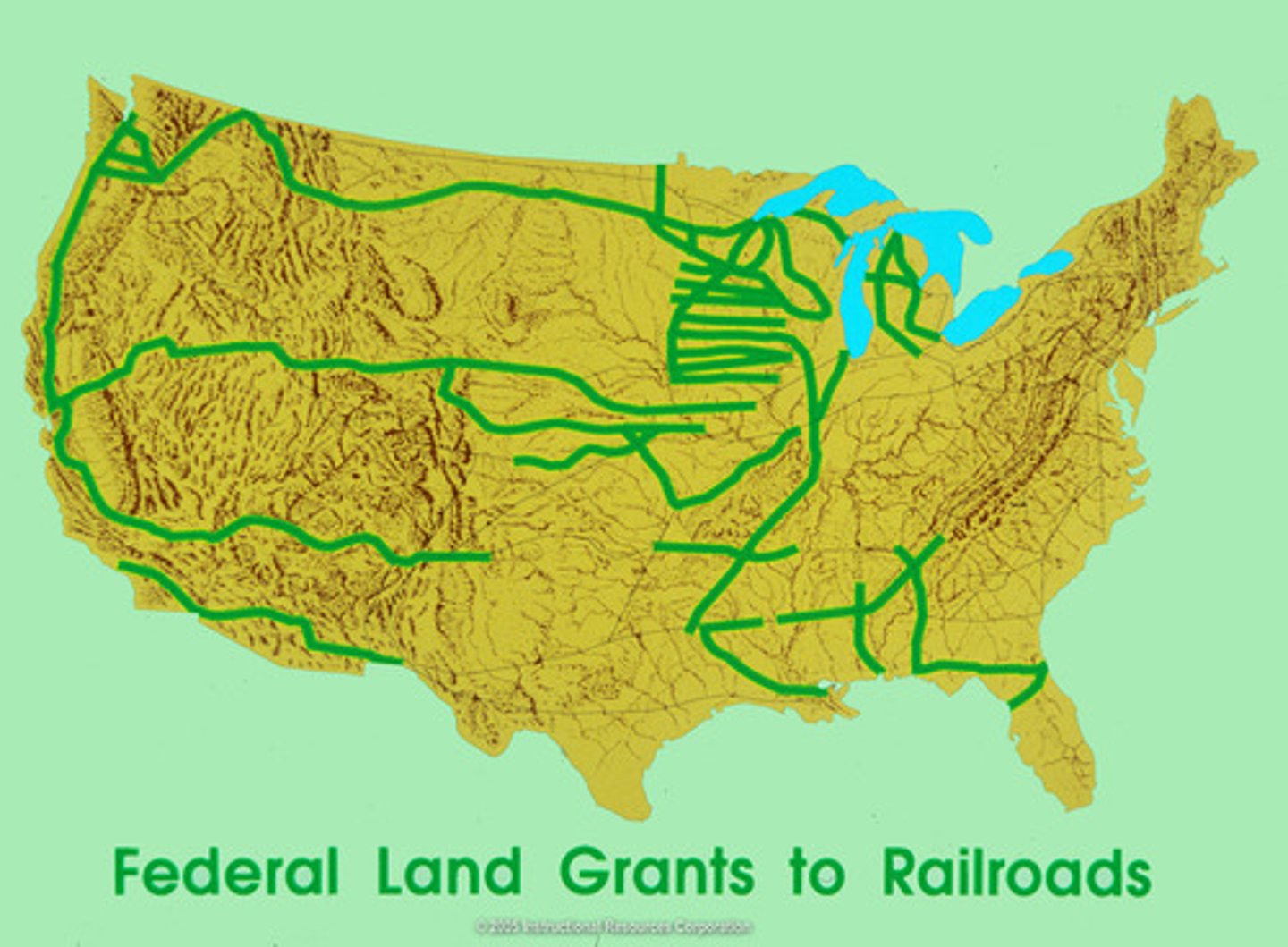
land grants
land given by government to universities and railroad companies
Dawes Act
(1887) land given to individual Indians to discourage tribal mindset; encouraged Indians to farm for a living instead of communally owning land

open range
the idea that cattle can be grazed on large tracts of public and/or private property; invention of barbed wire ended this idea and drove many small cattle ranches out of business and off their small plots of land

