Microbiology Lab Quiz 6
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is epidemiology?
study of when, where, how, who spread diseases
What is the principle of the epidemiology experiment?
To see how diseases spread
What is a Epidemiologist?
a specialist in the study of outbreaks of disease within a population group
What is an epidemic?
- When a disease is spread throughout a population in a short time
- Example: COVID19 in China at the beginning
What is a pandemic?
- When a disease is spread worldwide in a short time.
- Example: COVID19 in China now
What is an outbreak?
- Two or more linked cases of the same illness
- Example: Beginning of the COVID19 pandemic
What is a sporadic disease?
- Disease that occurs occasionally
- Example: Flu every year in US
What is a communicable disease?
- Direct: person to person; shaking hands, kissing, etc.
- Indirect: living or non-living objects; tissues, cups, sneezing, etc.
What organisms were involved in the Epidemiology experiment?
- Normal microbiota: E. coli
- Pathogen (dummy): S. marcescens
What is the function of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention?
- CDC
- The nation's premiere health promotion, prevention, and preparedness agency and global leader in public health
What is MMWR?
Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
What is transformation?
Uptake of naked DNA by the cell
What is the purpose of using the TENS solution in the transformation experiment?
It has ingredients in it to break down the cells' membranes, killing the ADP-1 (the wild type that did have the enzyme)
In the transformation experiment, which organism was considered the "wild type"?
ADP-1 (Acinetobacter spp.)
Which plate in the transformation experiment served as the negative control to ensure that the wild type cells were completely lysed?
Plate #3; Was divided into quadrants but did NOT have ADP-6 spread over the surface
In the transformation experiment, which organism is "transformed"?
ADP-6
Which bacteria has the _______ enzyme that allows it to grow in Para hydroxybenzoate media?
protocatechuate oxygenase
______________ are cells that are able to undergo the process of transformation naturally
naturally competent cells (Bacillus spp and S. pneumoniae)
What is the function of the Tris-HCl buffer?
maintain pH
What is the function of EDTA?
Chelating agent
What is the function of NaOH?
Breaks the cell wall
What is the function of SDS?
solubilizes the cell membrane as it is a detergent
What was the name of the organism that was the plasmid donor in the conjugation experiment?
Pseudomonas putida PAW-15
What is the name of the organism that was the plasmid recipient in the conjugation experiment?
Pseudomonas putida 503CA
What criteria enables a bacterial cell to carry out conjugation?
- Opposite mating type (but SAME species), one has the plasmid (the F factor) and the other doesn't
- Cell to cell contact through the pilus
- A conjuble plasmid (it has to have the tra genes in order to be conjuble... tra stands for transfer)
What is the phenotype of the recipient organism in the conjugation experiment? (in reference to presence of plasmid and amino acid requirement)
leu+ and Tol-
What is the phenotype of the daughter cell in the conjugation experiment? (in reference to presence of plasmid and amino acid requirement)
leu+ and Tol+
What is the phenotype of the donor organism in the conjugation experiment? (in reference to presence of plasmid and amino acid requirement)
leu- and Tol+.
Glucose Minimal Media (GMM) was used as a control plate to see the growth of which organisms?
We grew all 3 orgs on GMM (E. coli, Pseudomonas putida 503CA, and Pseudomonas putida PAW-15)
- Pseudomonas putida 503CA and E. coli are both prototrophs meaning they can make their own leucine... so both of them grew on GMM
Why are samples sent for DNA sequencing?
The samples were sent off to sequence the DNA that we cut and "amplified" through PCR. That was the 16s rRNA gene, which is used to figure out the identity of the bacteria through the search tool.
What is nucleotide BLAST?
compares one or more nucleotide query sequences to a subject nucleotide sequence or a database of nucleotide sequences
What is the purpose of performing the BLAST analysis?
finds regions of local similarity between protein or nucleotide sequences
What is E-value?
Expect value (E) is a parameter that describes the number of hits one can "expect" to see by chance when searching a database of a particular size
What is Query coverage?
Percentage of the query sequence length that is included in the alignment
What is % of identity?
Percentage of residues that match up in the alignment.
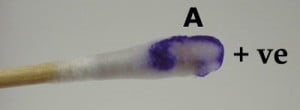
What is the use and relevance of the Oxidase test?
Tests for the presence of CYTOCHROME C OXIDASE, a redox protein present in the electron transport chain
What reagent is used in the Oxidase tesT?
TMPD
What is the principle of the oxidase test?
If the bacteria has the enzyme cytochrome C oxidase, then it will oxidize the reagent. When the reagent is oxidized, it turns purple.
Which organisms are used for the oxidase test?
Pseudomonas & Vibrionaceae are oxidase (+) and Enterobacteriaceae are oxidase (-)
Oxidase positive test
Pseudomonas & Vibrionaceae are oxidase (+)
Oxidase negative test
Enterobacteriaceae are oxidase (-)
