Endocrinology LD Overview
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
thyroid nodule dx
Initial
-TSH: low = hot, normal/high = cold (malignant)
-free T4
-thyroid ultrasound
-malignancy reg flag: size >1cm, irregular margin, taller than wide, hypoechoic
Confirmatory
-fine needle aspiration biopsy
-radioactive iodine uptake scan
Classification
-TIRADS score used to guide decision on FNA biopsy = score >3
-Bethesda are the results obtained from FNA
thyroid cancer dx
Initial
-TSH: low = hot, normal/high = cold (malignant)
-free T4
-thyroid ultrasound
-malignancy reg flag: size >1cm, irregular margin, taller than wide, hypoechoic
Labs
-serum calcitonin = elevated in medullary thyroid carcinoma
-serum thyroglobulin = elevated in most metastatic papillary and follicular tumors
Confirmatory
-fine needle aspiration biopsy
-radioactive iodine uptake scan
-PET scan, TNM staging
MEN syndrome dx
Genetic testing
-MEN 1: MEN1 gene
-MEN 2: RET proto oncogene
-early testing is crucial
pheochromocytoma dx
Labs
-plasma fractionated free metanephrines = elevated
Confirmatory
-urinary fractionated metanephrines = elevated
Imaging
-non contrast CT scan
-never perform needle biopsy
parathyroid carcinoma dx
Labs
-serum calcium and PTH levels = elevated
Imaging
-initial: neck ultrasound
Confirmatory
-histopathology
adrenal adenomas dx
Inital
-presenting signs and symptomas
Imahing
-CT scan: well circumscribed, homogenous, low attenuation
hypercalcemia of malignancy dx
Labs
-total calcium and ionized calcium = elevated
-low or normal PTH
-PTHrP = elevated (confirmatory)
Imaging
-aimed at identifying underlying malignancy
Cushing syndrome dx
-exclude the presence of endogenous glucocorticoid intake or other disease that cause hypercortisolism
First line
1. bedtime salivary cortisol: elevated
-2 swabs and collect saliva, done 2 nights after 10-11pm
2. 24 hour urinary free cortisol excretion: elevated
-collect urine, elevated on 2 separate occasions
3. overnight low dose dexamethasone suppression test: abnormal
-suppressed = rule out cushing
