Intro to Human Nutrition
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Nutrition
The science that studies how food, beverages, and their components affect the body through digestion, absorption, metabolism, and health
Nutrient
a substance that performs a necessary function in the body
Micronutrients
types of nutrients needed in smaller amounts for the body, like vitamins and minerals.
Macronutrients
various types of nutrients needed in larger amounts for the body, like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and water.
carbohydrate (hydrated carbon, or carbon with water)
a macronutrient that provides energy, primarily in the form of sugars and starches. They are digested to be broken down into glucose, the primary energy source. Some carbs, like fiber, are not fully digested.
Simple carbs
Monosaccharides provide a simple unit of sugar, like Glucose, Fructose, Galactose, Dextrose
Double carbs
Disaccharides provide 2 units of sugar, like Lactose, Sucrose, Maltose
Complex carbs
Oligosaccharides (3-10 units) and Polysaccharides are long chains of sugar molecules, like Cellulose, Starch, Glycogen
Proteins (Macro)
Large, complex molecules made up of smaller units called amino acids (chain of 20). They build and repair muscles, skin, and organs, make enzymes and hormones, support the immune system (like antibodies), transport molecules (like hemoglobin carries oxygen). They’re made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and nitrogen.
Lipids (Macro)
types of biological molecule that is not soluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents (like alcohol or chloroform). Lipids are essential to life and play several important roles in the body.
Non-polar solvents
liquids that do not have positive and negative charges separated (no poles) — meaning their molecules share electrons more evenly. This makes them hydrophobic, or “water-hating,” just like lipids.
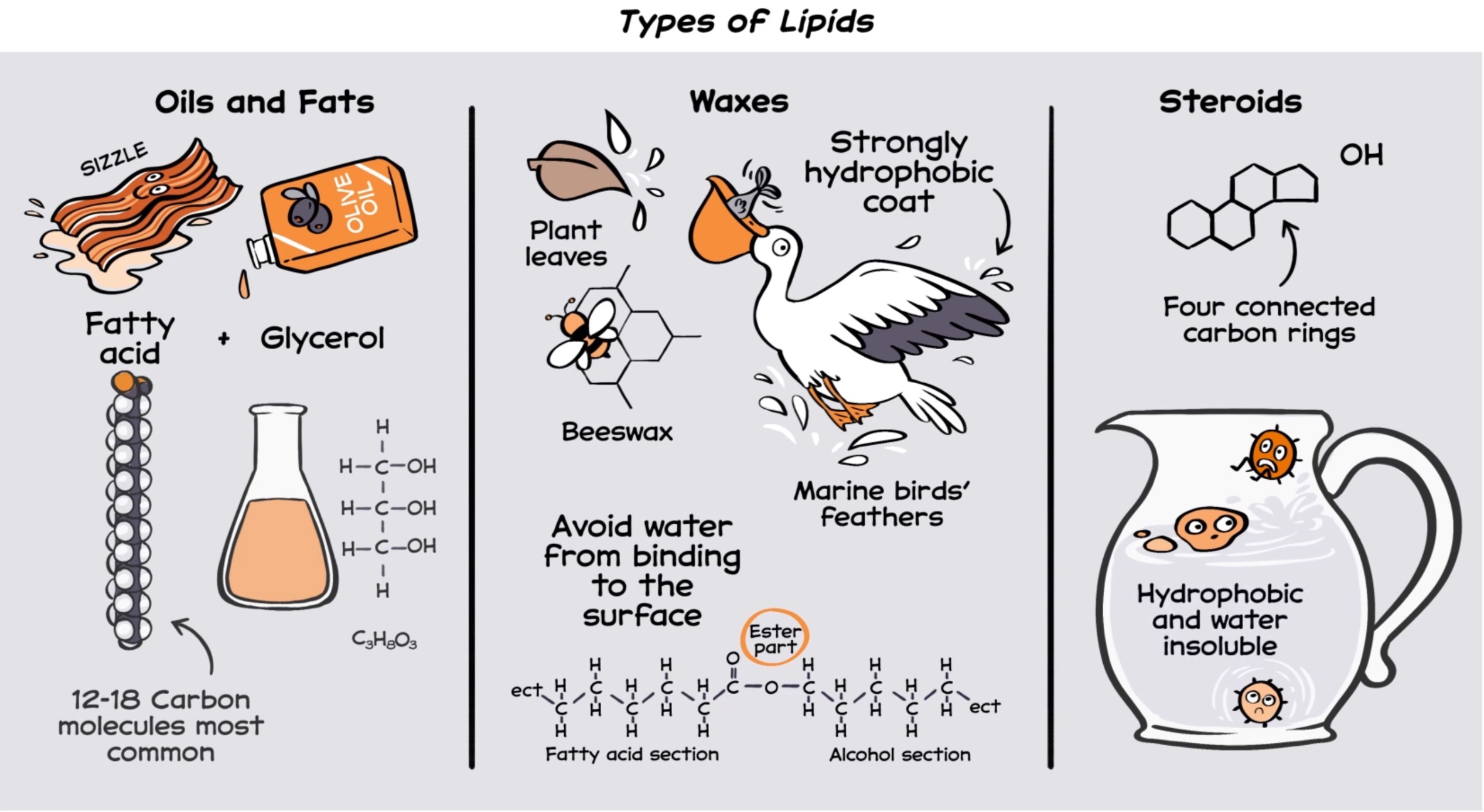
Common Types of Lipids
*Fats and oils (triglycerides) – used for long-term energy storage.
