ESHS 120 Exam 3 Pelvic Girdle
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
pelvic bones
ilium, ischium, pubis
iliac crest
upper margin of iliac bones
iliac fossa
The broad, slightly concave inner surface of the ilium.
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami
pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint at which two pubic bones fuse together; allows some movement to facilitate childbirth
ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine)
the top point of the iliac crest in front
AIIS (anterior inferior iliac spine)
a bony projection on the ilium below the ASIS
PSIS (posterior superior iliac spine)
the top point of the iliac crest in back
PIIS (posterior inferior iliac spine)
Lies inferior to the PSIS and serves as an attachment for the sacrotuberous ligament
ishial tuberosity
'butt bone'
origin of hamstrings
greater sciatic notch
allows blood vessels and the large sciatic nerve to pass from the pelvis posteriorly into the thigh
lesser sciatic notch
inferior to ischial spine
sacrum and coccyx
single bones that result from the fusion of several vertebrae
sacroiliac joint
the joint between the sacrum and the ilium; connection the axial and appendicular skeletons
acetabulofemoral joint
bones + joint type
femur + acetabulum of pelvic bone
ball & socket (enarthrodial joint)
acetabulofemoral
movements°
flexion: 0 - 130°
extension: 0 - 30°
abduction: 0 - 35°
adduction: 0 - 30°
internal rotation: 0 - 45°
external rotation: 0 - 50°
acetabulofemoral
ligaments
- iliofemoral (Y)
- pubofemoral
- teres
- acetabular labrum
- ishiofemoral
iliofemoral (Y) ligament
anteriorly; prevents hyperextension
pubofemoral ligament
