biology experimental methods
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
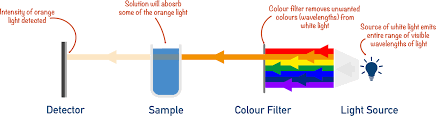
colorimeter/ spectrophotometer
measure amount of light that passes through a sample
isolate pigment in solution
place solution in glass cuvette
place cuvette in colorimeter/ spectrophotometer
pass different wavelengths through solution
record values from detector on other side of cuvette = determine how much of each wavelength was absorbed by solution
plot values to show absorption spectra for pigment
translation
mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome
mRNA serves as a template for protein synthesis
codons of mRNA specify positioning of amino acids along polypeptide OR codons guide the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide
tRNA molecules carry amino acids to mRNA OR ribosome
anticodons on tRNA complementary to codons on mRNA allow amino acids to be positioned correctly along the polypeptide OR anticodons bind to codons to bring corresponding amino acid to the ribosome
rRNA provides the ribosome's structural framework OR forms ribosomes
rRNA catalyses the formation of peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids
rRNA facilitates binding of mRNA and tRNA
mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA orchestrate protein synthesis during translation
propagate an action potential along + within a neuron
Stimulus ie change in membrane voltage triggers opening of sodium channels in presynaptic membrane.
Leads to depolarising of membrane.
If change in potential reaches threshold (-55mV) it triggers opening of voltage gated sodium channels.
Rapid influx of sodium ions = action potential.
+ feedback loop = more sodium channels open
After reaching +40mV, sodium channels begin to close, voltage gated potassium channels open.
Potassium ions move out of the cell, repolarising membrane, bringing it back towards resting potential.
Hyperpolarisation prevents further action potential until sodium potassium pump restores resting membrane potential + ion balance.
Action potential in one region means sodium ions diffuse along axon to different neighbouring regions, changes membrane potential in these regions
= region surpasses threshold potential
Action potential cannot go backwards
Action potential reached presynaptic knob, causing opening of voltage gated calcium ion channels
Influx of calcium ions causes vesicles containing neurotransmitter to fuse with presynaptic membrane
NT released into synaptic gap by exocytosis
NT diffuses across synapse + binds to receptors on postsynaptic membrane.
Triggers opening of sodium channels in postsynaptic membrane
If postsynaptic potential reaches threshold = action potential generated in the next neuron.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
Drugs used to downregulate several hormones.
Function of FSH is to stimulate follicle growth.
Function of LH is to trigger ovulation/ release mature eggs from ovaries.
Downregulation of LH + FSH also downregulates progesterone, oestrogen.
Oestrogen normally stimulates thickening of endometrium.
Progesterone normally maintains endometrium for implantation.
High doses of FSH are injected to trigger superovulation = development of many follicles. Increases the chance of successful fertilisation in IVF process.
GnRH agonists injected to prevent premature ovulation.
hCG injected to stimulate follicle maturation.
Progesterone injected before fertilised egg is implanted to improve chances of successful implantation.
cryogenic electron microscopy
observe protein structure
computer looks for patterns
observe individual atoms
rapidly evolving
freeze fracture microscopy
rapidly freeze sample, steel blade fractures sample at weakest point, remove ice, vapour attaches to surface to form a replica, view in electron microscope
karyogram
image of stained homologous chromosomes ordered by decreasing length/ position of centromere
in situ conservation
in natural habitat/ protected areas, no disruption to behaviour or evolution, cost effective, active management of invasive species, predators, feeding.
ex situ conservation
outside natural habitat/ in zoo, captive breeding and release, preservation of endangered species + their eggs, sperm, seeds.
simpsons diversity index
D = N(N-1)/ sum of (n(n-1)
N total organisms in all species, n = total organisms in each specific species, put together all different species as n(n-1) n(n-1) etc
stomatal density
peel off epidermis, mount on slide. count number of stomata = no stomata/ cm² (field of view)
capture mark release recapture + lincoln index
capture as many organisms of motile species in area as possible
mark each individual without increasing visibility to predators
release all marked individuals + allow them to settle back into habitat
set amount of time later, recapture as many individuals in area as possible
count marked + unmarked.
total population size = no. of animals 1st captured x all no. animals 2nd captured// no. marked animals recaptured.
quadrats
square with known dimensions
random/ systematic placement in area to measure abundance
abundance in each quadrat recorded
repeated sampling
mean of quadrats recording
extrapolate to estimate population size
gel electrophoresis
separates DNA molecules into shorter fragments.