-if abnormal use high dose dexamethasone test: partially suppressed = pituitary cause, unsuppressed = ectopic
Once hypercortisolsm is confirmed
-plasma ACTH level = high (Cushing disease)
-plasma ACTH level = low (Cushing syndrome)
-serum DHEA level: ACTH dependent
Imaging
-MRI brain/pituitary to find tumor as a cause
primary adrenal insufficiency dx
Initial
-total serum cortisol between 6-8am: low = adrenal insufficiency
-intermediate level = move on to confirmatory
-high level = rule out
-plasma ACTH
Confirmatory
-ACTH stimulation test: lack of rise = primary
- IV 250mg dose of ACTH (Cosyntropin), measured at 0, 30, 60min
Supportive
-serum electrolytes: hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, hypoglycemia
-plasma renin activity and aldosterone levels
Etiology
-21 hydroxylase antibodies = + for autoimmune
-T scan of adrenal gland
-TB test
-HIV testing
secondary adrenal insufficiency dx
Initial
-total serum cortisol between 6-8am: low = adrenal insufficiency
-intermediate level = move on to confirmatory
-high level = rule out
-plasma ACTH
Confirmatory
-ACTH stimulation test: normal = secondary
- IV 250mg dose of ACTH (Cosyntropin), measured at 0, 30, 60min
acute adrenal crisis dx
-measure serum cortisol and plasma ACTH
-hypotension + low serum cortisol = suggestive of crisis
-serum ACTH = elevated for primary AI and low for secondary AI
-other labs: Hyperkalemia, Hyponatremia, Hypoglycemia
congenital adrenal hyperplasia dx
Prenatally
-newborn screening serum 17 hydroxyprogesterone
Postnatally
-serum 21 hydroxylase deficiency testing
hyperaldosteronism dx
Primary
-plasma aldosterone concentration = elevated
-plasma renin activity = low
-PAC:PRA (aldosterone/renin) ratio = elevated
-all antihypertensives should be stopped before testing
Secondary
-plasma renin activity = elevated
-most common cause is diuretic therapy
Confirmation
-24 hour urine aldosterone, sodium, creatinine
-fludrocortisone suppression test
-saline suppression testing
Imaging
-CT adrenals for adenoma or hyperplasia
type 1 DM dx
Step 1: suspicion
-classic sx + random glucose >200
-fasting glucose >126 (8 hour fast) = diagnosis