anteroinferiorly; limits excessive extension & abduction
teres ligament
deep in acetabulum + femur head depression: slightly limits adduction
acetabular labrum
lip of fibrocartilage that surrounds outer margin of the acetabulum on the hip bone
enhances stability + provide shock absorption; can be torn
ischiofemoral ligament
posterior ligament of the hip that goes from ischium to femur; limits internal rotation
hip flexors
iliopsoas (iliacus + psoas major), sartorius, pectineus, rectus femoris, tensor fasciae latae
hip adductors
adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus, gracilis, pectineus
hip extensors
gluteus maximus, biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, external rotators, adductor magnus?
hip abductors
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae, gluteus maximus, external rotators, sartorius?
hip internal rotators
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae
6 deep external rotators
hip external rotation
piriformis, obturator externus, obturator internus, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, quadratus femoris
hip external rotators
gluteus maximus + piriformis, quadratus femoris, obturator internus, obturator externus, superior gemellus, inferior gemellus
ilipsoas
hip flexion
hip external rotation
rectus femoris
hip flexion
knee extension
sartorius
hip flexion + abduction + some external rotation
knee flexion + weak internal rotation
pectineus
hip flexion, adduction, external rotation
adductor brevis
hip adduction w/ external rotation
- assists in hip flexion
adductor longus
hip adduction, w/ external rotation
- assists in hip flexion
adductor magnus
hip adduction w/ external rotation + extension
