Chapter 5: Histology
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Histology definition
Study of Tissue
(Histology (microscopic anatomy)
- study of tissues and how they form organs)
How many cell types in body?
200 cells types in body's
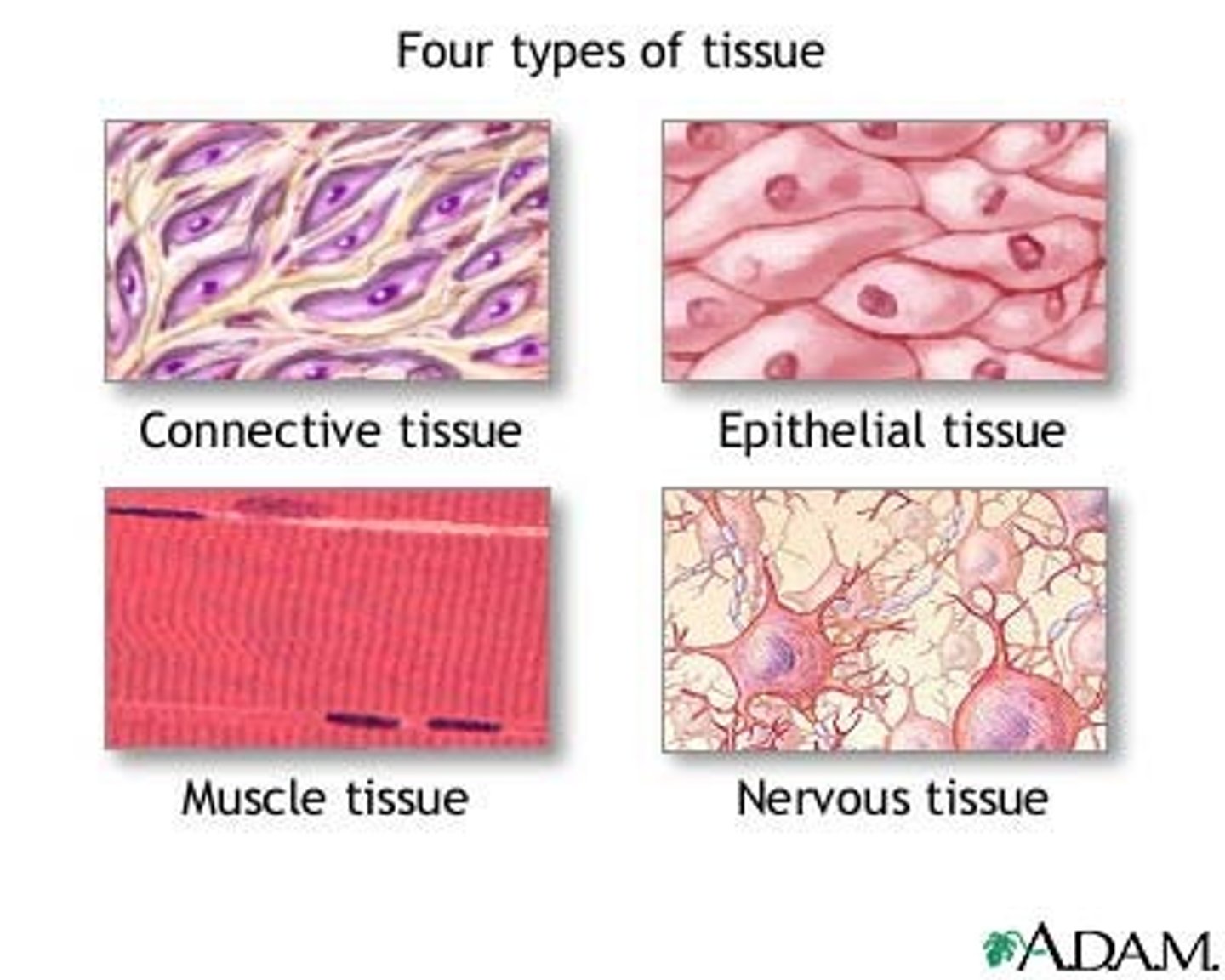
4 Basic Tissues
Epithelial: (Free surface)
Connective: (Matrix)
Muscle: (Contracts)
Nervous
Tissue Define
an aggregation of similarly specialized cells which together perform certain specific functions

Organ Define
complex and consists of at least 2 tissue types
Epithelial Tissue: General Features
- good at either protection or support not both
- occur in sheets and layers
- avascular
- highly cellular (not a lot of matrix)
- directional (apical vs basal)
- divides tissue from outside world
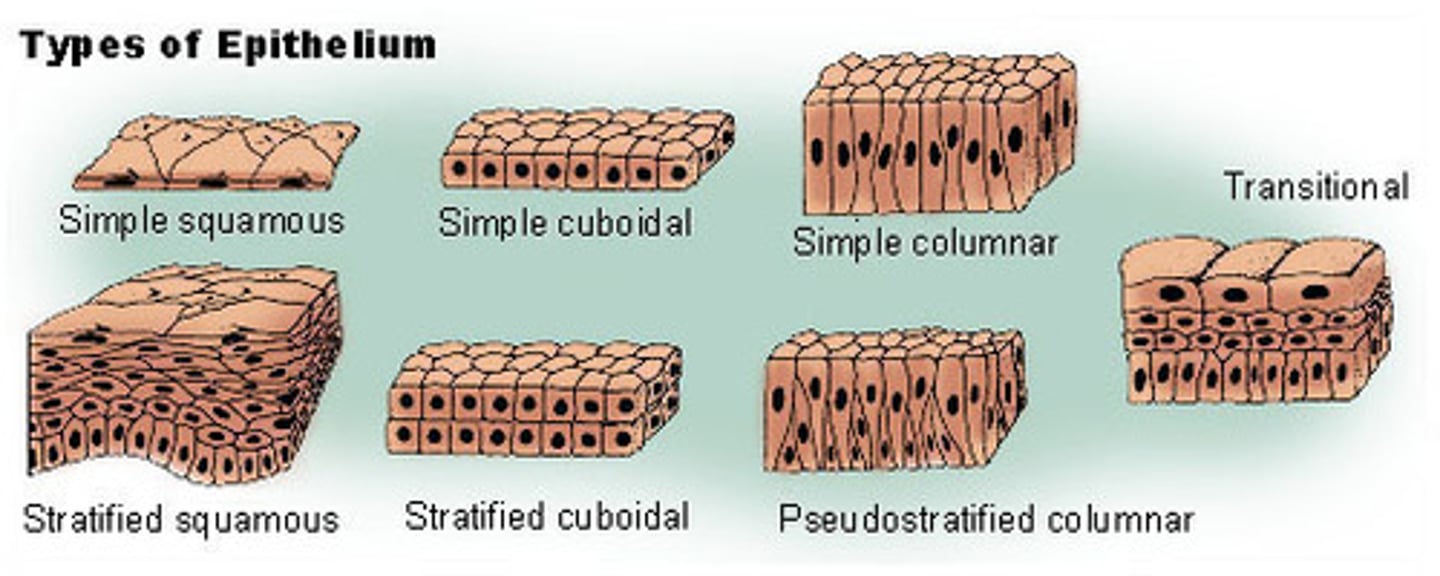
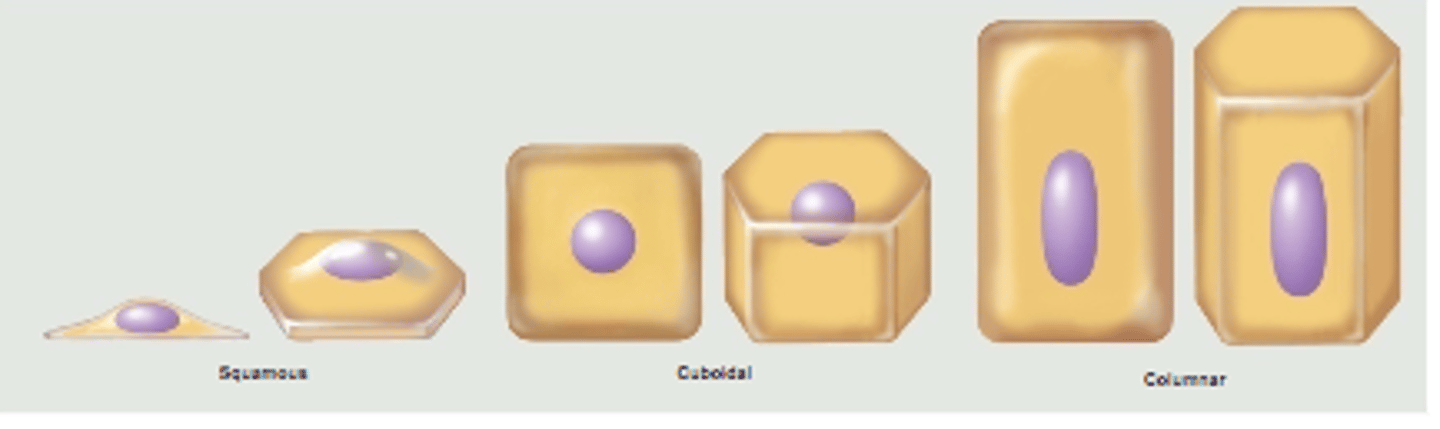
4 shapes of epithelial cells
Classified by shape of surface cells
- squamous (flat)
- cuboidal (cube shaped)
- columnar (tall column)
- transitional (shape varies with tissue stretching)
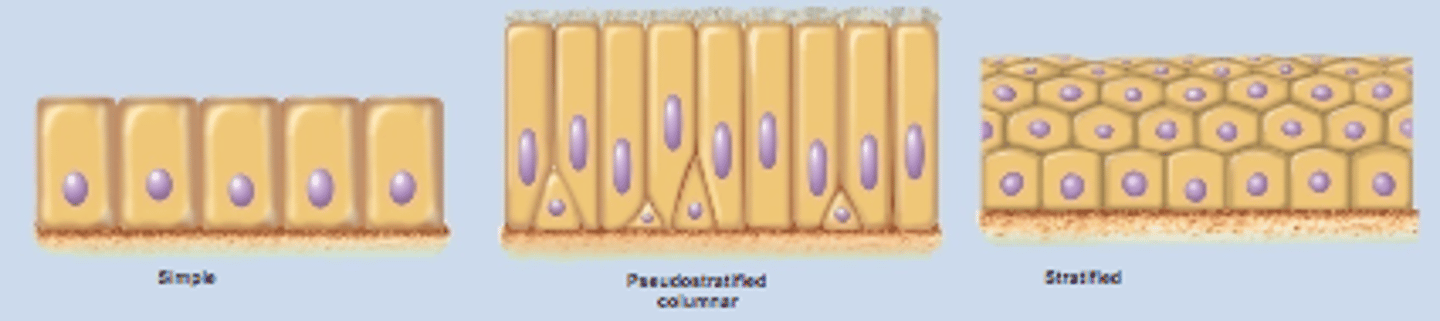
Arrangement of Epithelial Tissue
- simple (one cell thick)
- pseudostratified (single layer of cells where all cells don't reach apical surface)
- stratified (many layers thick)
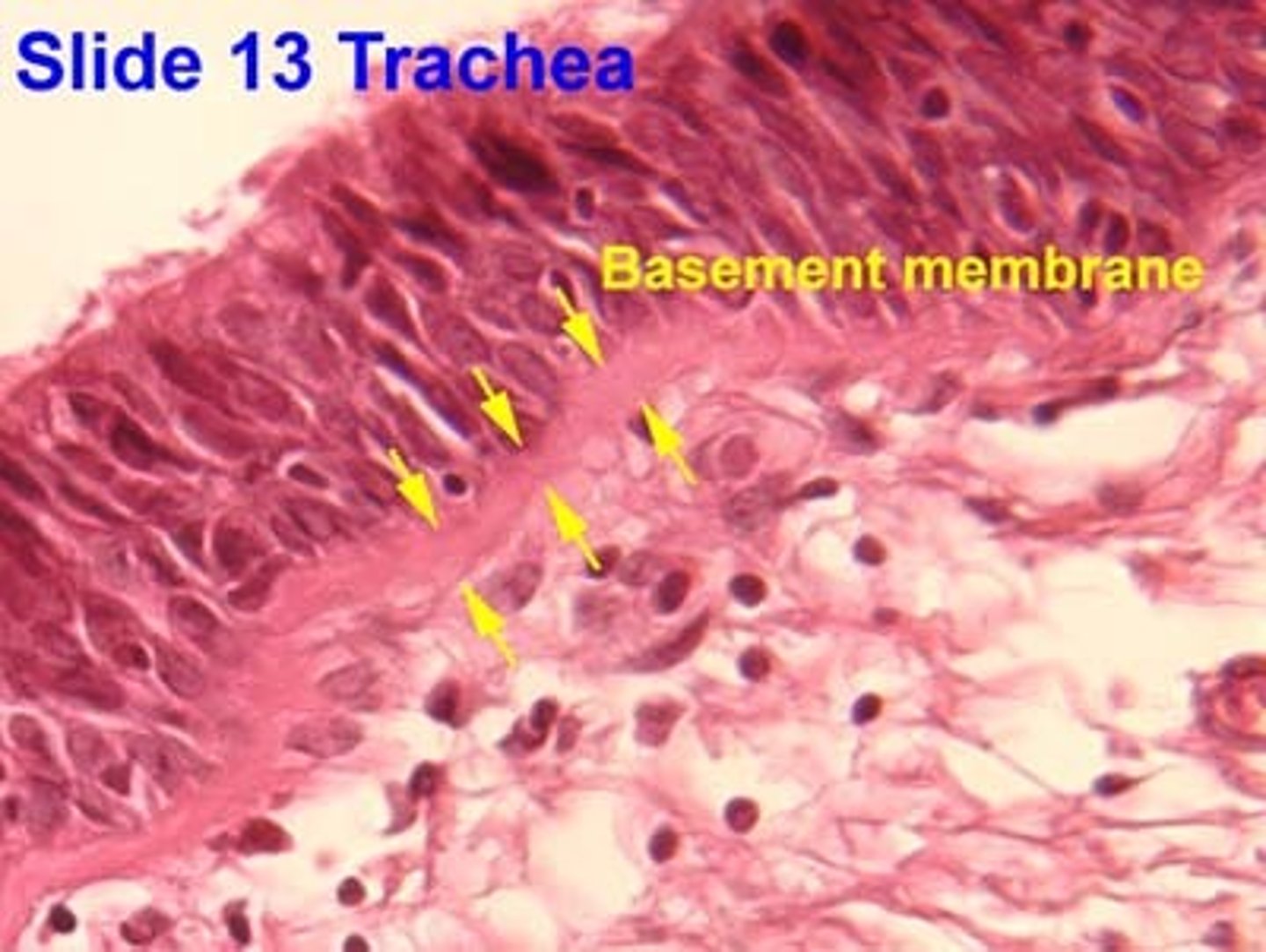
Basement Membrane
Basal lamina:
- from epithelial cells
- collagen fibers
Reticular lamina
- secreted by connective tissues
- reticular fibers
Holds cells to connective tissues
Guide for cell migration during development
5 systems that have epithelial tissue
Integument (external skin)