Bessemer process
A cheap and efficient process for making steel, developed around 1850; Widespread adoption in the US allowed steel production and industrialization to outpace all global industrial competitors.
vertical Integration
Strategy to maximize profits by attempting to own every step of the manufacturing process (ex. Carnegie Steel)
horizontal Integration
Strategy to maximize profits by attempting to purchase competing companies in the same industry; monopoly-building (ex. Rockefeller's Standard Oil)
prohibition
forbidding by law the manufacture, sale, or consumption of liquor

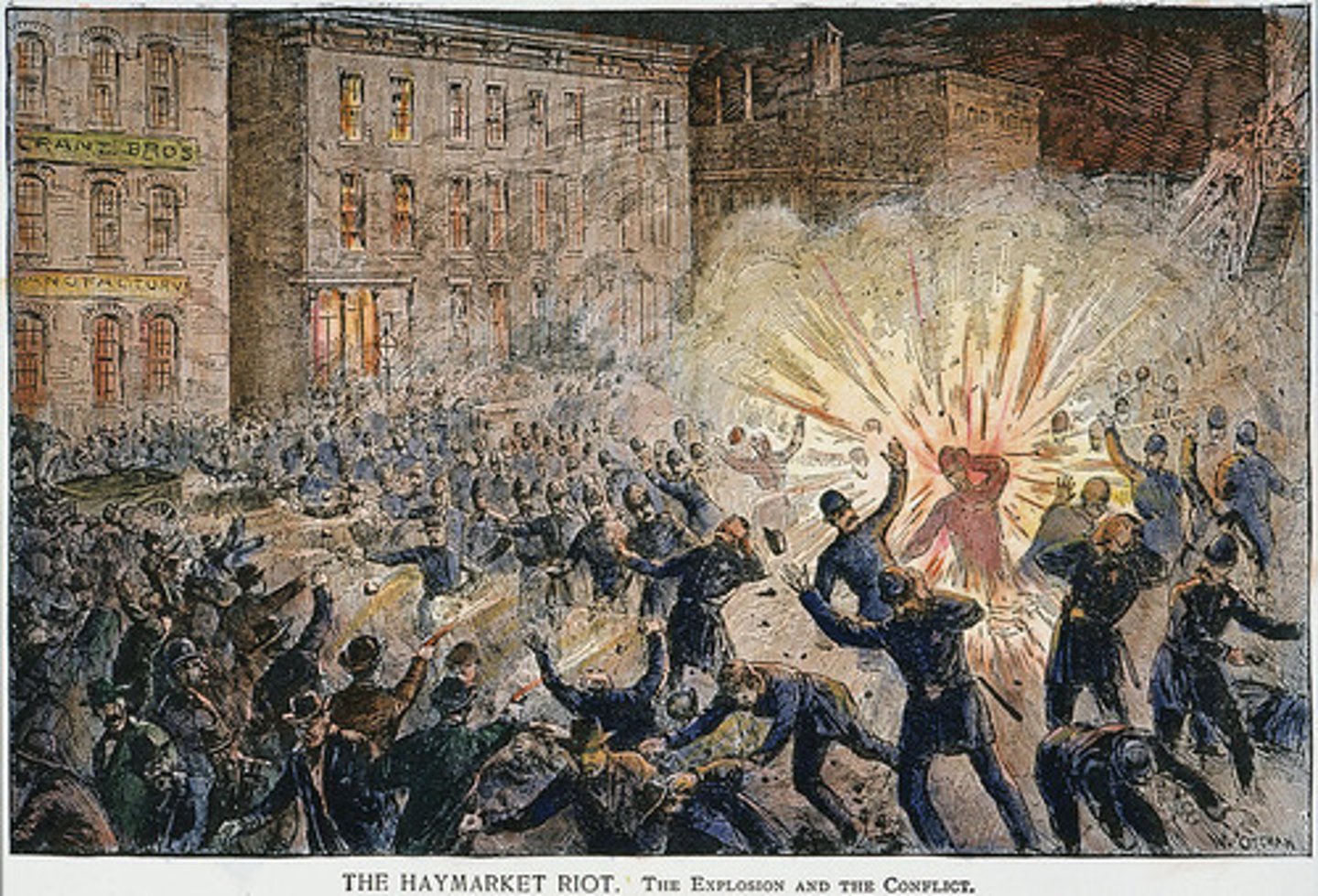
Haymarket Riot
(1886) Labor dispute in Chicago that ended with a bomb being thrown at police resulting in many deaths. Led to an unfavorable public opinion of organized labor.

