UCF FIN3403 - Exam #3, Chapter 9
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Assets
(Investment Decision)
Current Assets
Fixed Assets
Liabilities and Equity
(Financing Decision)
Current Liabilities
Long-term debt
Preferred Stock
Common Equity
Capital Structure
Long-term debt
Preferred Stock
Common Equity
Cost of Capital for Investors
For Investors, the rate of return on a security is a benefit of investing.
Ex. Investor with making 3% interest in the bank.
Cost of Capital
The cost of raising funds is the firm’s cost of capital.
Firms cost of long-term funds.
Cost of Capital for Financial Managers
That same rate of return is a cost of raising funds that are needed to operate the firm.
Ex. Bank having to pay 3% interest to hold money.
How can the firm raise capital?
Bonds
Preferred Stock
Common Stock
Each of these offers a rate of return to investors.
This return is a cost to the firm.
“Cost of capital” actually refers to the weighted cost of capital - a weighted average cost of financing sources.

Cost of Debt for the Issuing Firm
For the issuing firm, the cost of debt is:
the rate of return by investors, adjusted for flotation costs (any costs associated with issuing new bonds), and adjusted for taxes.
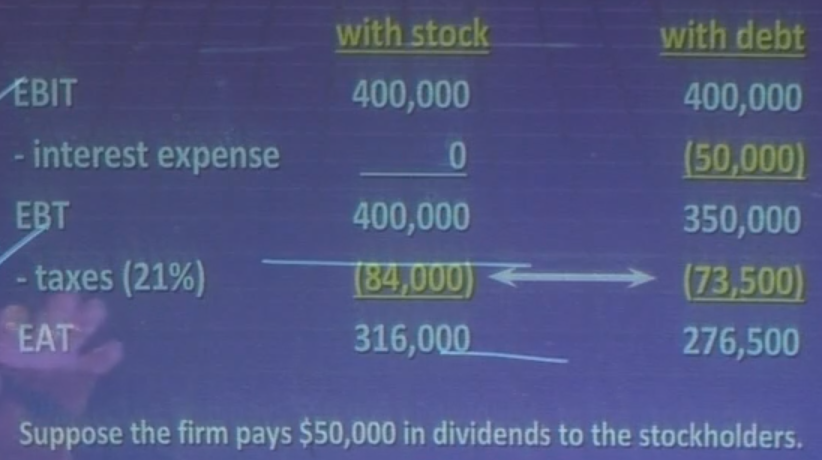
Tax Effects of Financing with Debt Example
With Stock
EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes): $400,000
- Interest Expense: $0.00
EBT (earnings before taxes): $400,000
- Taxes (21%): $84,000
EAT (earnings after taxes): $316,000
With Debt
EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes): $400,000
- Interest Expense: ($50,000)
EBT (earnings before taxes): $350,000
- Taxes (21%): $73,500
EAT (earnings after taxes): $276,000
With Stock and Dividend Payment
EBIT (earnings before interest and taxes): $400,000
- Interest Expense: $0.00
EBT (earnings before taxes): $400,000
- Taxes (21%): $84,000
EAT (earnings after taxes): $316,000
- Dividends: ($50,000)
Retained Earnings: $266,000
Kd
After-tax % cost of debt
kd
Before-tax % cost of debt
T
Marginal tax rate
After-Tax % Cost of Debt Problem Simple
Before tax is 10% and Marginal Tax rate is 21%
Kd = kd (1 - T)
Ex. 0.079 = 0.10 (1 - 0.21)
After-Tax and Before-Tax Cost of Debt Problem
Prescott Corporation issues a $1,000 par, 20 year bond paying the market rate of 10%. Coupons are semi-annual. The bond will sell for par since it pays the market rate, but flotation cost amount to $50 per bond.
Before-Tax % Cost of Debt
Financial Calculator: P/Y: 2, PMT: -50 (flotation), FV = -1000, PV = 950, N = 40, I/YR = ???
I/YR = 10.61%
After-Tax % Cost of Debt
Kd = kd (1 - T)
Kd = 0.1061 (1 - 0.21)
Kd = 8.4%
Kps
Cost of Preferred Stock
D
Dividend
NPnull
NPnull = price - flotation costs (net price)
Cost of Preferred Stock for Firms Problem
If Prescott Corporation issues preferred stock, it will pay a dividend of $8 per year and should be valued at $75 per share. If flotation costs amount to $1 per share, what is the cost of preferred stock for Prescott?
Kps = D / NP0
Kps = 8 / (75 - 1) = 8 / 74 = 10.81%

Are preferred stock dividends tax deductable?
Nope! Paid out of earnings after taxes.
Cost of Common Equity
Has internal (retained earnings) and external costs (common stock). Opportunity cost with retained earnings.
