2.2.2 computational methods
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
features that make a problem solvable by computational methods
a problem that can be solved using an algorithm is computable
problems can only be computable if they can be solved within a finite, realistic amount of time
problems that are solved computationally are constrained by factors such as processing power, speed and memory
tractable problem
any problem that can be solved in polynomial time or better (n2 polynomial, n linear, log n logarithmic)
the algorithm will run quick enough to be practical and useful
intractable problem
any problem that cant be solves in polynomial time or better (2n exponential, n! exponential)
problem recognition
ability to recognise and acknowledge that an issue exists, define the problem and determine exactly what it is
stakeholders state what they require from the finished product and this information is used to clearly define the problem and the system requirements
requirements may be defined by
analysing strengths and weaknesses with the current way this problem is being solved
considering types of data involved including inputs, outputs, stored data and amount of data
problem decomposition
a problem is continually broken down into smaller problems
this continues until each subproblem can be represented as a self-contained subroutine
aims to reduce the complexity of the problem by splitting it up into smaller sections which are more easy to understand
step-wise refinement - produce a top down approach
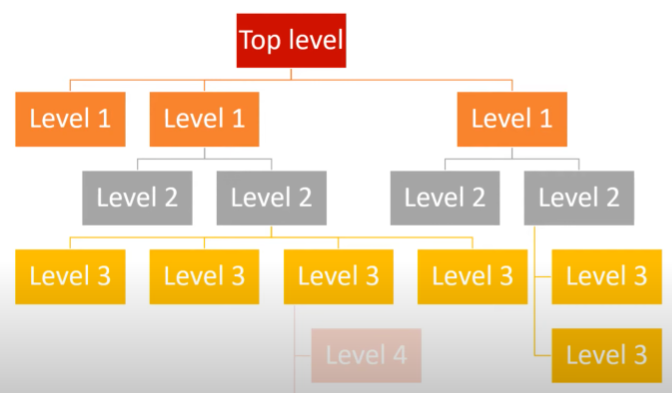
advantages of decomposition
smaller sections are more easy to understand and manage
by identifying subproblems, programmers may find that certain sections of the program can be implemented using pre-coded modules or libraries which saves time
different software development teams can be assigned separate sections of the code according to their specialisms
enables multiple parts of the project to be developed in parallel - faster
makes debugging simpler and less-time consuming, as it is easier to identify, locate and mitigate errors in individual modules
divide and conquer
problem solving technique broken down into 3 parts
divide - involves halving the size of the problem with every iteration
conquer - each individual subproblem is solved, often recursively
merge - the solutions to the subproblems are then recombined to form the final solution to the problem
example - binary search
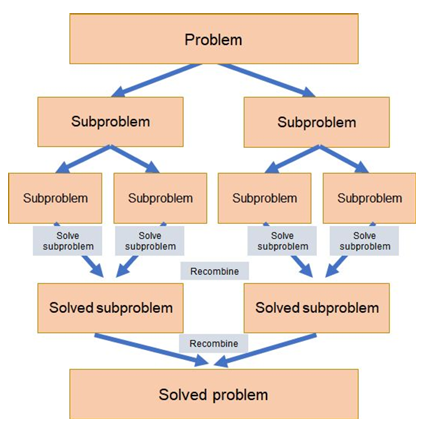
advantages of divide and conquer
the size of the problem is halved with each iteration which greatly simplifies very complex problems
this means that as the size of a problem grows, the time taken to solve it will not grow as significantly
as divide and conquer mostly makes use of recursion, it faces the same problems that all recursive functions face: stack overflow will cause the program to crash and large programs are very difficult to trace
abstraction
excessive details are removed to simplify a problem
allows programmers to focus on the core aspects required of the solution rather than worrying about unnecessary details
backtracking
incrementally building towards a solution
works by methodically visiting each path and building a solution based on the paths found to be correct
if a path is found to be invalid at any point, the algorithm backtracks to the previous stage and visits an alternate path
example - depth first traversal
data mining
a technique used to identify patterns or outliers in large sets of data (big data)
big data is typically collected from a variety of sources
data mining is used in software designed to spot trends or identify correlations between data
insights from data mining can be used to make predictions about the future based on previous trends
however, as data mining often involves the handling of personal data, it is crucial that it is dealt with in accordance with the present legislation regarding data protection
as of 2018, all data held and processed by organisations within the EU must follow the rules set by the GDPR
heuristics
a non-optimal, ‘rule-of-thumb’ approach to problem-solving which are used to find an approximate solution to a problem when the standard solution is unreasonably time-consuming or resource-intensive to find
the solution found through using heuristics is not perfectly accurate or complete, however the focus is on finding a quick solution that is good enough and heuristics provide a shortcut to this
example - A* algorithm, machine learning, language recognition
performance modelling
process of approximating how well models preform using mathematical approximations and simulations
uses of performance modelling
eliminates the need for true performance testing
provides a cheaper, less time-consuming or safer method of testing applications
results of performance modelling can help companies judge the capabilities of a system, how it will cope in different environments and assess whether it is safe to implement
useful for safety-critical computer systems, such as those used on an airplane, where it is not safe to do a real trial run before the system can be implemented
pipelining
splitting a large task into manageable chucks and overlapping these smaller processes to speed up the overall process - completing tasks simultaneously
visualisation
the ability to allow us to create a mental image of what a program will do or how it will work be we start to solve it
data can be presented in a way that is easier for us to understand using visualisation
makes it possible to identify trends that were not otherwise obvious
graphs, trees, charts, tables
concurrent processing
when multiple tasks are in progress at the same time, though not necessarily executing simultaneously
different processes can be executed (in parallel) by different processors/cores
each process is given a slice of processor time
benefits of concurrent processing
more efficient processor use / less idle time for processor
long running tasks do not delay short running tasks
tasks requiring preconditions can wait and then resume execution
user is able to interact with the computer while other tasks are running