Embryo: Week 3, Embryonic, and Fetal Periods
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
why is the 3rd week called the week of 3's?
(1) 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
(2) 3 cavities (amnion, yolk sac, chorion)
(3) 3 layered villi (syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, extraembryonic mesoderm)
3 germ layers
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
3 cavities
amnion
yolk sac
chorion
3 layers of villi
syncytiotrophoblast
cytotrophoblast
extraembryonic mesoderm
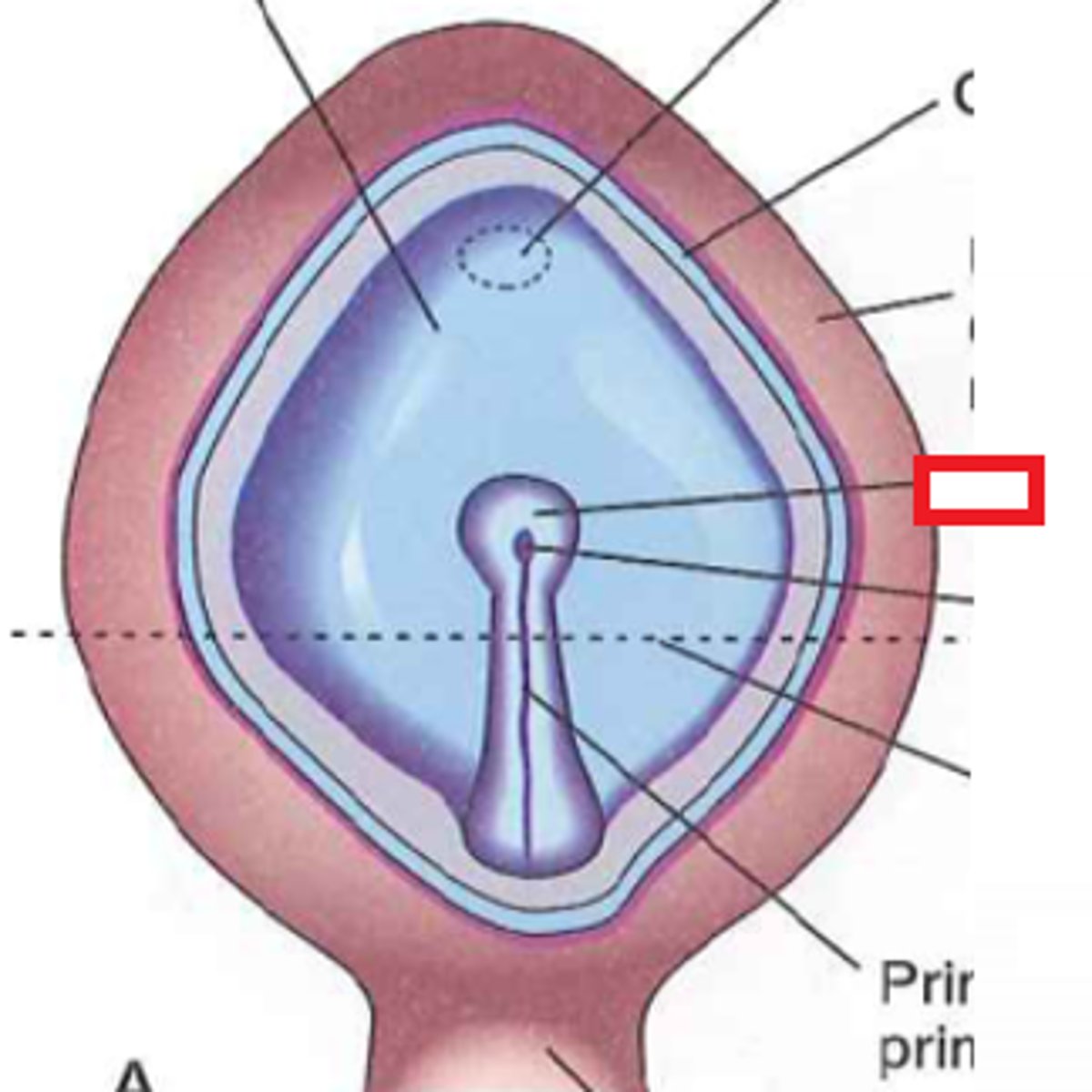
primitive streak
indentation into epiblast on dorsal side of embryo
primitive pit
Depression in primitive node
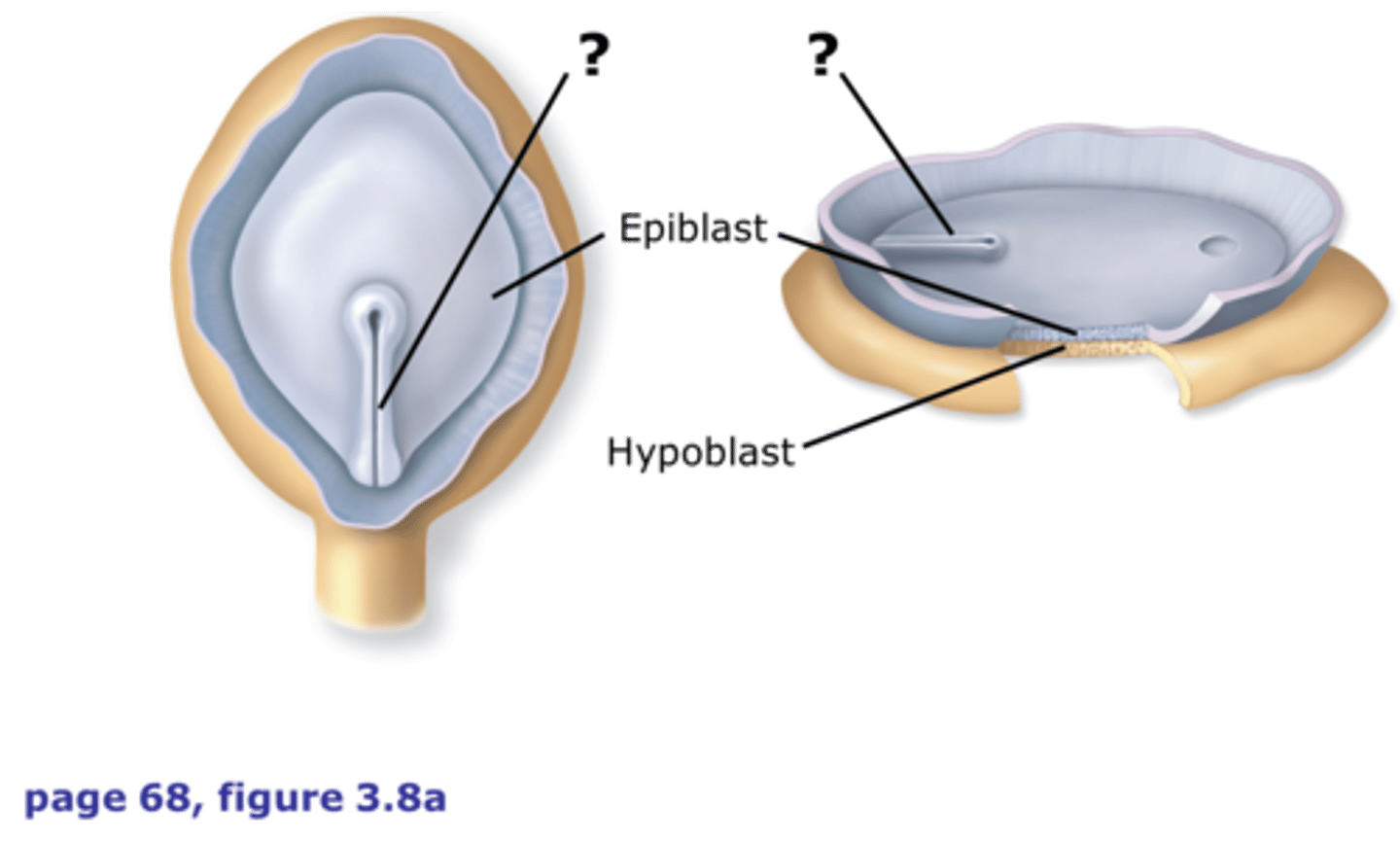
what do the following determine in the axes?
(1) epiblast cells
(2) hypoblast cells
(3) primitive streak
(4) primitive pit
(1) dorsal
(2) ventral
(3) caudal
(4) cranial
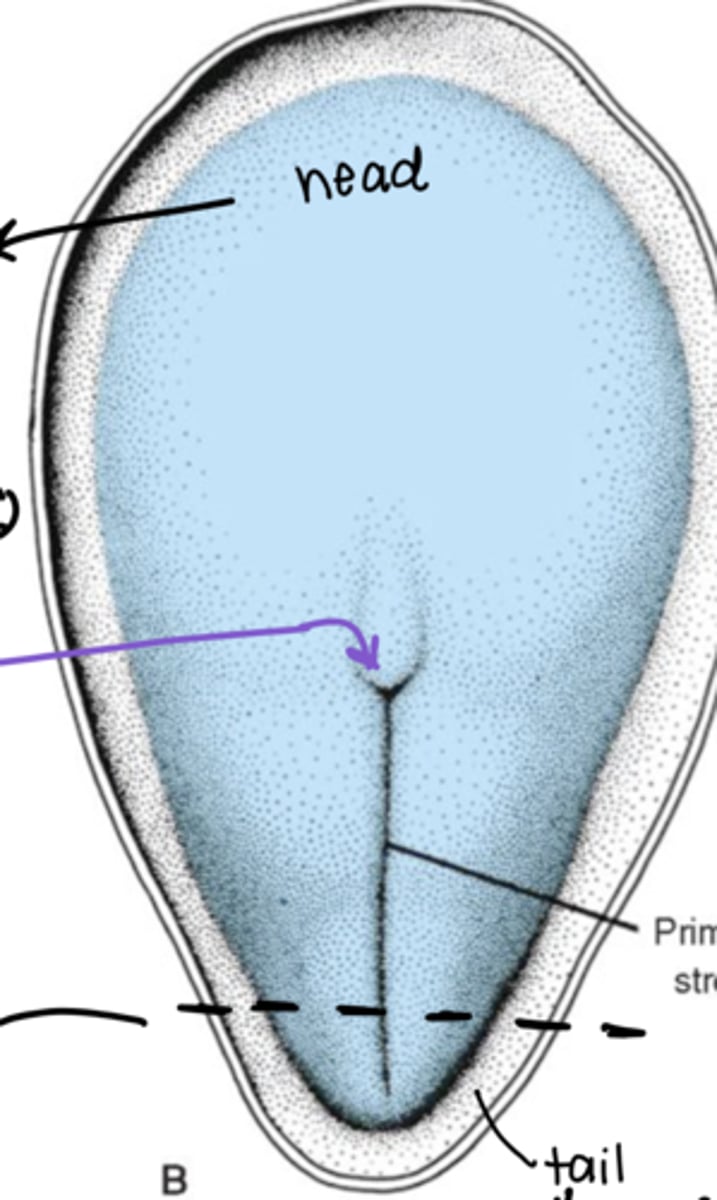
what happens to the hypoblast during gastrulation?