Digestive (digestive tract)
Pulmonary (lungs)
Urinary (urethra to kidney)
Reproductive (uterus/vagina)
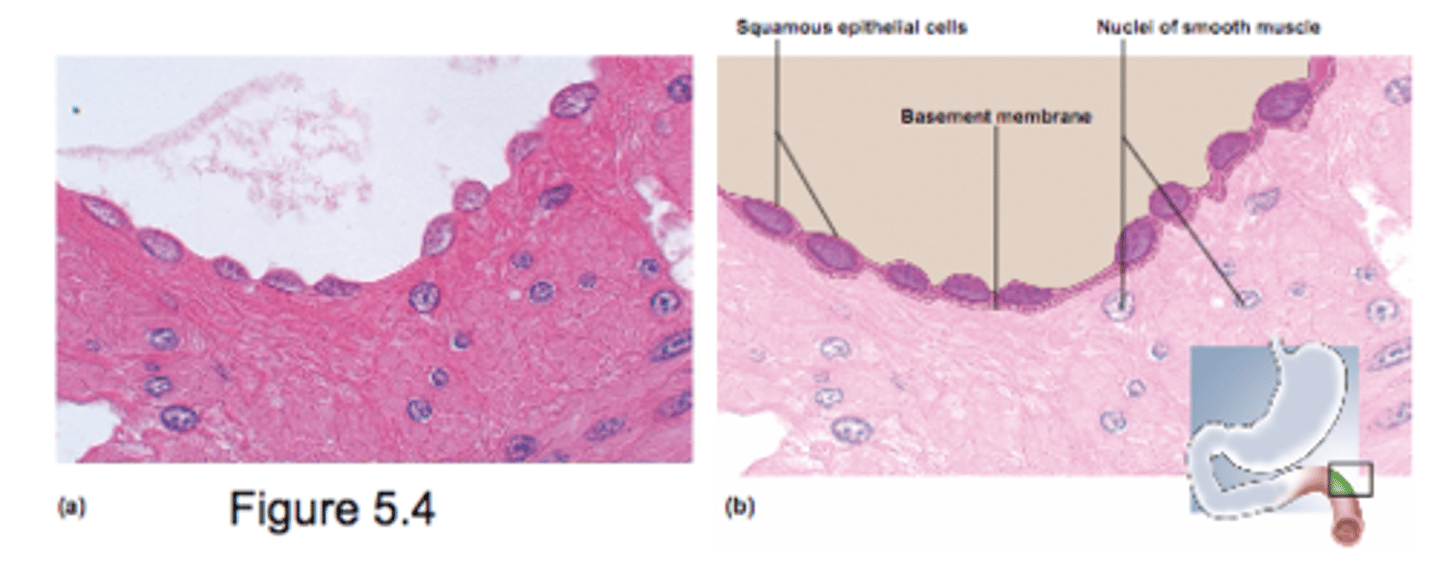
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Single layer of thin cells
- permits rapid diffusion of substances
- poor protection
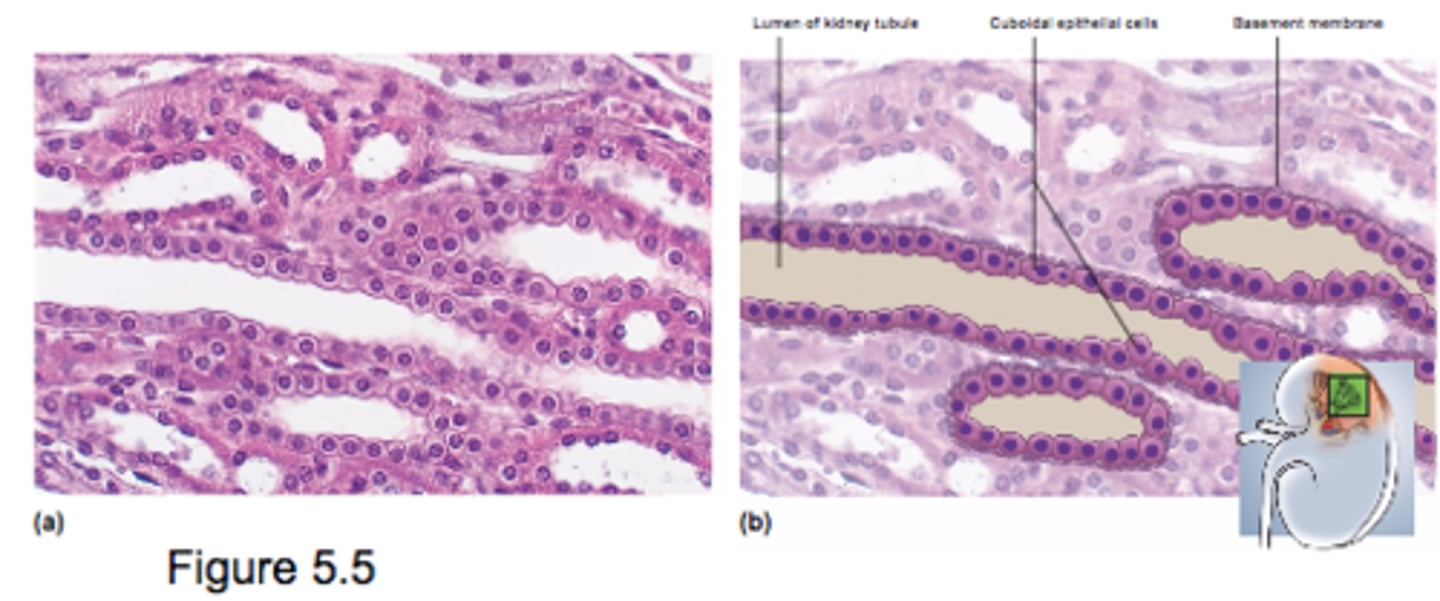
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- single layer of square or round cells
- active transport (absorption or secretion) requires space for organelles inside cell
- limited protectoin
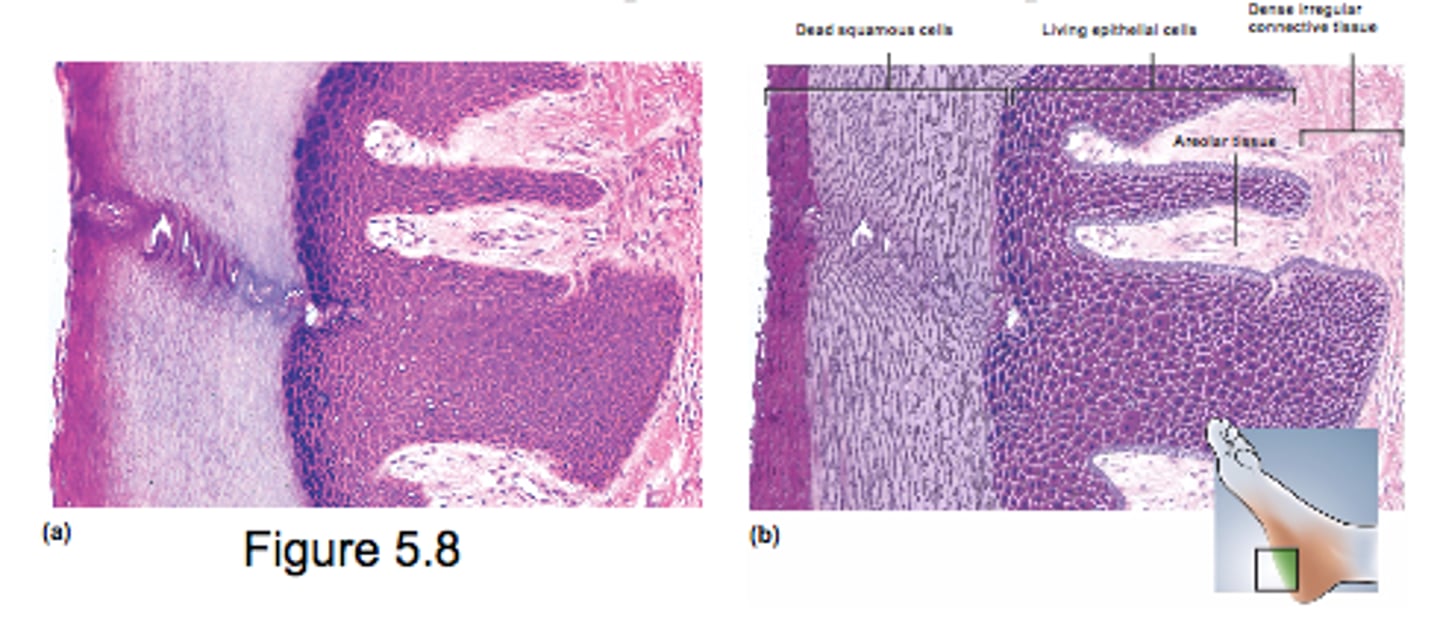
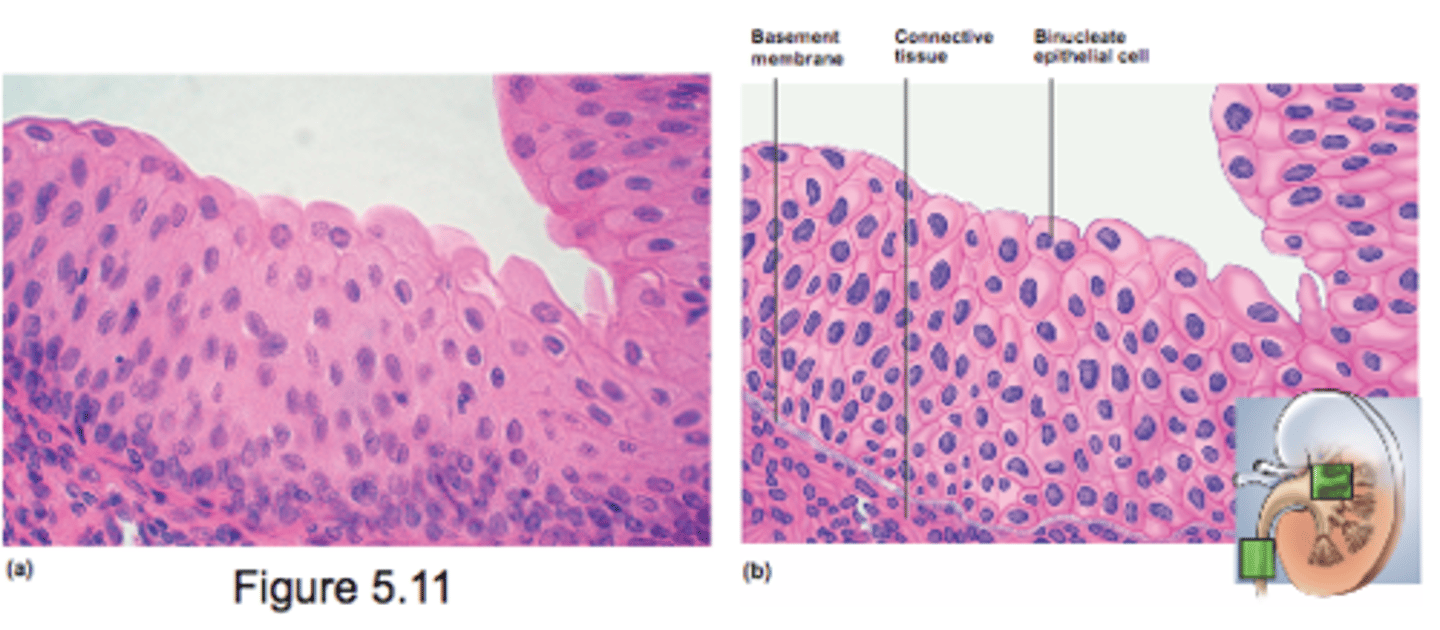
Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelia
internal mucousa that are protective but lack keratin
- tongue, oral mucosa, esophagus, vagina
- resists abrasion and penetration of pathogens
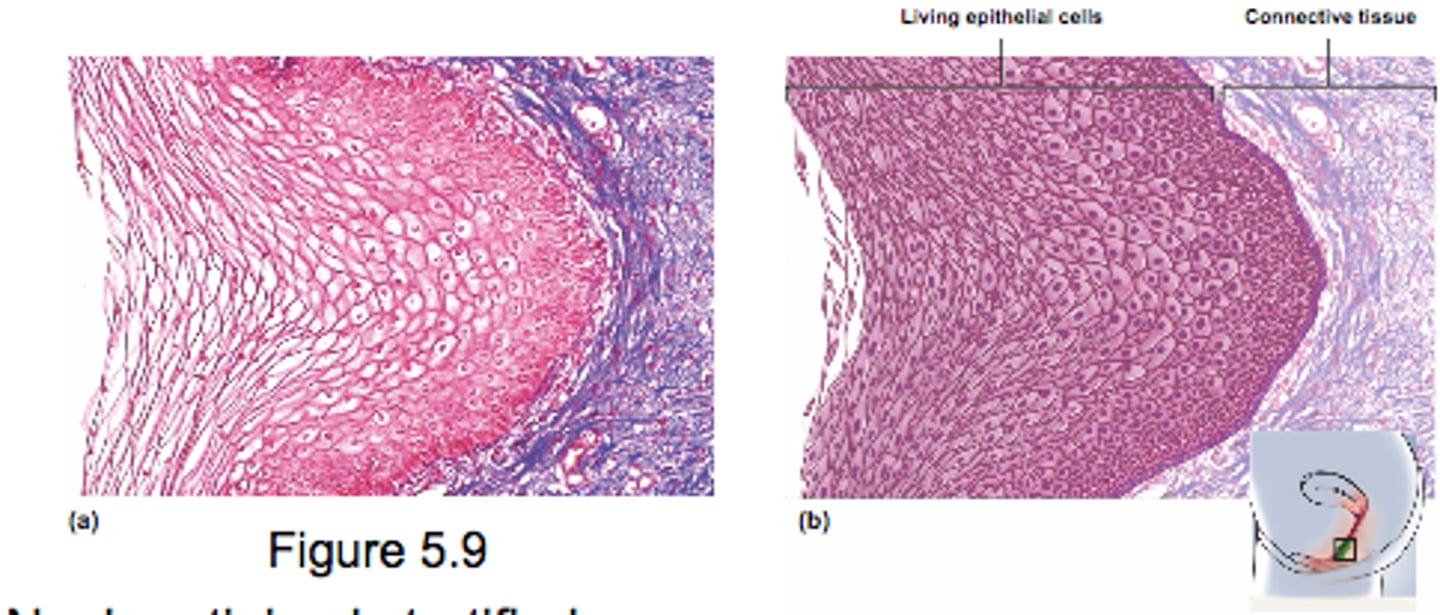
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelia
- found on skin surface
- keratin increases abrasion resistance
- multiple cell layers (cells flatter at surface)
- external epidermis
- excellent protection
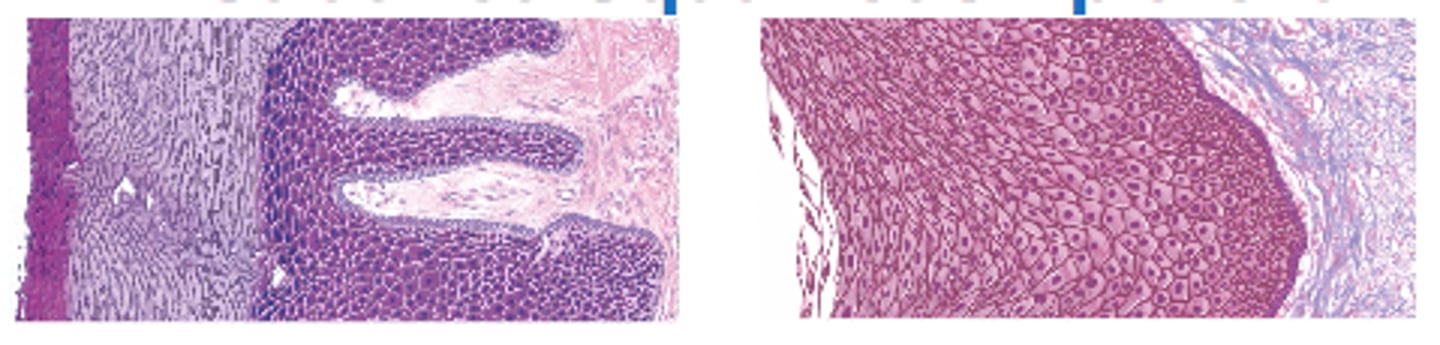
Stratified Squamous Epithelia
- deepest layers undergo continuous mitosis (daughter cells push toward surface and become flatter as they migrate)
- 2 kinds:
keratinized
non-keratinized
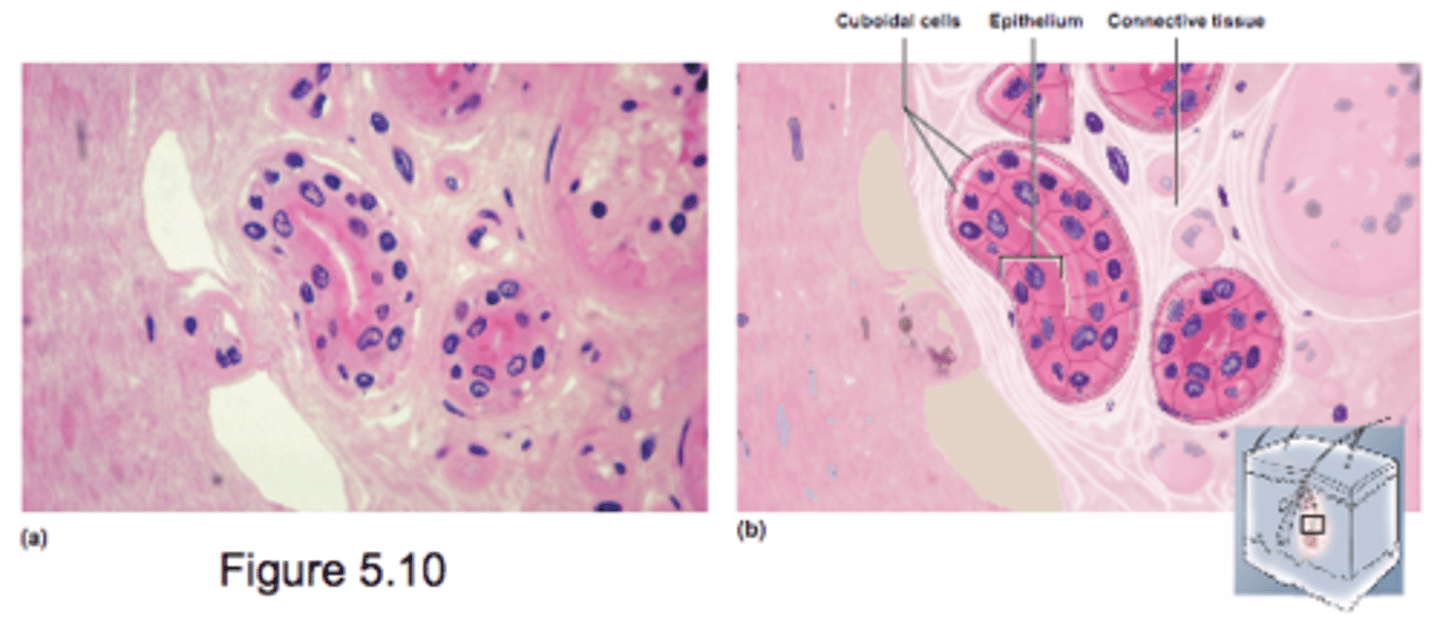
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelia
- 2 or more cell layers
- surface cells square or round
- uncommon
- seen in glands
Transitional Epithelium
- multilayered
- sufrace cells change from round to flat when stretched