*Phospholipids – major components of cell membranes. Protects a cell from outside intrusion.
*Steroids – like cholesterol (found only in animal fats), cortisol and hormones (e.g., estrogen, progesterone, testosterone). They do not contain fatty acids.
*Waxes – found in plants and animals for protection and waterproofing.
Common Non-polar Solvents
Hexane — Used in oil extraction from seeds
Chloroform — Used in labs (not common for home use)
Benzene — Used in industrial chemistry (toxic)
Ether — Used in labs and some medical settings
Toluene — Found in paint thinners
Oil — Natural example — cooking oils are non-polar
Triglycerides
comprises a glycerol (a type of alcohol) and three fatty acids. It include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (vegetable oils, fish oils and nuts), known as the healthier fats.
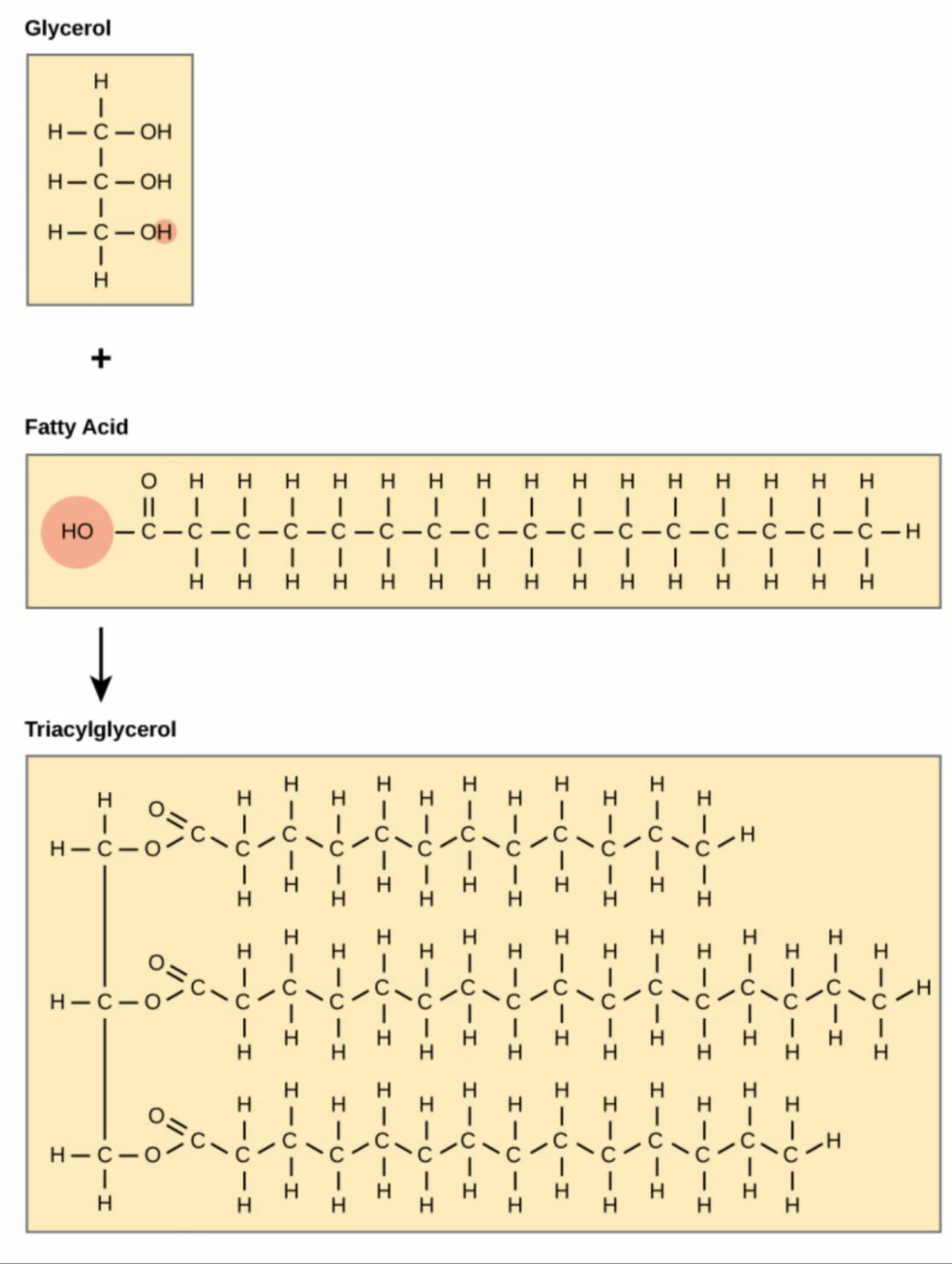
Fatty acid
an organic compound linking a fatty chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms on one end to an acid group at the other. They can be saturated, unsaturated, trans fats, or omega fatty acids (fish oils, some nuts oils). They (linoleic and linolenic) assist in absorbing and transporting fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Purposes of triglycerides
supplying energy, protecting against temperature extremes and shock, and helping the body use carbohydrates and protein efficiently
Difference between carbs and lipids
Carbs are water soluble and are great for short-term energy storage. Lipids are water insoluble and are great for long-term energy storage.