gracilis
hip adduction + internal rotation
weak knee flexion + internal rotation
semitendinosus
hip extension + internal rotation
knee flexion w/ internal rotation
semimembranosus
hip extension + internal rotation
knee flexion w/ internal rotation
biceps femoris
hip extension + external rotation
knee flexion w/ external rotation
gluteus maximus
hip extension + external rotation
- upper fibers assist in abduction
- lower fibers assist in adduction
gluteus medius
hip abduction
gluteus minimus
hip abduction w/ internal rotation + flexion
tensor fasciae latae
hip abduction + flexion
knee external rotation
typical causes of pelvic injury
significant trauma
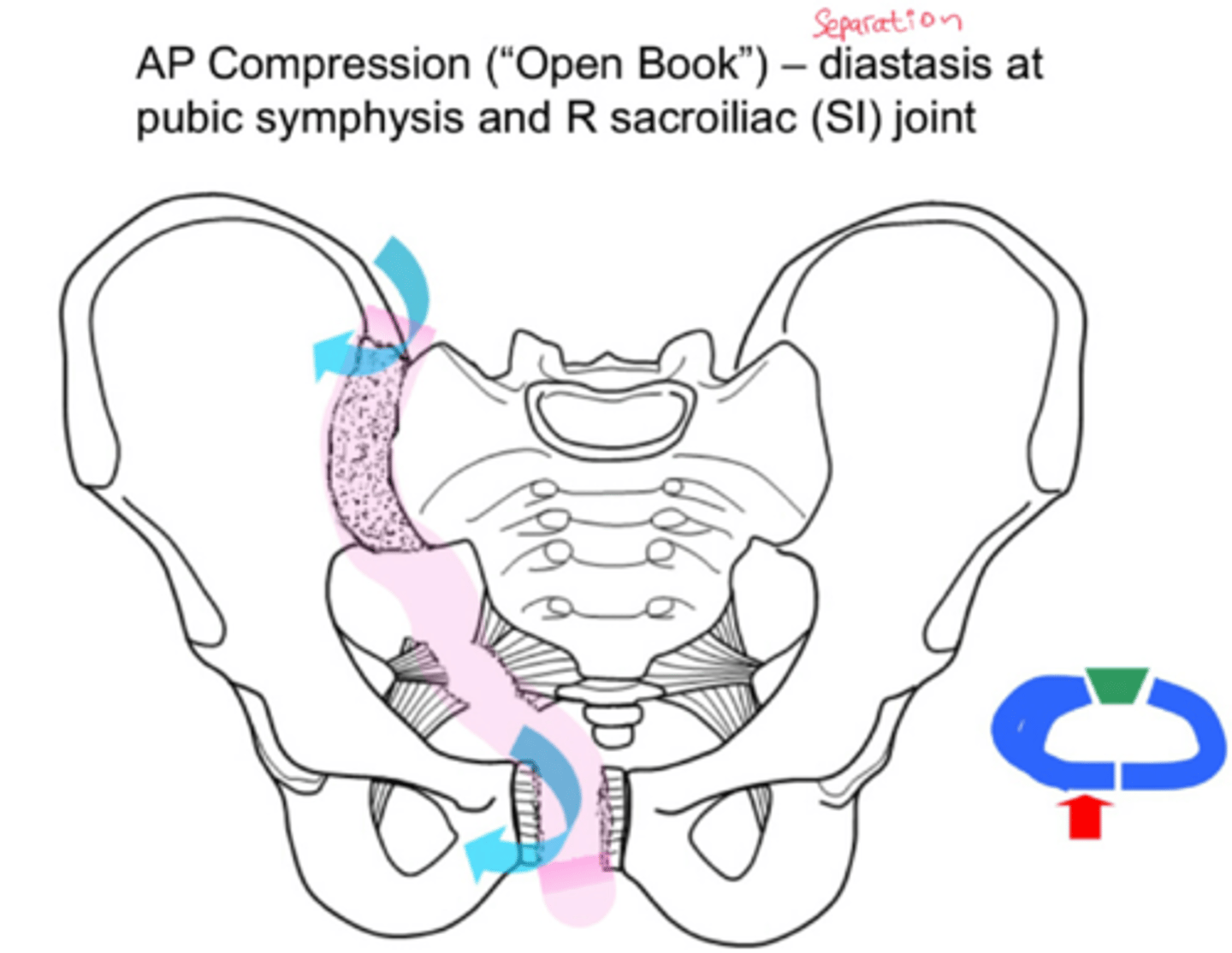
anterior-posterior (AP) compression fracture
widening pelvic ring +
widening SI joint, causing internal bleeding
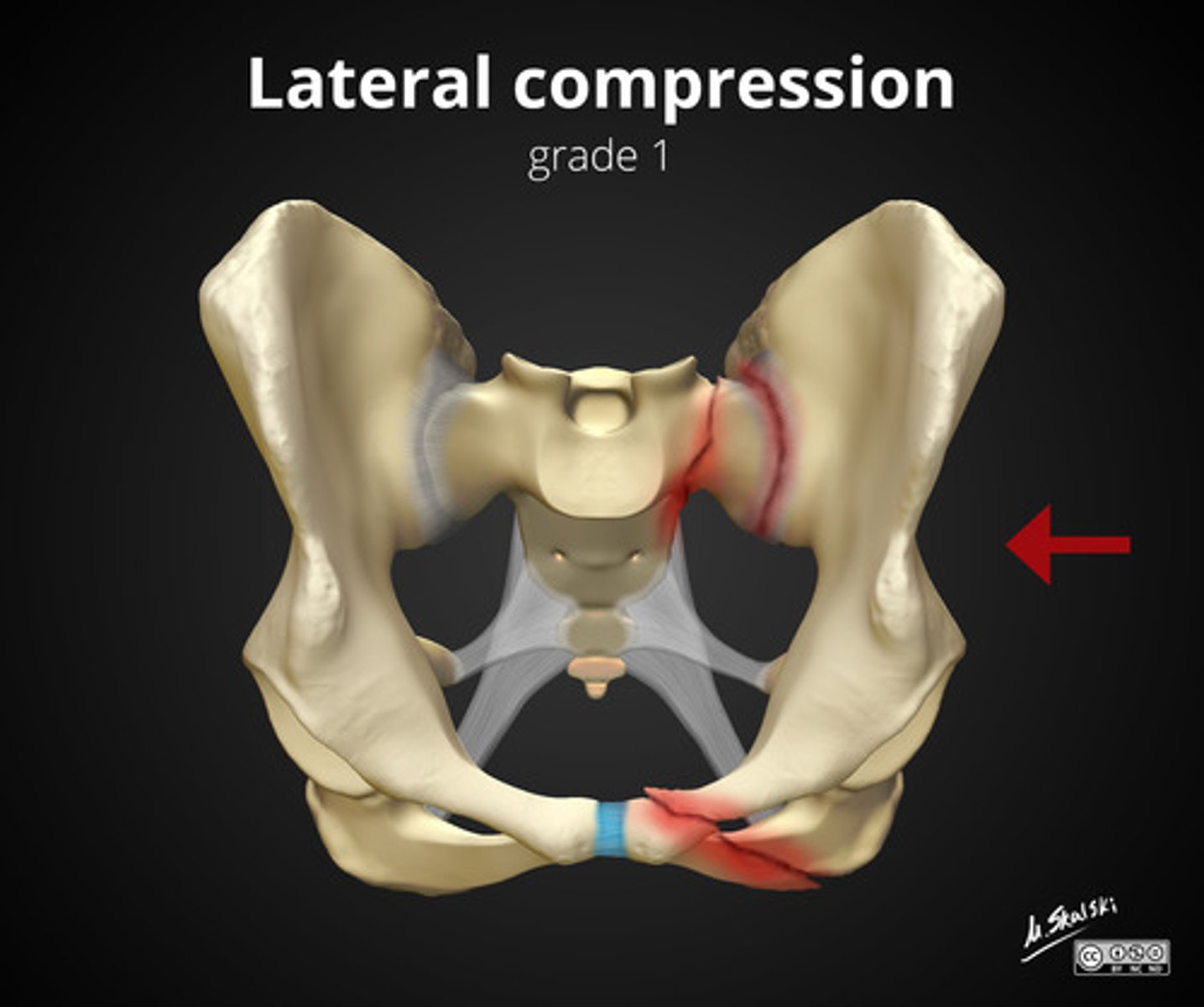
lateral compression fracture
Most common type of pelvic ring fracture?
side impact
may cause displaced fractures of pubis bone causing damage to organs
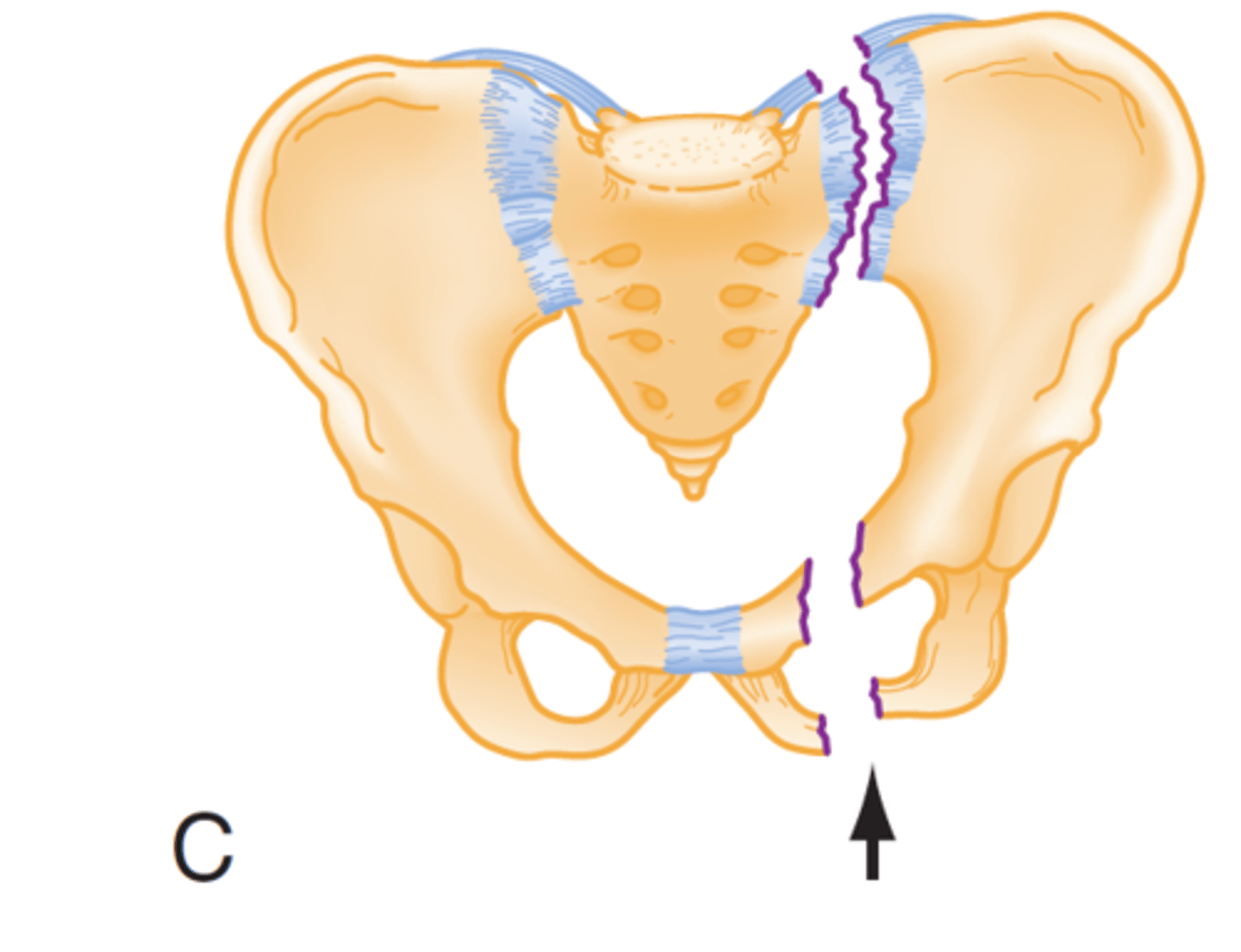
vertical shear injury
disruption in pelvic girdle, SI joint, ligaments, blood vessels
may lead to pelvic injury instability and severe internal bleeding
apophysitis
inflammation of growth plate w/ muscle attachments
- associated w/ muscle overuse
- common in growing teens
SI dysfunction
lower back and buttock pain to lower hip, groin, or upper thigh (one side or both)
SI dysfunction causes
- injury
- arthritis
- pregnancy
- infection
- repetitive stress activities
pelvic floor dysfunction
men + women affected
- leaking urine and failing to reach the bathroom
- pass air from the anus or vagina bending over or lifting