American Federation of Labor
The first federation of labor unions in the United States. Founded by Samuel Gompers in 1886

lobbyist
someone who promotes an interest or cause before a political body, often for pay

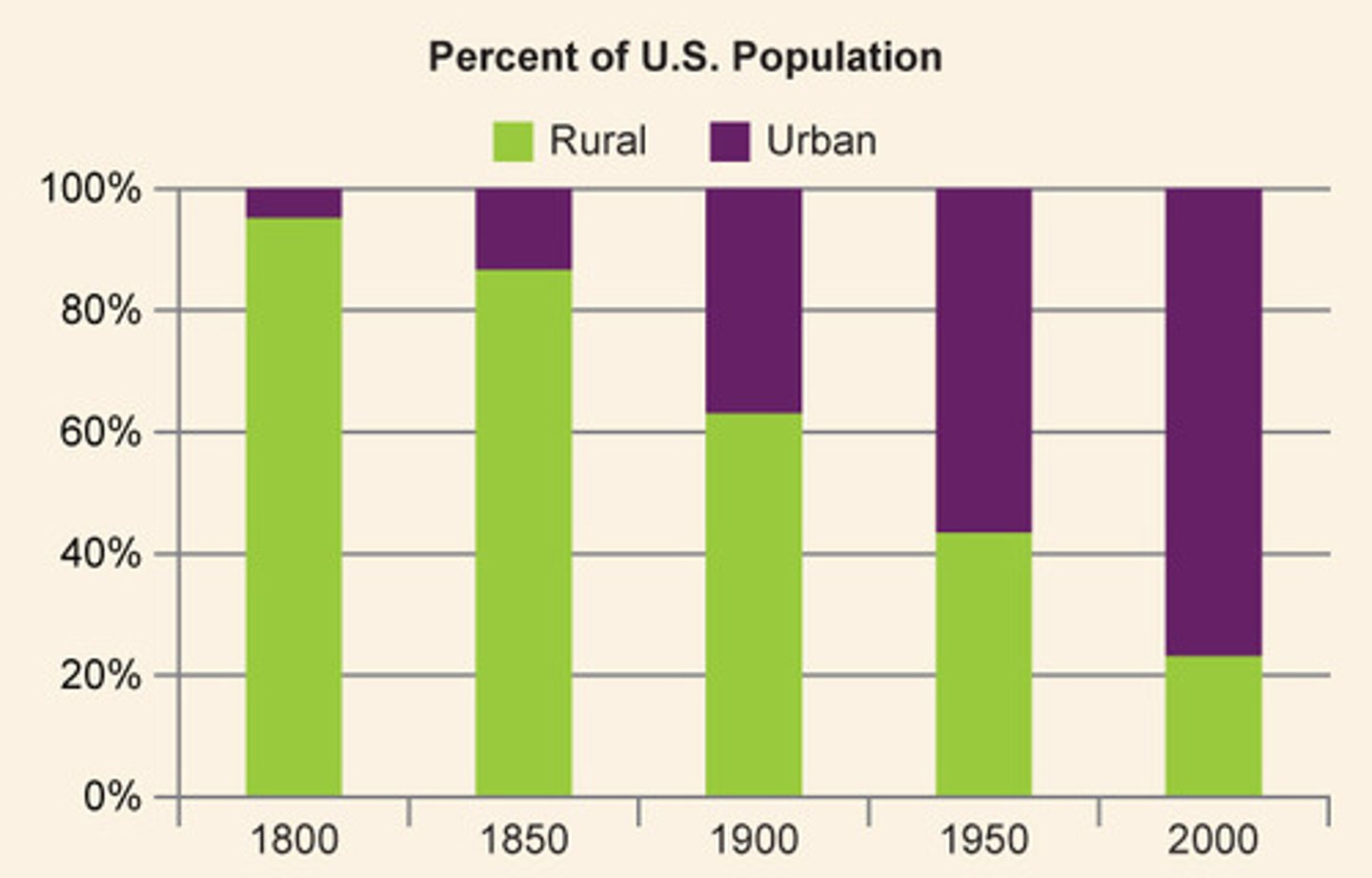
urbanization
movement of people from rural communities and settlements to big cities
"New Immigrants"
from southern and eastern Europe such as Russia, Poland, Italy, etc. that arrived in the US in the latter half of the 19th century

Chinese Exclusion Act
(1882) First law limiting immigration based on race; effectively stopped immigration from China.

political machine
Unofficial political organization that works to win elections in order to exercise power; Mostly affiliated with urban immigrant groups. E.G. Tweed Ring, Tammany Hall.