-2 hour glucose >200
-HbA1c >6.5 = diagnostic for MONITORING
Step 2: confirm
-anti-GAS antibodies (most common)
-anti-IA2
Step 3: assess Beta cell function
-C-peptide level = <0.6
-will distinguish T1 from T2
Step 4: rule out DKA
-serum or urine ketones = if present indicated DKA
-arterial blood gas
-BMP
GAD 65
-need to have everything else before ordering
-positive test indicates presence of autoantibodies which is characteristic of T1DM
islet autoantibodies
-appear when B cells are damaged
-can be used to estimate individuals risk of developing T1DM
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) dx
Step 1: assess DKA
-hyperglycemia: glucose >250
-pH <7.35
-serum ketones >3
Step 2: calculate anion gap
-anion gap = NA + (Cl + HCO3) = >10-12
Step 3: severity
-mild: 7.25-7.3, HCO3 15-18
-mod: 7.0-7.24, HCO2 10-14
-severe: <7, HCO3 <10
Step 4
-CBC, blood culture
-chest X ray, urinalysis
-ECG, lipase
when to check for ketones
-blood sugar >300
-nauseated and vomiting, abdominal pain
-cold or flu
-feel tired all the tome
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) dx
Step 1
-hyperglycemia: glucose >600
-hyperosmolality >320
-altered mental
-serum ketones <3
-pH >7.35
Step 2
-effective osmolality = 2(Na) + glucose/18
-320 confirms hyperosmolar state
-350 associated with coma
Step 3
-glasgow scale for mental status
-degree of dehydration
Step 4
-CBC, cultures, CMP, urinalysis, chest X ray, EC
hypoglycemia dx
Step 1
-glucose <70
-non diabetic <55 with sx
Step 2: Whipples triad
-sx consistent with hypoglycemia
-low plasma glucose concentration
-relief of sx with glucose administration
Step 3
-mild: patient can self treat
-mod: requires assistance but tolerate oral
-severe: parenteral therapy or glucagon
Step 4: etiology in non diabetics
-72 hour supervised fast = gold standard
-insulin, C peptide
-sulfonylurea, cortisol
dawn phenomenon dx
-check blood glucose at bedtime, 3am, upon waking
-pattern: normal bedtime > normal/elevated 3 am > elevated morning
-continuous glucose monitoring can confirm
Somogyi effect dx
-check blood glucose at bedtime, 3am, upon waking
