Etruscan Art and Archeology Final
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms

Name?
Inkwell from the Regolini Galassi Tomb Cerveteri 650 BCE

Name?
Sacrifice of Polyxena Vulci 550 BCE
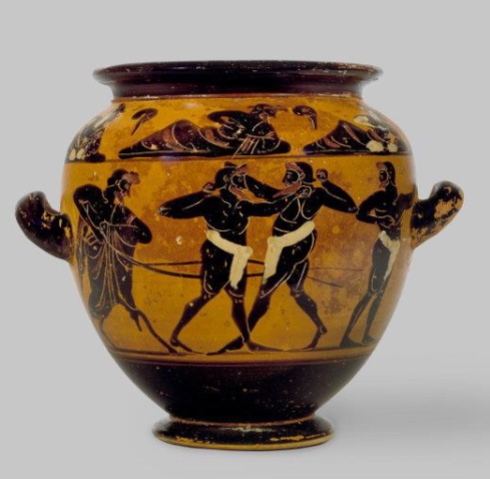

Name?
Perizoma group krater Vulci 525 BCE
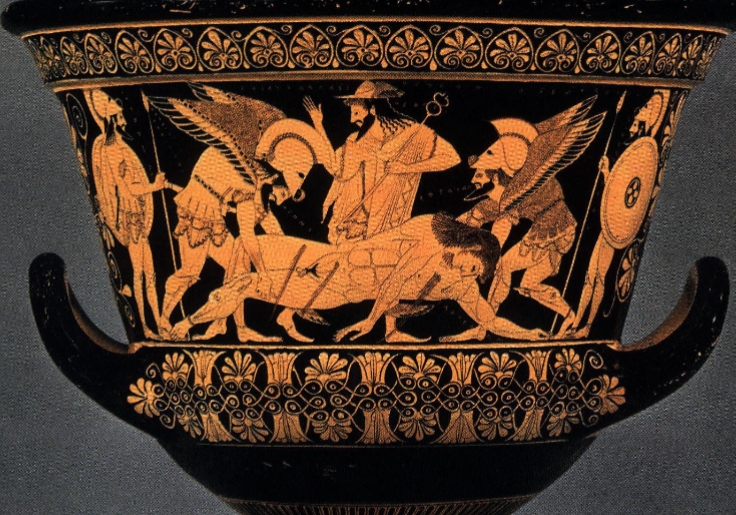

Name?
Euphronios krater Cervteri 510 BCE

Name?
San Paolo Ople Cerveteri 650 BCE
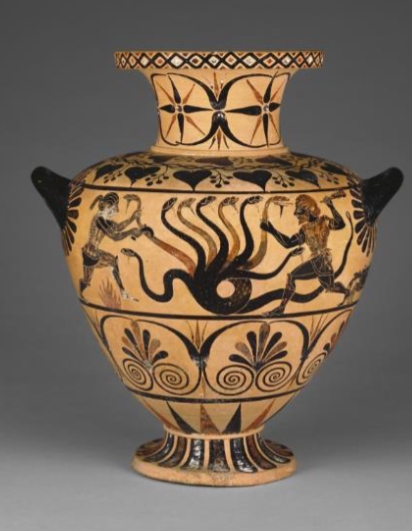

Name?
Hercules and the Hydra Cervteri 520 BCE
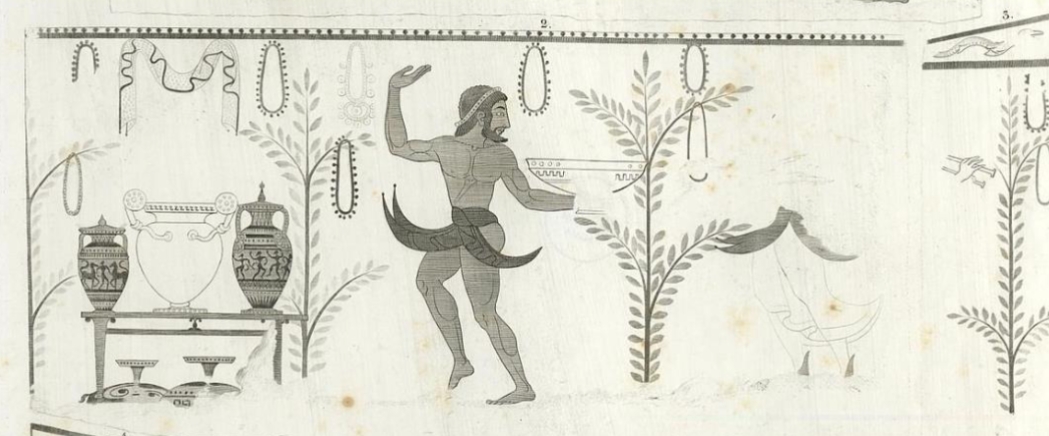

