Unit 7- Protein Synthesis, Mutation and Gene Control
TRANSCRIPTION
Process in which a sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary RNA sequence (DNA → mRNA)
TRANSLATION
Process of decoding an mRNA message into a polypeptide (protein) chain. tRNA brings in the correct amino acids
(RNA → PROTEIN)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
TRANSCRIPTION
Process in which a sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary RNA sequence (DNA → mRNA)
TRANSLATION
Process of decoding an mRNA message into a polypeptide (protein) chain. tRNA brings in the correct amino acids
(RNA → PROTEIN)
NUCLEOTIDE
subunit (monomer) consisting of a 5 carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base used to build nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA
RNA POLYMERASE
enzyme involved in RNA transcription that binds to DNA, separates the strands, and assembles nucleotide subunits into an RNA molecule
RIBOSOMAL RNA (r-RNA)
type of RNA made by the NUCLEOLUS that is used to make ribosomes
MESSENGER RNA (m-RNA)
type of RNA that carries copies of instructions for making proteins from DNA to the rest of the cell during transcription
TRANSFER RNA (t-RNA)
type of RNA that transfers amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis (translation)
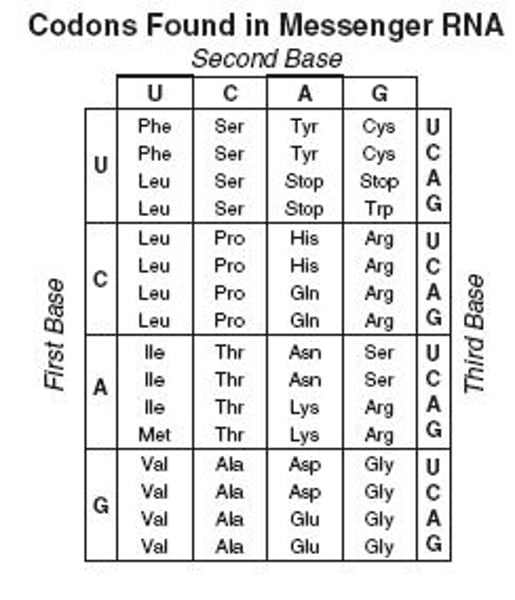
CODON
three nucleotide sequence on m-RNA that codes for a single amino acid, is on the mRNA and is read via the genetic code to determine the correct amino acid this codes for.
ANTICODON
group of three nucleotide bases on a t-RNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
OPERON
a group of genes operating together. On prokaryoes
INTRON
sequence of DNA that is NOT involved in coding for a protein which is cut out of the m-RNA molecule before it is read by the ribosomes
EXON
Expressed sequence of DNA that codes for a protein
REPRESSOR
molecule that binds to the operator region of an operon and "turns the gene off"
OPERATOR
region in an operon to which repressor proteins bind when the operon is "turned off"
PROMOTER
region in an operon to which RNA polymerase binds to begin transcription
HOX GENES
series of genes that control differentiation of cells and tissues in an embryo
TRANSPOSON
Region of DNA that can jump from one location to another which is thought to be involved in increasing mutations in cells "JUMPING GENE"
GENETIC CODE
collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis
Central Dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Peptide
short chain of amino acids
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids.
Uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA) and derived from pyrimidine
Mutation
change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information
Substitution
A mutation in which a nucleotide or a codon in DNA is replaced with a different nucleotide
Deletion
A change in DNA where one nucleotide is deleted.
Frame Shift
a genetic mutation caused by a deletion or insertion in a DNA sequence that shifts the way the sequence is read
Insertion
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene.
Inversion mutation
Mutation in which a chromosome piece reattaches to original chromosome but in reverse orientation
Chromosomal Mutation
A change in the chromosome structure, resulting in new gene combinations.
Duplication Mutation
A genetic mutation in which a region that contains a gene or an entire chromosome is duplicated, which results in multiple copies of that region or nucleotide.