-pattern: normal bedtime > low 3 am > elevated morning
-look for signs of nocturnal hypoglyecima
latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) dx
Step 1
-clinical suspicion
Step 2
-GAD antibodies > 10 = most common
-IA-2 antibodies
-ZnT8 antibodies
Step 3
-fasting C peptide
-fasting glucose >126
-HbA1c >7
metabolic syndrome dx
Presence of 3/5 criteria:
-elevated waist circumference >40 men, >35 women
-elevated triglycerides >150
-reduced HDL <40 men, <50 women
-elevated BP >135/85
-elevated fasting glucose >100
Tx for any of these criteria also counts
-FLP, HbA1c, BP, waist circumference
gestational diabetes dx
-all asymptomatic women screened 24 weeks
-50g screening test at 24-28 weeks >140 = abnormal
-if first test is abnormal then 100g 3 hour oral glucose test
-fasting >95
-1 hour >180
-2 hour >155
-3 hour >140
prediabetes dx
1. fasting plasma glucose = 100-125
2. 2 hour plasma glucose = 140-199
2. HbA1c = 5.7-6.4%
type 2 DM dx
1. fasting plasma glucose = >126
2. glucose tolerance = fasting >126 or 2 hour >200
-test of choice for gestational diabetes
3. HbA1c = >6.5
-diagnostic test of choice and monitor tx
4. random plasma glucose + sx = >200 + symptoms
type 2 DM screening
-tests used: fasting plasma glucose, 2 hour OGTT, HbA1c
Universal screening
-35 for all adults every 3 years for normal results
High risk: earlier and more often
-BMI >25 and
-first degree relative, africans, hx of CVD, HDL <35, PCOS, physically inactive, gestational diabetes, prediabetes, HIV, antipsychotic therapy
Children
-start at 10 or onset of puberty in overweight
-if normal screen every 3 years
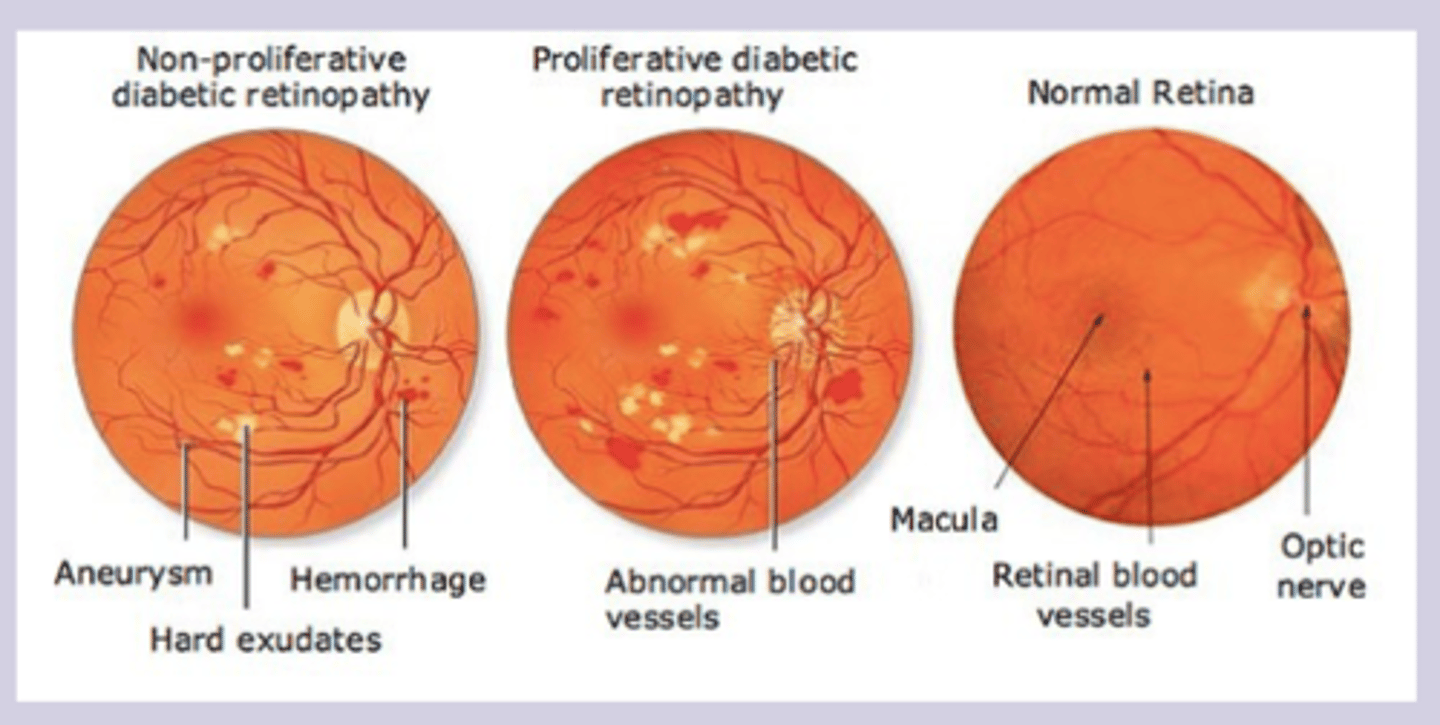
diabetic retinopathy dx
Dx
-fundoscopic dilated eye exam
-annual screening in diabetic patients
diabetic nephropathy dx
Dx
-decreased renal function + proteinuria + hx of DM
-urine albumin-creatinine ratio
-screening yearly: goal <30
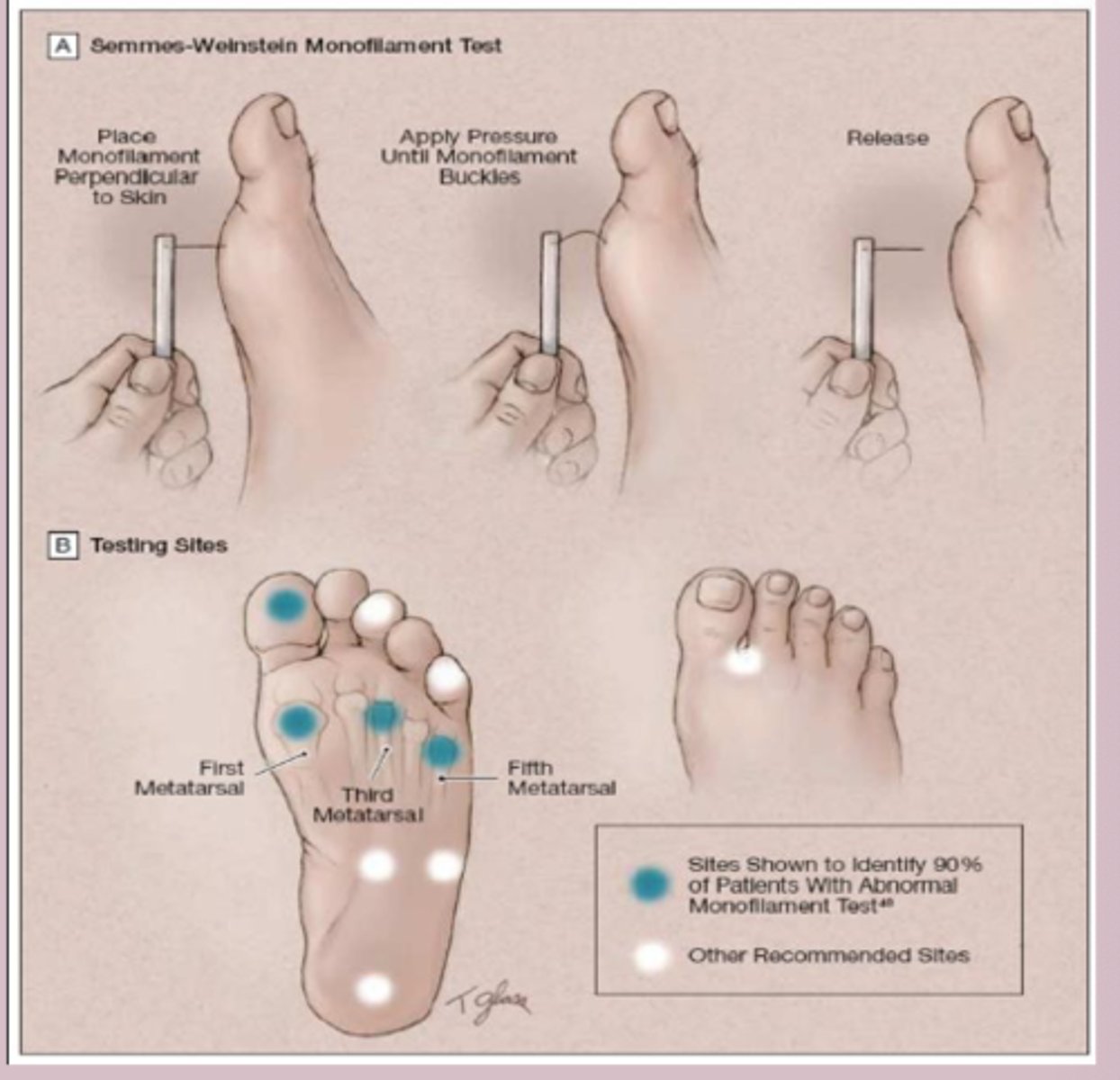
diabetic neuropathy dx
Dx
-comprehensive foot exam
-screening yearly foot exam
-skin inspection, pulses, ankle reflexes, proprioception of great toe, vibratory sensation, monofilament exam