- reduced sensation in the vagina
- tampons dislodge or fall out
- bulge at the vaginal opening
- sexual dysfunction
pelvic floor functions
1. pelvic organ support
2. bladder + bowel control
3. passing of urine + feces
4. sexual function
5. breathing
6. pregnancy + childbirth
hip osteoarthritis
degenerative arthritis characterized by the wearing away of the cartilage in the hip joint
- 2nd most common
hip osteoarthritis symptoms
- groin pain
- outer thigh pain
- buttocks pain
- difficulty walking
- worse in the morning
- limited ROM
- + FABER's test
FABER/Patrick's Test
flexion, abduction & ER of the hip
a. (+) sign: pain
b. Indications: problem with hip or SI joint
femoral acetabular impingement (FAI)
- one or both hip joints irregularly shaped, rubbing against each other
- may be due to malformation of acetabulum
FAI symptoms
- groin pain
- hip pain
- buttocks pain
- after intense activity
- ages 20-45
snapping hip syndrome
- snapping sensation or popping sound in movement
- muscle or tendon moves over bony protrusion in hip
snapping hip syndrome
muscles
anterior: IT band, rectus femoris, iliopsoas
posterior: biceps femoris
hip bursitis
inflamed bursa
- greater trochanter of hip bone
- iliopsoas bursa; groin area of hip
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
femoral head is displaced from femoral neck due to growth plate separation
- grade 1, 2, 3
piriformis syndrome
compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle
- pain + numbness of buttock and down back of the leg
piriformis syndrome causes
- trauma of hip or buttocks
- piriformis muscle hypertrophy in athletes
- sitting for prolonged periods
- bipartite (separated?) piriformis muscle