Plessy v. Ferguson (1896)
Legalized racial segregation in publicly owned facilities on the basis of "separate but equal."

Knights of Labor
American labor organization in the 1880s led by Terence V. Powderly. Organized a wide range of workers, including skilled and unskilled, and had broad reform goals.

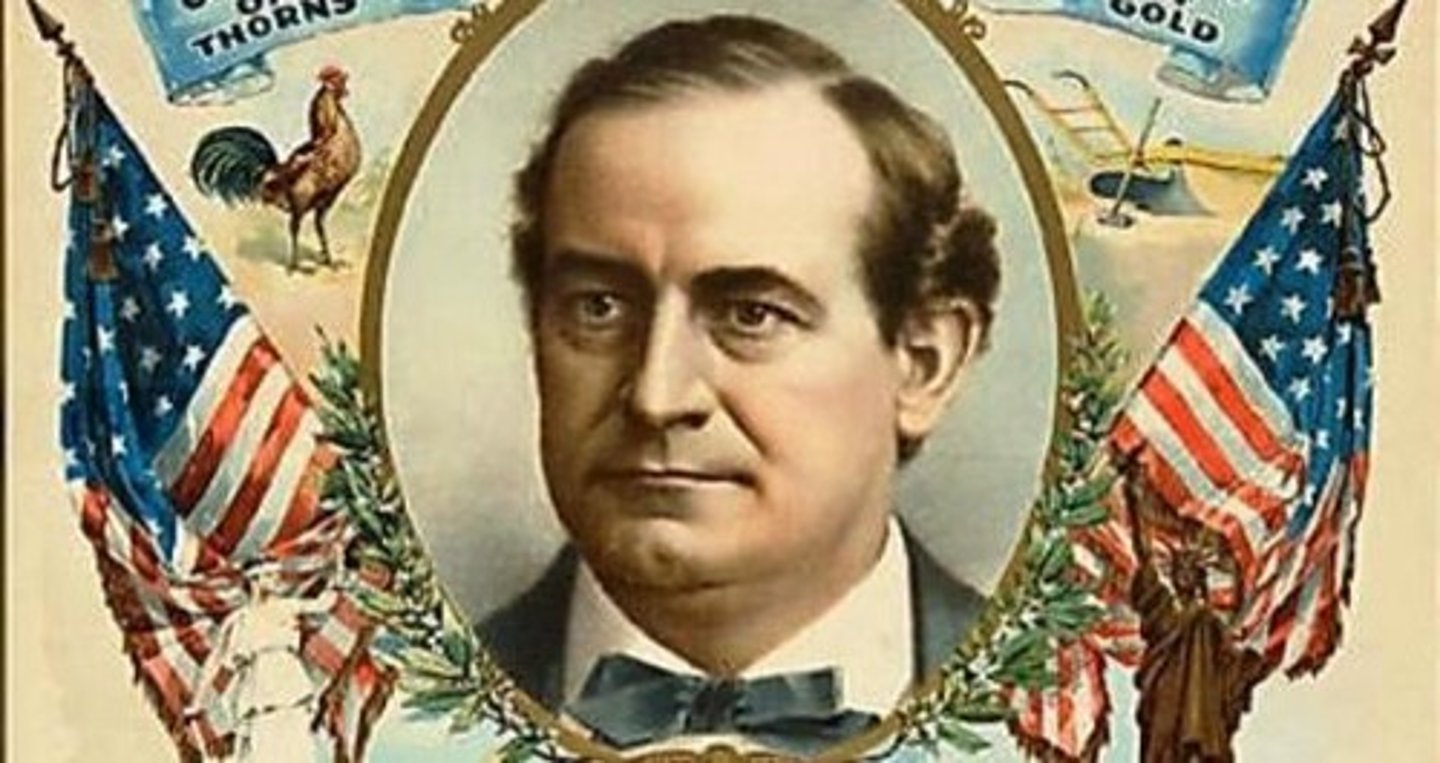
William Jennings Bryan
Democratic and Populist candidate for President in 1896 who advocated a policy of free silver

"New South"
After the Civil War, southerners promoted a new vision for a self-sufficient southern economy built on modern capitalist values, industrial growth, and improved transportation. In reality, this growth was fairly slow.