Cost of Internal Equity
Since the stockholders own the firm’s retained earnings, the cost is simply the stockholders’ required rate of return. Two ways to solve:
1. Dividend Growth Model (Expected return formula)
Kc = (D1 / Pnull) + G
2. Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
Kj = Krf + Bj (Km - Krf)
Cost of External Equity
Dividend Growth Model (Expected return formula)
Knt = (D1 / NP0) + g
Weighted Cost of Capital
The weighted cost of capital is just the weighted average cost of all of the financing sources.
Weighted Cost of Capital Balance Sheet Problem
Source Cost Structure
debt 6% 20%
preferred 10% 10%
common 16% 70%
debt: 0.06 × 0.20 = 0.012
preferred: 0.10 × 0.10 = 0.01
common: 0.16 × 0.70 = 0.112
0.112 + 0.01 + 0.012 = 13.4%
Look to invest in projects that yield a higher return.
Weighted (marginal) Cost of Capital Pre-Tax Problem
Bendex Corporation has a capital structure consisting of 40% debt and 60% equity. The firm is planning to raise $25 million to finance its capital investment projects.
Bendex can raise debt funds through bank loans at a pretax cost of 6%. A bond issue would have a pretax cost of 8%. Bendex’s common stock dividend is presently $2 per share. Bendex common is selling now for $50 per share. New common stock could be sold for $50 per share. Flotation costs would amount to $4.00 per share.
Over the past several years, Bendex’s earnings and dividends have grown at an average of 7% per year, and this growth rate is expected to continue for the foreseeable future. Bendex has a tax rate of 21%.
Given this information, calculate Bendex’s weighted (marginal) cost of capital.
Step 1: Financing mix?
60% equity and 40% debt.
Step 2: Costs of individual Sources of Funds
Debt: Cost of Bonds and Loans
Kd = kd (1 - T)
Kd = 0.06 (1 - 0.21) = 4.74% bank loans
Kd = 0.08 (1 - 0.21) = 6.32% for bonds
Equity: Cost of Internal and External
Find D1: D1 = D0 (1 + g)
Internal: Kc = (D1 / P0) + g —> (2.14 / 50) + 0.07 = 11.28%
External: Knc = (D1 / NP0) + g —→ (2.14 / 50-4) + 0.07 = 11.65%
Step 3: Marginal Cost of Capital
Using bank loans and internal equity: (0.4 × 4.74%) + (0.6 × 11.28%) = 8.66%
Using bonds and external equity: (0.4 × 6.32%) + (0.6 × 11.65%) = 9.52%
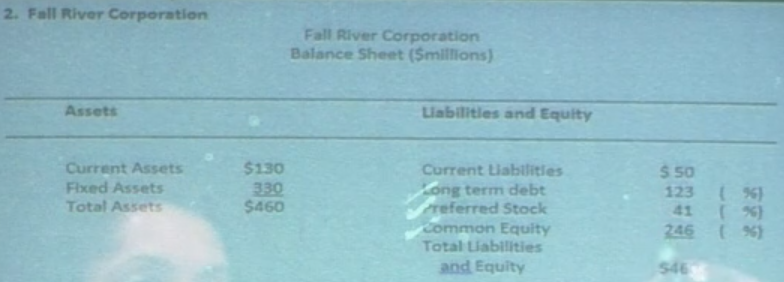
Weighted Cost of Capital Without Weights Given
Fall River can borrow funds from its bank at a pretax cost of 6.5%. Additional debt can be raised by selling bonds. The 20-year, $1,000 par value bonds would have an 8.5% coupon rate and semi-annual coupons. The bonds would sell for par value, but flotation costs would amount to 6%. Fall River’s tax rate is 21%.
Fall River can sell $100 par value preferred stock with a 9% dividend rate. The stocks would sell for par value and flotation costs would amount to 6%.
Fall River’s common stock dividend at the end of the year is expected to be $2.40 per share. This $2.40 dividend represents a growth rate of 6 percent over the previous year’s dividend. This growth rate is expected to continue. Fall River common stock is selling now for $50 per share. Flotation costs of $4 per share could be expected for any new issues of common stock.
Step 1: Financing mix?
Debt: 123/410 = 30%
Preferred Stock: 41/410 = 10%
Equity: 246/410 = 60%
Step 2: Costs of individual Sources of Funds
Debt: Cost of Bonds and Loans
Kd = kd (1 - T)
Kd = 0.065 (1 - 0.21) = 5.14% bank loans
Bonds: P/Y = 2, N = 40, FV = -1000, PMT = -42.50, PV = 940, I/Y?
9.16%
Kd = kd (1 - T) = 0.0916 (1 - 0.21) = 7.24% bonds
Cost of Preferred Stock
Kp = (D/NP0) = 0.09 / (100 - 6) = 9.57%
Equity: Cost of Internal and External
Find D1: D1 = D0 (1+g)
Internal: Kc = (D1 / P0) + g —→ (2.40) / 50) + 0.06 = 10.8%
External: Knc (D1 / NP0) + g —→ (2.40 / 46) + 0.06 = 11.22%
Find WACC using loans, preferred and internal equity:
(0.30 × 5.14%) + (0.10 × 9.57%) + (0.60 × 10.80%) = 8.98%