Fats and oils (triglycerides)
Fats provide more than twice the energy of carbohydrates and proteins. Most unhealthy fats are solid at room temp and used by animals for insulation, protection and long-term energy storage. Fats also give the body its shape and insulate it, assisting in maintaining body temperature. Oils are unsaturated fats and liquid at room temp and used by plants for long-term energy storage.
Healthy fats
They tend to be liquid at room temperature, so most oils are part of the unsaturated fats group. Monounsaturated fat and polyunsaturated fat are known to have the benefit of lowering blood cholesterol levels and combating other associated adverse outcomes of bad fats. Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation, which helps decrease cholesterol build-up in artery walls and pain from arthritis.
Phospholipids
Essential molecules that act as the building blocks of cell membranes, allowing cells to function and interact with their environment. They have a unique structure that makes them ideal for forming membranes: Head (made of a phosphate group, which is polar and hydrophilic) and Tails (made of two fatty acid chains, are non-polar and hydrophobic)
Steroids
lipids that share a common 4-ring carbon structure rather than chain-like. They are vital for: hormonal regulation, membrane structure, metabolism, reproduction
Types of Steroids
Cholesterol, Steroid Hormones, Vitamin D, Anabolic Steroids
Cholesterol
Most basic and essential steroid. It helps maintain cell membrane fluidity and stability and serves as a precursor for other steroids.
Steroid Hormones
Made from cholesterol and function as chemical messengers in the body. They are sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone) and corticosteroids (cortisol - regulates stress and metabolism, aldosterone - controls salt and water balance)
Vitamin D
A steroid derivative involved in calcium absorption and bone health.
Anabolic Steroids
Synthetic variants of testosterone, and used to build muscle mass but can have serious side effects when abused
Waxes
a type of lipid made up of long-chain fatty acids combined with long-chain alcohols or other hydrocarbons. They are hydrophobic, solid at room temperature, and protective and moisture-resistant. They are found in nature (plants, animals) and many human-made products
Functions of waxes
They are found on leaves, stems, and fruits as a cuticle (waxy coating) and they help prevent water loss and protects from insects or pathogens. Bees produce beeswax to build honeycombs. Earwax (cerumen) in humans protects the ear canal. Some birds and mammals secrete waxes to waterproof fur or feathers. They are also found in candles, polishes, cosmetics, food coatings
Linoleic acid
Omega-6 fatty acid and is important for cell membranes, helps with skin health and healing, can convert to arachidonic acid (found in animal products and vegetable oils), which can produce inflammatory compounds. They are found in vegetable oils (sunflower, corn, soybean, safflower), nuts, seeds.
Linolenic acid
Omega-3 fatty acid and is anti-inflammatory, can convert to EPA and DHA (beneficial omega-3s found in fish), supports heart, brain, and immune function. They are found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, leafy greens.
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
key types of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and it anti-inflammatory, supports heart health, reduces blood clotting, improves mood. It helps lower triglycerides, supports mental health (can reduce symptoms of depression), regulates the body’s inflammatory response. It is found in fatty fish (like salmon, sardines, mackerel), algae oil.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
key types of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and is good for Brain development, eye health, memory, and nervous system function. It is crucial for babies' brain and eye development, makes up a large part of the brain and retina, supports brain function and reduces age-related cognitive decline. It is found in fatty fish (like salmon, sardines, mackerel), algae oil.