Name?
Tomb of the Painted Vases Tarquinia 500 BCE
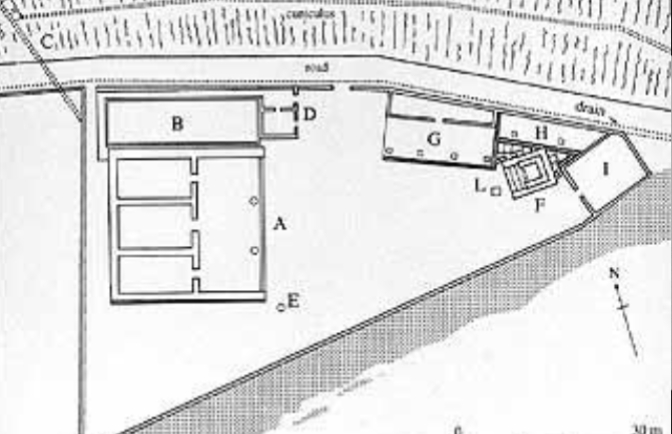
Name?
Plan of the Portanaccio Sanctuary Veii 500 BCE
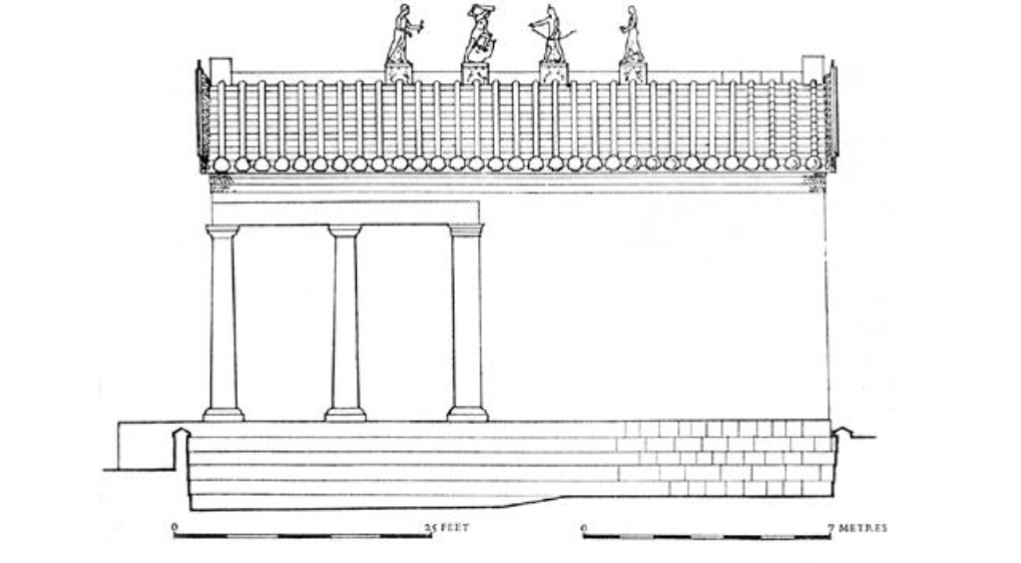
Name?
Temple at Veii 510 BCE

Name?
Apollo at Veii 510 BCE

Name?
Female Goddess (Leto) Veii 510 BCE
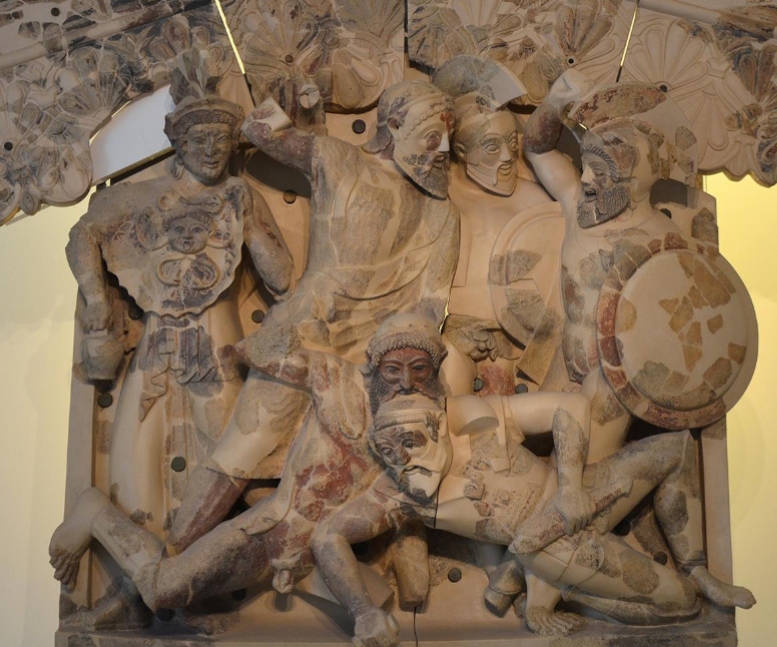