Homestead and Pullman Strikes
Industrial lockouts and strikes that showed battle between corporations and labor unions. Ended with government intervention on the side of big business.
Tammany Hall
Political machine of New York City that was well-known for its corruption; lead by William Boss Tweed

Andrew Carnegie
Titan of Industry: Steel; Author of Gospel of Wealth

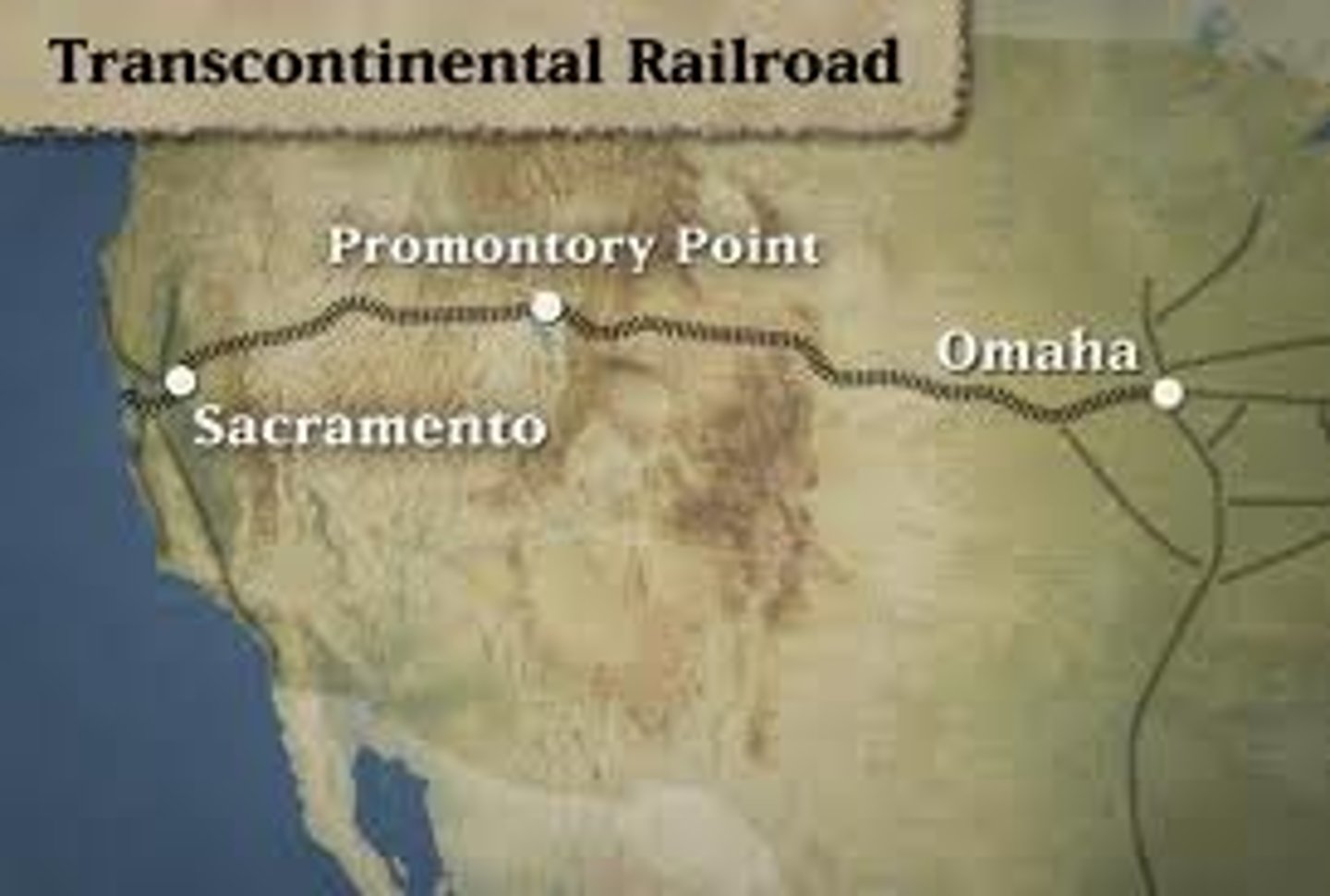
transcontinental railroads
Rail line that crosses the continent connecting East to West; Opened new markets and helped spur the Industrial Revolution
Social Gospel
Protestant movement preaching that all true Christians should be concerned with the plight of immigrants and other poor residents of American cities and should financially support efforts to improve lives of these poor urban dwellers. Settlement houses were often financed by funds raised by ministers of this movement.
Grange Movement and Farmers Alliance
Grassroots movements that attempted to address the plight of farmers in the late 1800s; attempted to regulate railroads and enlarge opportunity for credit; evolved into Populist movement.

