GE5-MIDTERM
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Latin America
Refers to countries that were colonized by the Spainards in the American continent.
latin America
It is also called Latin-America since people who lived there were poor and underdeveloped countries.
West and East in 1944
This is when the newly discovered lands outside Europe were divided into two - the West belonging to the Crown of Castile (now part of Spain) and the belonging to the Portuguese Empire.
Cold War
a period of geopolitical tension between the US and Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and Eastern Bloc, that startedin 1947 and lasted to 1991.
“cold”
it is called ___ because the feature heavy weights, the Socvient Union and US, were nominally “at peace”.
The Cold War between US and USSR
created a division between the Capitalist/Democratic states and the Communist states
Capitalist/Democratic states
Marked by democratic elections, freedom and rule of laww, characteristics typically associated with democracy.
Communist States
dictatorship of proletariat, where the advanced elements of the proletariat are the ruling class.
First World
The capital economist were considered
Second World
Communist economists were reffered as
Third World
This refersto countries that did not belong to either types of formal economies
first world
encompassed all industrialized, democratic countries, which were assumed to be allied with the United Stated in its struggle against the Soviet Union. Finland and Switzerland maintained stict neutrality.
second world
was anchored on the industrialized, communist realm of the Soviet Union and its Eastern European satellites, yet it often included poor communist states located else where
False(not purely)
Global divides are purely of a geographical division but rather focused on socio-economic and political affiliations and status
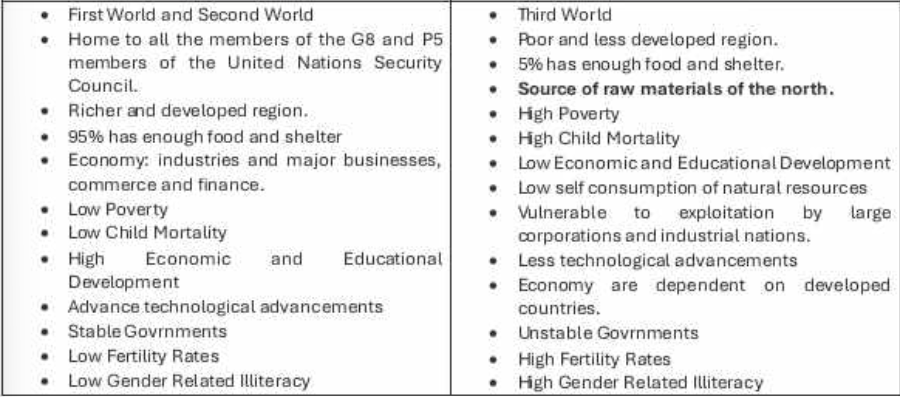
Global South
are countries that are less developed and characterized by low level of economiic developement, large inequalities in living standards and low life expectancy.
global South
developing countries which represents mainly agrarian economies in Africa, India, Latin, America, and others that are not as economically sound and politically stable.
global south
tend to be characterizedby war, conflict, poverty and tyranny.
Global North
are considered as the high incomes countries such as Norway, Canada, US, Belgium, Iceland, Japan, Sweden, Netherlands, and most of Western Europe.
global north
refers to developed societies of Europe and North America, which are characterized by established wealth, technological advancement, political stability, zero population growth and dominance of world trade and politics.
North and South Divide
after the cold war, many see primary global division as being between North and South.
19th Century
The World was largely divided into several empired in
“civilized”
Each empire possessed a ___ central that were more or less primitive or even “ barbaric”
1952 by Alfred Sauvy
Third World was coined in
Alfred Sauvy
a French demographer, athropologist, and economic historian who compared it with the Third Estate, a concept that emerge in the context of the French Revolution.
Fist Estate
clergy and the monarch
Second Estate
nobility
Third Estate
balance of French population as contrasted the poor countries to the First Word and Second World
Global North and Global South
Regionalism
Political ideology that favors a specific region over a greater area.
regionalism
Result due to political separations, regions, geography, cultural boundaries, Linguistic religions, and managerial.
Regionalization
process of dividing an area into smaller segments called regions
Globalization
people are unified
regionalisM
Theory ot practice rather than central system.
Why do countries form a regional organizations?
They form regional organization as way of coping with challenges of globalization. Also helps us in decision-making.
ASIAN REGIONALISM
product of economic interaction between Asian countries.
asian regionalism
Asian economies have grown not only richer, but also closer together.
EAST ASIAN ECONOMIES
focused on exporting to developed markets.
AKAMATSU (1962)
Japanese Economist. Compared this pattern of development to flying geese.