Name?
Pedimental Relief at Pyrgi Temple A 470 BCE
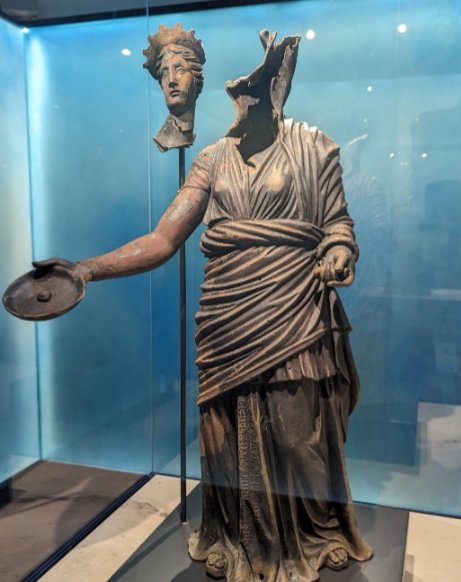

Name?
Statuette of a female sacrificing (goddess?), San Casciano dei Bagni late 2nd c

Name?
Statuette of an emaciated man San Casciano dei Bagni early 1st c

Name?
Statue of Mars Todi late 5th/early 4th

Name?
Mirror of Khalkas inspecting a liver Vulci late 5th
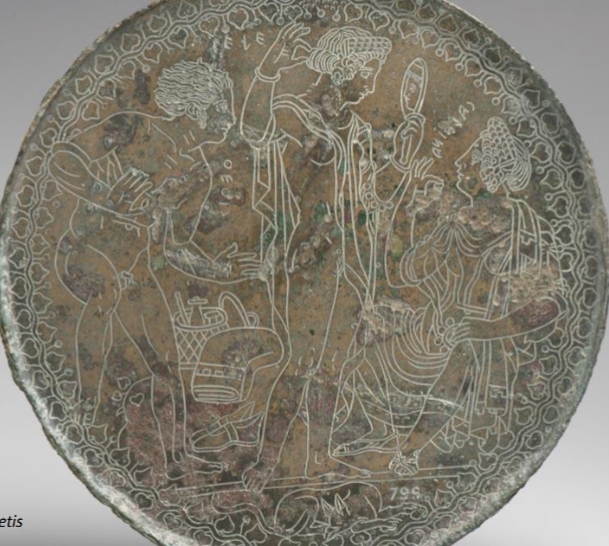

Name?
Mirror of Marriage of Pele and Thetis 350 BCE

Name?
Mirror of Uni nursing Hercle Volterra
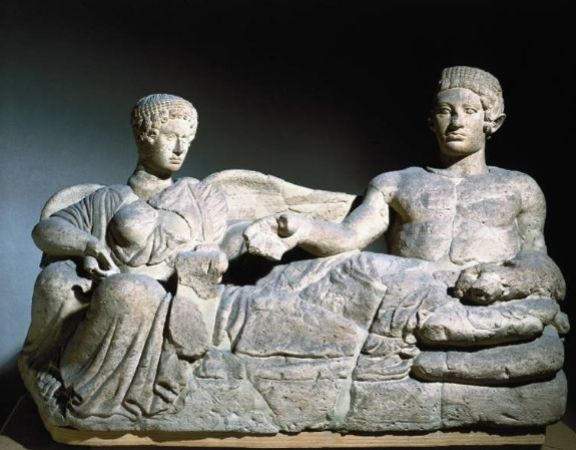

Name?
Youth and Female Demon (Vanth) Cinerary Urn 400 BCE
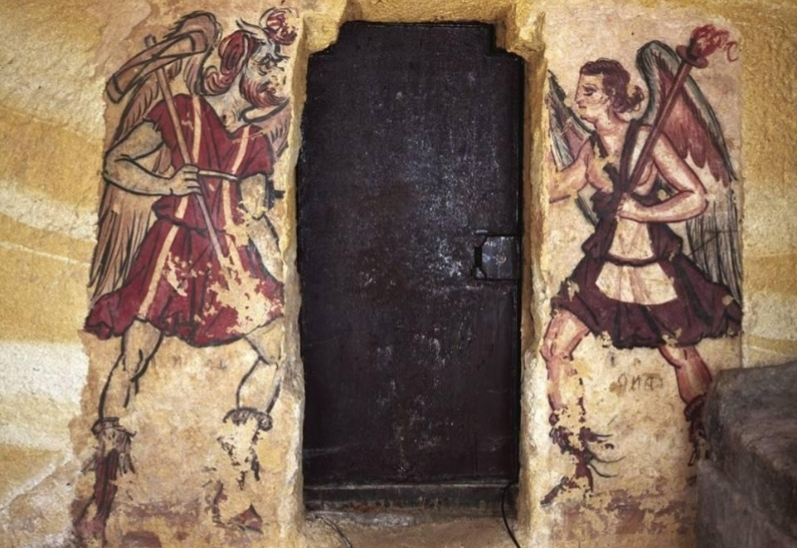

