BIO 201: Chapter 2.1 Osseous Tissue Histology and Physiology
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
four shapes of bones
long, short, flat, and irregular
compact bone
made up of multiple layers that are solid and dense
spongy bone
made up of deep loosely organized sponge
osteon
basic organizational and functional unit of osseous tissue
- present in both compact and spongy bones but much more in compact bone
- densely packed in compact bone
- scattered throughout the trabeculae (flat thin plates) and spicules (rods or spines) of spongy bone
layers of an osteon
- concentric lamellae: surrounds the central canal passageway
- interstitial lamellae: located in spaces between each osteon
- circumferential lamellar: runs parallel to the bone's surface, surrounding the circumference of the bone, is the most superficial lamellae
central canal
passageway that houses blood vessels and nerves
osteocytes
mature bone cells in between each lamellae in lacunae
lacunae
small gaps/pits/holes in the bone matrix that have an osteocyte inside
canaliculi
channels through the hard bone matrix that allow osteocytes to communicate with each other and the rest of the body
osteoblasts
immature bone forming/building cells that produce collagen fibers during bone formation
osteoclast
bone dissolving/crushing cells
long bones
cylindrical bones that are longer than they are wide
diaphysis
long central portion or shaft of a long bone that houses the medullary cavity
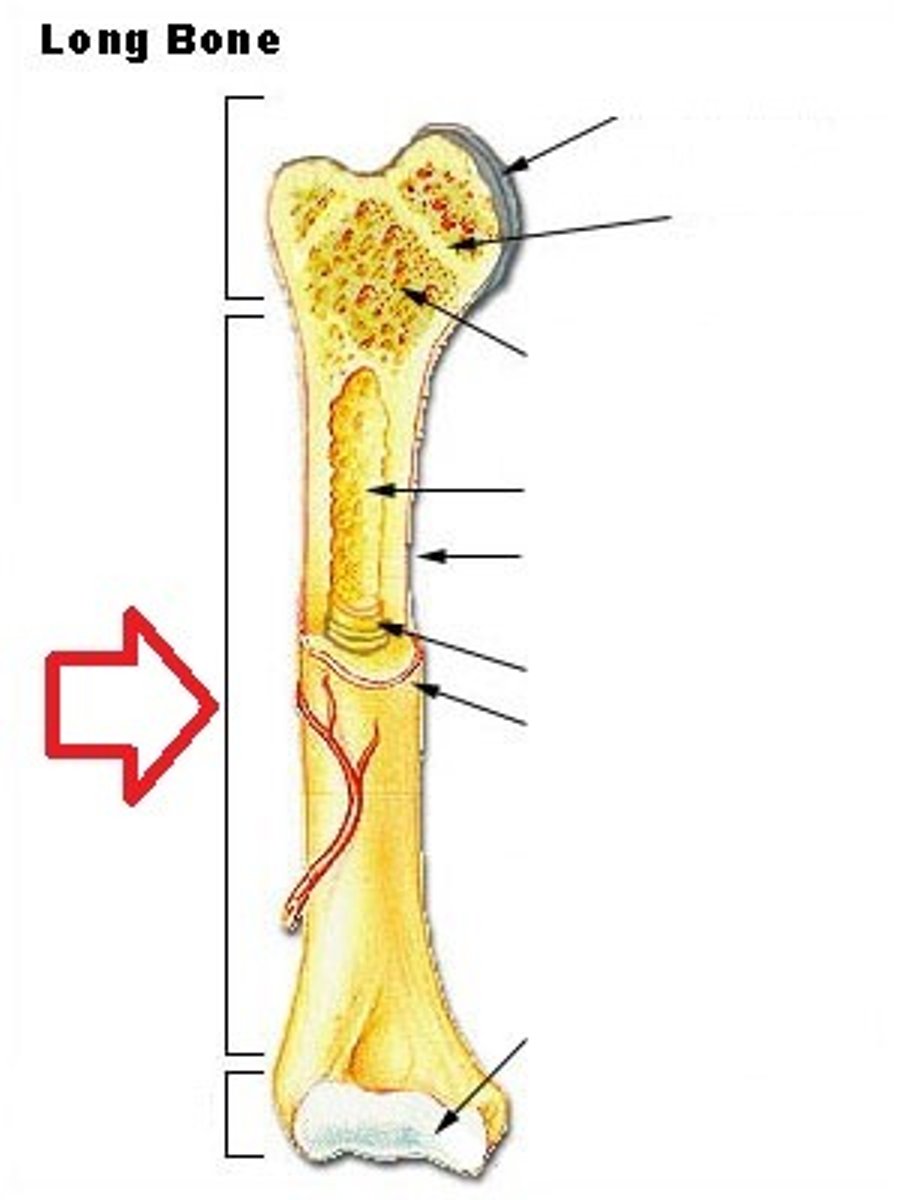
medullary cavity
contains yellow bone marrow and is lined by endosteum
endosteum
deep thin layer of epithelium that lines the medullary cavity, spongy bones, and canals within bone
epiphysis
complex end piece of long bones filled with red bone marrow
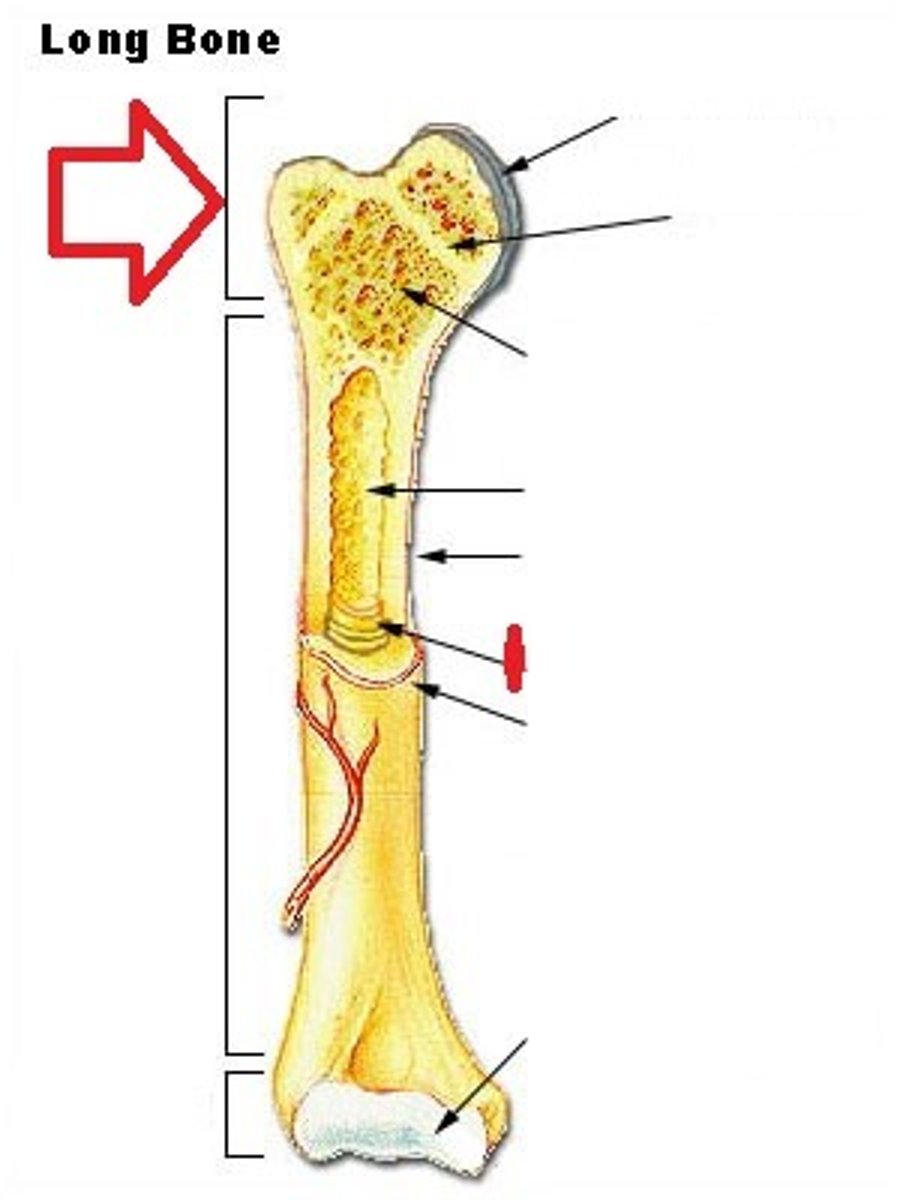