it disappears
all germ layers stem from the _____ in the embryoblast
epiblast
what is the fate of the first cells to "dive" into the primitive streak?
endoderm
what is the fate of the second cells to "dive" into the primitive streak?
mesoderm
what is the fate of the cells that don't "dive" into the primitive streak?
ectoderm
steps in notochord formation:
(1) primitive pit forms (with primitive streak)
(2) "tunnels" through embryo to prechordial plate (head)
what is the "tunneling" structure called during neurulation?
notochordal plate
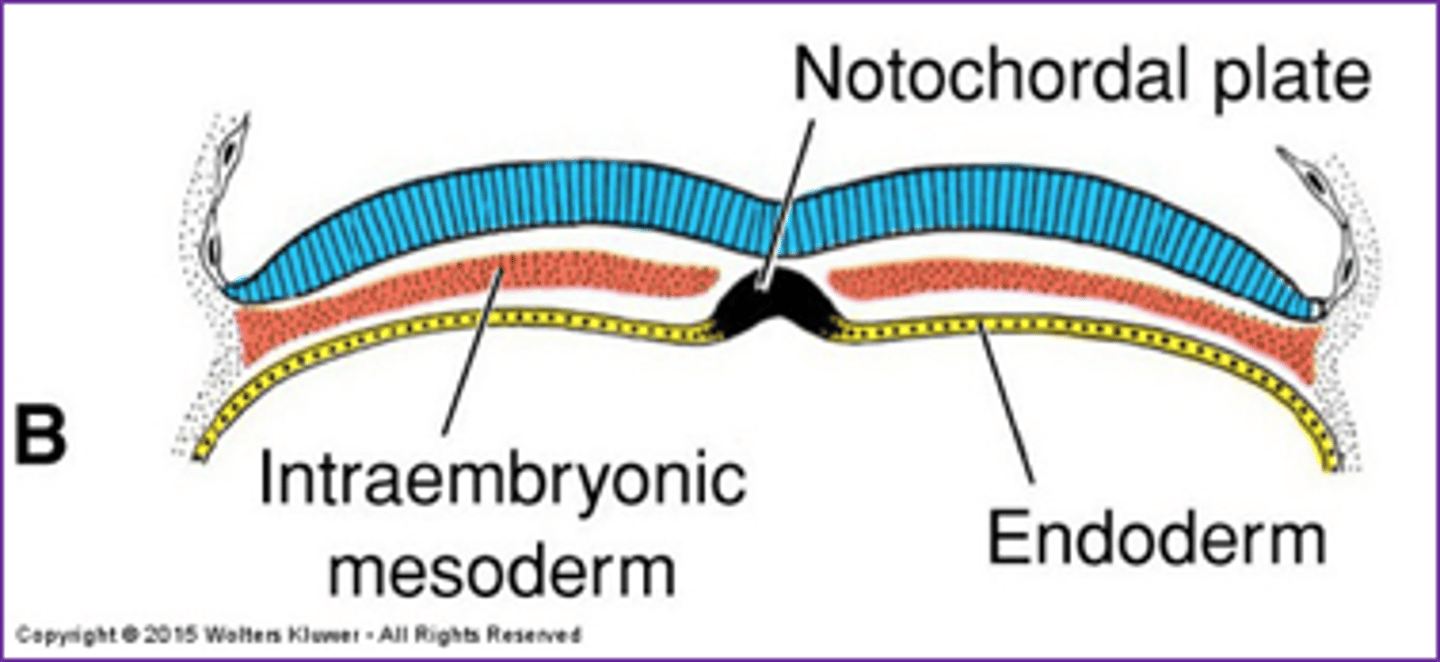
what germ layer(s) does the notochord stem from?
(1) endoderm
(2) mesoderm
what does the notochord become / influence?
(1) CNS
(2) vertebral column
(3) midline
(4) NUCLEUS PULPOSUS