cardiovascular complication dx
Dx
-blood pressure screening at every visit <130/80
-lipid screening: dx at <40 > at dx and every 5 years
peripheral artery disease dx
Dx
-ankle brachial index, angiography
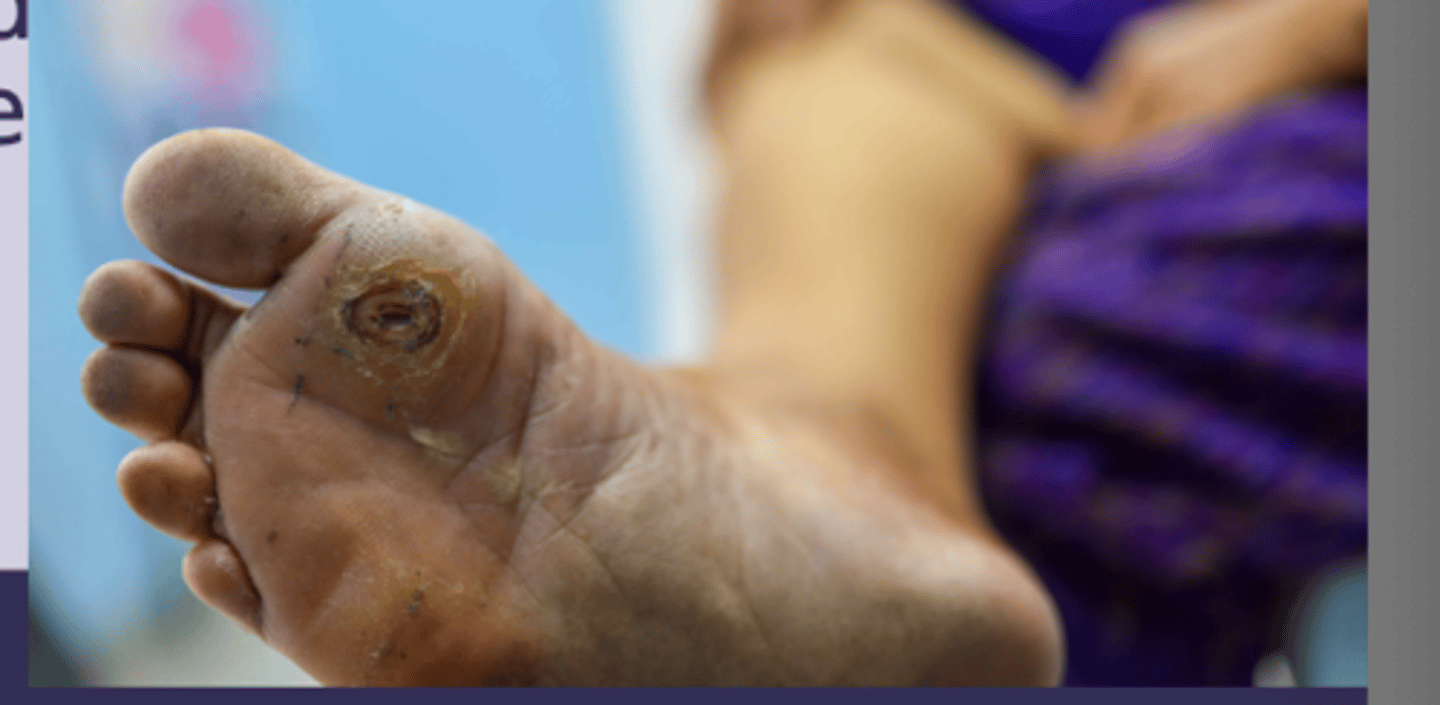
diabetic foot ulcer
-neuropathy, vascular insufficiency, infection
Prevention
-regular foot exam
-full monofilament exam yearly
hyperparathyroidism dx
Initial workup
-serum calcium, serum PTH, phosphorus
-serum 25(OH)vitD, serum creatinine, 24 hour urine
-DEXA scan, renal US or CT
Primary
-increase PTH + increase calcium + decrease phosphorus
Secondary
-increase PTH, low to normal calcium + increase phosphorus and vit D
Tertiary
-increase PTH + increase calcium
Primary hyperparathyroidism dx
Step 1
-BMP shows elevated calcium levels >10.2
-Paynes formula
Step 2
-PTH level = elevated
-confirmatory
Step 3
-parathyroid ultrasound to show parathyroid adenoma
-Vit d levels
secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism dx
Secondary
-elevated PTH + low or normal Ca + high phosphorus (due to impaired phosphate excretion by kidney)
-vit D levels
Tertiary
-elevated PTH + high Ca
-loss of normal feedback loop
Other labs
-serum creatinine, eGFR
-urinary calcium and phosphate
-ALP level
hypoparathyroidism dx
Labs
-low calcium + high phosphorus + low PTH
-24 hour urine calcium
-genetic testing for DiGeorge
-DEXA, CT/MRI
-EKG
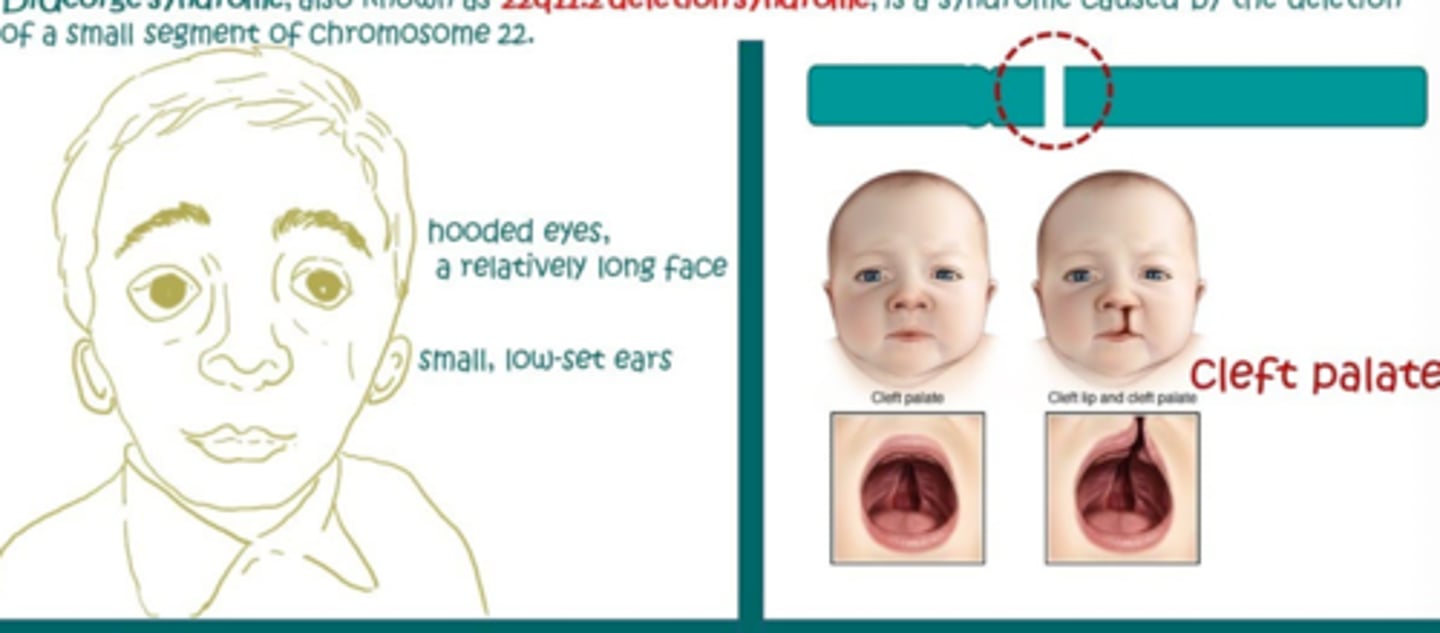
DiGeorge Syndrome
-22q11.2 deletion syndrome
-parathyroid glands fail to develop properly or absent
Sx
-cardiac anomalies, abnormal facies, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcemia
-CATCH-22
Tx
-lifelong calcium and Vit D
-regular monitoring of calcium
-thymic transplant
hypothyroidism dx
-TSH = high
If abnormal
-free T4
-if decreased = overt hypothyroidism
-if normal = subclinical hypothyroidism
Once diagnosis is confirmed establish etiology
-TPO and Tg antibodies
-present in 95% of patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism
Imaging
-not a primary tool used to assess structure
-first: ultrasound
-thyroid scintigraphy for functional status