Regionalization and Globalization
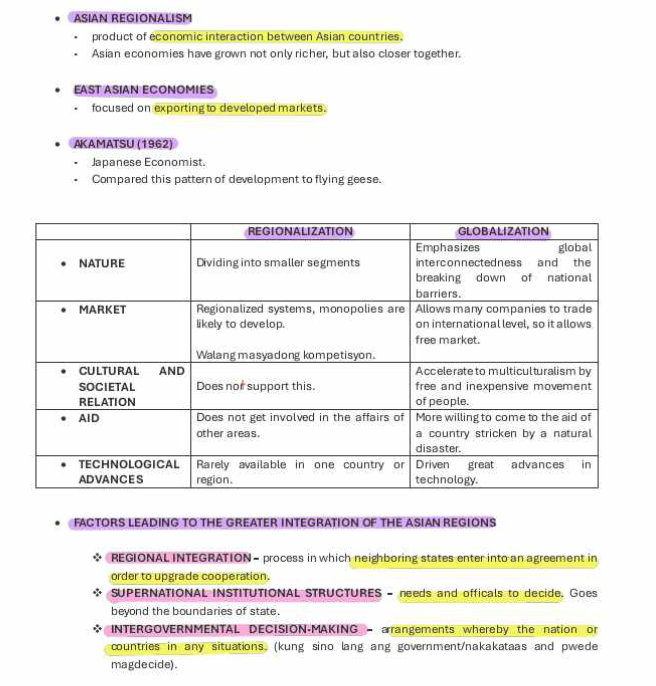
REGIONAL INTEGRATION
process in which neighboring states enter into an agreement in order to upgrade cooperation.
SUPERNATIONAL INSTITUTIONAL STRUCTURES
needs and officals to decide. Goes beyond the boundaries of state.
INTERGOVERNMENTAL DECISION-MAKING
arrangements whereby the nation or countries in any situations.
REGIONAL INTE GRATION
often focused on removing barriers to free trade region, increase the free movement of people, and social integration.
INTRA-REGIONAL TRADE
focuses on economic exchge primarily between countries of the same region or economiczone.
MEDIA
refers to the communicaton channels through which we disseminate newa, music, movies, education, promotional messages and other data.
CULTURE
can be defined as all the ways of life including arts, beliefs and institutions that are passed down from generation to generation.
Media
the term media comes from the word medium which is defined as channel, means, or method. A generic term for all human-invented technology that extends the range, speed, or chanels of communication. Can also be tied to what we call mass media, or the media that reach large audiences.
medium
the term media comes from the word ____ which is defined as channel, means, or method.
GLOBAL MEDIA CULTURES
Globalization entails the spread of various cultures.
Globalization also involves the spread ofideas.
Globalization relies on media as its main conduit for the spread of global culture and ideas.
THE DIFFERENT FORMS OF MEDIA
1. Print Media
2. Broadcast Media
3. Digital Media
Print Media
media consisting of paper and ink, reproduced in a printing process that is traditionally mechanical.
Broadcast Media
media such as rado and television that reach target audiences using airwaves as the transmission medium.
Digital Media
also known as new media, consisting of contents that are organized and distributed on digital platforms.
GLOBAL MEDIA
The mass communication on aglobal level, allowing people across the world to share and access the same information.
MARSHALL MCLUHAN
Once declared that "the medium is the message".
Television
is not a simple bearer of messages; it also shapes the social behavior of users and reorient family behavior.
Smartphones
allows users to keep in touch instantly with multiple people at the same time.
Marshall McLuhan
added that different media simultaneously extend and amputate human sense.
ALBERT BANDURA'S SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
emphasizes the imporatance of observing, modeling, and imitating the behaviors, attitudes, and emotional reactions of others.
Albert Bandura’s Social Learning Theory
Bobo Doll experiment.
RELIGION
a system of beliefs and practices.
"religare"
Religion comes from the Latin “____” which means"to bind together again that whichwas once bound but has since been torn apart or broken"
The Globalization of Religion
Religion
RELIGION HAS THE MOST DIFFICULT RELATIONSHIP WITH GLOBALISM
RELIGIOUS PEOPLE
GLOBALIST
GLOBALIST
are less worried about whether they will end up in heaven or hell.
RELIGIOUS PEOPLE
are less concerned with wealth and all that comes along with it.
Religous People
.Sacred.
. Follows divine commandments.
. Less concerned with wealth.
.Duty is to live a virtous and sinless life.
. Concerned with spreading of holy ideas
globally.
.Aspires to become a saint.
Globalism
. Places value on material wealth.
. Abides by human-made laws
. Less worried about whether they will end up
in heaven or hell.
. Their skills are more monotous.
.Globalist wishes to spread goods and services.
. Trains to bea business person.
WHEN DID GLOBALIZATION STARTED TO INFLUENCE RELIGION?
Evoling trade routes led to the colonization of the Asia, Africa, Central and South America. Religion became an integral part of colonization and later on globalization.
THE IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION
Flattens cultural differences
Erodes local customs and beliefs.
Spreads secular, capitalist way of life.