Americanization
Process of assimilating immigrants into American culture by teaching English, American history, and citizenship.

John D. Rockefeller
Titan of industry: Oil

Second Industrial Revolution
Spurred by machine tools, interchangeable parts, Bessemer process of mass steel production, transcontinental railroad, immigrant labor

J.P. Morgan
Titan of industry: Banking

Cornelius Vanderbilt
Titan of industry: Railroads

middle class
a social class made up of skilled workers, professionals, business people, and wealthy farmers
Standard Oil
John D. Rockefeller's company that gained a monopoly over the world petroleum market with the practice of trusts and swift elimination of competition.

Carnegie Steel
A steel producing company created by Andrew Carnegie to manage business at his steel mills in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania area in the late 19th century. Significance: had a monopoly in the steel industry. vertical integrations.

Credit Mobilier scandal
corruption in the railroads allowing men to change the government very high amounts for the work to be done
Rutherford B. Hayes
won the election of 1876 in exchange for withdrawing the federal troops from the remaining southern states

Ulysses S. Grant

Compromise of 1877
South to gain removal of last troops from Reconstruction; North wins Hayes as president
Jim Crow laws
State-level legal codes, literacy requirement for voting, voter registration laws and poll taxes meant to deter blacks from voting
Pendleton Act
(1883) Legislation that began the federal merit system
Civil Service Commission
Created by Pendleton Act to oversee examinations for potential government employees
Sherman Anti-Trust Act of 1890
an 1890 law that banned the formation of trusts and monopolies in the United States
yellow journalism
sensational and exaggerated news stories

Ghost Dance
A religious revitalization campaign reminiscent of the pan-Indian movements led by earlier prophets.