NOTOCHORD FINAL FATE =
NUCLEUS PULPOSUS
neurenteric canal
connection between amniotic cavity and yolk sac at primitive pit
**"tunnel" from notochord formation
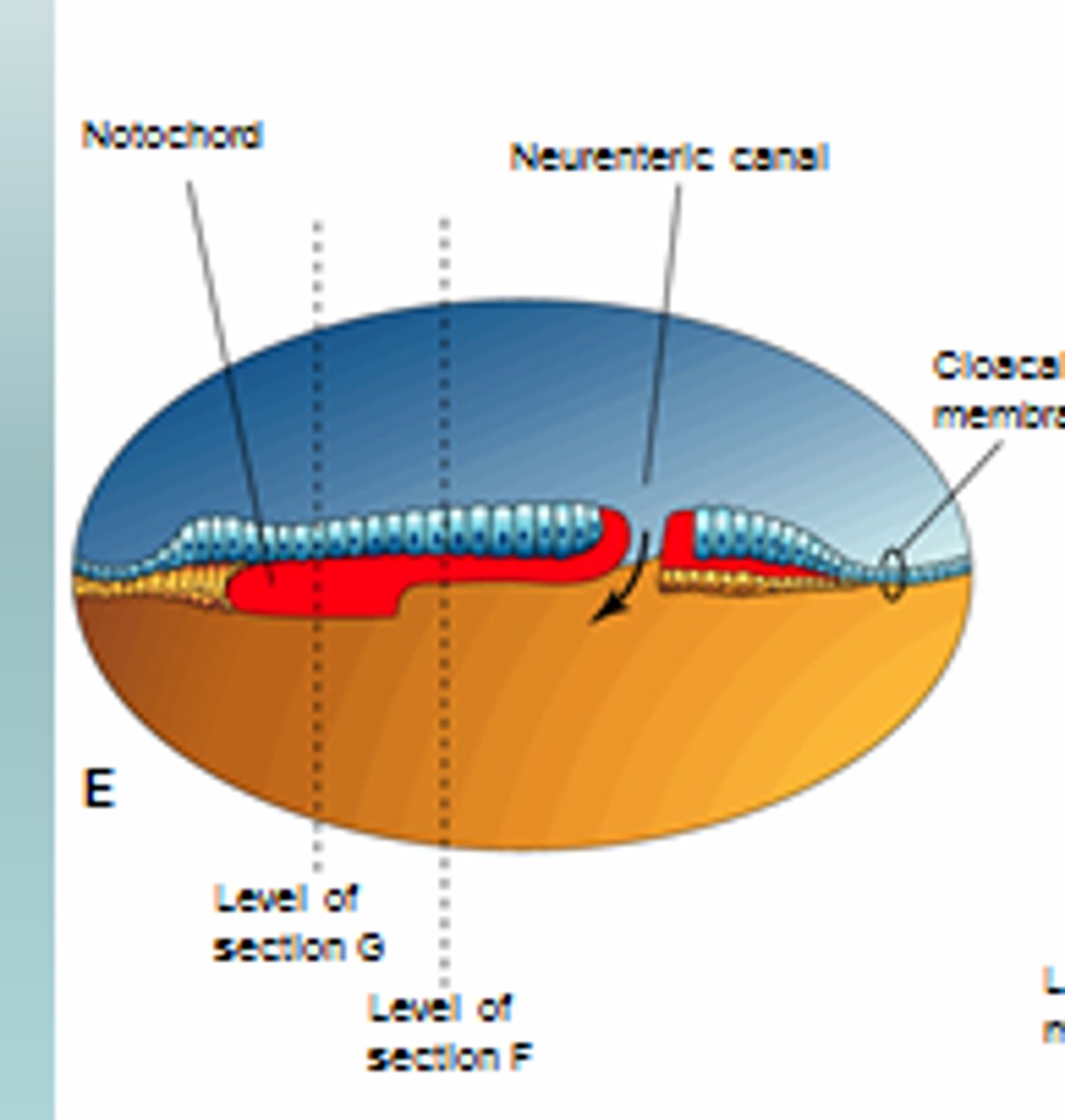
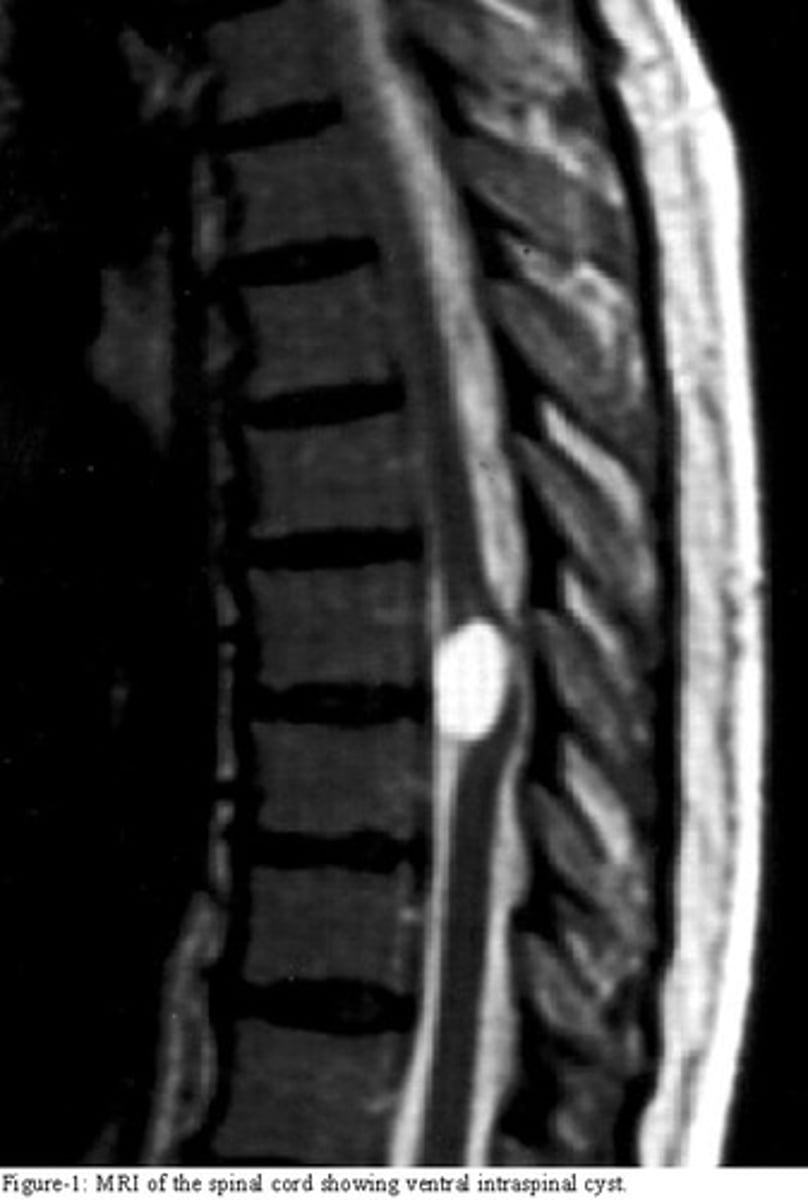
neurenteric cysts
masses of endodermally derived tissue commonly associated with the spinal cord; derived from the neurenteric canal where ectoderm and endoderm are closely associated
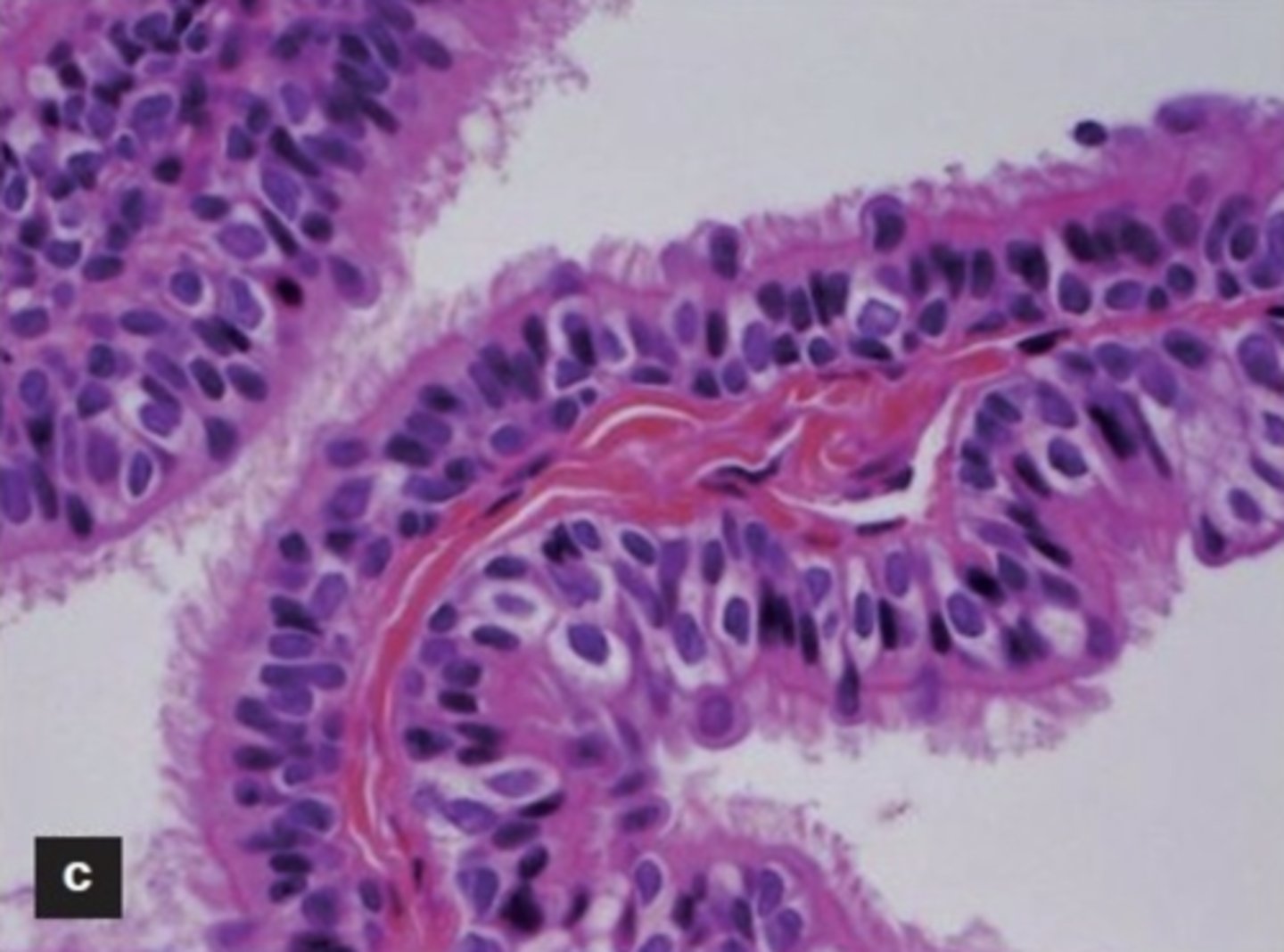
things from the neurenteric cysts article:
- columnar or cuboidal epithelium w/ or w/o cilia + mucus gobules
- surgical resection
- spinal cord tumors
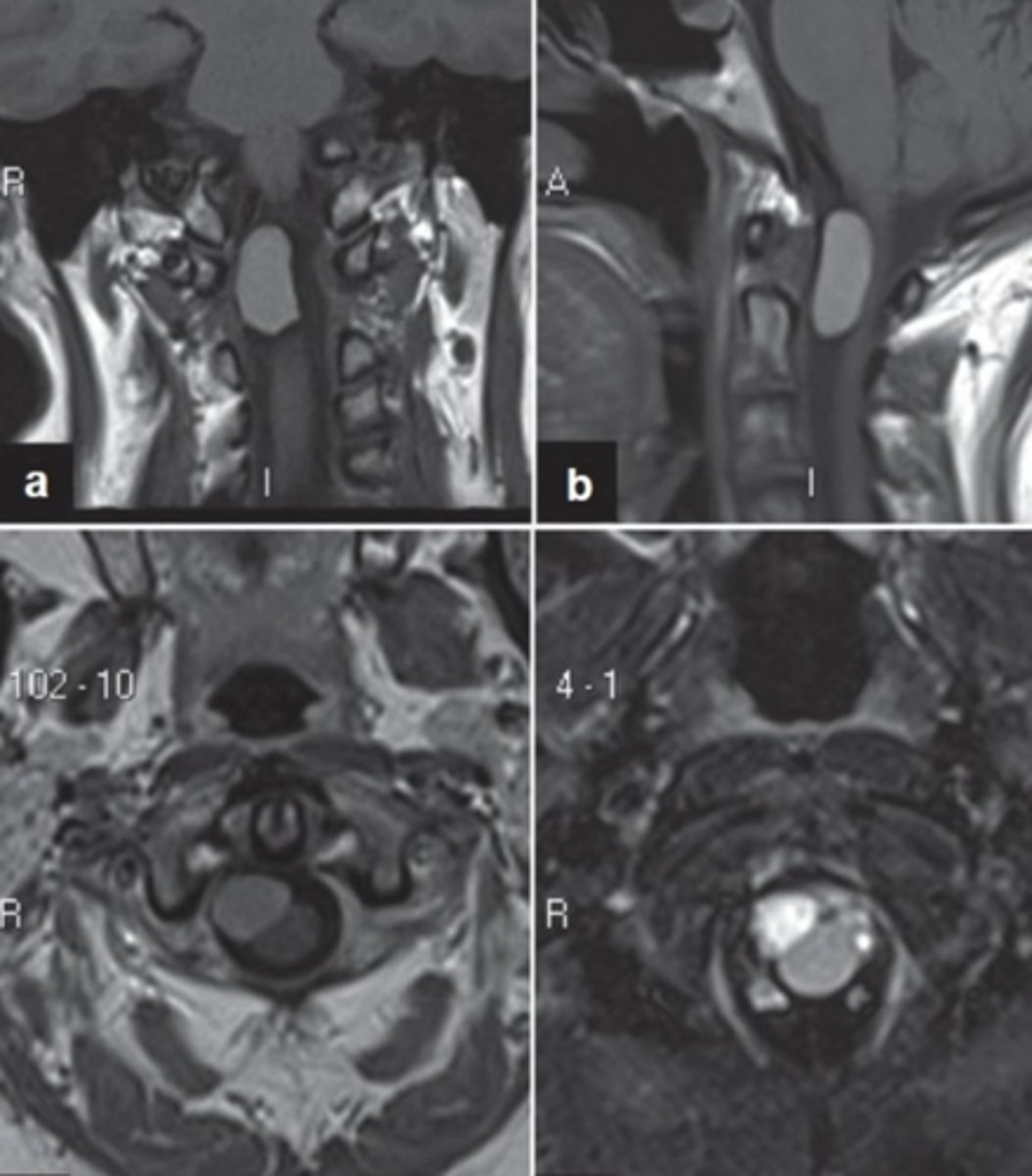
what is the characteristic epithelium shown in neurenteric cysts?
what type is shown in the image?
