Neuro-embryology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
1
New cards
Week 1- Formation of the Blastocyst
• Day 1: Fertilization
• Day 2: Two Cell stage
• Day4: Morula
• Day 5: Early Blastocyst
• Day 2: Two Cell stage
• Day4: Morula
• Day 5: Early Blastocyst
2
New cards
trophoblast
Outer layer of blastocyst thins to one cell layer thickness
3
New cards
embryoblast
the inner cell mass of blastocyst differentiates
4
New cards
Week 2 - “Week of Two’s”
* Implantation
* Embryoblast (Inner cell mass) differentiates into two layers :
* Epiblast
* Hypoblast
* These two layers form the bilaminar embryonic disc
* The trophoblast differentiates into two layers:
* Syncytiotrophoblast
* Cytotrophoblast
* Embryoblast (Inner cell mass) differentiates into two layers :
* Epiblast
* Hypoblast
* These two layers form the bilaminar embryonic disc
* The trophoblast differentiates into two layers:
* Syncytiotrophoblast
* Cytotrophoblast
5
New cards
Describe the blastocyst on day 5 and on day 6
day 5: organizing, early
day 6: well organized, implanting
day 6: well organized, implanting
6
New cards
what stage is the embryo in on day 4?
morula
7
New cards
What part of the trophoblast implants?
Synctiotrophoblast
8
New cards
What part of the trophoblast is close to the bilaminar disc
Cytotrophoblast
9
New cards
Embryonic stem cells
totipotent, pluripotent
10
New cards
Adult stem cells
multipotent, oligopotent
11
New cards
Totipotent
Can create any cells of the body and placental cells, represents the first fertilized cell and first few divisions, can develop into any mature cell type
12
New cards
Pluripotent
Derived from totipotent stem cells cand form any of the 3 germ cell layers, can develop into any mature cell type
13
New cards
Multipotent
These stem cells can develop into a group of related cells, are also contained in the amniotic fluid
14
New cards
Oligopotent
Very limited cells, can differentiate into specific cells only, example myeloid or lymphoid cells
15
New cards
Unipotent
Can produce only their own type of cell, and can self-renew
16
New cards
Induced Pluripotent
These are adult cells that are reprogrammed by genetic protein transcription to become pluripotent
17
New cards
What 2 cavities form in week 2
amniotic cavity and yolk sac
18
New cards
When does the amniotic disc form?
week 2
19
New cards
Day 9
lacunae or clefts appear
20
New cards
Day 12
extra-embryonic coelom and chorionic cavity starts to appear
21
New cards
Day 14
* primitive utero-placental circulation begins
* blastocyst is fully embedded, and mucosa has healed
* **primitive streak** appears on the epiblast
* epiblast shows an orientation (up, left/right)
* blastocyst is fully embedded, and mucosa has healed
* **primitive streak** appears on the epiblast
* epiblast shows an orientation (up, left/right)
22
New cards
What factors are secreted to inhibit the nodal activity in the cranial end of the embryo
* cerebus
* LEFTY
* LEFTY
23
New cards
What establishes Left/Right in an embryo? How?
Sonic hedgehog ligand by stimulating Nodal and LEFTY
24
New cards
What side is LEFTY expressed on?
Left lol
25
New cards
What side is activism expressed on?
Right
26
New cards
Why is Sonic hedgehog ligand important during **week 5-6**?
it is responsible for formation and patterning of the neural tube
* creates separation of lobe and face
* creates two eyes
* creates separation of lobe and face
* creates two eyes
27
New cards
What are the degrees of severity for holoprosencephaly?
1. lobar
2. semilobar
3. alobar
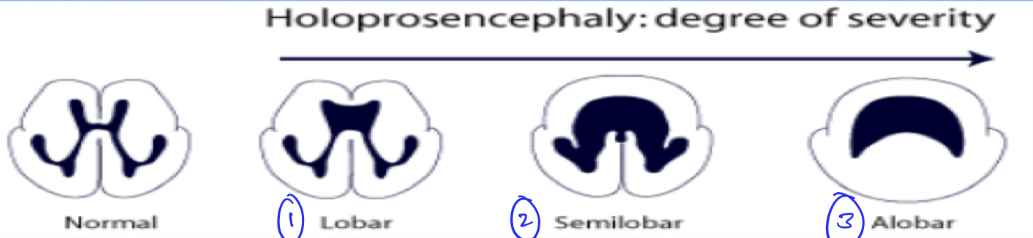
28
New cards
Gastrulation
epiblast forms the 3 germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
29
New cards
When does gastrulation occur?
week 3
30
New cards
Describe the gastrulation process
1. epiblast invaginates to form the endo- and mesoderm
2. ectoderm forms the neural plate and becomes neuroectoderm
3. invaginating cells reach the prechordal plate and form the notochordal plate
31
New cards
When does neurulation occur?