Enforcement Act
equal accommodations in public places and no racial discrimination in court
interlocking directorate
practice of having executives or directors from one company serve on the Board of Directors of another company. J.P. Morgan is associated with this.
trust
A group of corporations run by a single board of directors, A monopoly that controls goods and services, often in combinations that reduce competition; John Rockefeller is associated with this.
pool
informal agreement between a group of people or leaders of a company to keep their prices high and to keep competition low; associated with railroads because of the Interstate Commerce
vertical integration
it is when you combine into one organization all phases of manufacturing from mining to marketing. This makes supplies more reliable and improved efficiency. It controlled the quality of the product at all stages of production; associated with Andrew Carnegie
knight of labor`
-leadership of terence v powderly
-worker cooperatives 'to make each man his employer'
-abolition of child labor
-abolition of trusts and monopolies
-included black people and women
-failed because they tried to unionize everyone; too many workers
molly maguire
A Irish miner's union that was established in Pennsylvania during the 1860s and 1870s; tens of thousands of Irish were forced to flee their homeland during the potato famine, but were not welcomed in America, who regarded them as a social menace and competition for jobs; forced to fend for themselves, they banded together to improve their social, financial, and political situation.
-helped unskiiled group, the irisih, who had unskilled labor, mining
american federation of labor
-founded by samuel gompers
-focused on higher wages and improved working conditions
-largest union with one million members
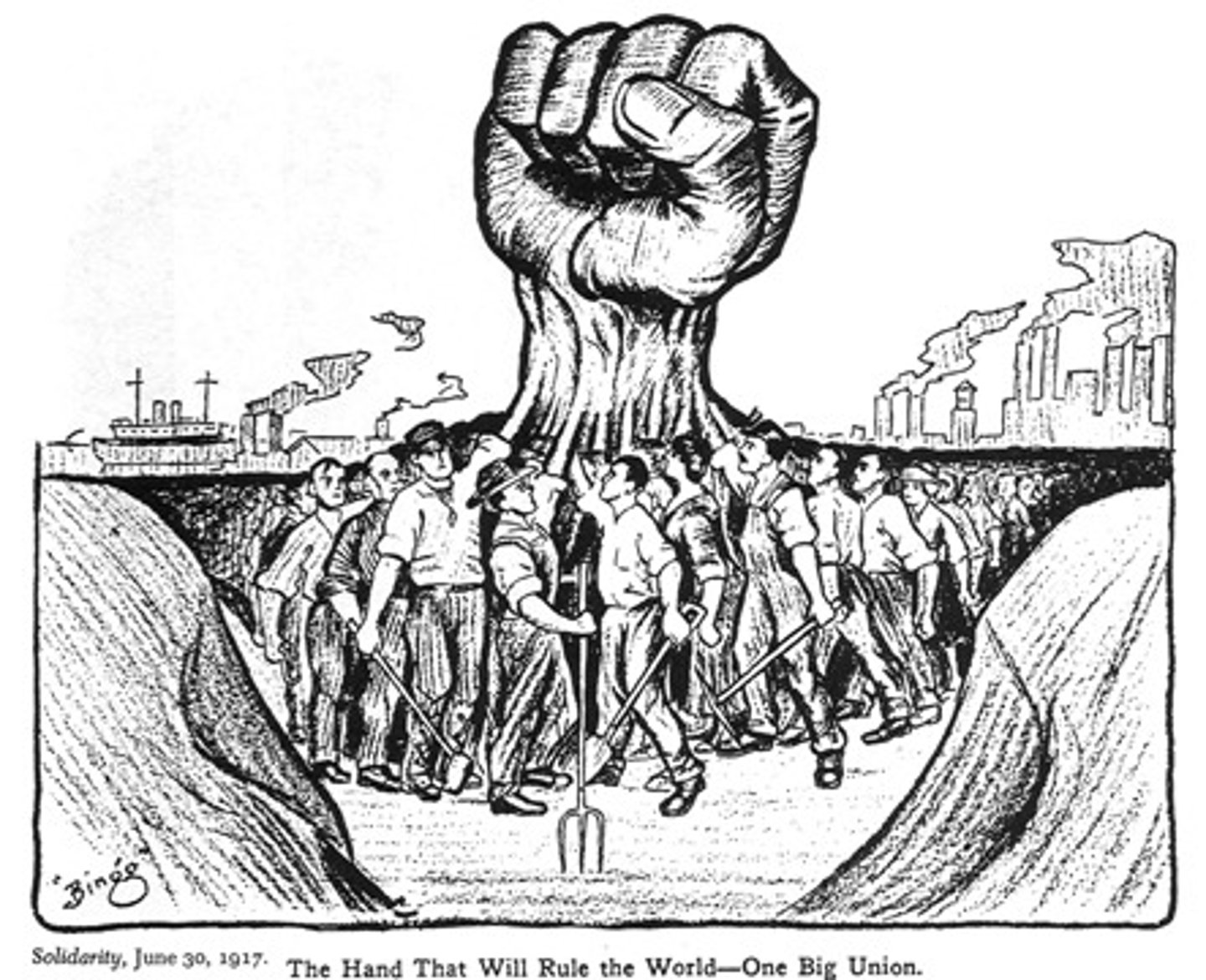
industrial workers of the world
-Led by "Mother" Jones, Elizabeth Flynn, Big Bill Haywood, and Eugene Debs;
-strove to unite all laborers, including unskilled workers and African Americans
-its goal was to create "One Big Union"
-embraced the rhetoric of class conflict and endorsed violent tactics
-collapsed during WWI.
-failed because they believed in socialism
what two factors hindered the new south
-late in industrialization
-poorly educated working class
-poor political leadership
-sharecropping
what ways did individuals and the government get involved in the preservation of the natural environment
-national parks
-advocated creation of forest reserves and a federal forest service
-forest reserve act and forest management act withdrew federal timberlands from development and regulated their use
-sierra club
-there used to be millions of buffalo, now there is only 10,000--that's how much we cared about our land
positive impacts of transcontinental railroad
-created jobs for the poor
-promoted expansion in the west
negative impacts of transcontinental railroad
-destroyed native american people and land
-killed off buffalo
what was the major aspects of the dawes severalty act
-broke up native tribes and made them civilized
-millions of land distributed to native americans
-century of dishonor be helen hunt jackson
what was booker t washington's basic message to the black population
-preaches virtues of hard work, moderation, and economic self-help
-hard work will prove we deserve rights headass
how did w.e.b. dubois' message differ from booker t washington's
-dubois said segregation ends now; bring us our rights
-washington said let's work for our rights, guys
what is nativism and the group that associated with this ideology
support for native-born americans and hatred for immigration; American Protective Association
list and describe three platform issues defined within the omaha platform
1) director election of us senators
2) unlimited coinage of silver
3) graduated income tax
gold standard
all paper money would be backed only by
bimetalism
value of the monetary unit is defined as equivalent to both a certain quantity of gold and to a certain quantity of silver
greenback
Name for Union paper money not backed by gold or silver. Value would fluctuate depending on status of the war
thoroughly describe why the populists wanted to embrace bimetalism
wanted to increase money supply and money circulation. bimetalism was wanted so it can cause inflation so they can pay for their debt/mortages.
what role did settlement houses have in the assimilation of immigrants
allowed immigrants in poverty to go through social services such as teaching english and providing elementary education
what was the main goal of the preservationists and list one way in which they were successful in their efforts
preservationists aimed to preserve natural areas from human interference. they were successful in their efforts through the sierra club
what were the beliefs of the "know-nothing party"? what were their goals?
know-nothing party believed in nativism and helping native-born americans getting job. their goals were to stop immigrants like catholic irish from taking their jobs. abolitionists and hated immigrants and native americans.