put DNA fragments in porous gel
apply electricity, negative electrode to DNA end
moves DNA through gel (DNA negative)
shorter fragments move through the pores further = travel further.
applications = paternity/ forensic DNA testing
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
amplifies DNA using Taq polymerase (heat resistant enzyme)
denaturation - heating breaks bonds
annealing - cooling binds primer
extension
application: testing for coronavirus
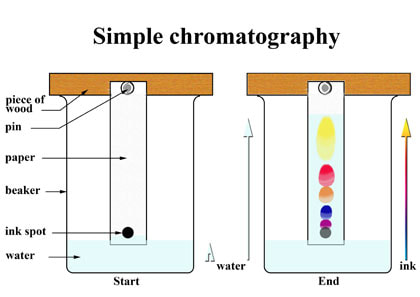
chromatography
separate photosynthetic pigments
tear up leaf, grind, add acetone, dry out.
transfer small amount of pigment solution to paper strip, 10mm from end.
use something to hold paper, insert into specimen tube, mark below spot on tube, remove.
pour solvent into specimen tube to marked point.
place strip into tube, seal.
leave for 5 minutes
when solvent has nearly reached top of strip, remove.
mark lines where solvent reached + at initial pigment spot. mark pigments in middle with x.
measure (mm) distance between 2 lines (solvent travelled) + distance moved by each pigment.
calculate Rf value = distance run by pigment/ distance moved by solvent
centrifugation
separate cells into types of organelle
mix cells with ice cold extraction buffer
gently blitz in scientific blender
filter resulting homogenate
centrifuge: organelles are denser than extraction buffer = sediment to bottom, form pellet
remaining liquid (supernatant) discarded
pellet mixed with another solution to resuspend organelles
mixture centrifuged again (speed + duration carefully chosen)
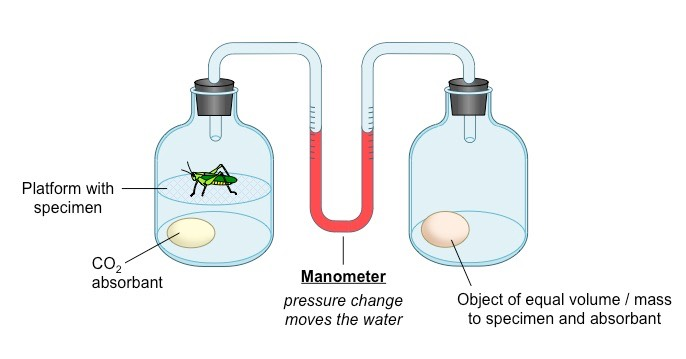
respirometer
measures rate of cell respiration using oxygen uptake
sealed glass/ plastic container with enough oxygen for organism/ tissue inside to remain healthy
base (alkali) to absorb co2 produced in respiration (e.g. potassium hydroxide)
capillary tube containing fluid connected to container, measures changes in volume of air in respirometer
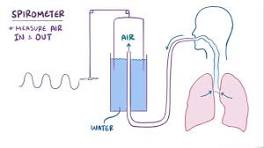
spirometer
measures lung volumes
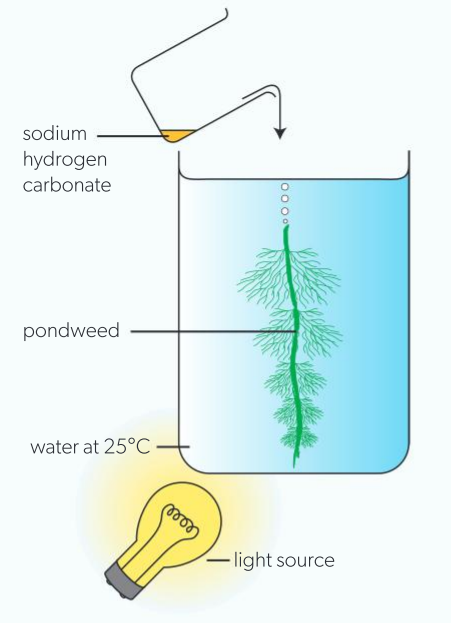
measuring photosynthesis: co2 concentration
boil water to fill beaker, allow to cool (removes co2, other dissolved gases)
repeatedly pour water from 1 beaker to another (oxygenise)
cut end of pondweed stem, place upside down in water
add enough sodium hydrogen carbonate to beaker to raise co2 concentration to 0.01 mol dm-3. if bubbles emerge, count for 30s, repeat until 2/3 consistent results emerge.