congenital hypothyroidism dx
-TSH testing screening in newborns
-serum TSH, T4
autoimmune Hashimoto thyroiditis
-cell mediated and antibody mediated destruction of thyroid gland
-autoantibodies against thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin, TSH receptor
Subclinical hypothyroidism
-compensation phase: normal thyroid hormones are maintained to rise TSH
-later unbound T4 levels fall and TSH level rise further > sx become apparent
hyperthyroidism dx
Labs
-low TSH
-free T4 ordered when TSH is abnormal = high
Determine etiology
-thyroid stimulating immunoglobin
-radioactive iodine uptake scan (scintigraphy) = general hig uptake suggest Grave disease
-US for pregnant
-if Graves: TSI and TRAb antibodies
thyroiditis
-most common: chronic Hashimoto thyroiditis
-postpartum thyroiditis and subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis > transient hyperthyroidism
-TPO antibodies or Tg antibodies = high
painful subacute thyroiditis dx
Dx
-antithyroid antibodies = low, ESR = elevated
-hyperthyroid > euthyroid > hypothyroid > euthyroid
-biopsy = multinucleated giant cells
infectious suppurative thyroiditis dx
Dx
-febrile with leukocytosis
-elevated ESR
-thyroid function = normal
IgA related thyroiditis
-replacement of thyroid tissue with fibrosis tissue > thyroid gland become form and fixed
Sx
-hypothyroidism
-difficulty swallowing
-hard woody thyroid gland
Tx
-thyroid hormone replacement
-surgery for severe cases
acromegaly dx
Labs
-first line: serum IGF-1 level = elevated
Confirmatory
-oral glucose tolerance test with GH measurement = GH fails to suppress
Imaging
-MRI pituitary to assess for pituitary adenoma
-visual field testing
gigantism dx
-clinical suspicion
Labs
-IGF-1 levels = elevated
-GH suppression test = failure to suppress
-genetic testing
Imaging
-MRI pituitary for pituitary adenomas
-visual field testing
-bone assessment
dwarfism dx
Labs
-FGFR3 mutation
-IGF-1 levels
-GH stimulation test
-thyroid function test, CBC, CMP
Imaging
-US: width to femur length ration = higher
-Xray/MRI/CT: small flat squared iliac wings, large skull, shortened vertebral body