- columnar or cuboidal
- pseudostratified columnar
what does the image show?
neurenteric cyst
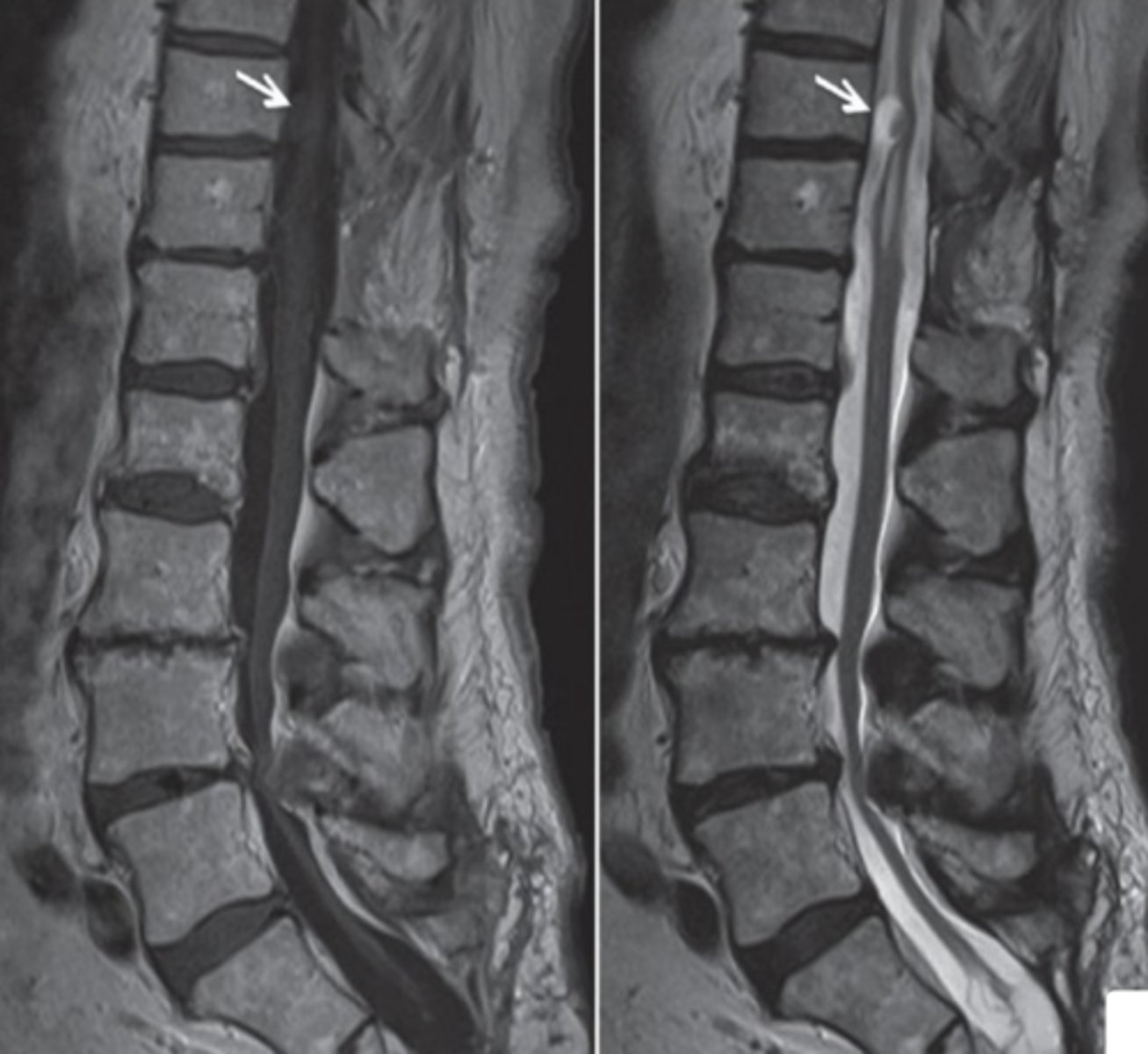
what do these images show?
neurenteric cyst
what are the stages of embryonic folding?
(1) longitudinal fold
(2) transverse fold
longitudinal fold
head and tail fold;
formation of primary curvature
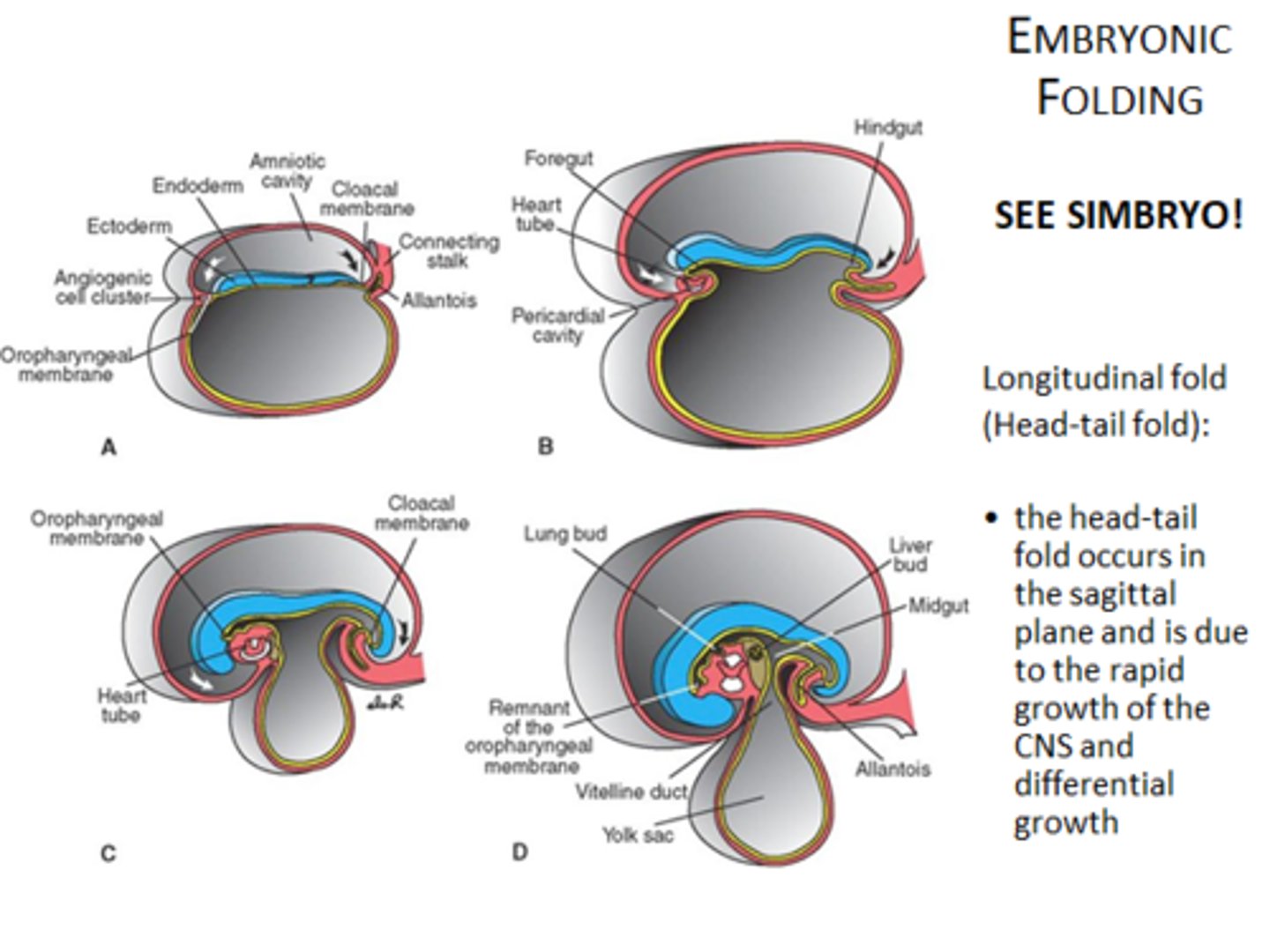
transverse fold
lateral edges of ectoderm fuse with each other ventrally
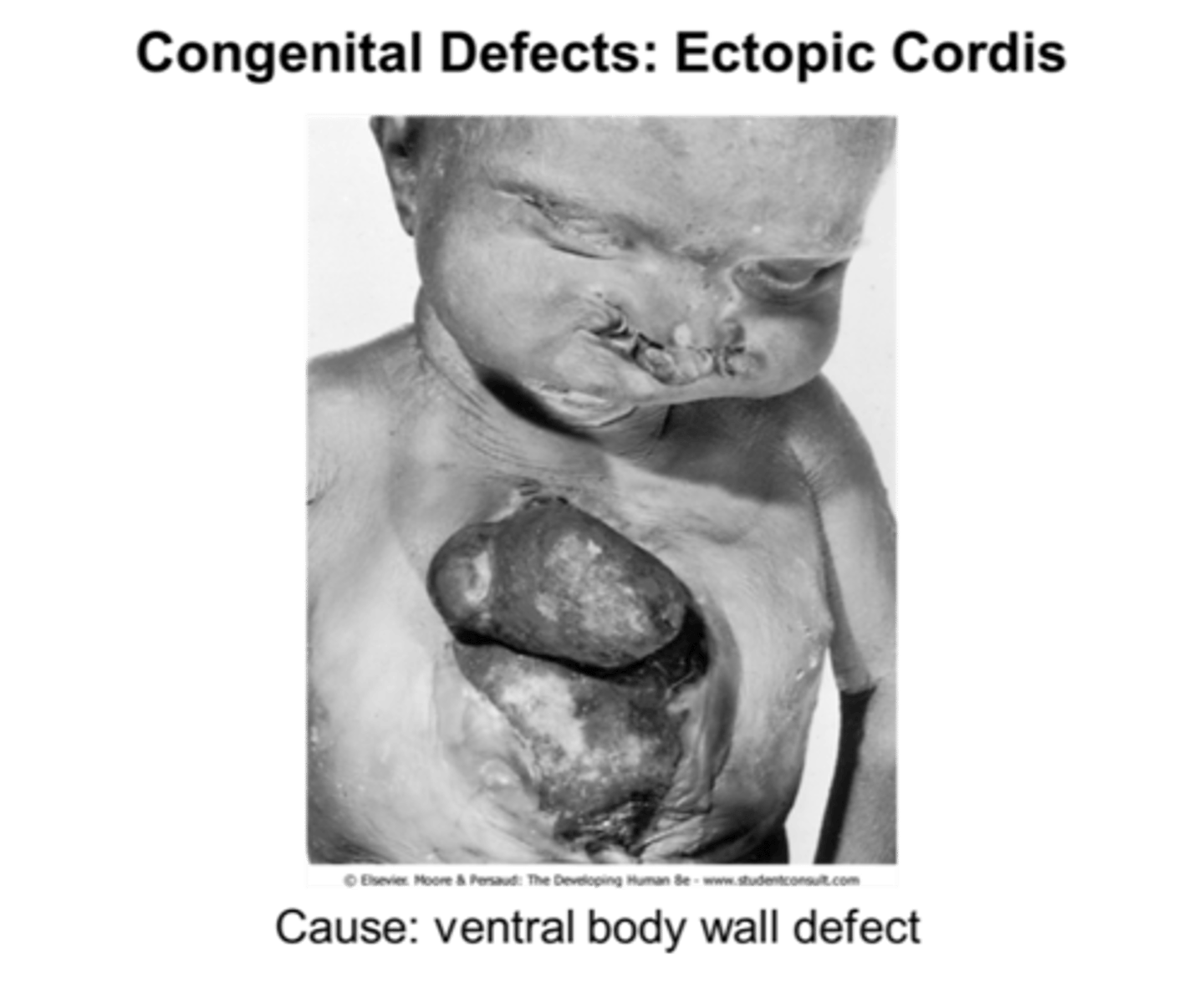
what would failure of transverse fold closure result in?