how did william lloyd garrison contribute to the abolitionist movement? what did he advocate for?
he published the abolitionist newspaper "the liberator" and he advocated immediate aboliton of slavery; founded the american antislavery society. his work was banned in the south and he ends up falling out with frederick douglas/black community
what impact did the publication of uncle tom's cabin have?
uncle tom's cabin regarded slave owners as monstously cruel and inhuman; lincoln said she was the one to start the civil war
describe the grange movement and list/describe two of their major issues
the grange movements is an organization that initially helped farms socially and educationally, but then it mainly focused on economics and politics, defending members against middlemen, trusts, and railroads. they established cooperatives and granger laws.
list and describe two methods the federal government used to promote westward migration
federal land grants and the transcontinental railroad
what logic and reasoning was used by the south when seceding from the union
the south didn't want lincoln as president and thought the north was trying to strip them of their rights so they pulled what america pulled during the american revolution
who is most associated with the gospel of wealth, and what were its basic tenents
john d. rockefeller was most associated with gospel of wealth; the gospel of wealth; god gives wealth to people and he expects them to give it away in philanthropic efforts
gospel of wealth
God gave money to people in order for people philanthropic efforts
social gospel
the religious doctrines preached by those who believed that the churches should directly address economic and social problems; demanded better housing and living condition
social darwinism
survival of the fittest when it comes to the marketplace; wealth was placed in the hands of the fit.
what was the biggest struggle the native american population faced during the last half of the 19th century
the biggest struggle was assimilation. native americans were stripped from their culture and forced to learn english and become white which was hard for them.
how does the concept of social darwinism relate to the gospel of wealth?
the fittest people were selected under god's decision so they are the most worthy of wealth
what is meant by uneven distribution of wealth? compare wealth disparity between the giant industrialists and the average wage earner
95% of money belonged to the 1% wealthy. Barely any wealth people but they had all the money. want to redistribute wealth without making it socailism. 16th amendment destroyed this through graduated taxes
what were the consequences of the dred scott decision of 1857?
declared all parts of west territory free to slavery, got rid of the missouri compromise, and denied blacks rights
what was the federal government's role in promoting industrial growth
there was federal land grants made to people. move west and acquire land. also the dawes act for natives to keep land if they took care of it. allowed railroads to build out.
what was the federal government's role in regulating immigration
chinese immigration act banned chinese laborers for coming so native born americans can work there
what was the federal government's role in assuring for the welfare of the poor and unemployed
they didn't have a role. survival of the fittest, social darwinism, and all that. let them negroes fiend for themselves.
what was the federal government's role in regulating the national economy
replaced currency whether it was with the gold standard, greenbacks, or the use of silver; also consider the sherman antitrust act
explain how immigration changed the social and economic landscape of america
racism came into play. there were settlement houses, tenements, and separate neighborhoods based off of race. worked for a cheaper cost making things a lot cheaper. larger work forces. americans cry for the jobs that they don't want. many unskilled workers went to the cities. those with skills came more westward/midwest
what was the basis for the conflict between white settlers, indians, and mexican americans?
they all wanted gold. white settlers would enter native and mexican american land just to settle there and take up all the gold. once the gold was gone, they left. examples of this is pikes peak, california gold rush, and cornstocke lode. mexicans lost a lot of land, so they went to california, but they were still considered citizens.`
in what ways did the government fail in the treatment of the native americans?
the government basically culturally raped them and forced their assimilation. with the dawes act, they really effed them over by making reservations of land when they liked to share. century of dishonor by helen hunt jackson spread around which showed injustice of natives, so cleveland passed the dawes severalty act thinking that he was doing the right thing.
in what ways did the federal government and the supreme court support jim crow laws
in the plessy v ferguson case, the government ruled "separate, but equal." so segregation was okay guys