pituitary adenoma dx
Labs
-prolactin, GH, IGF-1
-TSH, free T4, ACTH, cortisol
-FSH, LH, testosterone
Imaging
-gold standard: MRI pituitary with gadolinium
hypopituitarism dx
Labs
-8 am cortisol, ACTH
-TSH, free T4
-FSH, LH, testosterone, prolactin, IGF-1
-insulin tolerance test = gold standard for GH and ACTH
Imaging
-MRI pituitary with godolinium
hyperpituitarism dx
Labs
-prolactin = elevated
-GH = IGF level, OGTT, GH measurement
-ACTH = 24 hour urine cortisol, dexamethasone suppression test
-TSH = elevated
prolactinomas dx
Labs
-serum prolactin = 200 strongly suggests prolactinoma
-pregnancy test, TSH, free T4, CMP
Imaging
-MRI pituitary with gadolinium
diabetes insipidus dx
Labs
-24 hour urine volume, serum osmolality and sodium
-urine volume >3L
-urine osmolality <300, serum osmolality >295
-gold standard = water deprivation test <300
Desmopressin stimulation test
-central = >50% increase in urine osmolality
-nephrogenic = <50% increase in urine osmolality
Imaging
-MRI brain with gadolinium
SIADH dx
Schwartz-Bartter criteria
-serum sodium <135
-serum osmolality <275
-urine osmolality >100
-urine NA >30
-clinical euvolemia
-normal renal, adrenal, thyroid function
-rule out meds
Imaging
-identify underlying cause
male primary hypogonadism dx
Step 1
-total testosterone = <200
-free testosterone = 18-60 <35, >70yo <30
-free and total testosterone = low
-nonfasting in the morning
Step 2
-differentiate primary from secondary
-serum LH = high
Step 3
-karyotype for klinefelter's
-serum prolactin = normal in primary
male secondary hypogonadism dx
Step 1
-total testosterone = <200
-free testosterone = 18-60 <35, >70yo <30
-free and total testosterone = low
-nonfasting in the morning
-repeat
Step 2
-differentiate primary from secondary
-serum LH = low
Step 3
-serum PRL: elevated if prolactinoma present
-MRI of pituitary/hypothalamus to search for lesion
females hypogonadism dx
Step 1
-primary = elevated FSH/LH, low estrogen
-secondary = low FSH/LH, low estrogen
Step 2
-primary: karyotypes, ultrasound
-secondary: serum prolactin, MRI of pituitary/hypothalamus