- urinary tract only (bladder)
2 Parts of Extracellular Material
1. fibrous proteins
2. ground substance
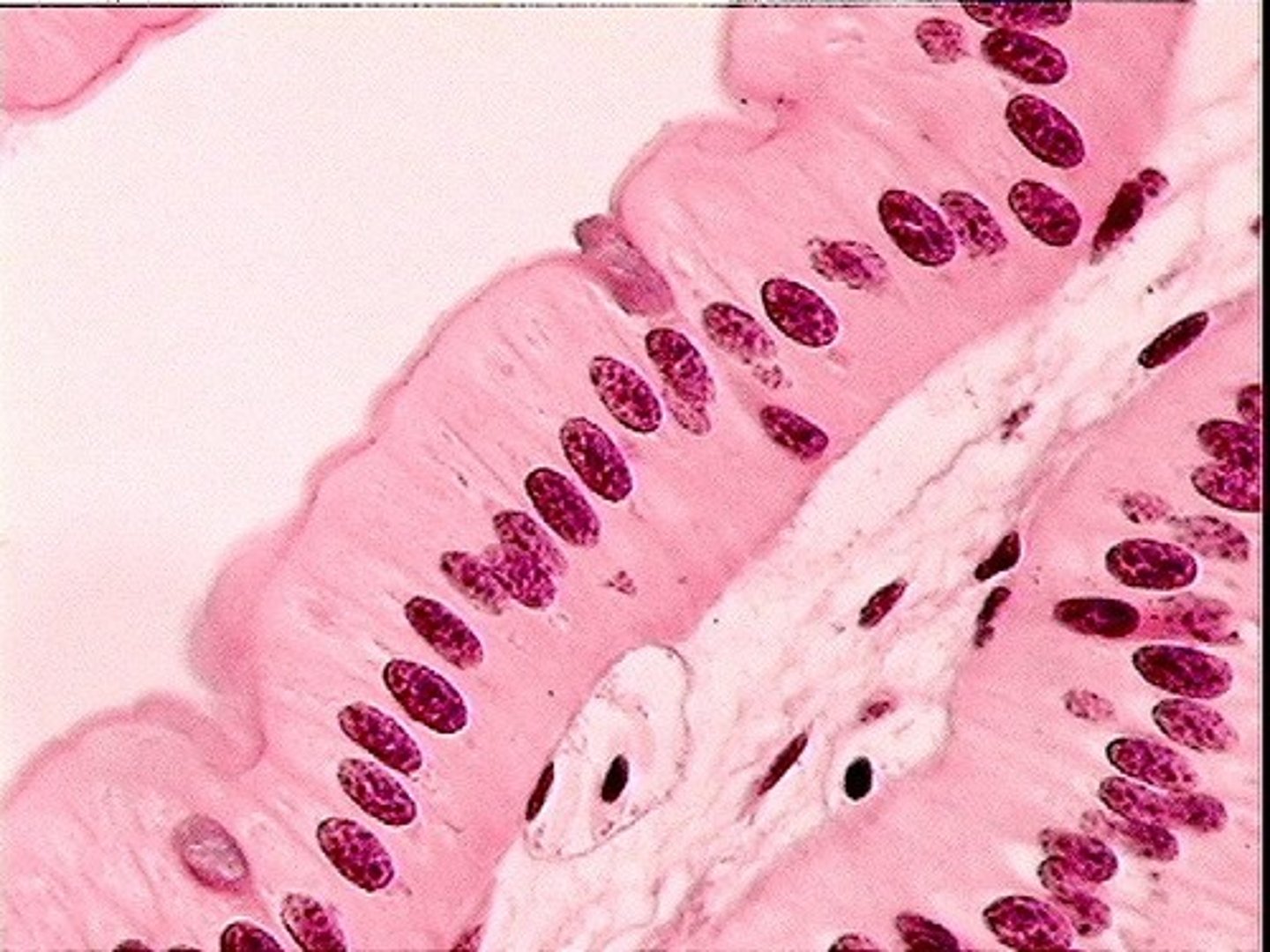
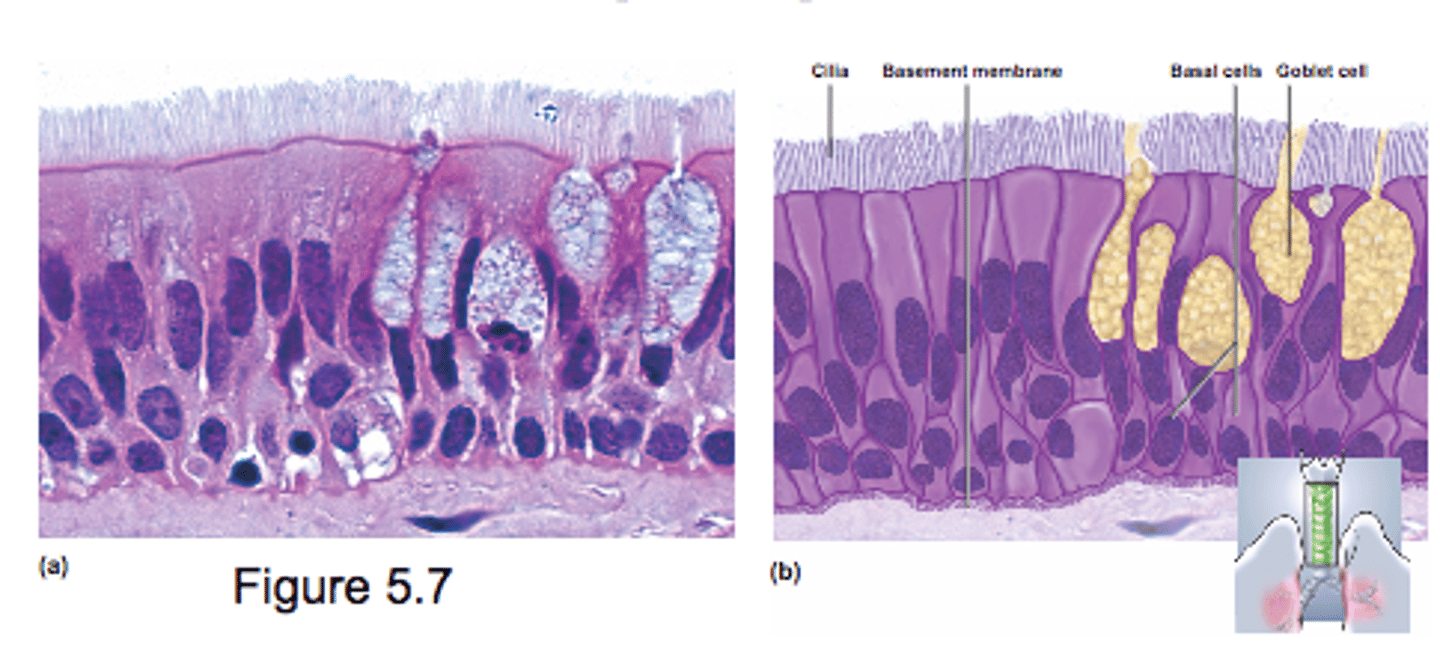
Pseudostratified Epithelium
- Looks multilayered (all cells touch basal layer)
- nuclei at several layers
- often ciliated (lungs)
Connective Tissue Functional Diversity
- bind organs
- support/physical protection
- immune protection
- movement
- storage
- transport
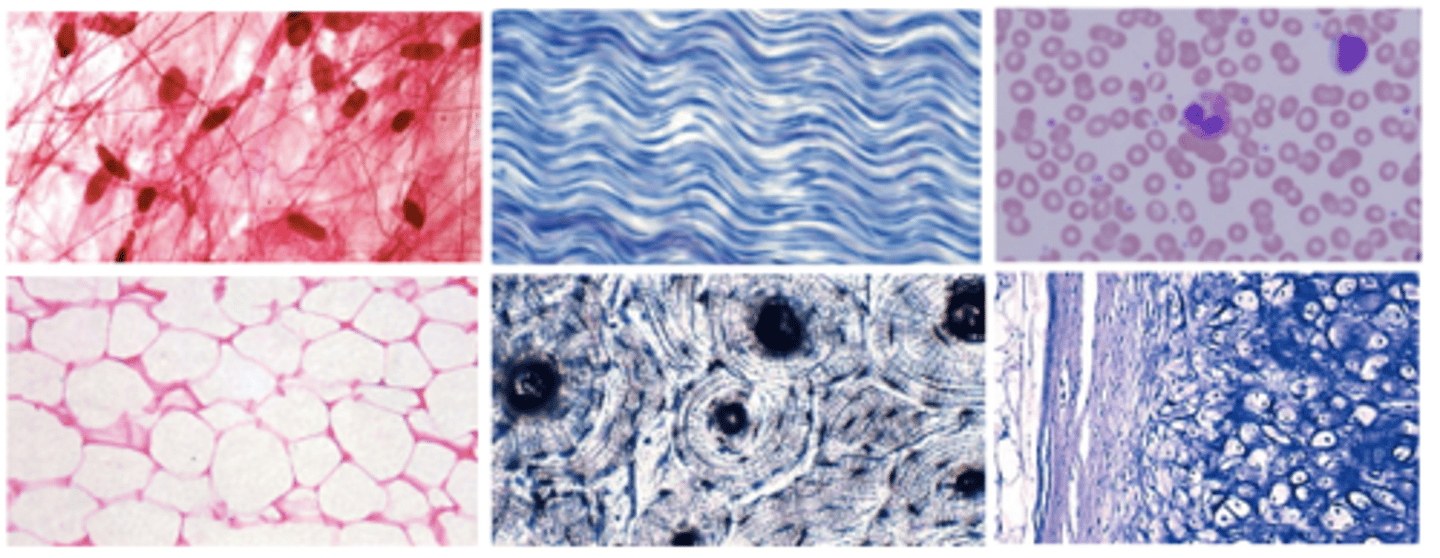
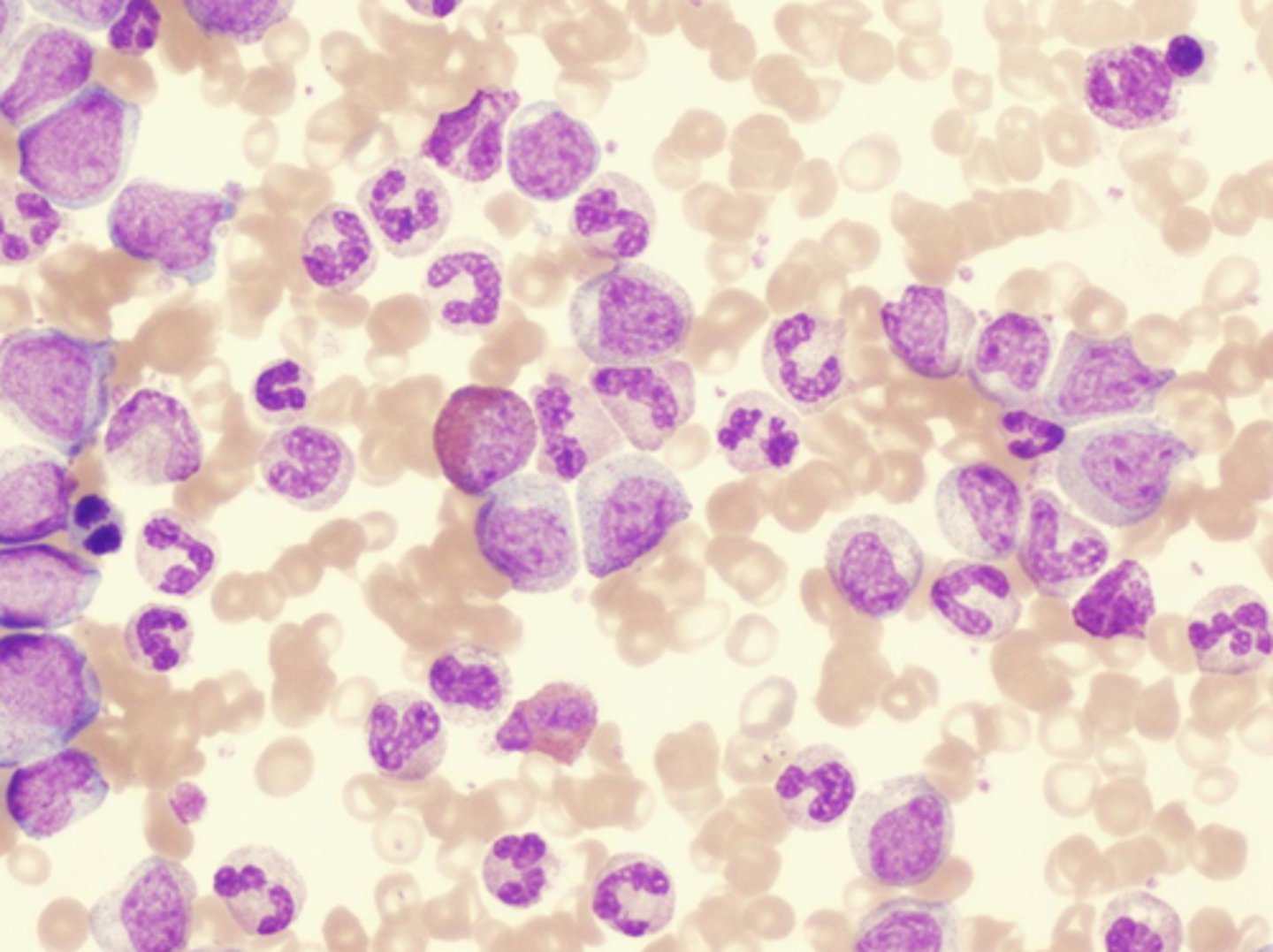
Cells of Connective Tissue
Fibroblasts
Macrophages
Neutrophils
Mast cells
Plasma
Adipocytes
Osteyocyte (bone)
Chondrocyte (cartilage)
Areolar Tissues (no defining structure)
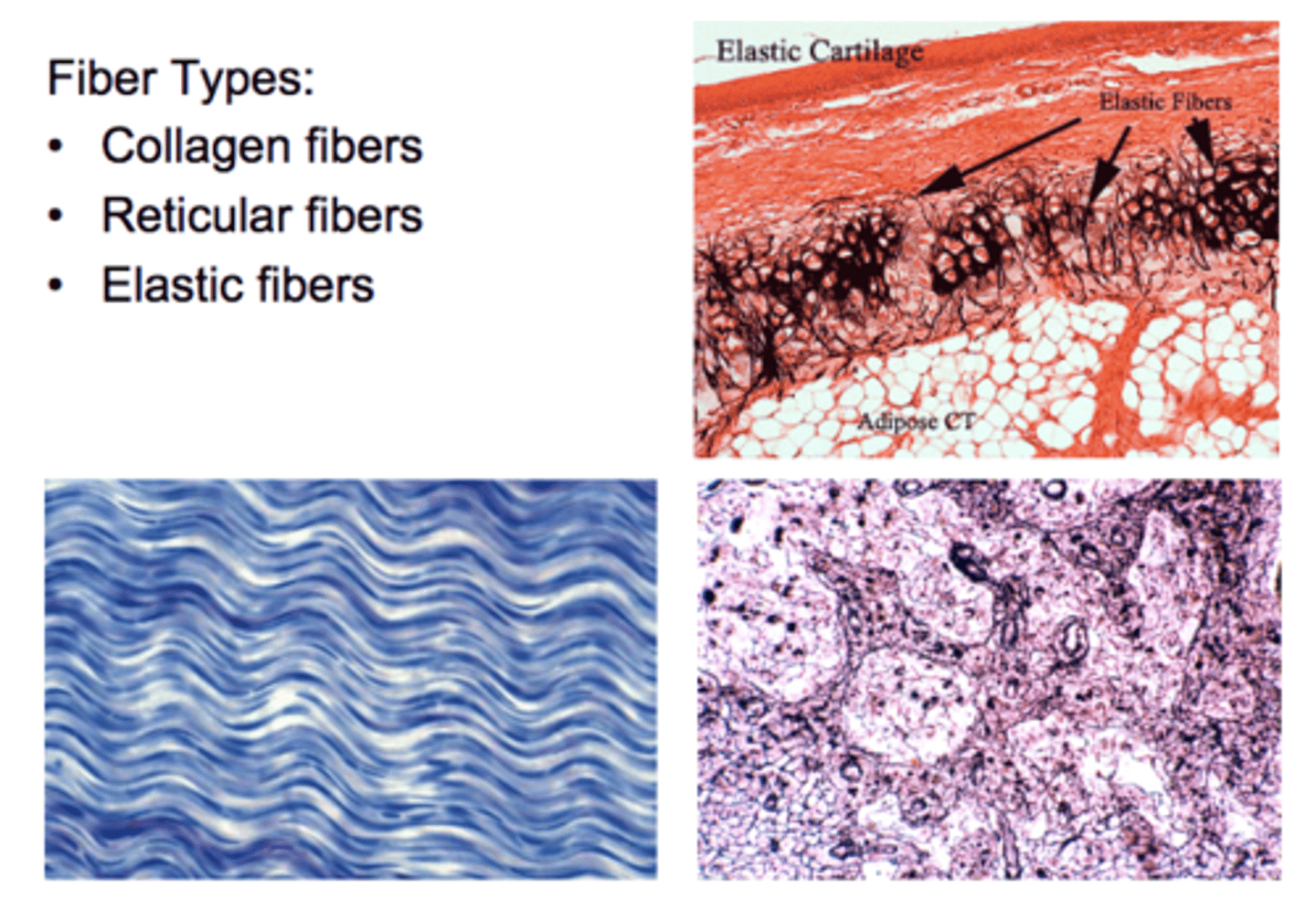
Fibers of Connective Tissue
Collagen
Elastic
Reticular
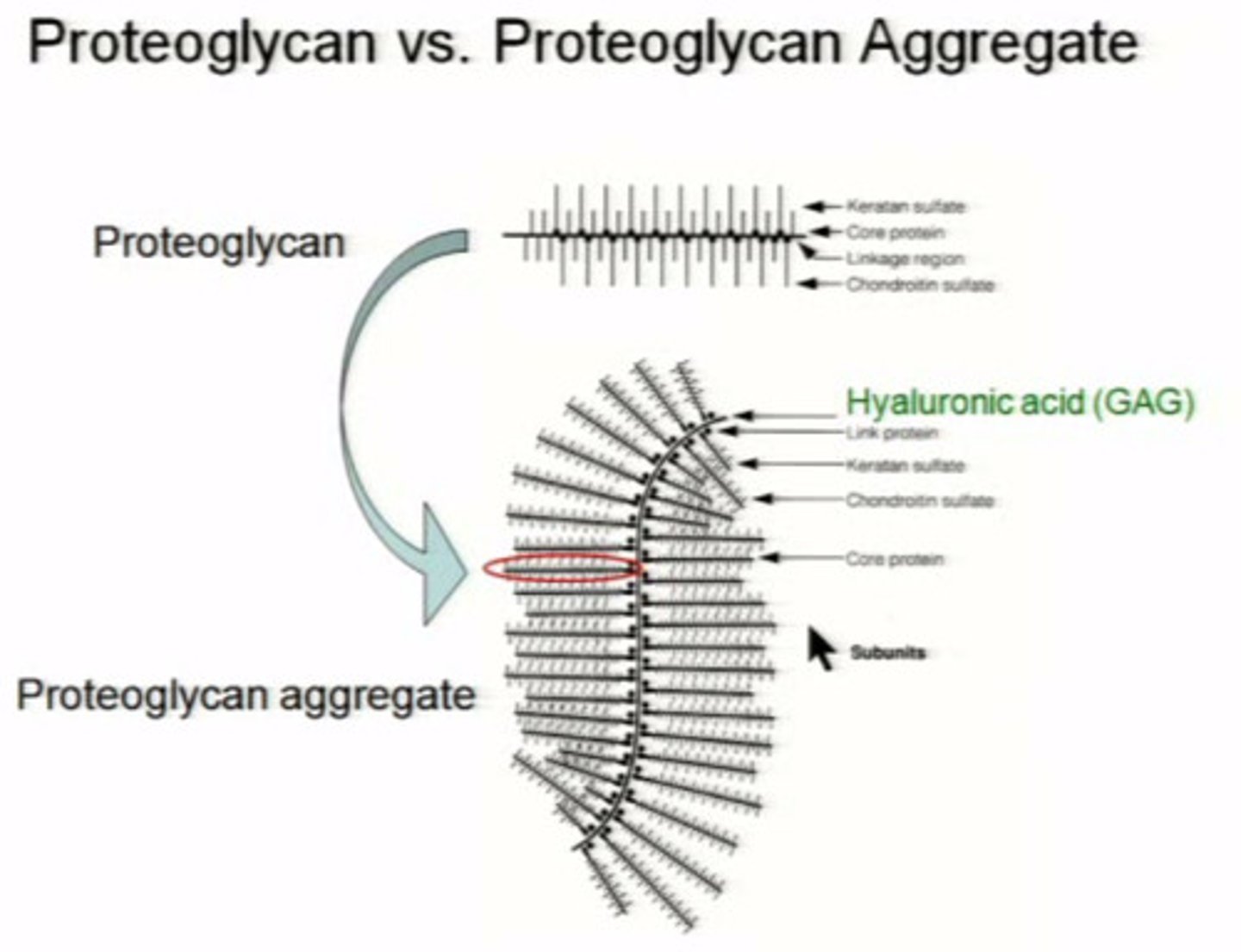
Ground Substance
Fluid to gelatinous
Fluid: interstitial or plasma
Solid/crystalline: bone
often intermediate and gelatinous: due to proteoglycans that associate with water
Proteoglycan Molecule
carbohydrate binds to water
Types of Fibrous Connective Tissue
Loose connective tissue
- gel like ground substance between cells
3 types
- areolar
- reticular
- adipose
Dense connective tissue
- fibers fill the spaces between cells
2 types (varying fiber orientation)
- dense regular connective tissue
- dense irregular connective tissue
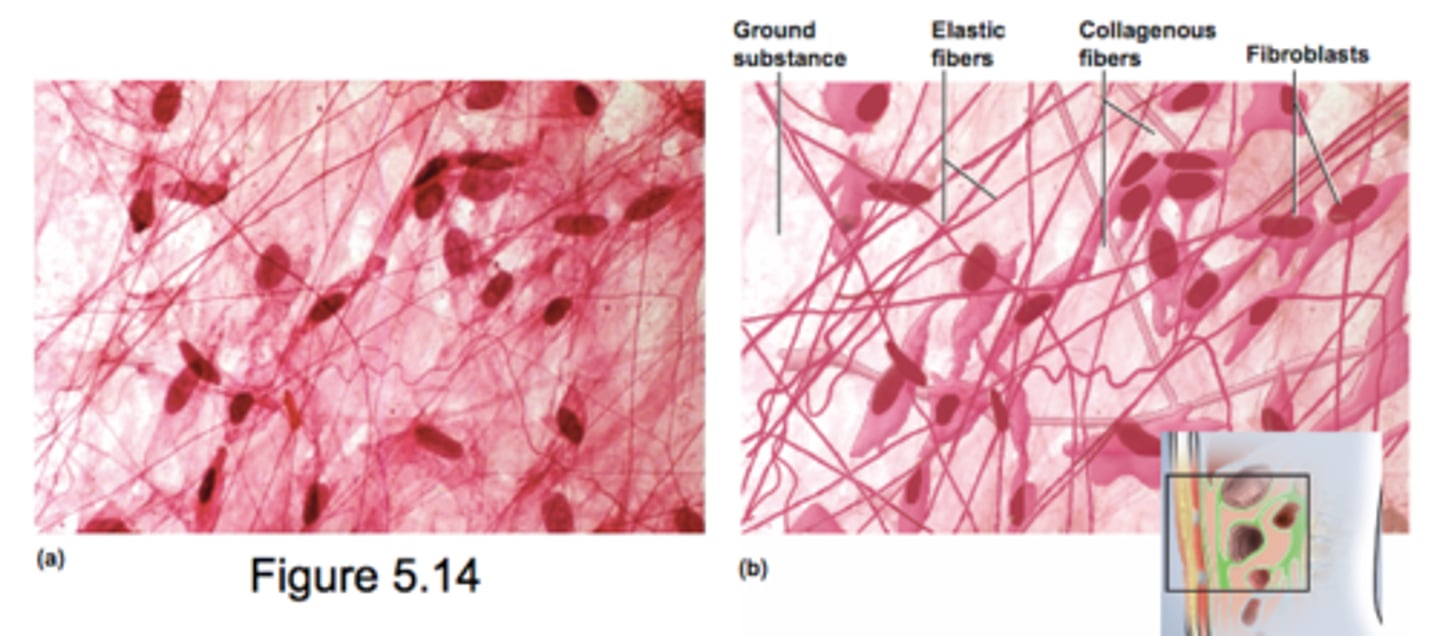
Areolar Connective Tissue
underlines all epithelia and packages organs
All 3 fibers
- collagen
- reticular
- elastic
Gelatinous ground substance
Nuclei mostly fibroblasts