Day 18-24
32
New cards
Neurulation
process by which the neural plate forms the neural tube
33
New cards
What initiates neurulation?
non-migrating neuroectoderm
34
New cards
Describe day 18
* neuroectoderm induces neurulation
* midline mesenchyme releases chemical signals to ectoderm and forms neural plate
* notochord detaches and forms solid cord
* midline mesenchyme releases chemical signals to ectoderm and forms neural plate
* notochord detaches and forms solid cord
35
New cards
What is the neural plate notochord derived from
epiblast cells that invaginate and become part of the hypoblast
36
New cards
describe day 20
* folds form around the neural streak
* form a neural groove
* lateral folds of the neural plate elevate to form the **neural folds**
* top of the cells on the neural folds develop the **neural crest cells**
* form a neural groove
* lateral folds of the neural plate elevate to form the **neural folds**
* top of the cells on the neural folds develop the **neural crest cells**
37
New cards
describe Day 22
* parasail mesoderm forms the somites
* the cranial and caudal neuropores remain open
* neural tube starts to close
* the cranial and caudal neuropores remain open
* neural tube starts to close
38
New cards
describe Day 24
* neural fold cells leave behind the neural crest cells
* neural crest cells develop the dorsal root ganglia
* rostral end of neural tube closes
* neural crest cells develop the dorsal root ganglia
* rostral end of neural tube closes
39
New cards
Day 26
caudal end of the neural tube closes
40
New cards
Somites become _
spinal vertebrae
41
New cards
Neural tube becomes _
CNS
42
New cards
Neural crest becomes _
PNS
43
New cards
Neural crest develops to form _
neuroectoderm
44
New cards
What can failure of migration of neural crest cells cause in the PNS?
* congenital deafness
* cardiac abnormalities
* autonomic abnormalities
* pigmentary abnormalities
* cardiac abnormalities
* autonomic abnormalities
* pigmentary abnormalities
45
New cards
Albinism
pigmentary abnormality where there is a block of tyrosine by tyronsinase into melanin
46
New cards
Type of albinism when there is failure of migration for **neuroectoderm**
* ocular albinism due to low number of mature ocular melanosomes
* iris and RPE affected, macular hypoplasia and nystagmus
* iris and RPE affected, macular hypoplasia and nystagmus
47
New cards
Type of albinism when there is failure of migration for **neural crest**
albinoidism - skin, hair, iris stroma
48
New cards
Type of albinism when there is failure of migration for **neuroectoderm and neural crest**
oculocutaneous albinism due to inadequate melanization of a normal number of melanocytes
49
New cards
Facial abnormality that can occur due to failed neural crest migration
* neurocristopathies
* treacher-collins-franschetti syndrome
* cleft lip and cleft palate
* treacher-collins-franschetti syndrome
* cleft lip and cleft palate
50
New cards
What does fetal alcohol syndrome impair?
neural crest migration
51
New cards
General effects of FAS
* mental disabilities
* progression of symptoms
* progression of symptoms
52
New cards
Ocular effects of FAS
* causes reduction of retinal cells
* microphthalmia (small eye)
* optic nerve hypoplasia (small ON)
* microphthalmia (small eye)
* optic nerve hypoplasia (small ON)
53
New cards
In the neural tube, what is the ant. and post. neuropore in contact with?
amniotic fluid
54
New cards
What does the neural tube become?
* ventricular system of the brain
* central spinal canal
* central spinal canal
55
New cards
What does the outmost layer of the spinal cord become?
marginal layer → white matter of spinal cord
56
New cards
gray matter of dorsal half forms
alar plate
57
New cards
gray matter of ventral half forms
basal plate
58
New cards
Sulcus limitans
separated the neural tube into ventral and dorsal halves
59
New cards
Notochord cells
make Sonic hedgehog and induces the floor plate to also make SH
60
New cards
Longitudinal groove
occurs in the lateral wall of neural tube
61
New cards
How old is the embryo when it has 8 somites
22 days
62
New cards
How old is the embryo when it has 10 somites
23 days
63
New cards
Somitomeres turn into..?
somites
64
New cards
What do somites turn into?
axial skeleton (skull and spine, hence spinal vertebrae)
65
New cards
How many somites can an embryo have when it is 20-21 days
1-4
66
New cards
How many somites can an embryo have when it is 28-30 days
30-35
67
New cards
What does the intermediate mesoderm become?
urogenital system
68
New cards
What does the intermediate mesoderm line?