ectopic chordis (heart on exterior)
what is the result of embryonic folding?
closing of embryo... flat layers to 3 dimensional embryo
ectopia chordis
failure to close transverse fold -- heart on outside of body
KNOW THIS ORIENTATION
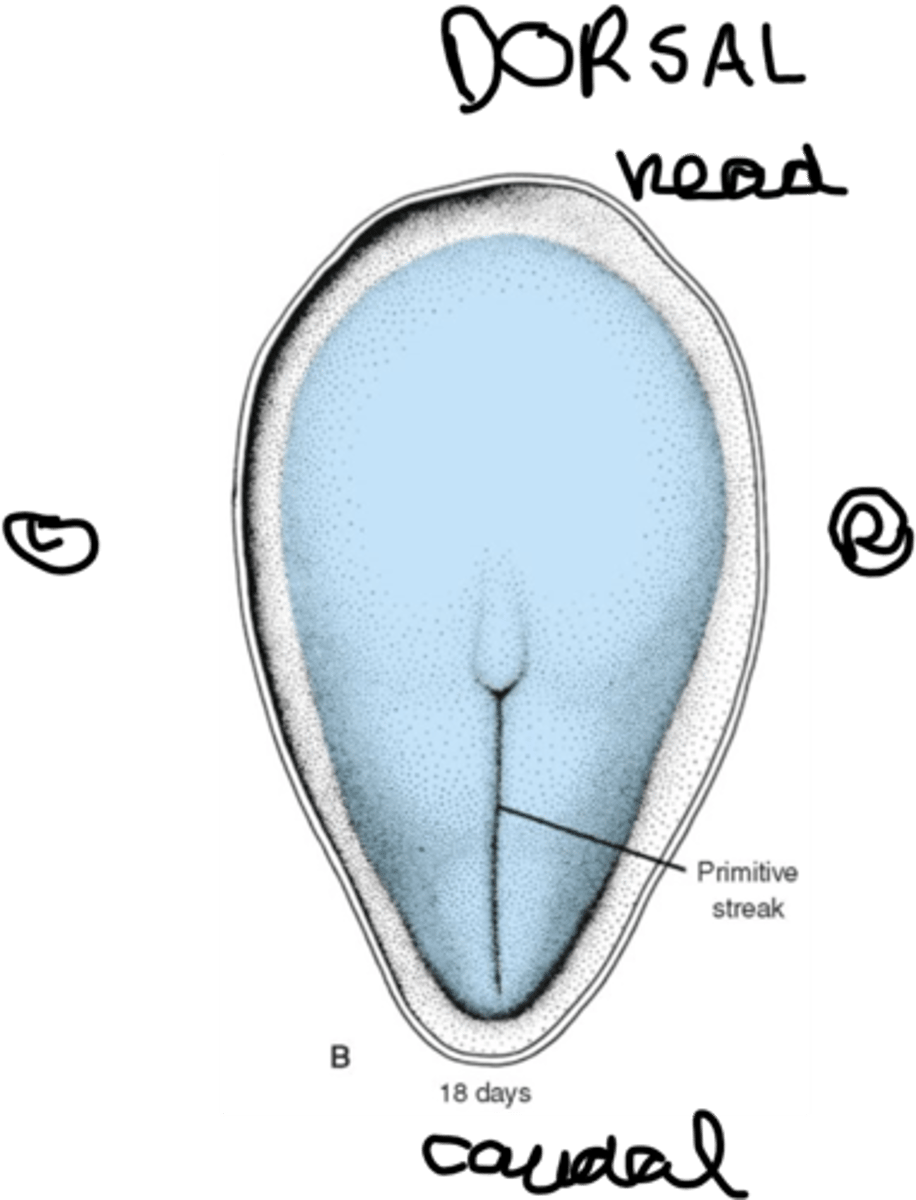
what is the order of events in the 3rd week?
(1) gastrulation (forming trilaminar embryo)
(2) notochord formation (via primitive streak + pit)
(3) neurulation (formation of neural tube)
(4) longitudinal + transverse folding (closes off embryo)
situs inversus
reversed position of organs caused by a defect in body axis development
- defective cilia
**respiratory infections + infertility
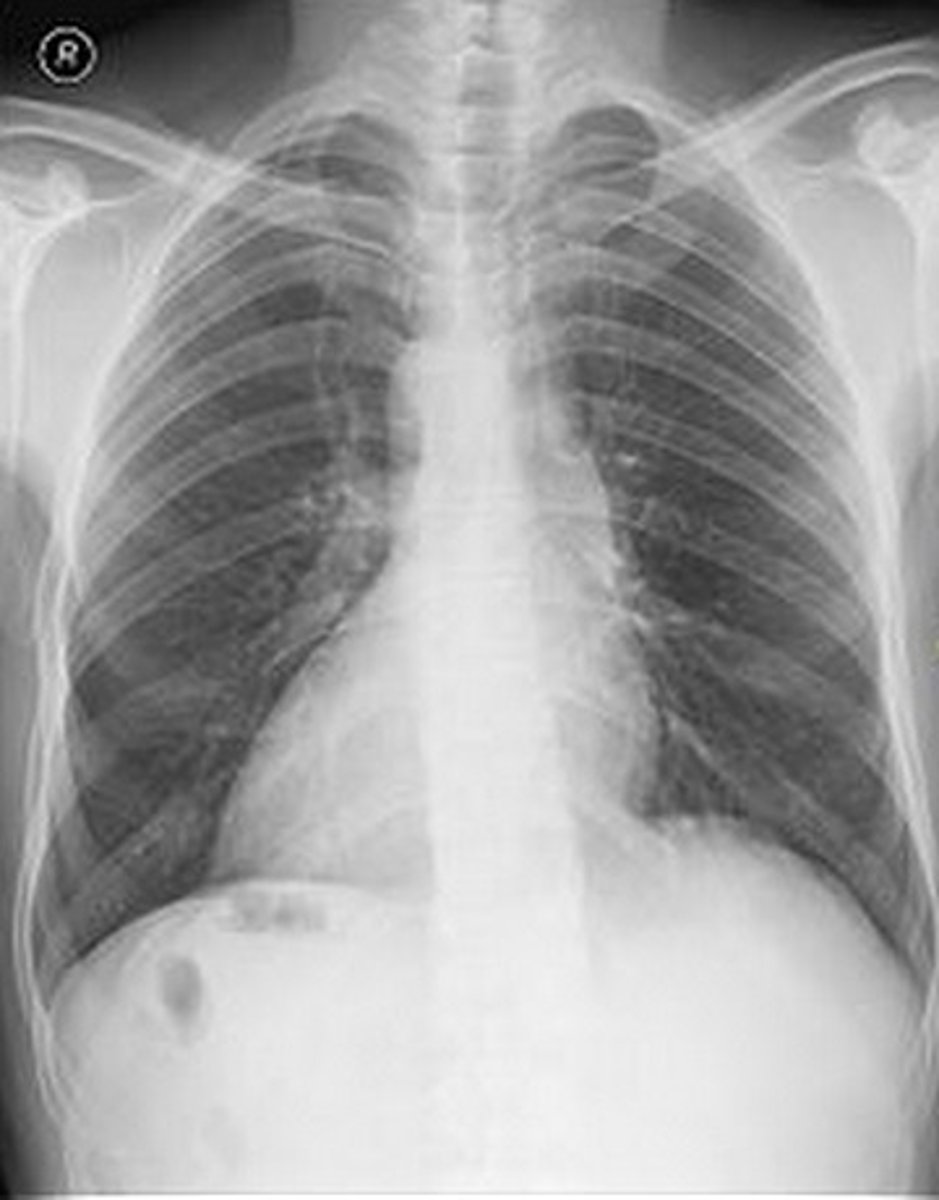
dextrocardia
heart displaced to the right caused by defect in body axis development
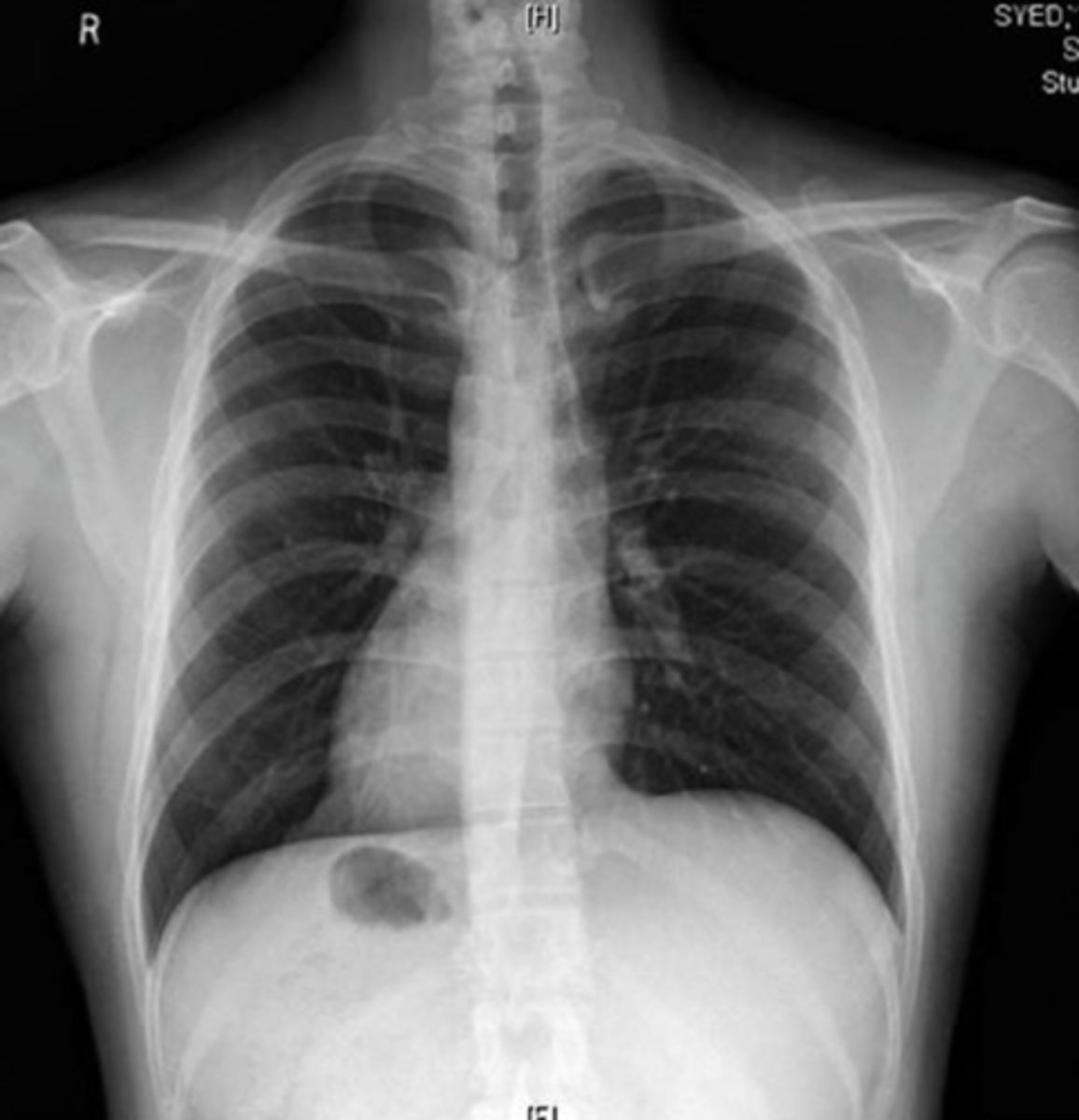
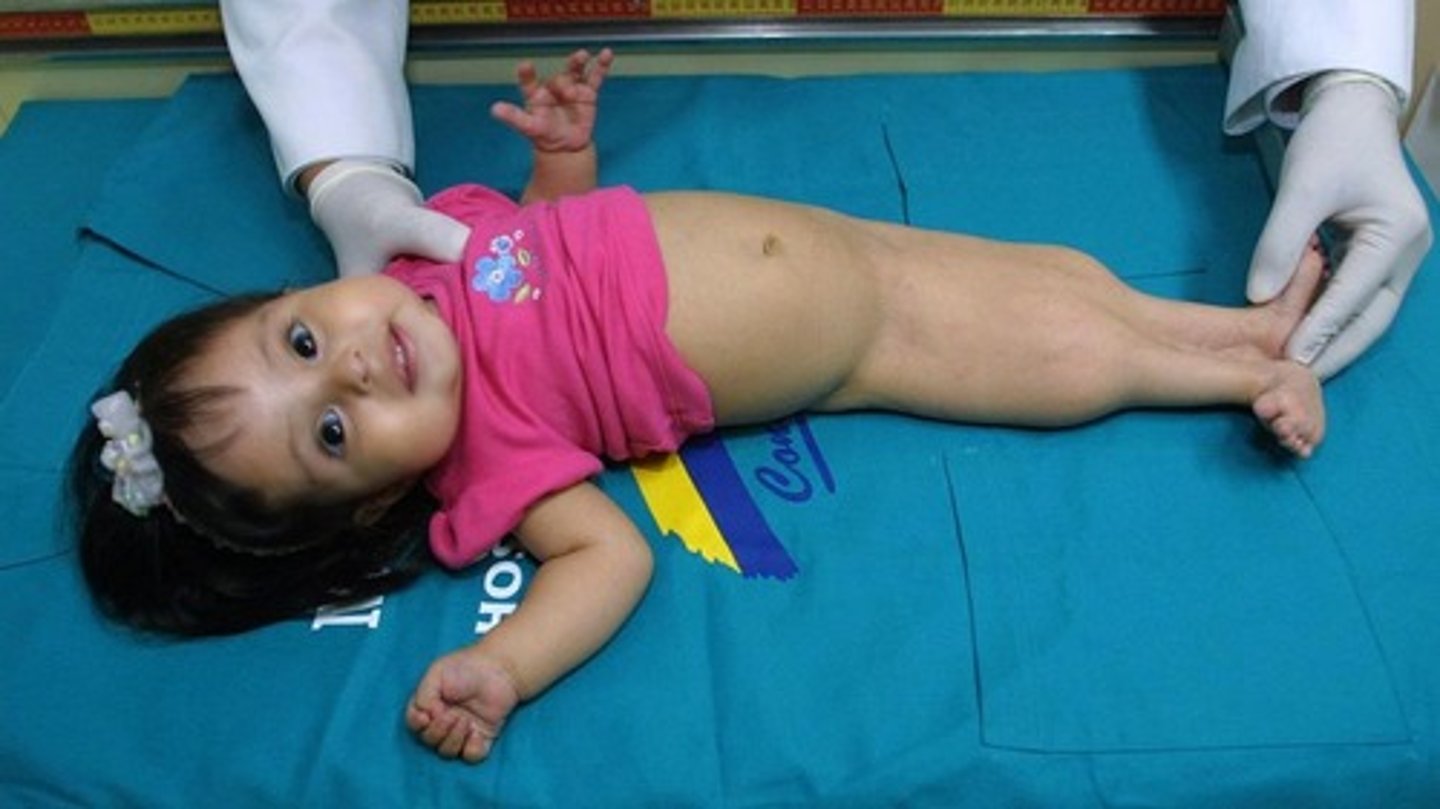
caudal dysgenesis
Insufficient mesoderm during gastrulation
Issues with formation of lower limbs
Sirenomelia - aka Mermaid syndrome
sirenomelia