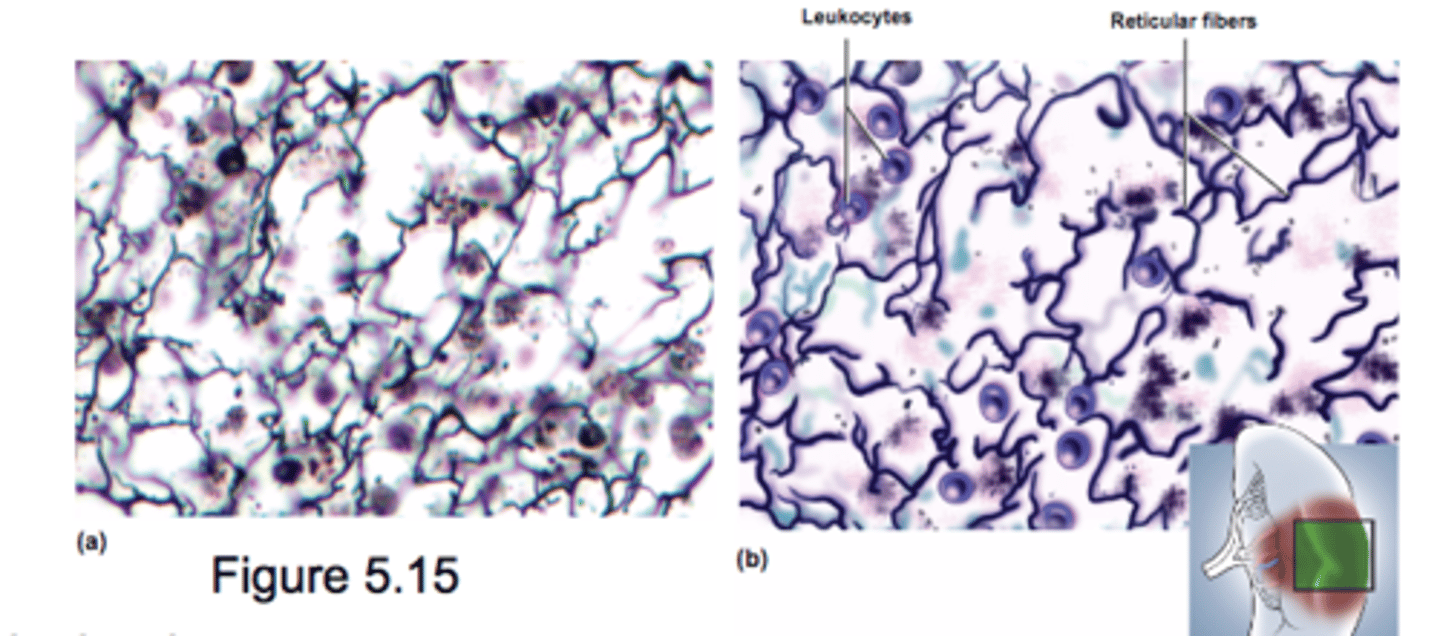
Reticular Tissue
Loose network of reticular fiber and cells
Forms supportive framework (stroma) for lymphatic organs
- lymph nodes
- spleen
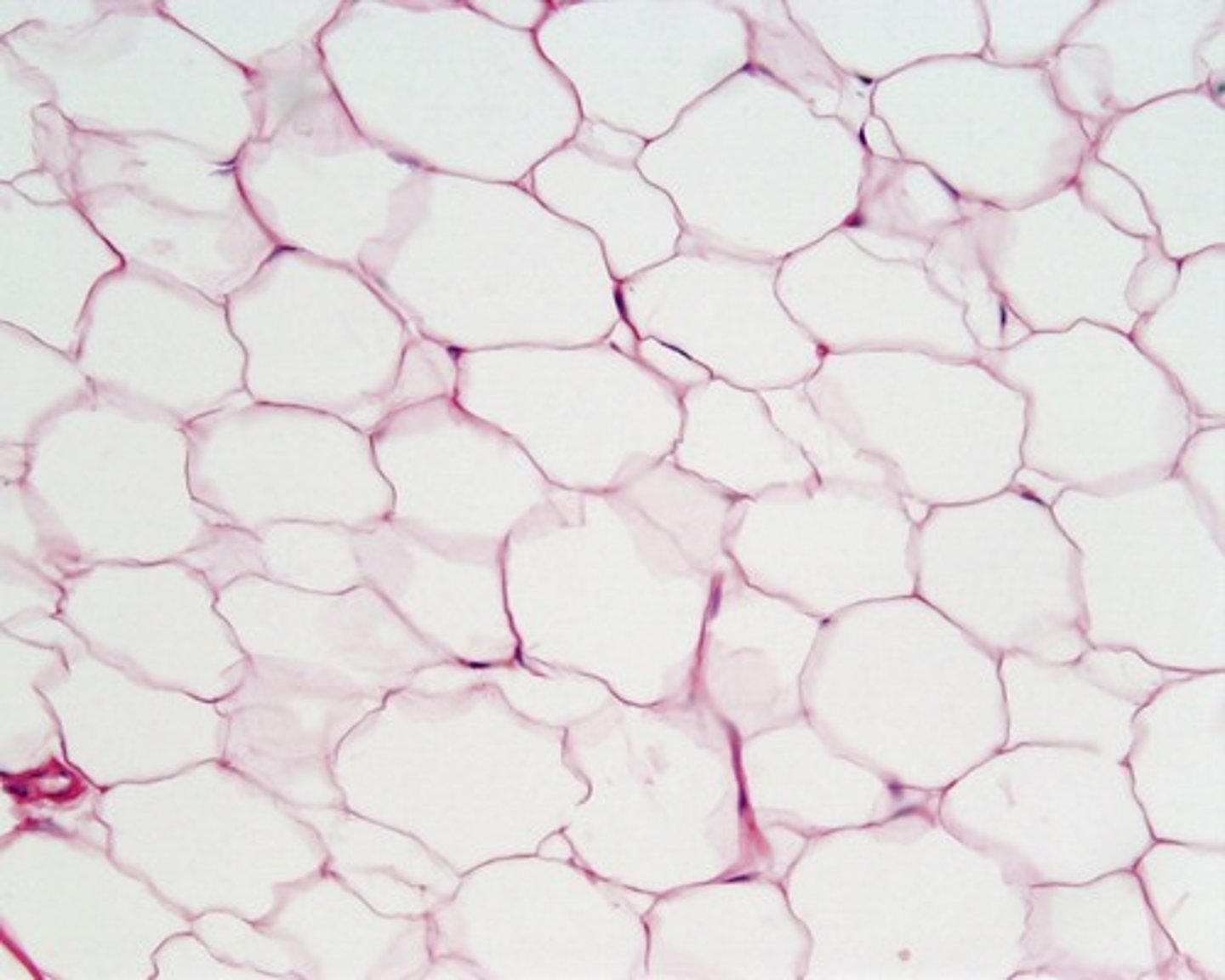
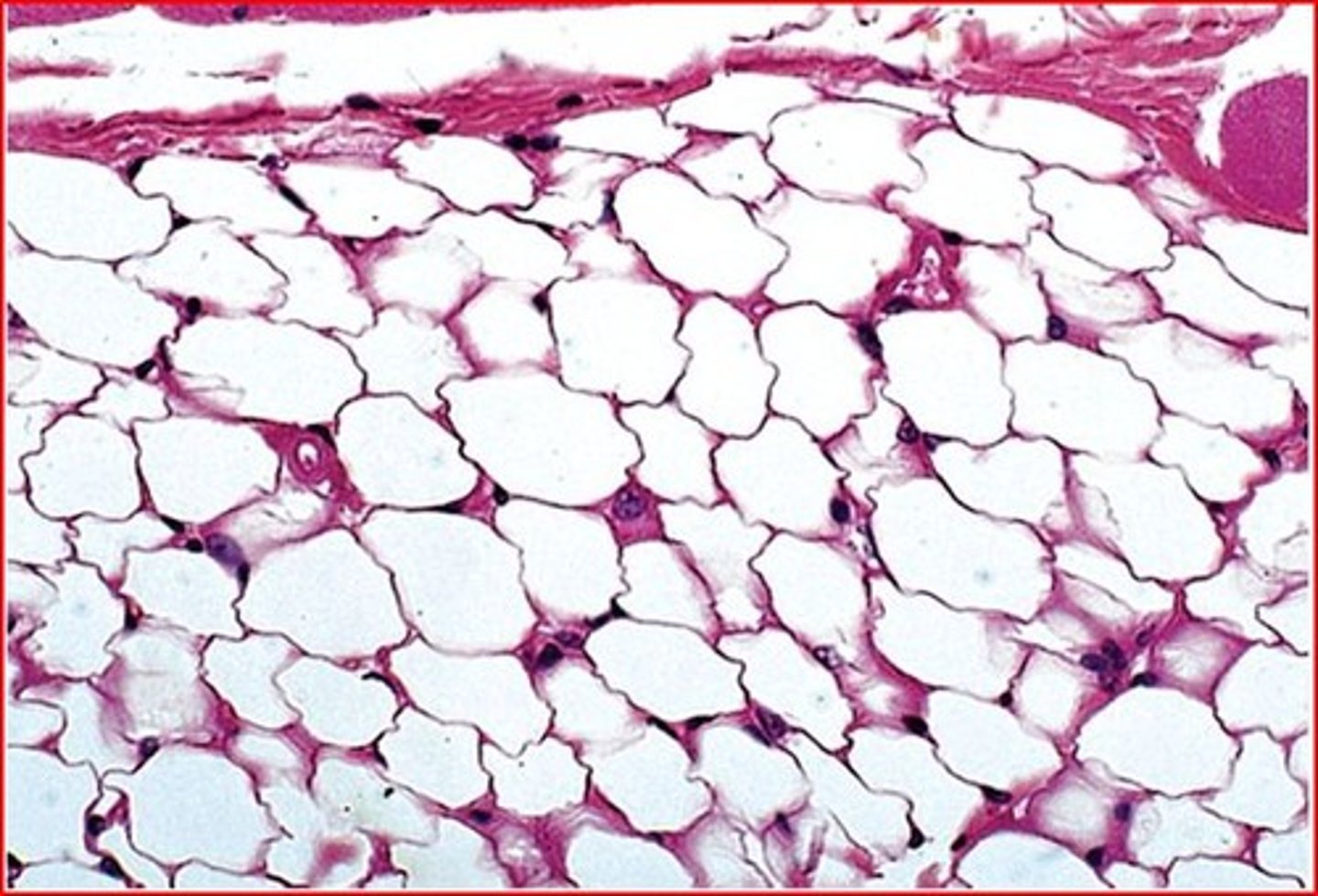
Adipose Tissue
dominant cell type
energy storage, insulation, cushioning
subcutaneous fat and organ packaging
primarly cellular: little extracellular matrix
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Densely packed parallel collagen fibers
Compressed fibroblast nuclei
withstands stress in one direction
very low cellular component (Lots of extracellular collagen)
Tendons & Ligaments
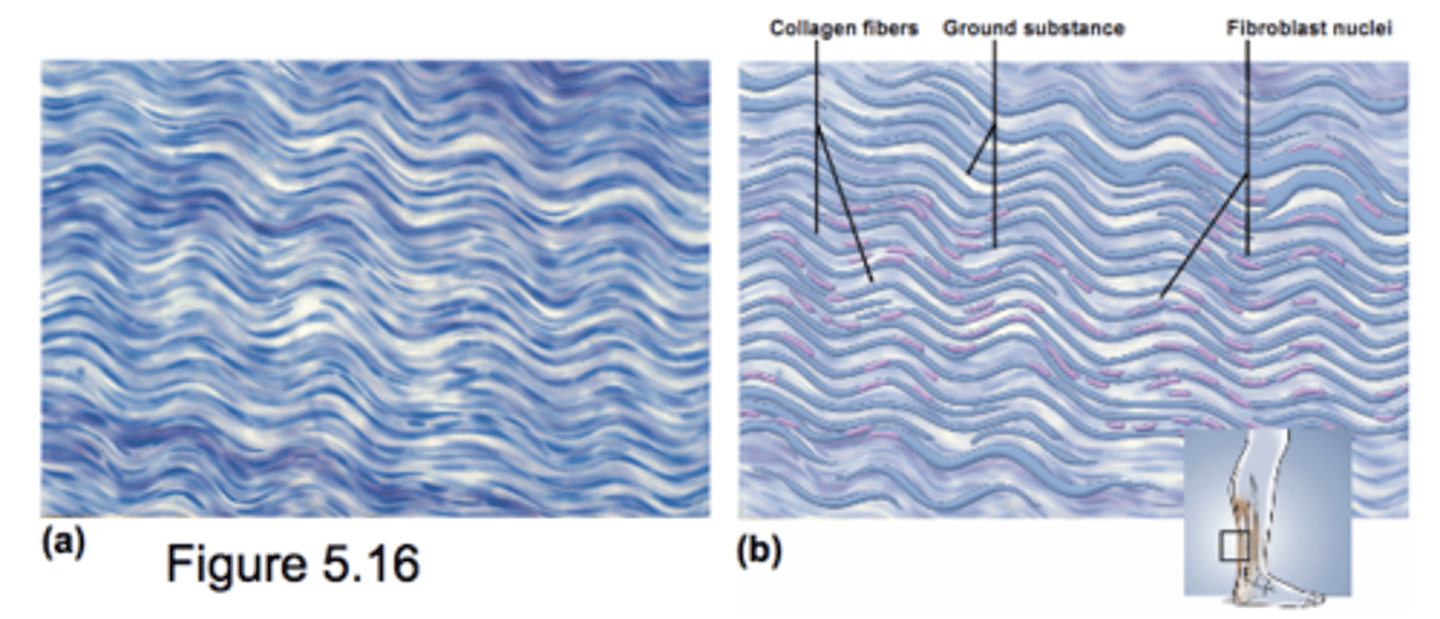
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
densely packed, randomly arranged, collagen fibers
Withstand stress applied in multiple dimensions
Deeper layer of skin
Capsules around organs
Fibroblast mostly extracellular
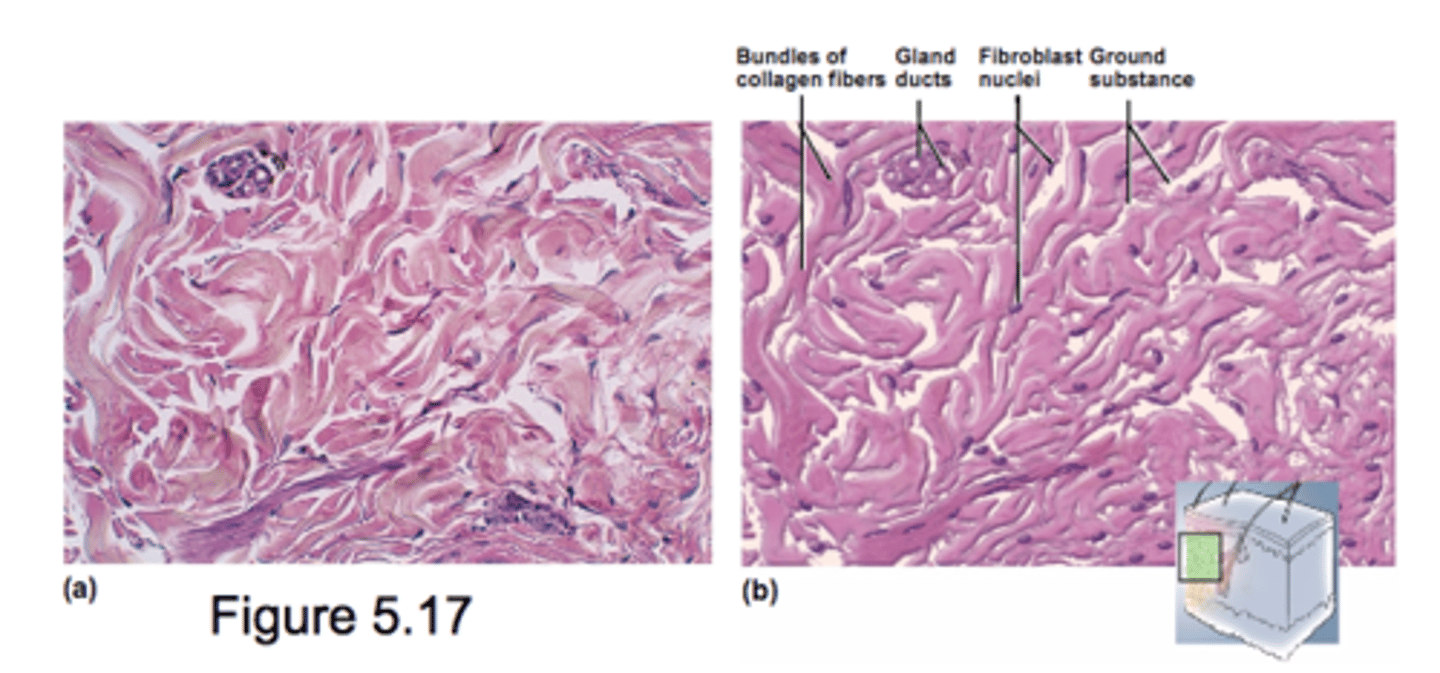
Cartilage
Supportive CT with rubbery matrix
chondrocytes are unique cell type
Avascular
- diffusion brings nutrients and removes waste
- heals slowly
Major types (depend on fiber types)
-hyaline
- elastic
- fibrocartilage
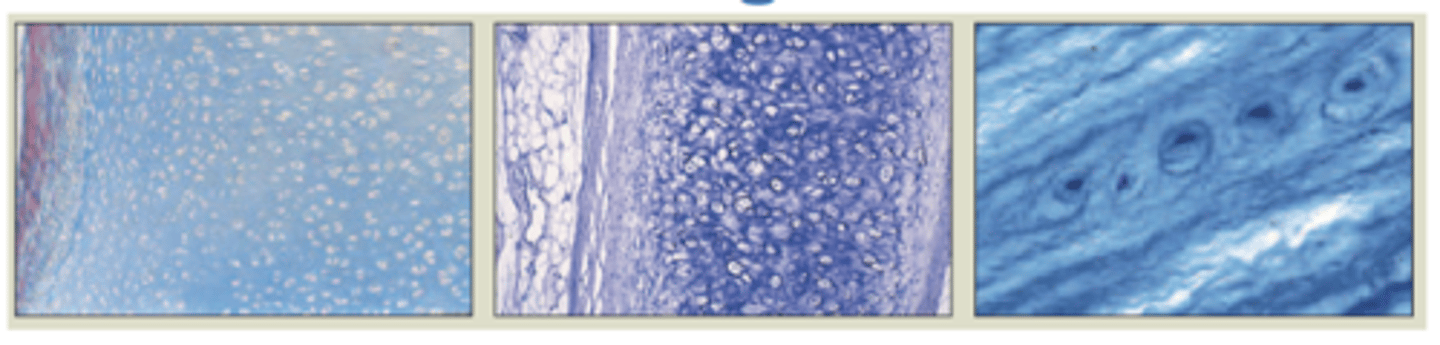
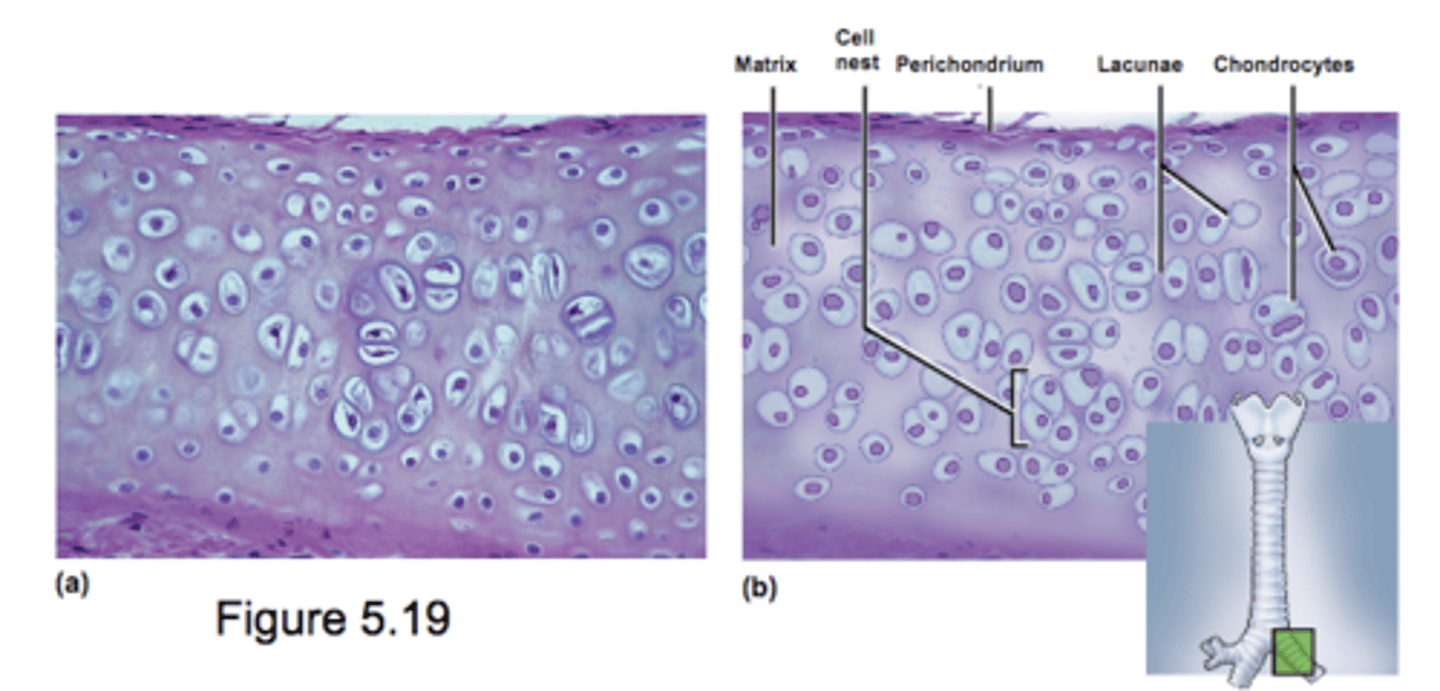
Hyaline Cartilage
Most common type of cartilage
Clear glassy matrix because of unusual fineness of collagen fibers
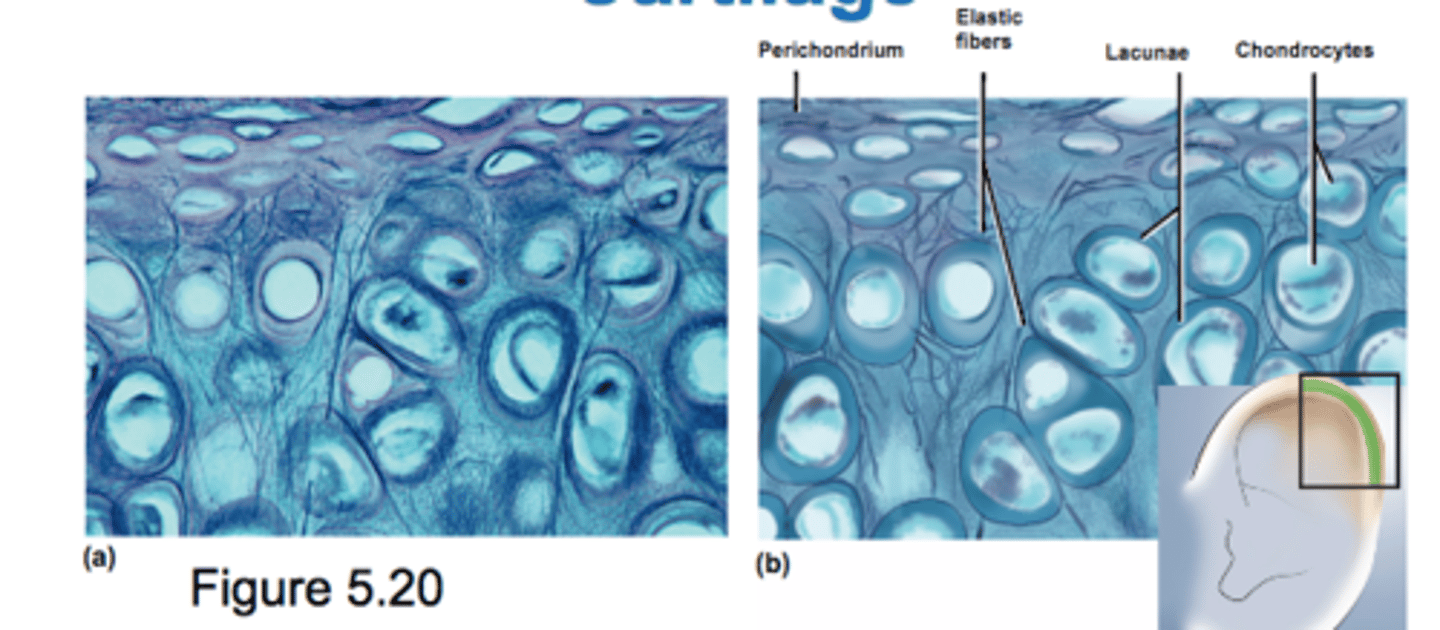
Elastic Cartilage
only cartilage containing elastic fibers
flexible elastic support
external ear
epiglottis
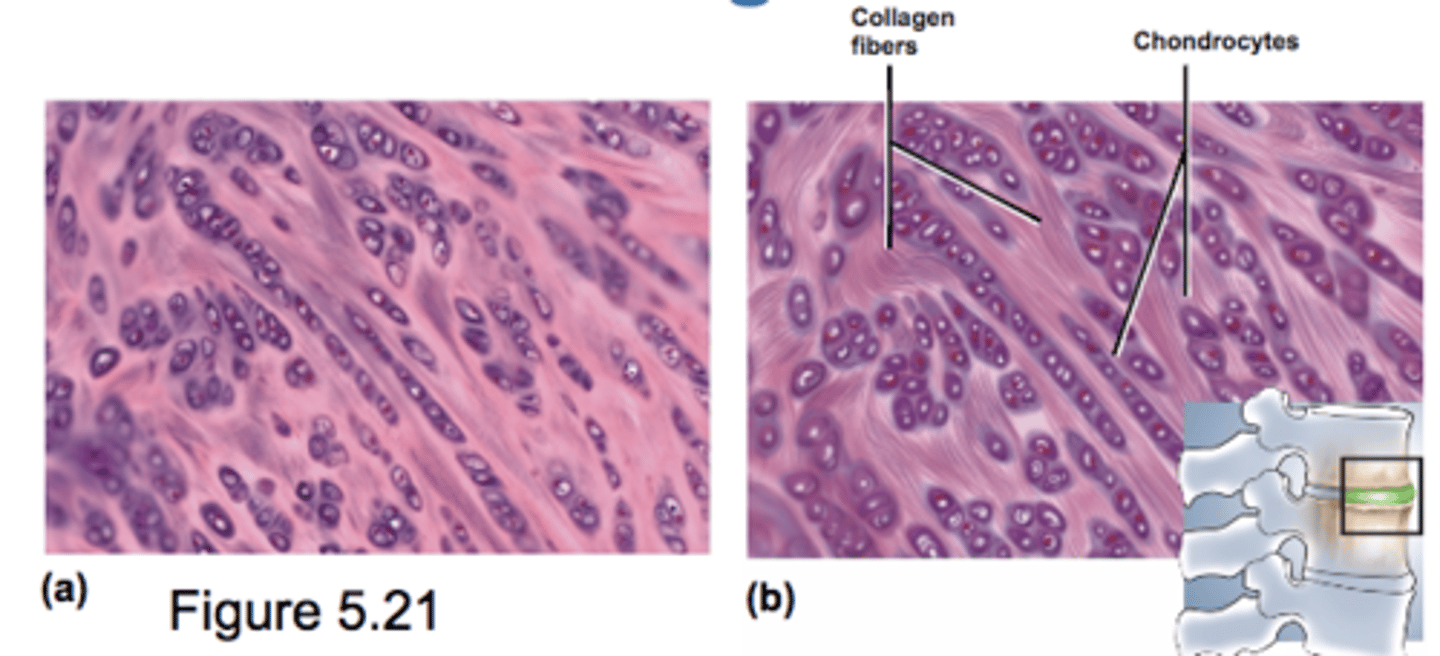
Fibrocartilage