* wall of gut
* peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities and secrete serous fluid
* peritoneal, pleural, and pericardial cavities and secrete serous fluid
69
New cards
When does secondary neurulation occur
Week 5-6
70
New cards
How does the sacral spinal chord form?
secondary neurulation
71
New cards
Describe the process of secondary neurulation
* caudal cell mass consisting of mesenchyme cells form medullary cord
* form vacuoles that coalesce to form a central canal
* neural tube and sacral tube join
* form vacuoles that coalesce to form a central canal
* neural tube and sacral tube join
72
New cards
Rostral neural tube defective closure
anencephaly
73
New cards
How can neural tube defects be detected in maternal circulation?
alpha-fetoprotein
74
New cards
What supplements can mothers take to prevent neural tube defects?
Folic acid
75
New cards
Open neural tube defects
* entire CNS affected
* anencephaly
* hydrocephalus
* Chiari II malformation
* anencephaly
* hydrocephalus
* Chiari II malformation
76
New cards
Closed neural tube defects
* spine only affected
* spina bifida
* no exposed neural tissue
* skin of defect may be dysplastic
* spina bifida
* no exposed neural tissue
* skin of defect may be dysplastic
77
New cards
Spina bifida occulta
malformation of one or more of the vertebrae of the spine (usually no problems)
78
New cards
Meningocele
meninges protrude through a gap in the spine
79
New cards
Myelomeningocele
meninges and spinal cord develops in a fluid-filled sac outside of the body
80
New cards
What is a Chiari Type 2 Malformation
cerebellum and caudal brainstem are pushed down into foramen magnum
81
New cards
Week 4/Day 28
* post. neuropore closes
* neurulation complete
* closed spinal cord
* development of sulcus limitans and sonic hedgehog
* neurulation complete
* closed spinal cord
* development of sulcus limitans and sonic hedgehog
82
New cards
What placodes can be seen at week 4?
* otic placodes
* olfactory placodes
* medial & lateral
* optic placodes
* profundal/trigeminal placodes
* olfactory placodes
* medial & lateral
* optic placodes
* profundal/trigeminal placodes
83
New cards
Structures from Telencephalon
* ==cerebral hemispheres==
* ==lateral ventricles==
* ==intraventricular foramina of monro==
* ~~hippocampus~~
* ~~basal ganglia~~
* ~~amygdala~~
* ~~cerebrum~~
* ==lateral ventricles==
* ==intraventricular foramina of monro==
* ~~hippocampus~~
* ~~basal ganglia~~
* ~~amygdala~~
* ~~cerebrum~~
84
New cards
Structures from Diencephalon
* ==optic cup and stalk==
* ==pituitary==
* ==epiphysis==
* ~~thalamus~~
* ~~hypothalamus~~
* ==pituitary==
* ==epiphysis==
* ~~thalamus~~
* ~~hypothalamus~~
85
New cards
Structures from Mesencephalon
* oculomotor and trochlear motor nuclei
* EW nucleus
* Crus Cerebri
* Superior and inferior colliculus
* EW nucleus
* Crus Cerebri
* Superior and inferior colliculus
86
New cards
Structures from Myelencephalon
Medulla oblongata
87
New cards
Structures from Metencephalon
* ~~Pons~~
* ~~Cerebellum~~
* Pontine Nuclei
* Rhombic lips
* ~~Cerebellum~~
* Pontine Nuclei
* Rhombic lips
88
New cards
What do the rhombic lips form?
cerebellum
89
New cards
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
coordination center for posture and movement
90
New cards
What is the pons responsible for?
pathway for nerve fibers from the spinal cord to cerebellum and cerebrum
91
New cards
What are the type of motor neurons that arise from the basal plate of the metencephalon
* somatic efferent
* special visceral efferent
* general visceral efferent
* special visceral efferent
* general visceral efferent
92
New cards
Somatic Efferent motor neuron
gives rise to the nuclei of the abducens nerve
93
New cards
SVE motor neuron
contains the nuclei of the trigeminal and facial nerves
94
New cards
GVE motor neurons
axons supply the sub-mandibular and sublingual glands
95
New cards
What is the phylogenically oldest lobe of the cerebellum?
flocculus
96
New cards
Noduloflocular lobe responsible for..?
eye movements