red bone marrow
tissue that produces blood cells
epiphyseal line
scar of where the diaphysis and epiphyses fuse together during development
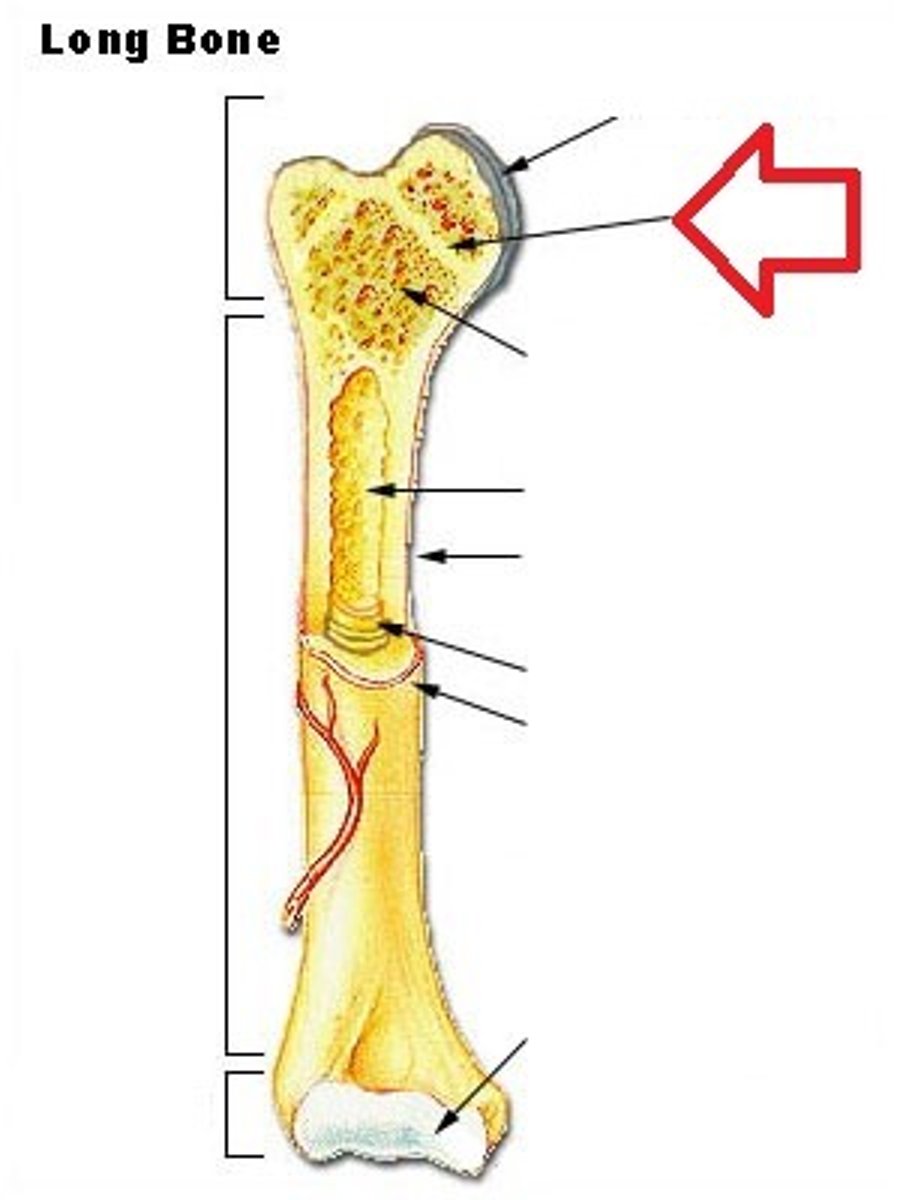
periosteum
superficial thin layer of dense connective tissue that encases living bone tissue
articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage that cushions the long bones where they meet at synovial joints and helps joints articulate
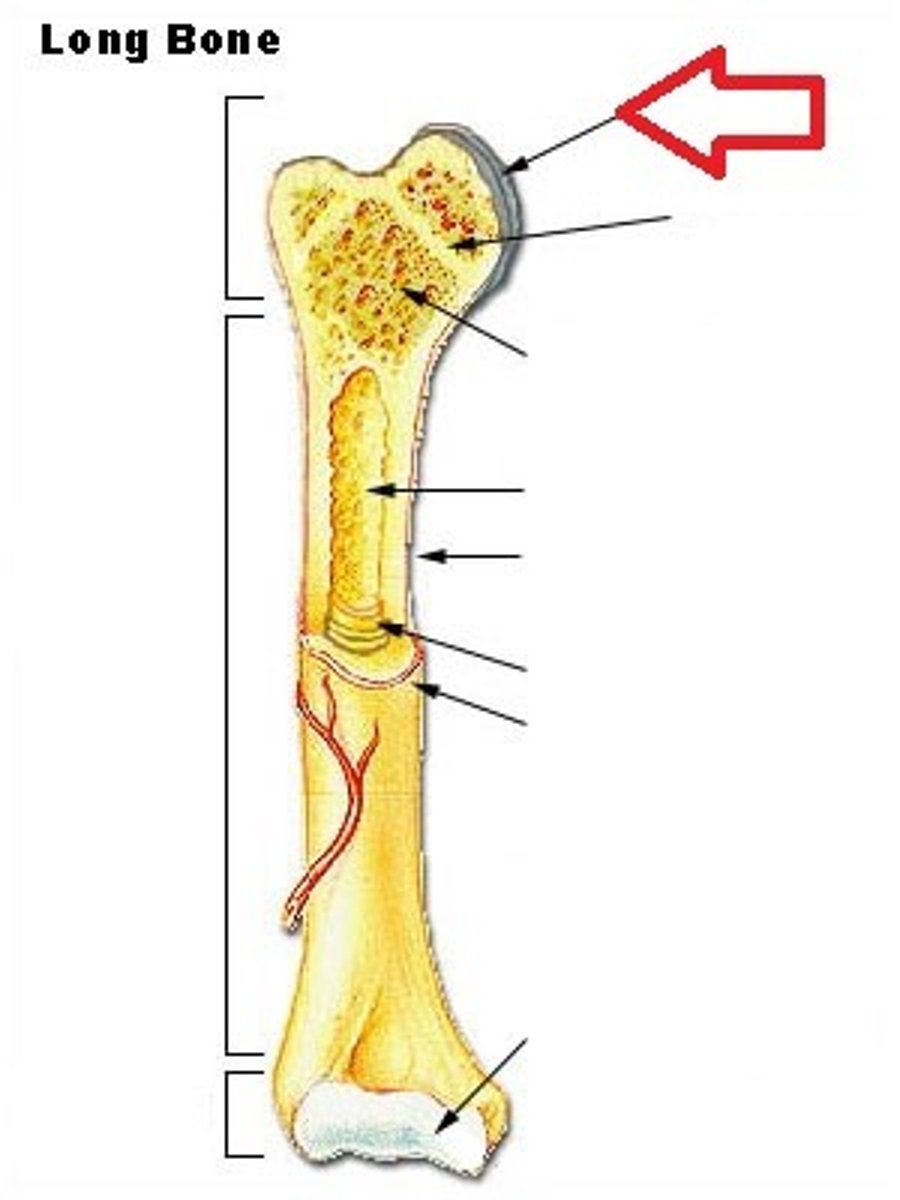
synovial fluid
fluid produced in the synovial joints that help joints articulate easily
nutrient foramina
holes that allow blood vessels and nerves to pierce and enter the bone
perforating fibers
part of the periosteum which penetrate into the bone matrix to help with its attachment to bone
true
true or false: flat bones lack a medullary cavity
Wolff's Law of Bone
bone grows stronger to better withstand the regular forces it encounters and the architecture of a bone is determined by the mechanical stresses placed on it
hormones that control and regulate the availability of free calcium in the bloodstream
parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitriol, and calcitonin
parathyroid (PTH) hormone and calcitriol
encourage bone resorption
bone resorption
breakdown/dissolving of the matrix of osseous tissue and returning of minerals, like calcium, to the blood stream
parathyroid glands
release parathyroid hormone (PTH)
kidneys
secrete calcitriol
calcitonin
promotes bone deposition (mineralization) of the mineral components of bone, lowering blood calcium levels
parafollicular cells in thyroid gland
release calcitonin
high blood calcium levels can be lowered by
releasing calcitonin in the bloodstream
low blood calcium levels can be increased by
releasing PTH or calcitriol in the bloodstream