large, coarse bundles of parallel collagen fibers
resists compression and absorbs shock
found in symphyses (intervertebral and pubic) and menisci in knee
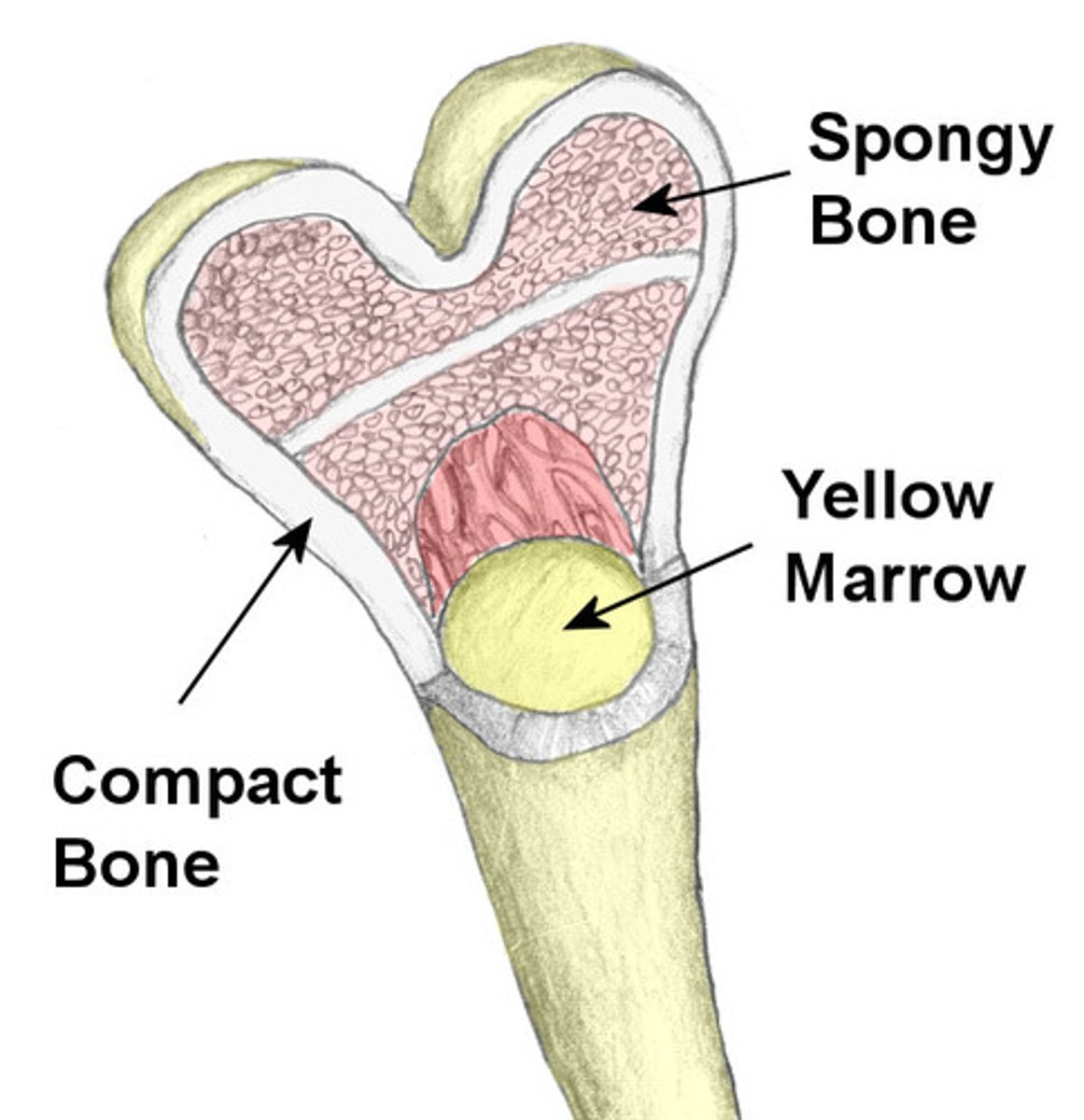
2 Forms of Osseous Tissue
Spongy Bone
Compact Bone
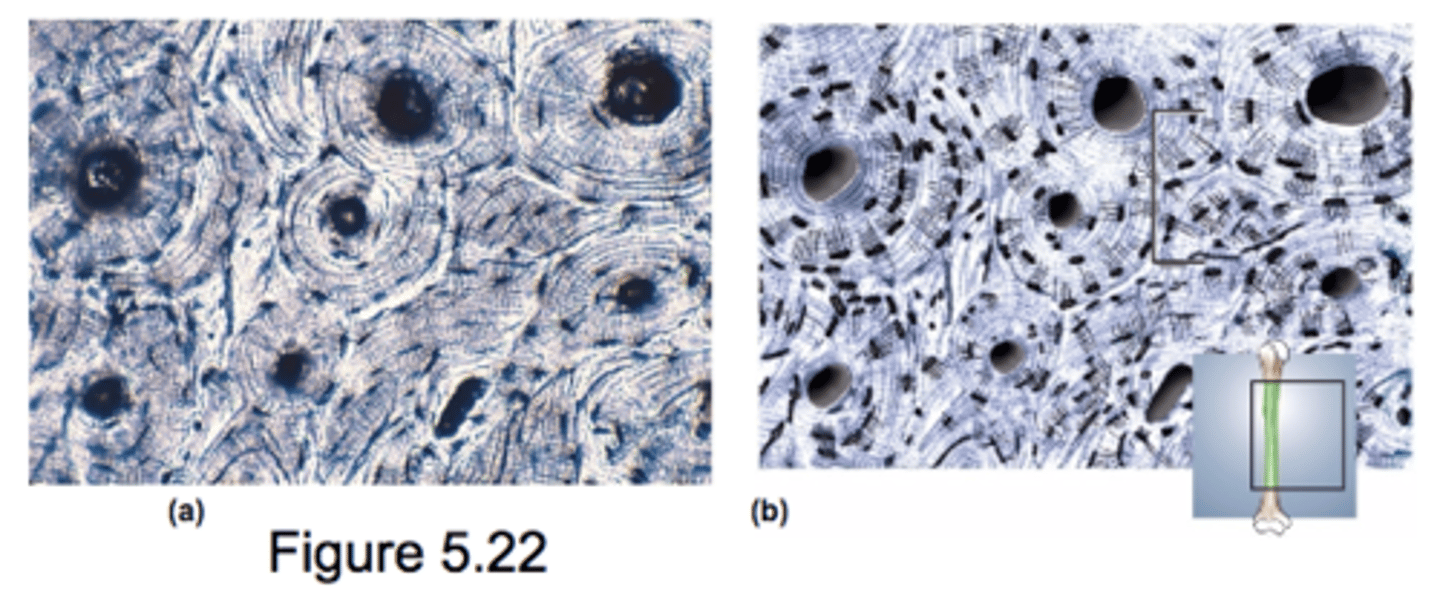
Osseous Tissue
low cellular proportion: primarily solid extracellular matrix
osteocytes are defining cell type
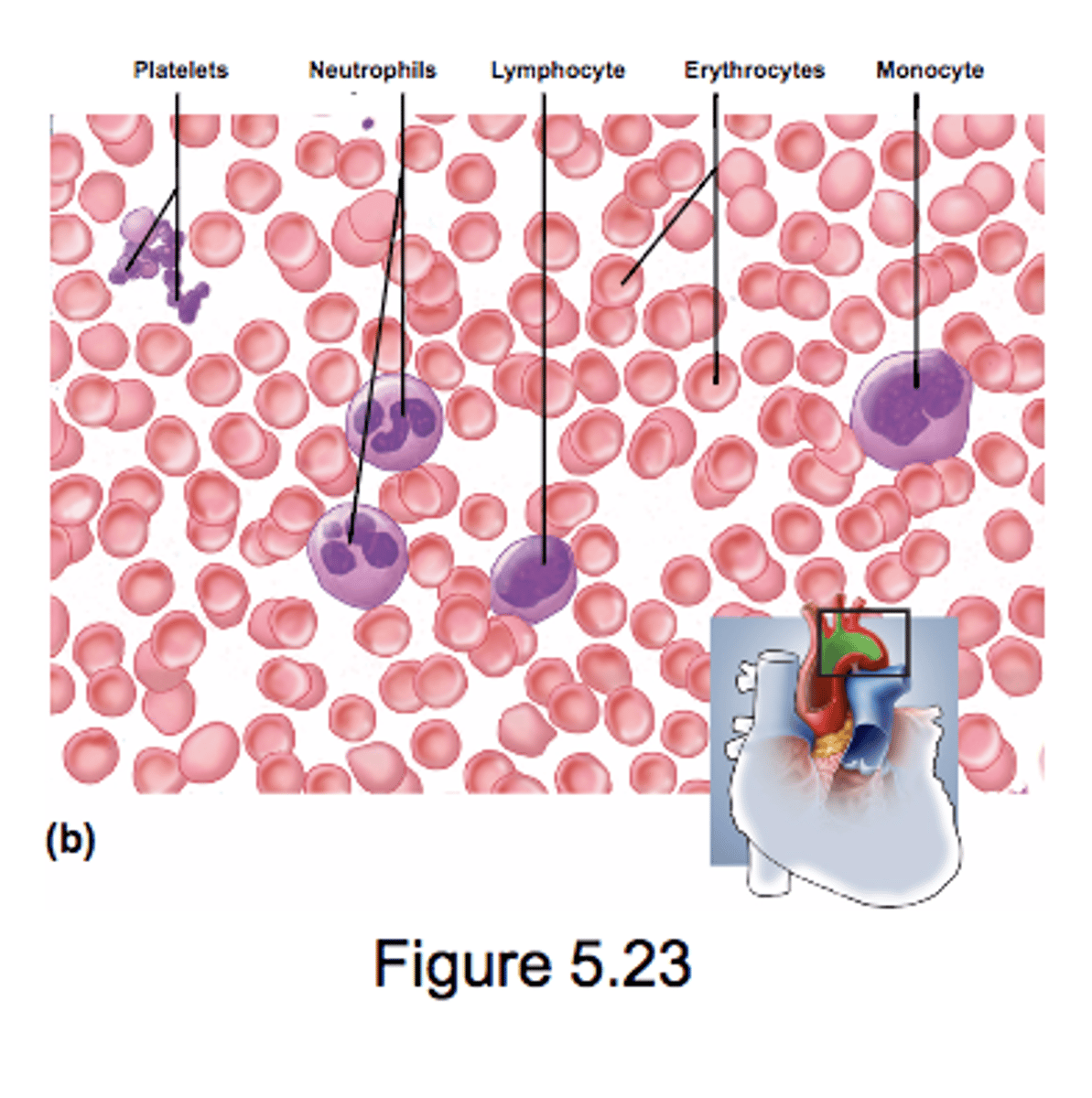
Blood
Fluid connective tissue
transports cells and dissolved matter from place to place
approx. 50% cellular & 50% acellular matrix
plasma is acellular matrix (lacks fibers unless coagulation occurs)
cellular portion: blood cells and cell fragments
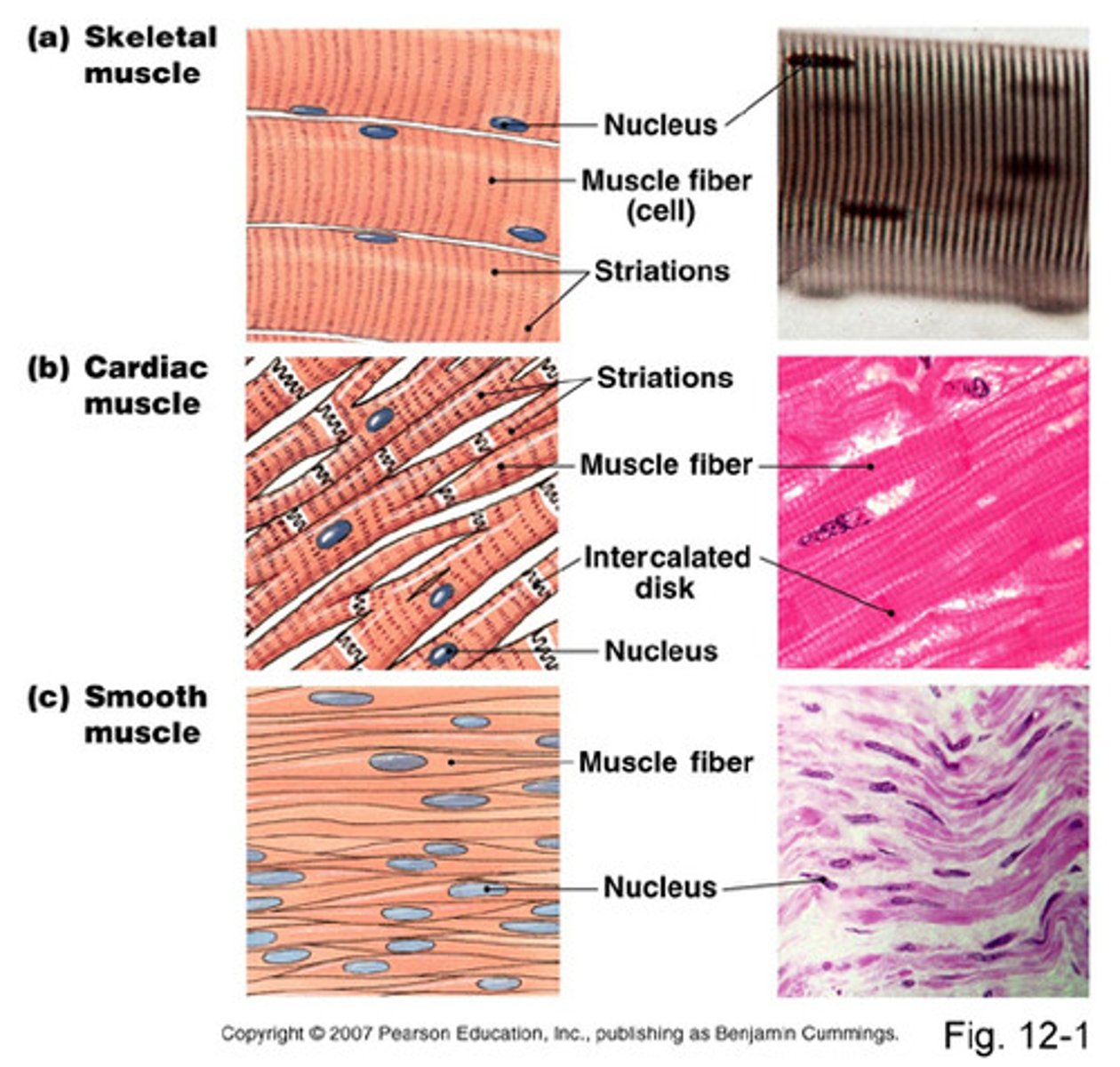
3 Types of Muscle Tissue
- skeletal
- cardiac
- smooth (vasoconstriction)
4 characteristics of muscle tissue
1. excitable
2. specialized to contract in response to stimulation
3. exert physical force on bones, other tissues and organs
4. moves limbs, digestion, waste elimination, breathing, speech and blood circulation
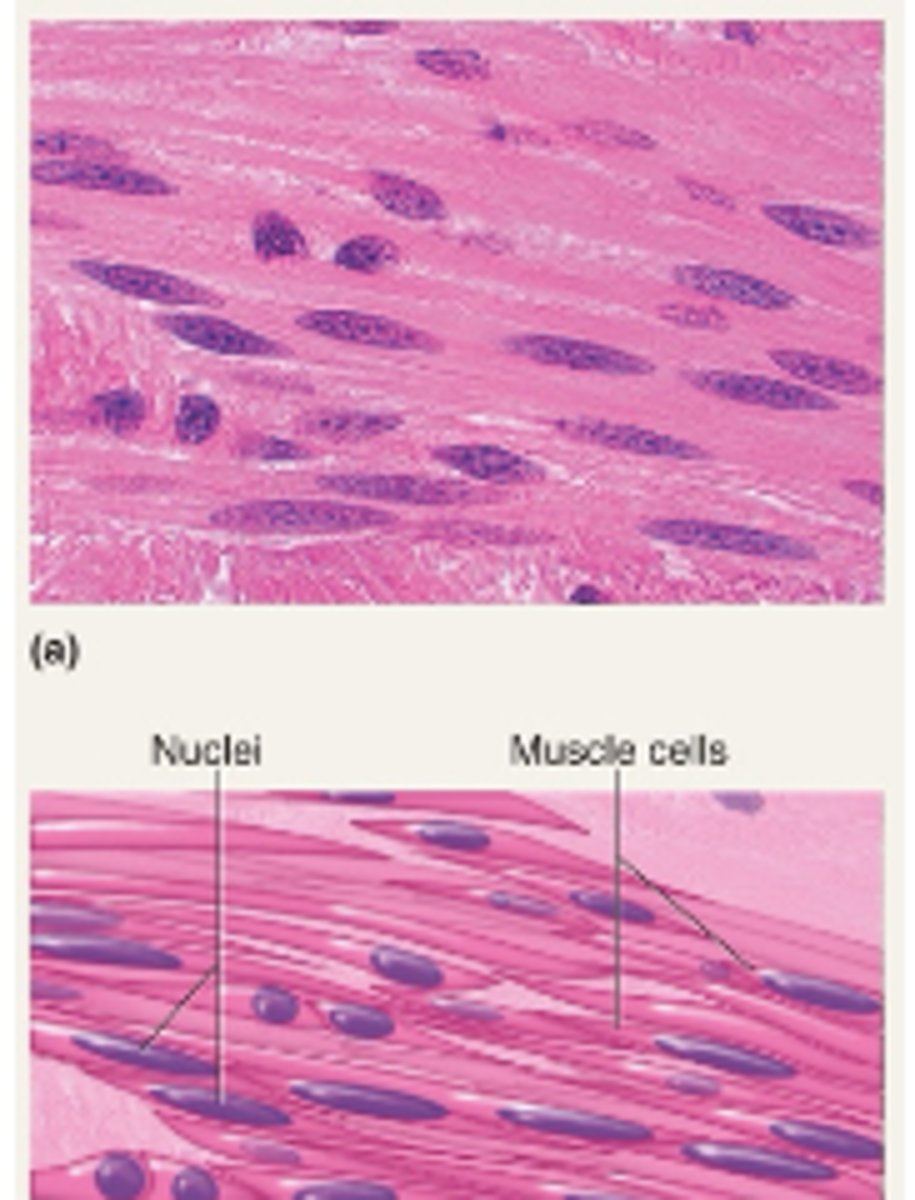
Skeletal Muscle
Cells are long cylinders with many peripheral nuclei
Visible striations
Voluntary control
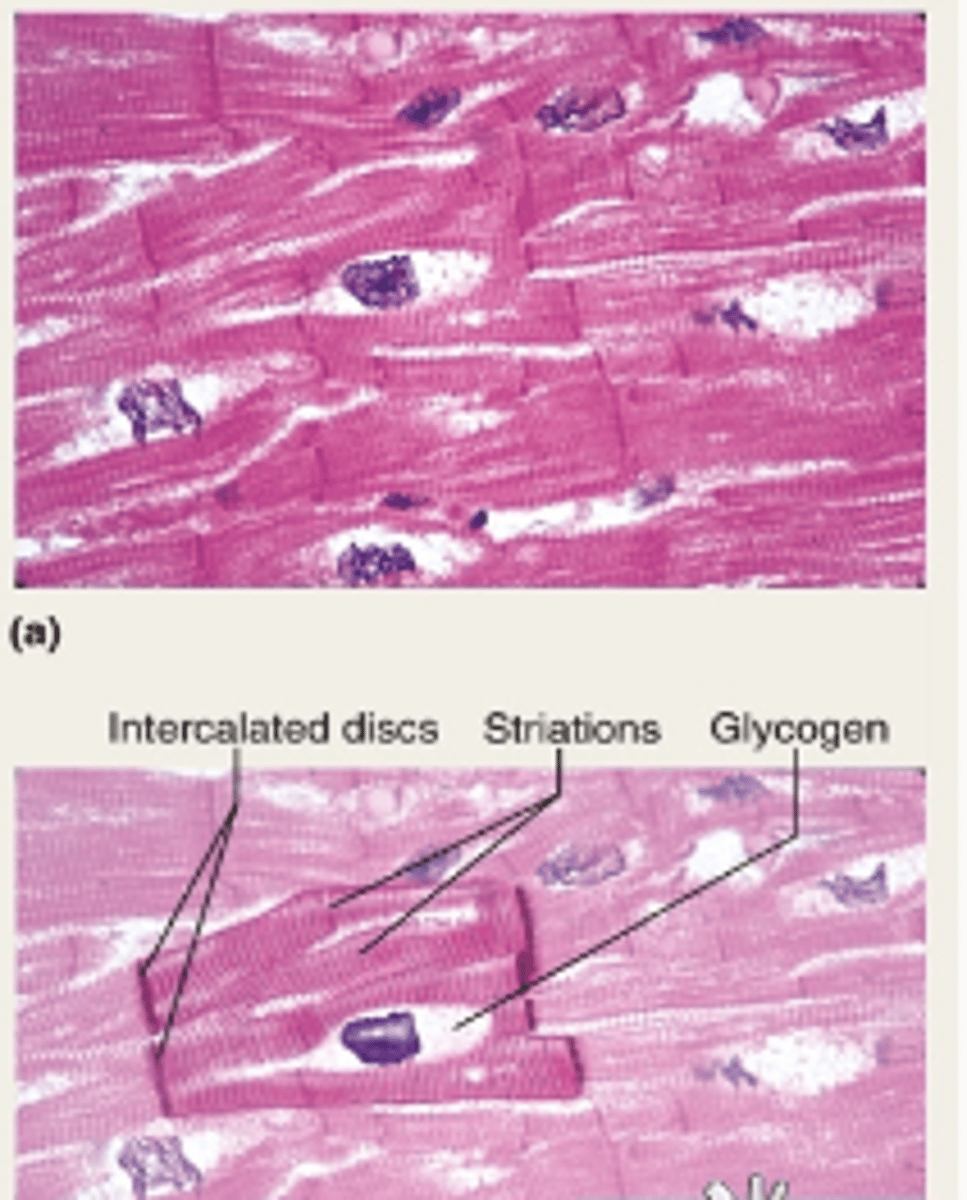
Cardiac Muscle
Cells are branched cylinders with one nuclei
Involuntary and striated
Attached by desmosomes
Communicate by intercalated discs
Smooth Muscle
Spindle shaped cells with a single central nuclei
Walls of hollow organs
- blood vessels
- GI tract
- bladder
Involuntary and non-striated
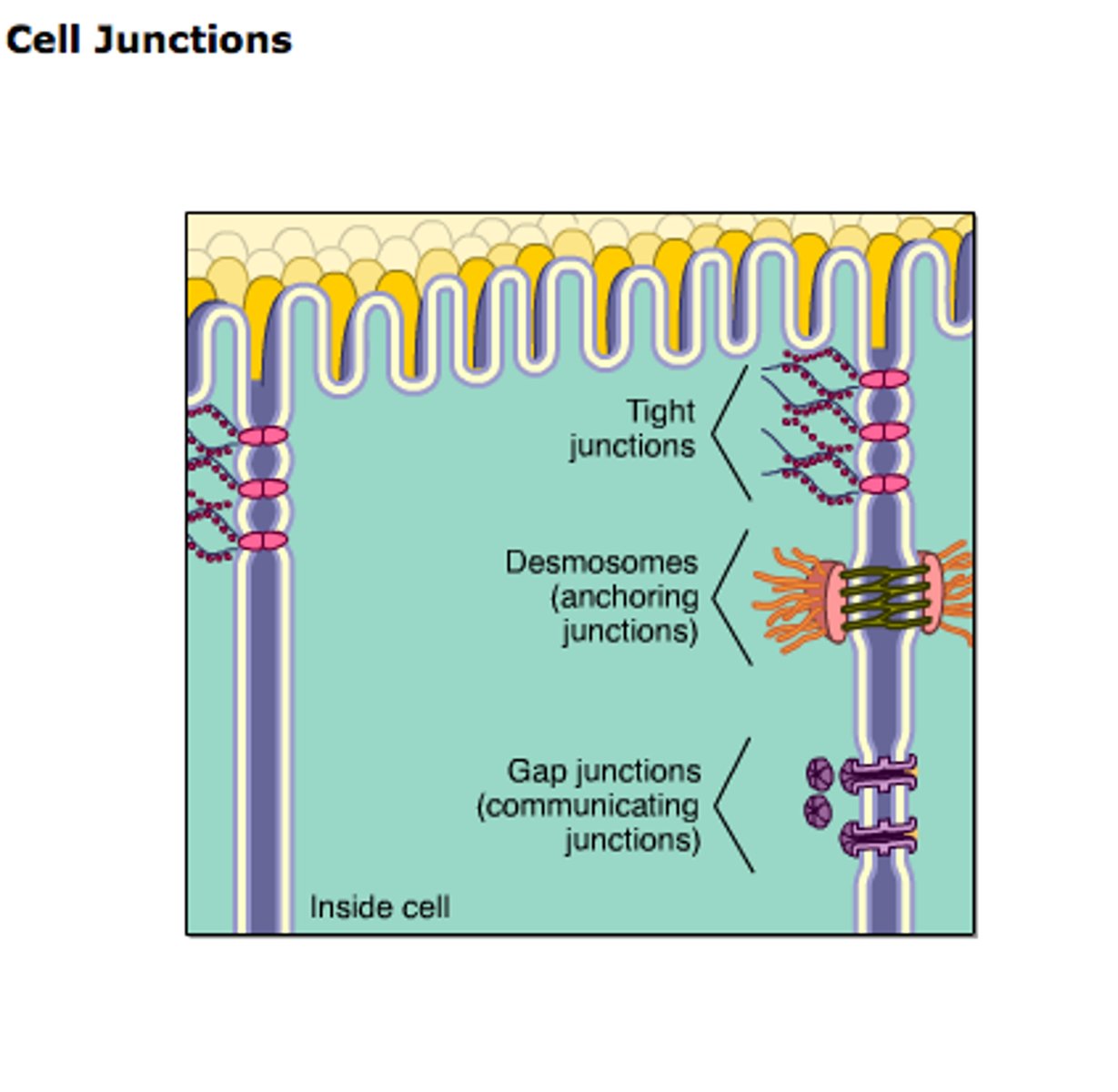
Cell Junctions