fusion of hind limbs caused by caused by not having enough mesoderm??
**mermaid syndrome
what would you expect to see in a pre-natal history if a fetus has sirenomelia? why?
oligohydraminos -- not able to urinate the swallowed amniotic fluid
examples of midline defects
(1) incisors fused
(2) cyclopsia
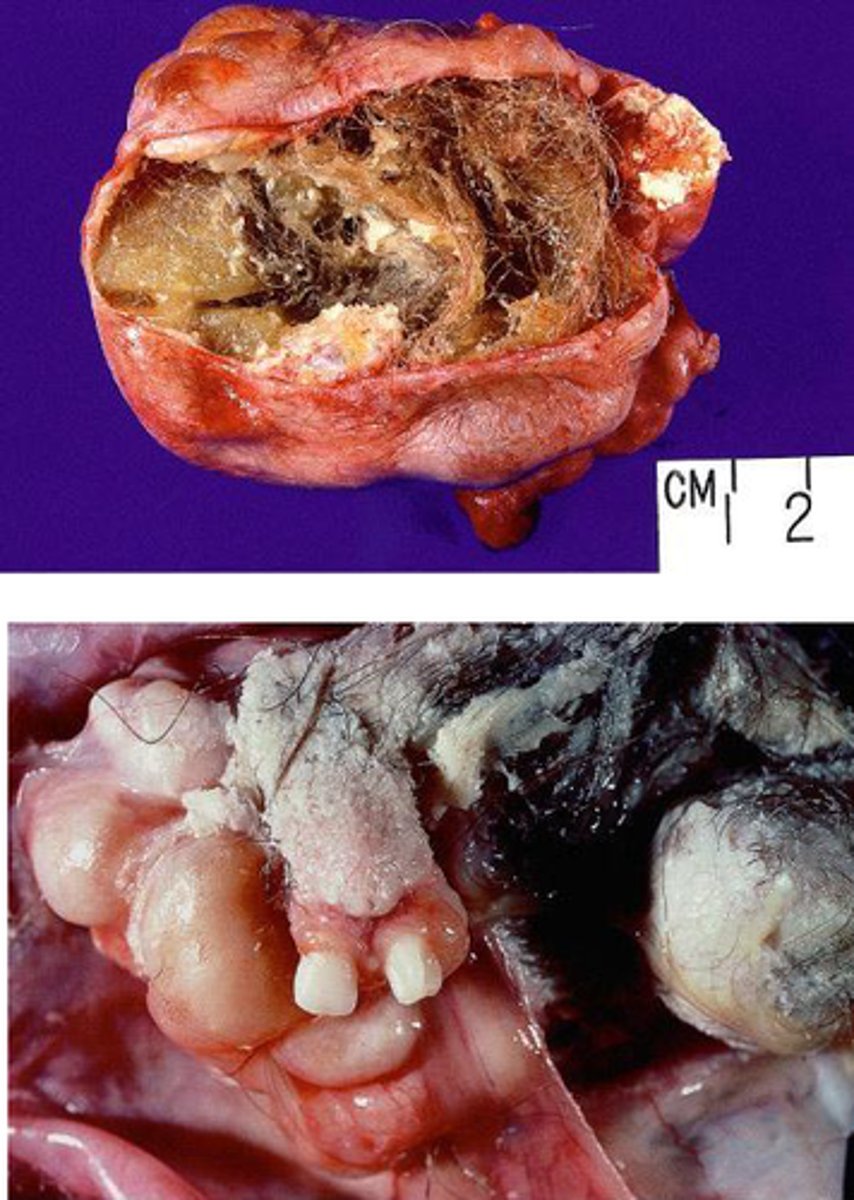
sacrococcygeal teratoma
mass derived from primitive streak -- ALL 3 GERM LAYERS
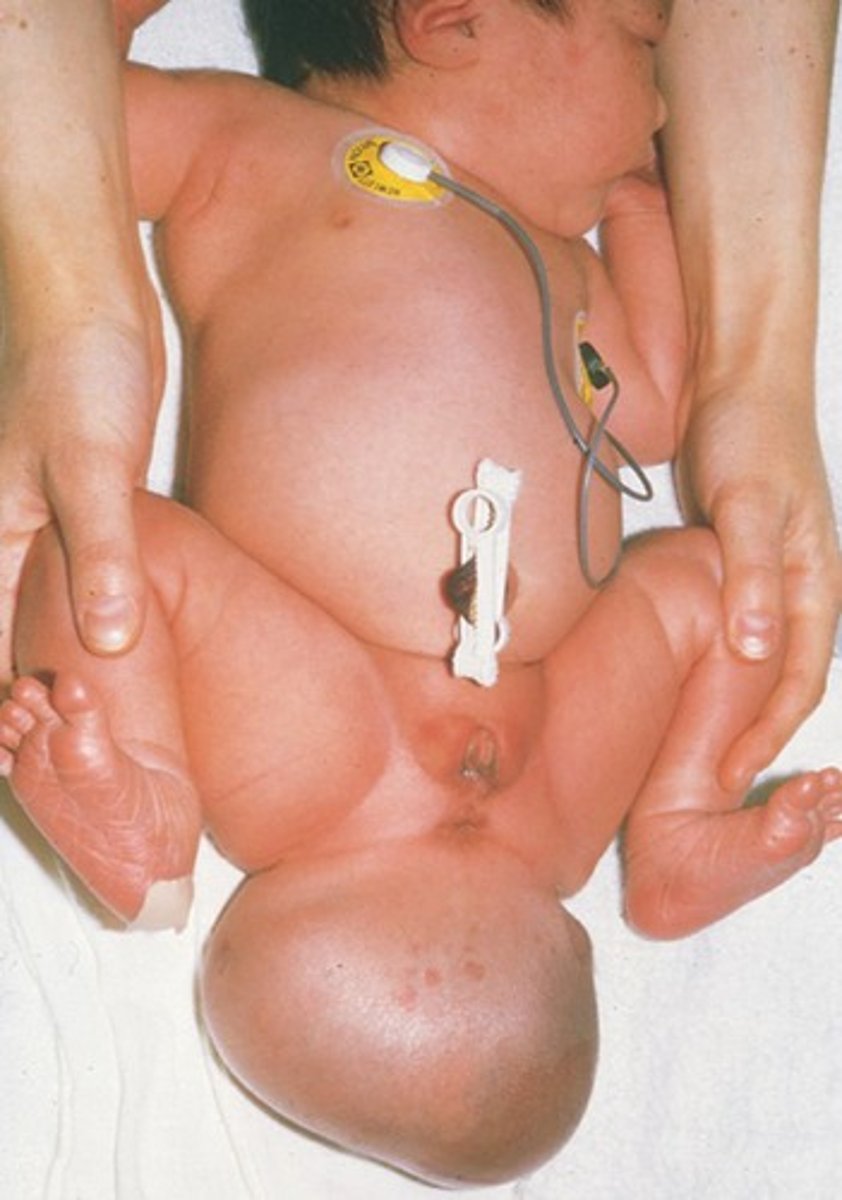
teratoma
tumor of all 3 germ layers
major thing that happens in:
(1) embryonic period
(2) fetal period
(1) organogenesis
(2) viable
malignant epithelial tumor
carcinoma (sarcomas?)
benign epithelial tumor
angioma, papilloma, adenoma
malignant CT tumor
sarcoma
benign CT tumor
fibroma, lipoma, osteoma, chondroma
malignant muscle tumor
sarcomyoma
benign muscle tumor
myoma
KNOW THE FATES OF 3 GERM LAYERS (BLACK SLIDE WITH BLUE, RED, and YELLOW TEXT)
KNOW THE FATES OF 3 GERM LAYERS (BLACK SLIDE WITH BLUE, RED, and YELLOW TEXT)
neurulation