raise concentration by another 0.01 mol dm-3
repeat until further increases in co2 do not affect rate of bubble production
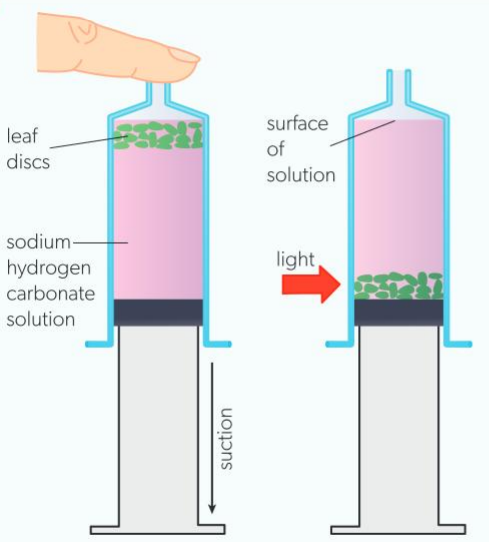
measuring photosynthesis: light intensity
remove barrel from 10cm³ plastic syringe, cover end with finger, pour 10cm³ of 0.2 mol mm-3 sodium hydrogen carbonate in.
put 10 leaf discs in solution, replace plunger
hold syringe vertically, squeeze air out, put finger on nozzle, pull barrel (suction)
repeat until leaf discs denser than solution, sink to bottom
place syringe in vertical position at measured distance from light source
time how long it takes each disc to reach surface
measure light intensity using lux meter
repeat with syringe at different distances from light source (relative intensity = 1/distance²)
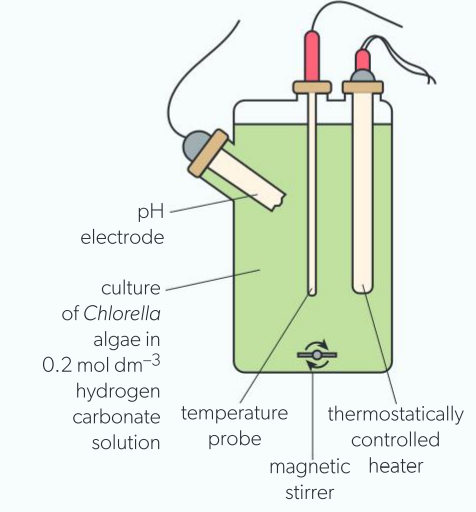
measuring photosynthesis: temperature
photosynthetic rates measured using data logger _ oxygen electrode/ pH electrode: as co2 absorbed from water + used in photosynthesis, pH drops.
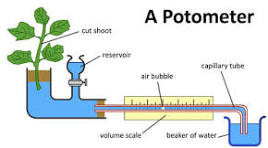
potometer
as plant takes up water through roots, bubble moves along capillary tube. distance bubble travels and time taken are measured. reservoir resets bubble to conduct new measurements.
light v electron microscopy
light:
at magnifications above 400x, cannot produce focused image
examine living material + produce coloured imaging
electron:
viable at higher magnifications
allow identification of cell ultrastructures
only allow black and white images
methods to prepare material always kill cells/ they die in microscopy regardless
mesocosms
e.g. fenced off enclosures in grassland/ forest - terrestrial mesocosms, tanks in laboratories - aquatic ecosystems, sealed terrariums.
must contain:
energy source (sunlight) for photosynthetic producers
nutrient cycling via saprotrophs/ detritivores
moistened soil (abiotic components)
enclosed greenhouse co2 enrichment experiments
predict future rates of photosynthesis + plant growth in response to human activity.
co2 levels artificially increases in indoor greenhouses using compressed gas tanks/ fermentation buckets. act as closed system - high control of extraneous variables, do not reflect natural environment. only plants that grow in small spaces can be measured.
free air co2 enrichment experiments (FACE)
predict future rates of photosynthesis + plant growth in response to human activity.
placement of pipes that emit co2 around experimental area, concentration monitored by sensors that adjust flow. represent open systems, incorporate natural conditions (rainfall, temp fluctuations) but certain conditions (sunlight) cannot be controlled. can measure effects on larger trees, consider impact of competition between plant species.