Tight junctions
Adherens junctions
Gap junctions
Desmosomes
Hemidesmosomes
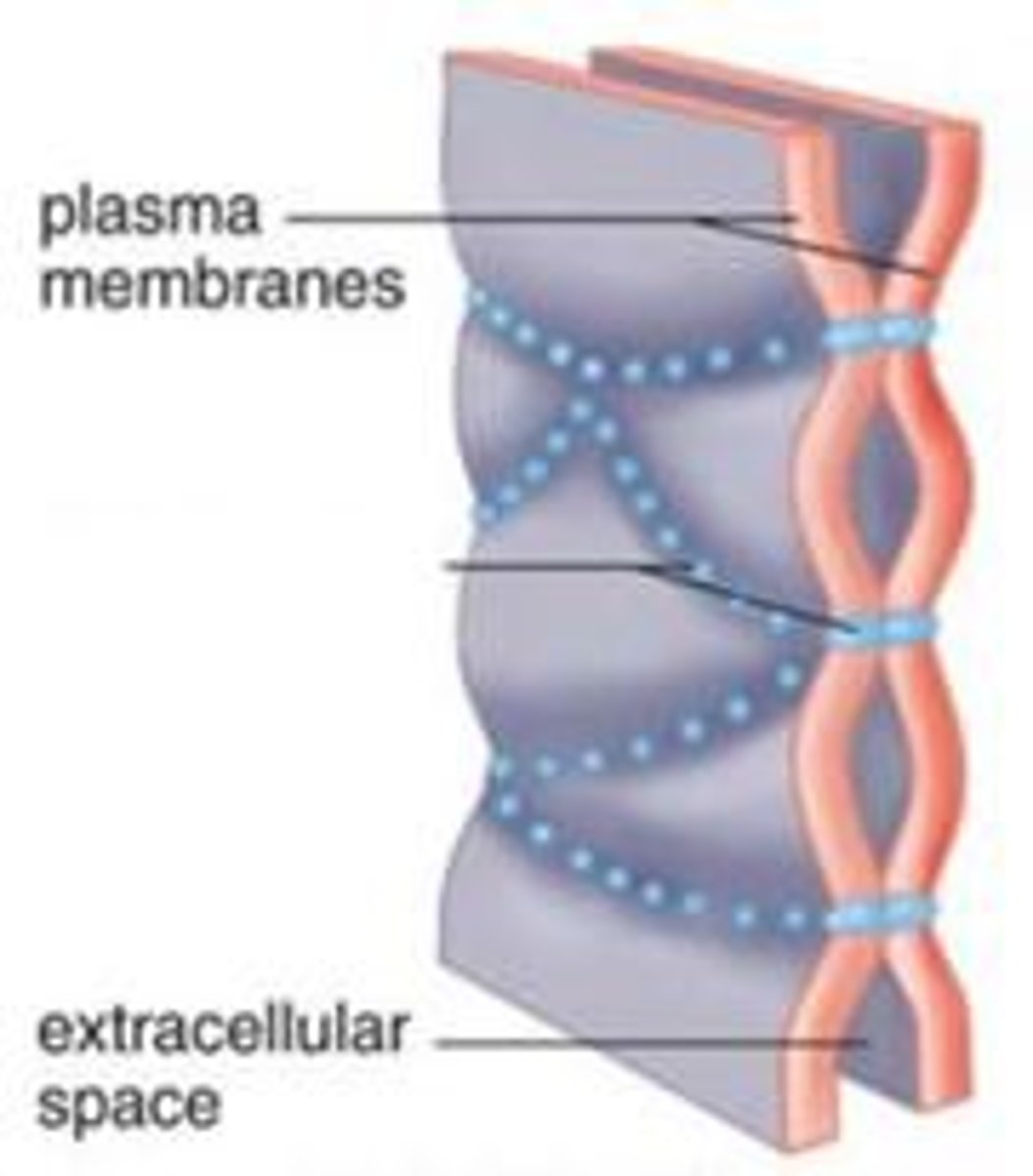
Tight Junctions
Watertight seal between cells
Plasma membrane fused with strip of proteins
Common between cells that line GI and bladder
(like zipper)
Partial fusion of portions of the cell
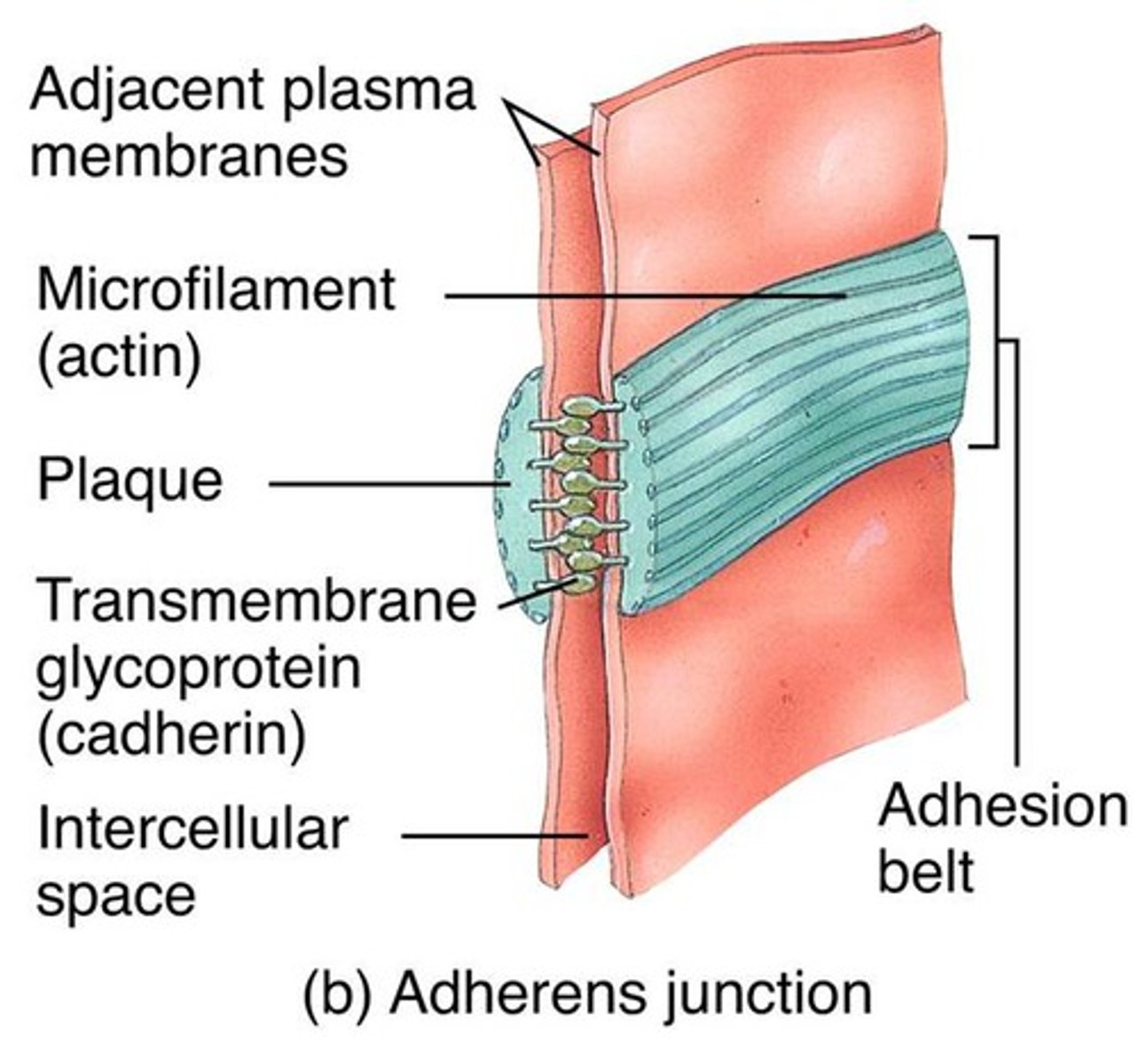
Adherens Junctions
Hold epithelial cells together
Structural components
- plaque
dense layer of proteins inside cell membranes
- microfilaments
extend into cytoplasm
- integral membrane proteins
connect to membrane of other cell
(like velcro)
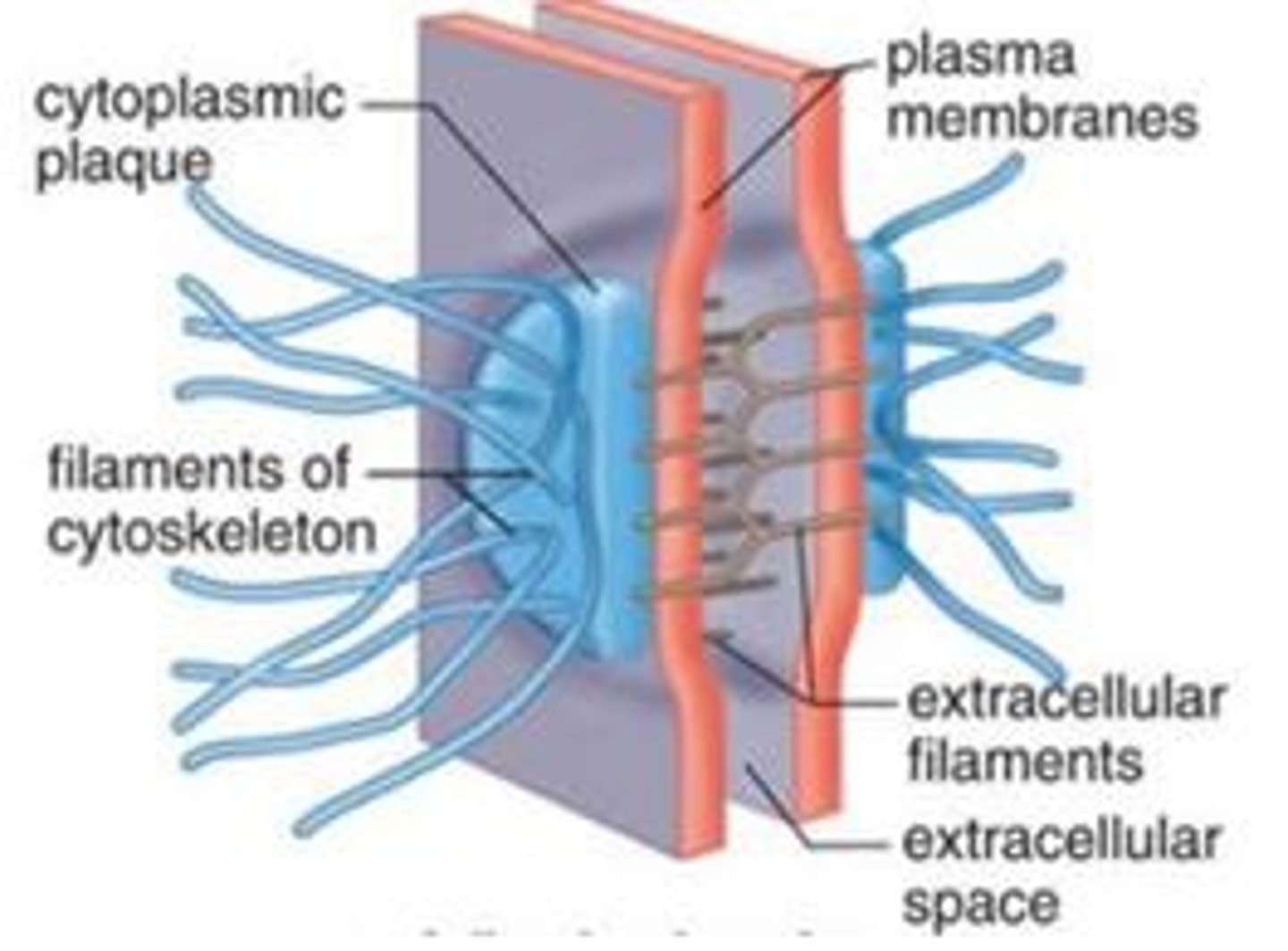
Desmosomes
Resists cellular separation and cell disruption
Similar structure to adherens except intracellular intermediate filaments cross cytoplasm of cell
Cellular support of cardiac muscle
(plaque like glue - can't break)
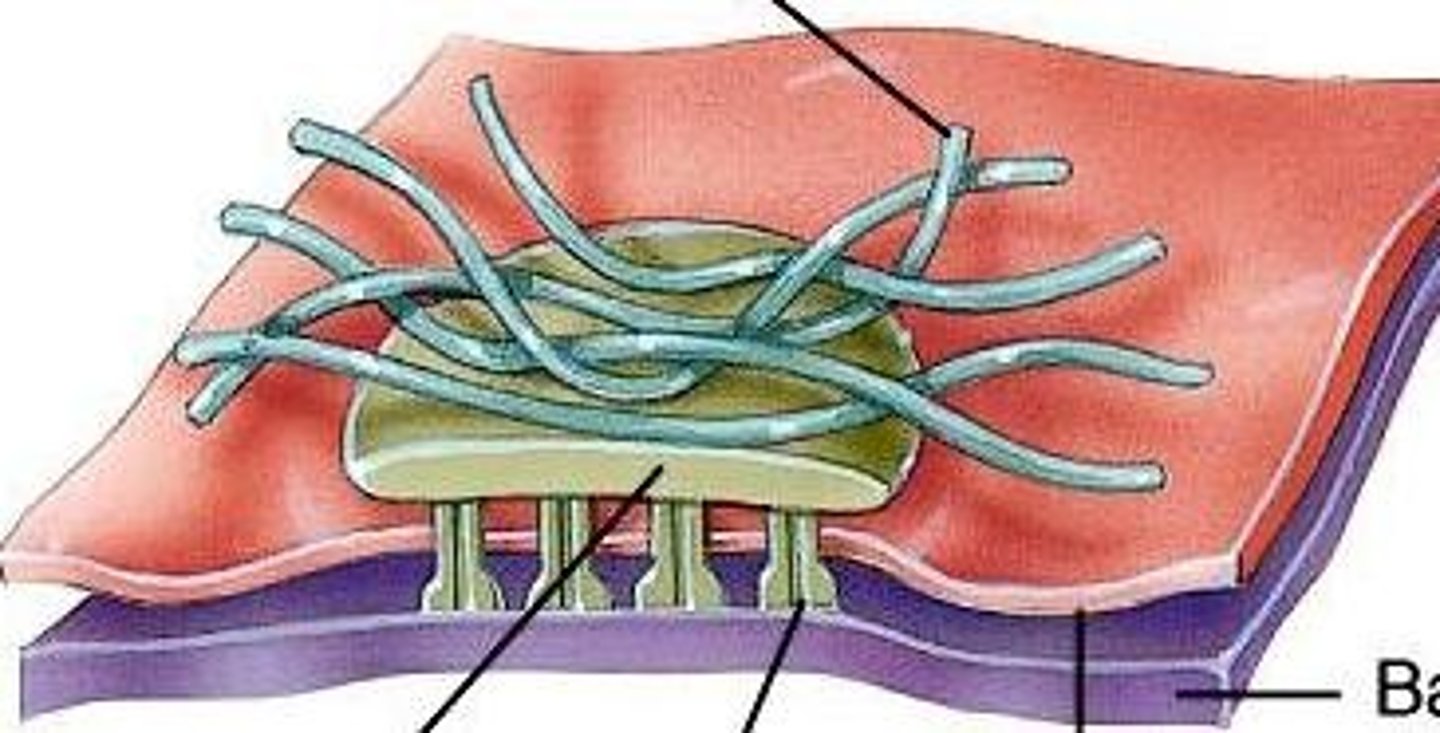
Hemidesmosomes
Half a desmosome
Connect cells to extracellular material
- basement membrane
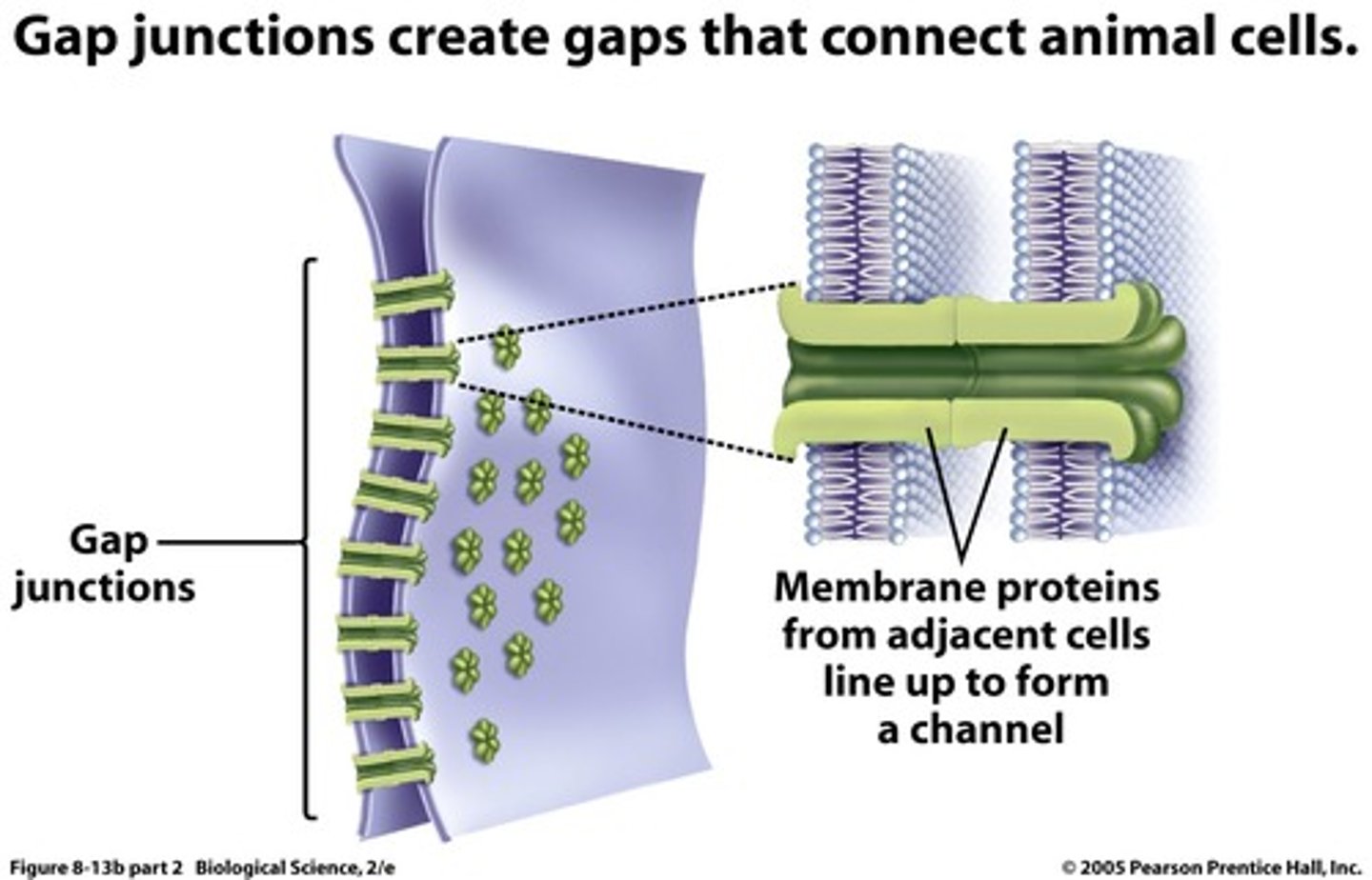
Gap Junctions
Tiny space between plasma membranes of 2 cells
Crossed by protein channels called connexons forming fluid filled tunnels
Cell communication with ions and small molecules
Muscle and nerve impulses spread cell to cells
- heart and smooth muscle of gut
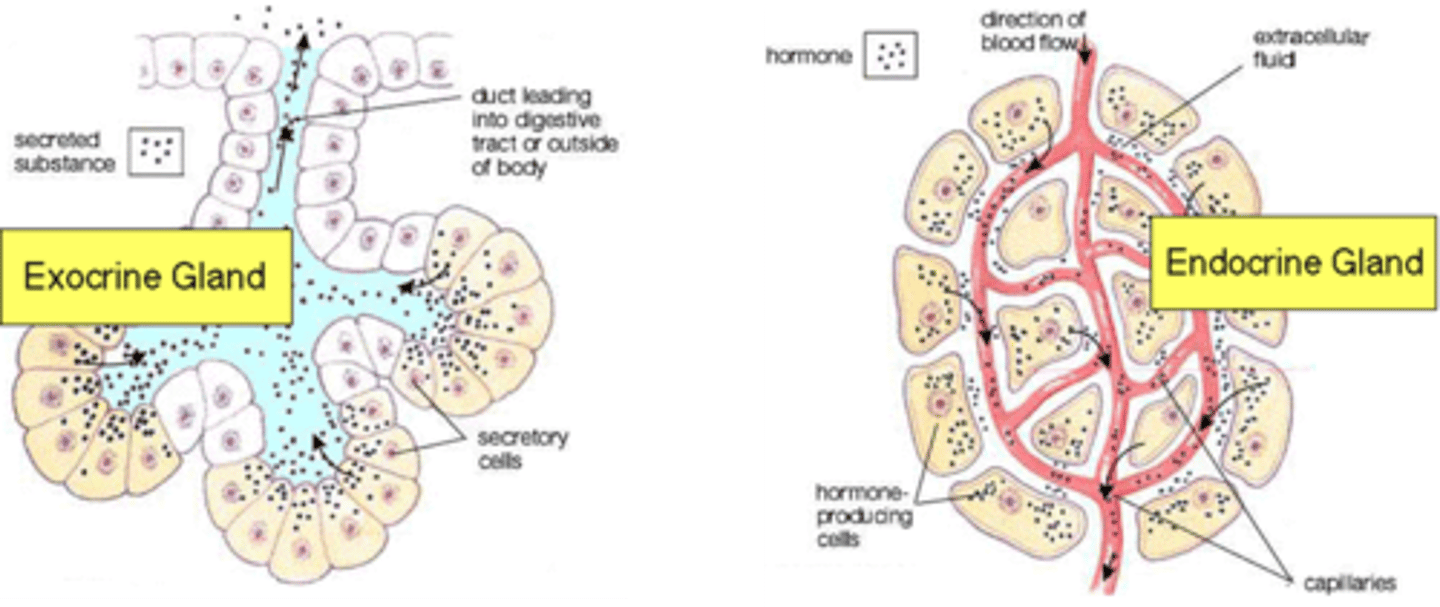
Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Glands secrete substances for elimination or for use elsewhere in body
- composed primarily of epithelial tissue
Exocrine glands connect to surface
- epithelial tubes
Endocrine glands have no ducts