(1) thickening of neuroectoderm (neural plate)
(2) invagination
(3) pinching off
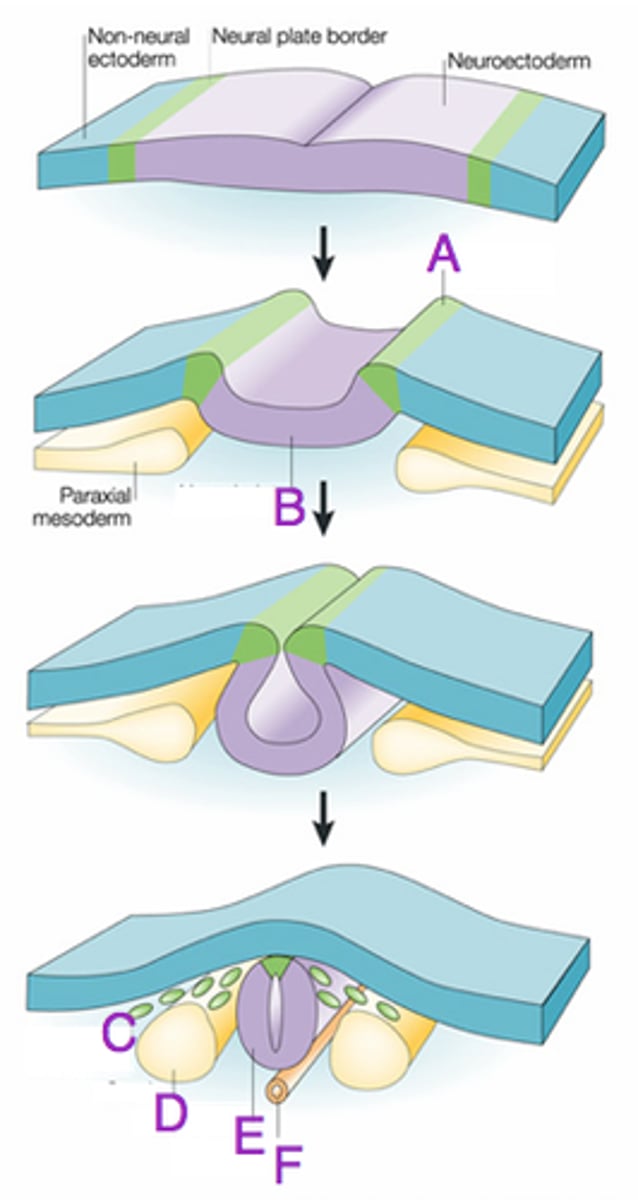
neural crest cells
cells at tip of neural fold; migrate throughout embryo; come from surface ectoderm
when does cranial neuropore close?
caudal neuropore?
(1) day 24-25
(2) day 26-27
neural tube
end result of neurulation
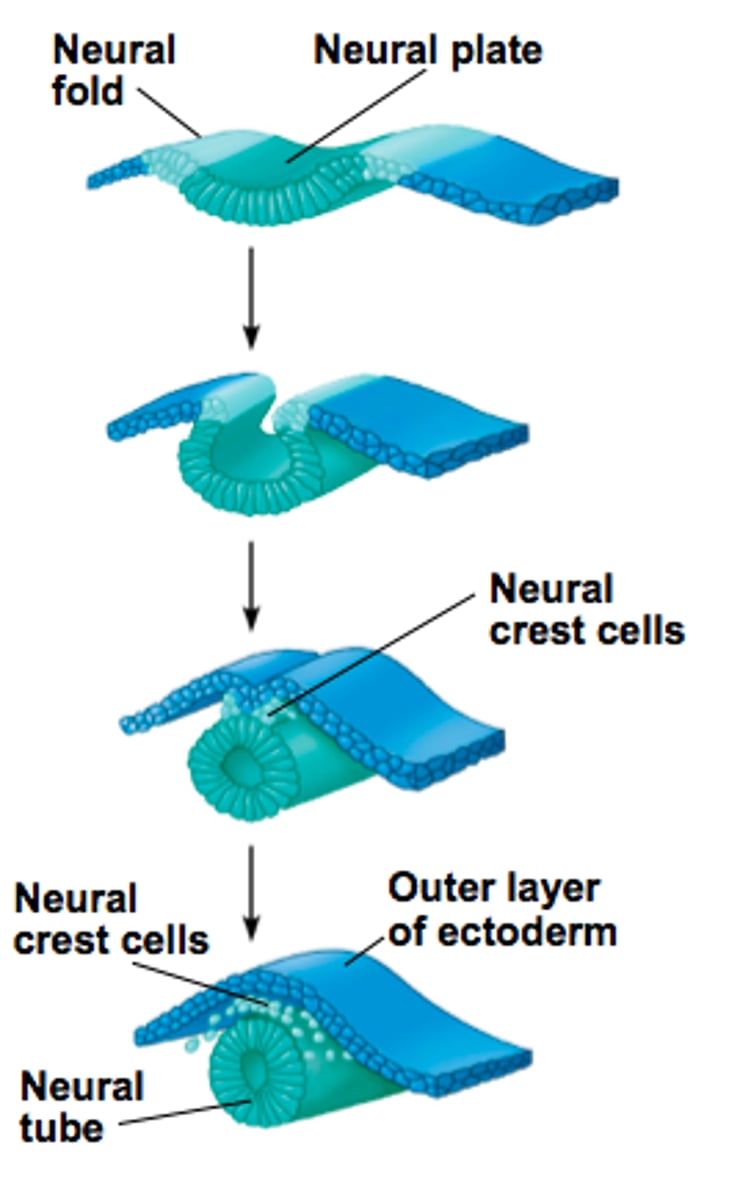
what do neural crest cells form?
ganglia (parasympathetic, sensory, autonomic, dorsal root)
where do neural crest cells come from?
surface ectoderm
what does surface ectoderm give rise to? (other than neural crest cells)
(1) skin, hair, nails, cutaneous + mammary glands
(2) anterior pituitary
(3) enamel of teeth
(4) internal ear
(5) lens of the eye
mesodermal derivatives include:
(1) paraxial
(2) intermediate
(3) lateral
what is the fate of the paraxial mesoderm?
somites --> dermatomes, myotomes --> SKELETAL MUSCLE
what is the fate of the intermediate mesoderm?
urogenital systems
what is the fate of the lateral mesoderm?