Name?
Charun and Vanth, Tomb of the Anina Family Tarquinia 3rd
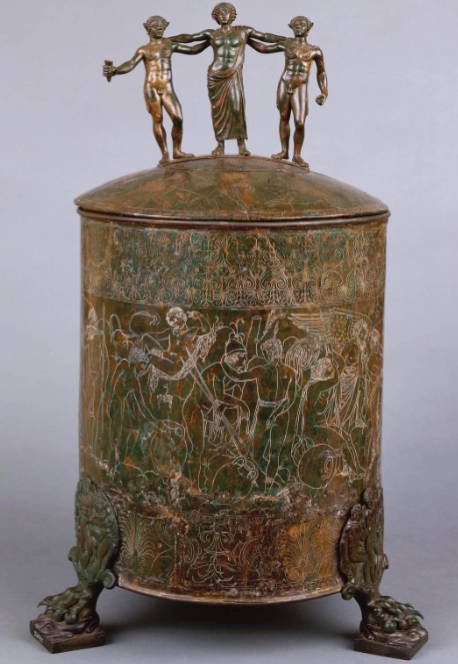

Name?
Ficaroni cista Praeneste 350 BCE
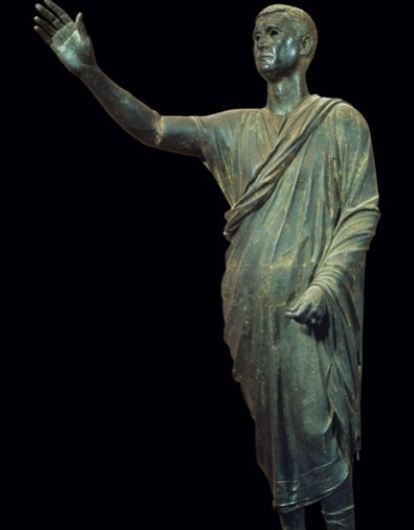

Name?
Orator statue Florence early 1st
a tall ancient Greek or Roman jar with two handles and a narrow neck.
amphora
refers to a type of pottery that is fine and delicate, with thin walls and carefully made
Bucchero sottile
refers to a type of Etruscan terracotta that is heavy and thick, often used for mixing wine and water
Bucchero pesante
a large bowl used in ancient Greece for mixing wine.
Krater
a type of Attic vase invented in the late 6th century BC specifically designed for export to Etruria. The amphora is characterized by its long conical neck, thin flaring mouth, and high foot.
nikosthenic amphora
a type of ceramic vessel, particularly a bowl with a rounded bottom and often no handles
ople
a type of bronze container or box, most commonly used by elite women for storing toiletry items, such as cosmetics, combs, jewelry, or other personal objects.
cista
a term found inscribed on various funerary objects, and it means: → “For the tomb” or “For burial”
suthina
refers to the way tombs, temples, or cities are aligned along a central axis, often with intentional symbolic, religious, or functional meaning.
axial orientation
temple that is surrounded on all sides by a single row of columns.
peripteral
a high, solid platform that elevates the temple structure above ground level.
podium
refers to the front area of the temple, also called the pronaos, which is the covered space with columns leading into the main sanctuary.
porch
a three-part inner sanctuary, or cella, located at the back of the temple.
tripartite cella
a form of divination—the practice of interpreting the will of the gods by observing signs in nature, especially the behavior of birds.
Augury
a death deity or underworld demon who serves as a guide or guardian of the dead.
Charun
a type of female spirit or divine figure associated with protection, fertility, beauty
Lasa
a form of divination focused on interpreting the internal organs of sacrificed animals, especially the liver, to understand the will of the gods.
haruspicy
chief god of the Etruscan pantheon, roughly equivalent to the Greek Zeus and the Roman Jupiter.
Tinia
major goddess in Etruscan religion, often considered the queen of the gods and the wife of Tinia, the chief god. She is roughly equivalent to the Greek Hera and Roman Juno.
Uni
prominent female spirit or deity in Etruscan mythology, associated primarily with death, the underworld, and guiding souls
Vanth