- secrete products (hormones) in bloodstream
Mixed organs
- liver
secretes bile into ducts, albumin into blood
- gonads
release gametes, secretes hormones into blood
- pancreas
secretes digestive enzymes and hormones
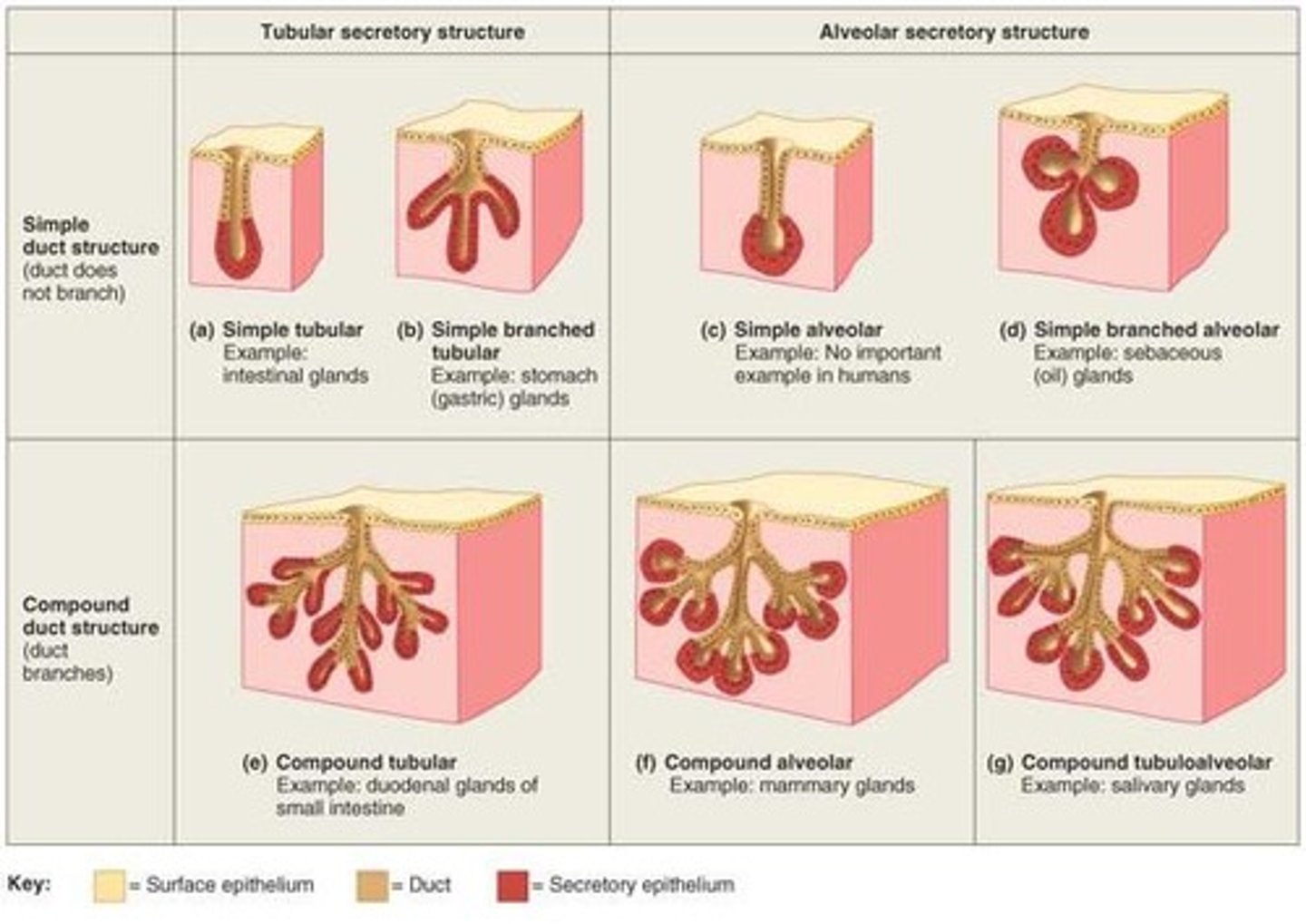
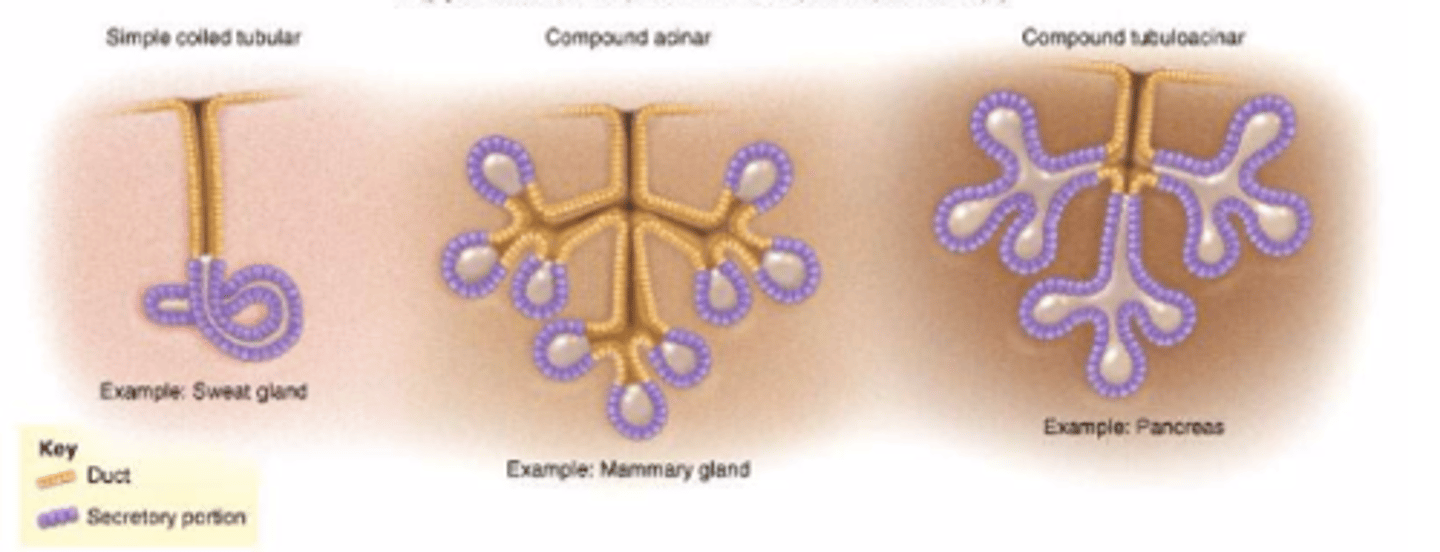
Types of Exocrine Glands
Simple glands have unbranched duct
Compound glands have a branched ducts
Shape of gland
- acinar (alveolar)
secretory cells form dilated sac instead of a tube
- tubuloacinar
secretory cells in both tubes and sacs
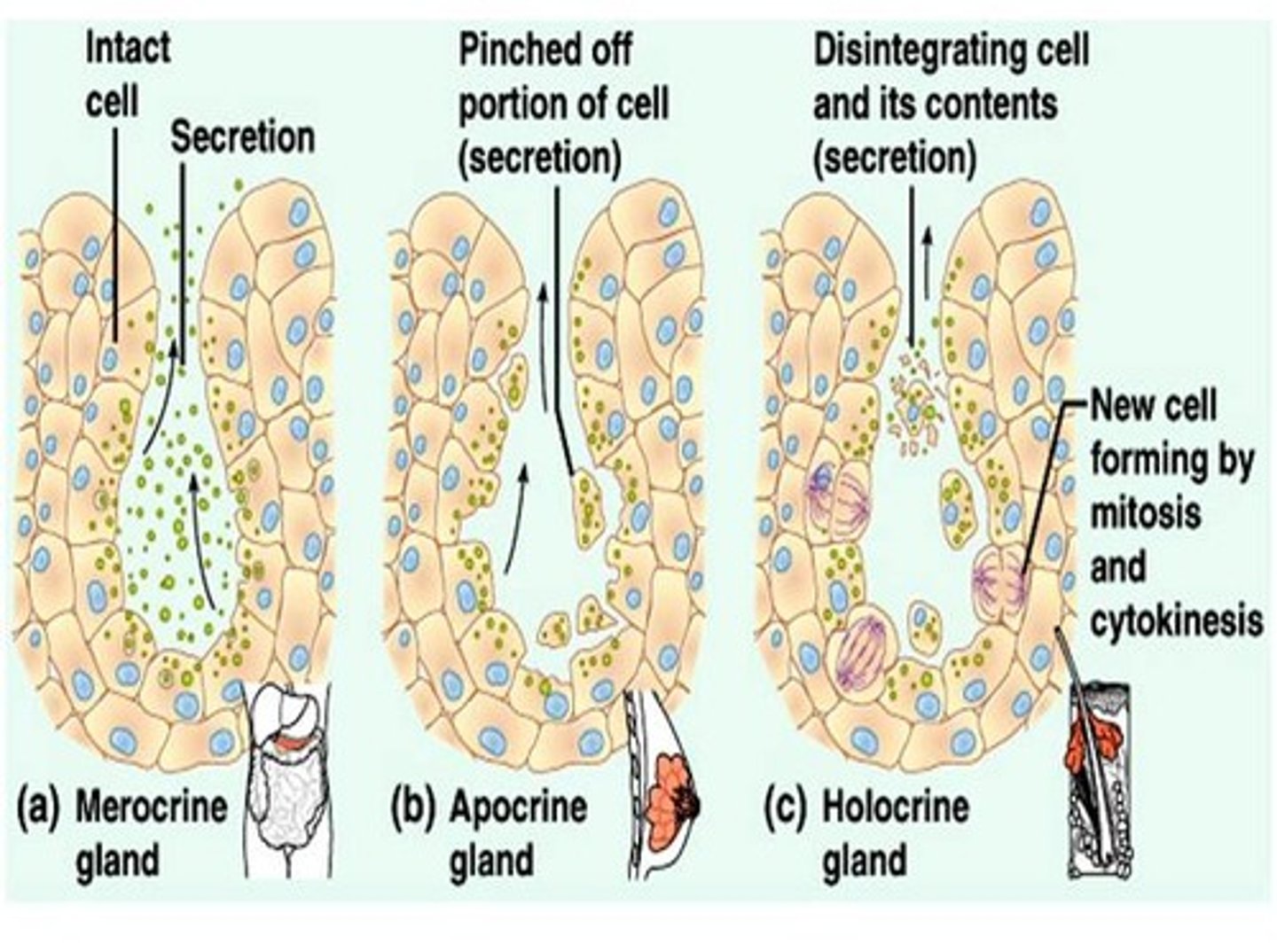
Methods of Glandular Secretion
Merocrine
- cells release products by exocytosis
- saliva, digestive enzymes, sweat
Apocrine
- upper parts of cell possibly pinches off and dies
- smelly sweat and milk
Holocrine
- whole cells die and rupture to release their products
- oil glands
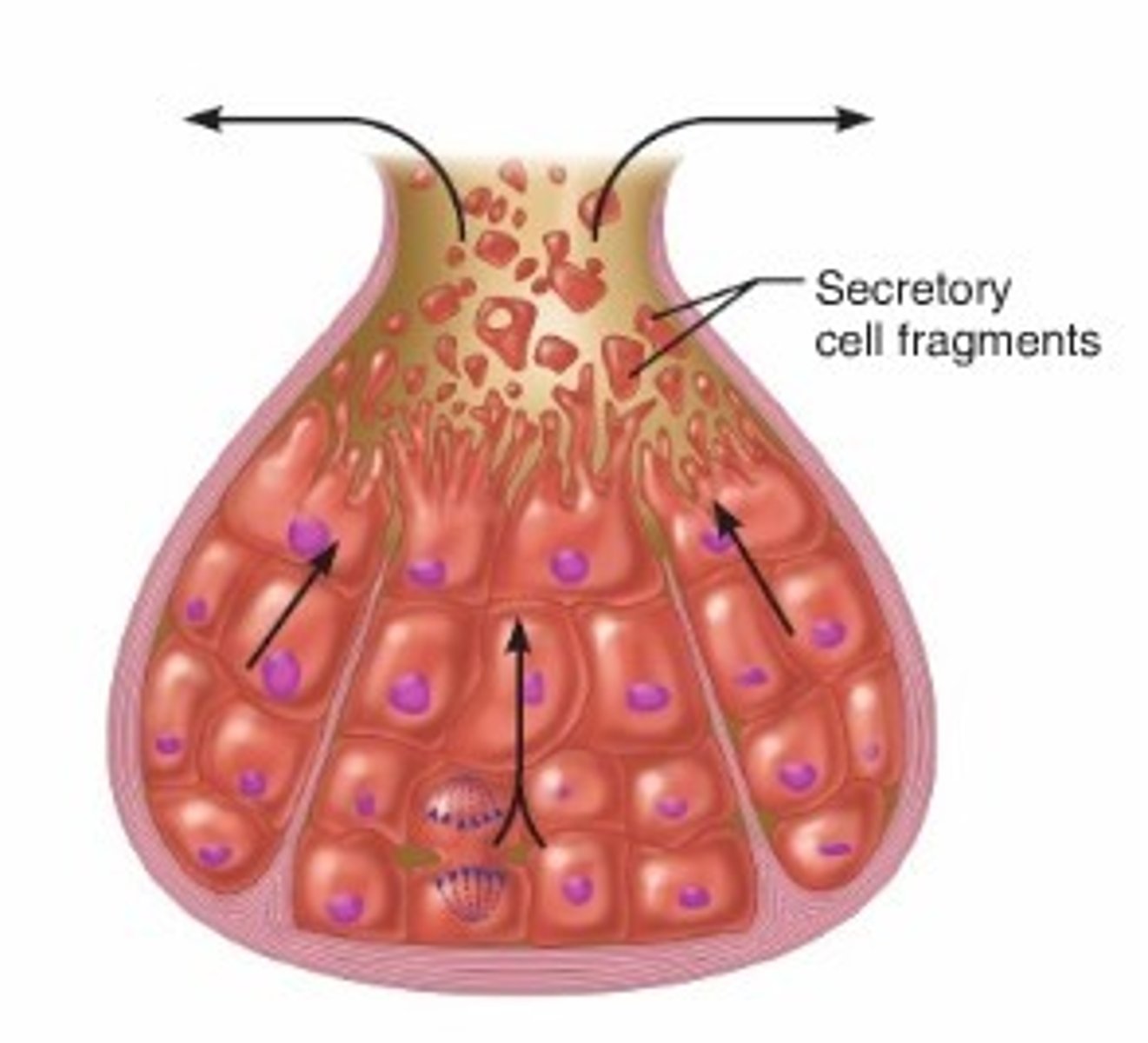
Holocrine Gland
Secretory cells disintegrate in order to deliver their accumulated product and some cell fragments
Oil producing glands of scalp
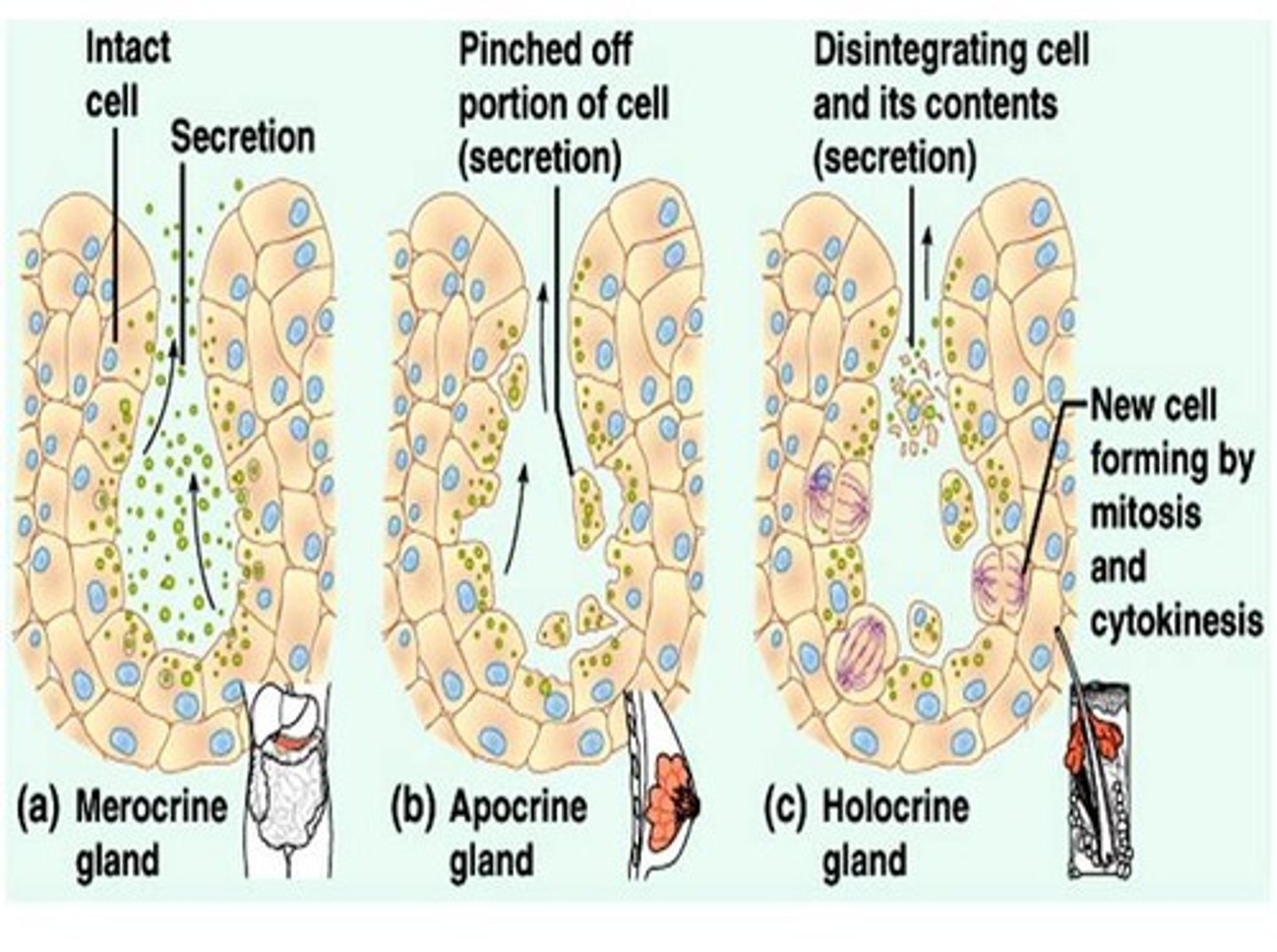
Merocrine and Apocrine Secretion
Merocrine glands release their product by exocytosis
- tears, gastric glands, pancreas,
Apocrine glands are really merocrine glands but confusing appearance
- apical cytoplasm not lost as used to be believed
- mammary and armpit sweat glands
Mucous Membranes
Consists of
- epithelium
- lamina propria
- muscularis mucosae
Lines passageways that open to exterior
- digestive
- respiratory
- urinary
- reproductive
Mucous coating and movement of cilia trap and remove foreign particles/bacteria from internal surfaces