**ORGANS
(1) somatic -- associated with ectoderm
(2) splanchnic -- associated with endoderm
what is the fate of the endoderm?
- form primitive gut tube with 2 membranes (buccopharyngeal and cloacal)
- visceral epithelium
- parenchyma (secretory part) of thyroid, parathyroid, liver, and pancreas
- STROMA (CT) of tonsils + thymus
stomodeum
primitive mouth
proctodeum
primitive anus
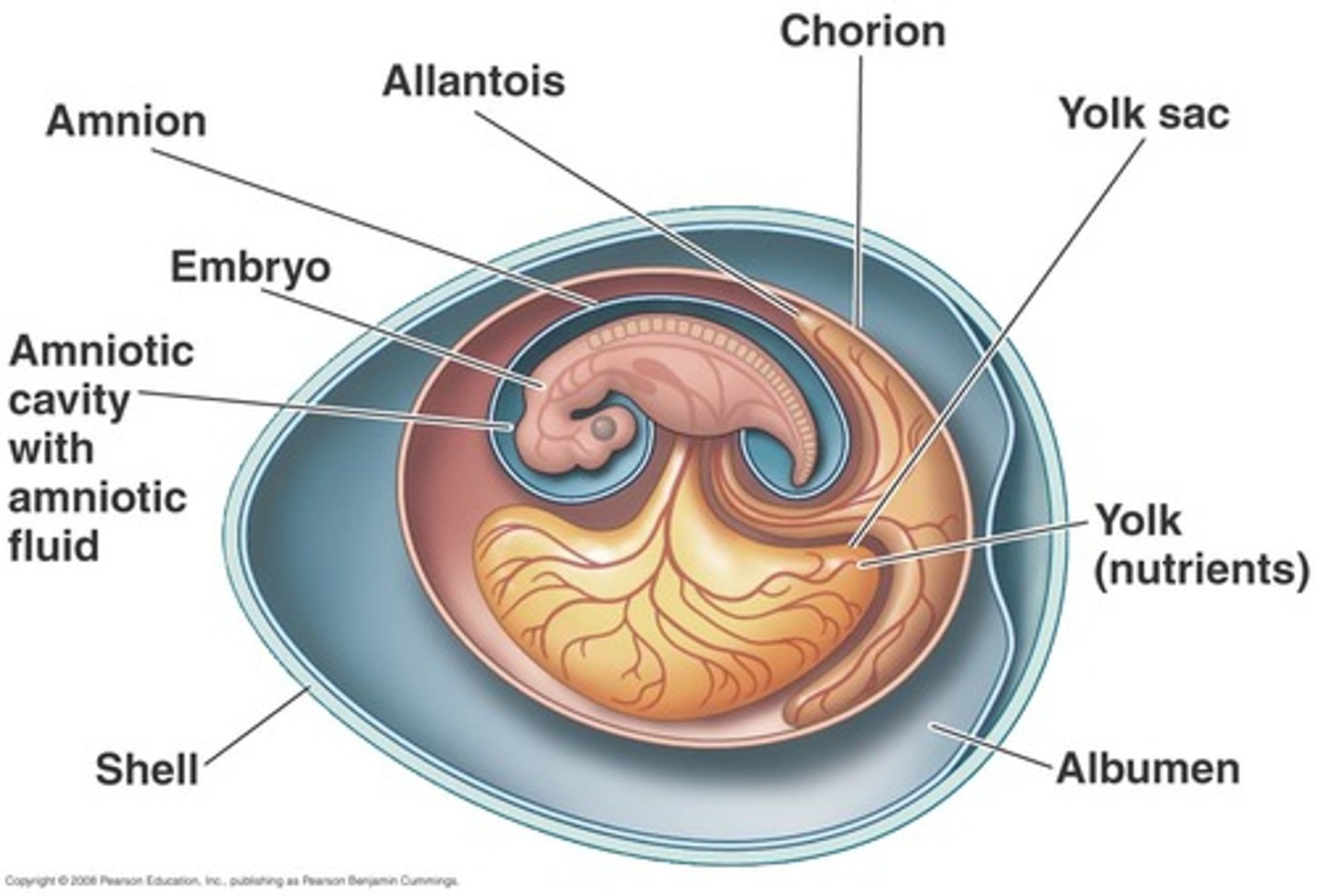
what is the vitelline duct + allantois?
(1) vitelline duct = connects to yolk sac
(2) allantois = connects to bladder
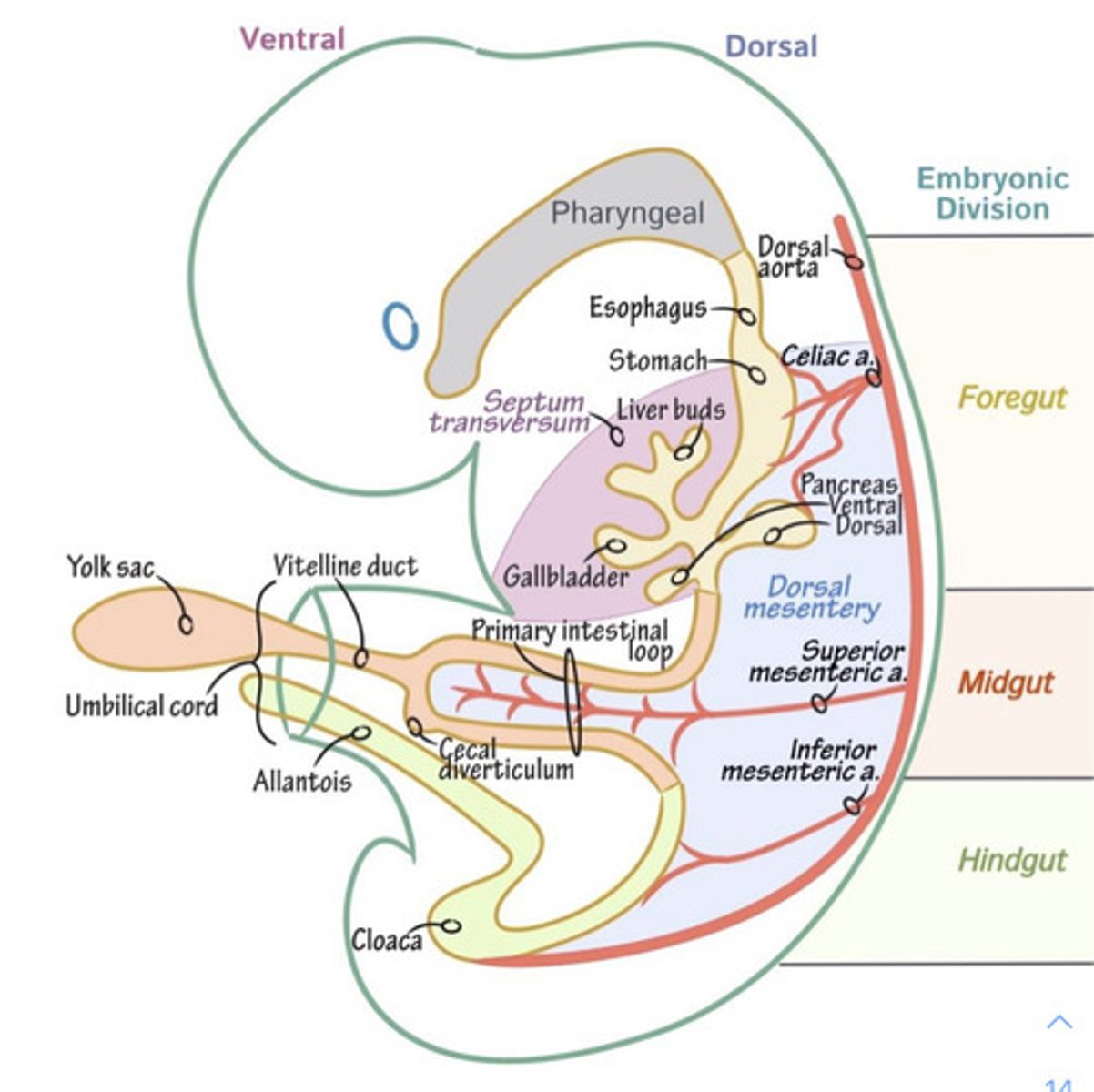
vitelline duct
the structure that connects the developing embryo to the secondary yolk sac
allantois
involved in early fluid exchange between the embryo and the yolk sac // connects to bladder
what are the structures at risk of congenital defects during the fetal period?
(1) brain
(2) eyes
(3) ears
(4) teeth
(5) palate
(6) external genitalia
name the important events for: weeks 9-12
(1) liver making RBC's
(2) external genitalia = male vs. female
name the important events for: weeks 13-16
(1) bone formation
(2) eyes move forward
name the important events for: weeks 17-20
(1) primary oocytes develop
(2) testes descend
name the important events for: weeks 21-25
(1) lungs produce surfactant
name the important events for: weeks 26-29
(1) lungs breath on own
(2) regulate temperature + breathing
(3) spleen --> bone marrow @ 28 weeks
name the important events for: weeks 30-34
NOTHING IMPORTANT
name the important events for: weeks 35-birth
(1) "finishing period" -- cardiovascular + respiratory
(2) fat accumulation
when are the following organs responsible for RBC formation?
(1) spleen
(2) bone marrow
(3) liver
(4) yolk sac
(1) 12-24 weeks
(2) 30+ weeks
(3) 12-30 weeks
(4) 0-12 weeks
when is amniocentesis performed?
when risk of congenital defects is higher than normal:
- mother is advanced age
- mother of down syndrome child
- chromosomal abnormalities
- X-linked carriers
** history of neural tube defects
- inborn errors of metabolism
what are the layers that must be penetrated by needle during amniocentesis?
(1) skin, fascia, etc.
(2) perimetrium
(3) myometrium
(4) endometrium
(5) syncytiotrophoblast
(6) cytotrophoblast
(7) extraembryonic mesoderm
(8) amnion
**STOP
alpha fetoprotein
protein produced by fetal liver; if hole in ectoderm / fetus, alpha fetoprotein will show up in amniotic fluid
what if alpha fetoprotein is found in a blood sample from a 23 year old male?
cancer