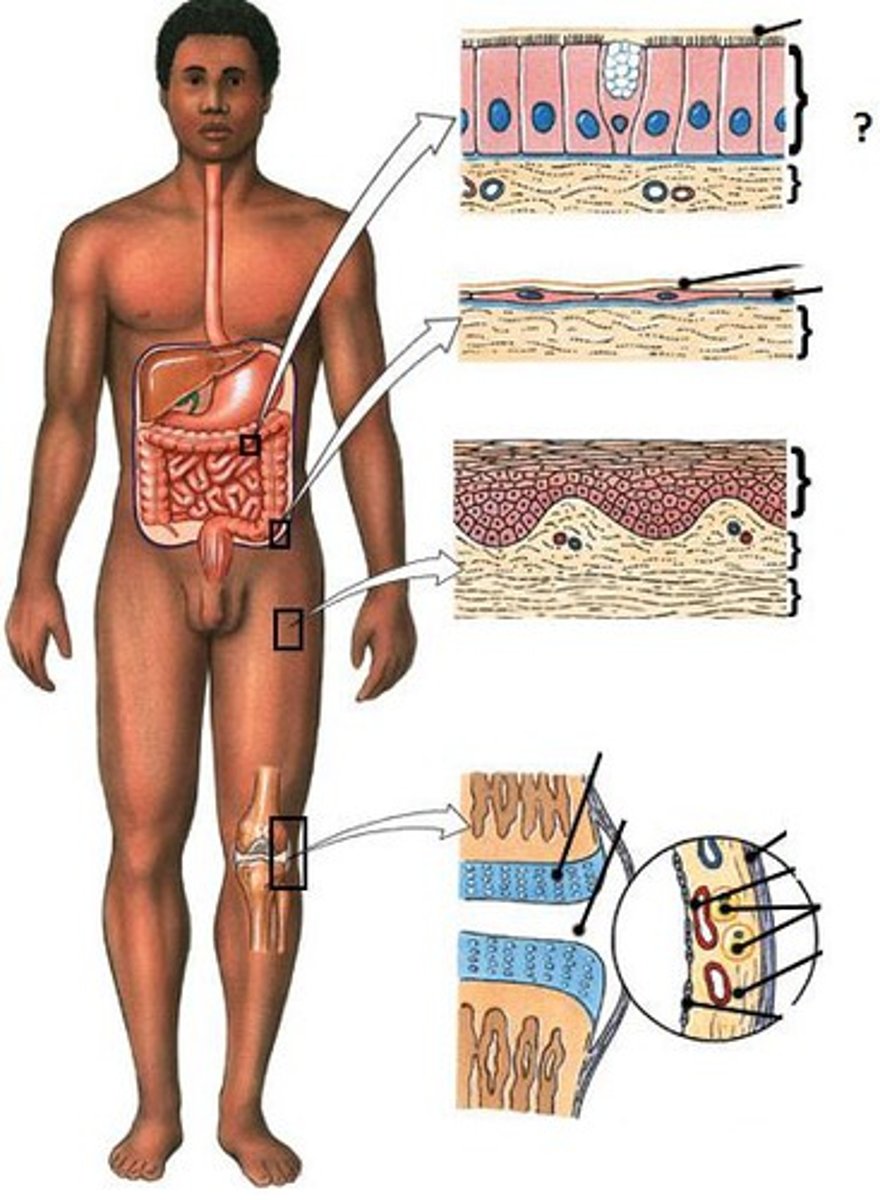
which primary tissue type does internal lining of intestine belong?
epithelial
what are the 4 primary tissues types
muscular, nervous, connective, epithelial
what primary tissue type do neuroglial cells belong to?
nervous
what primary tissue type does smooth muscle cells belong to?
muscular
what primary tissue type does adipose tissue belong to?
connective
what primary tissue type does cartilage belong to?
connective
what common cells are found in many diffrent types of connective tissue?
fibroblast (make elastic and reticular fibers and collagen)
Membrane excitability due to rapid changes in membrane potential is most pronounced in what two primary tissue types?
nervous and muscular
What two categorical components make up the extracellular matrix of connective tissue?
fibrous proteins and ground substance
When I rub my skin, am I touching the basolateral or apical side of that tissue?
apical (also where food touches)
What "specific" type of tissue (specific category and primary tissue type) underlies most epithelia?
primary: connective
specific: areolar
Name two categories of tissue where avascularity is a characteristic.
epithelial tissue and cartilage connective tissue are avascular
What type of connective tissue typically forms the strong capsule of organs?
dense irregular connective tissue
Characterize adipose tissue, blood, dense regular connective tissue, and stratified squamous epithelium in general as having a High, Moderate, or Low cellular contribution to the total volume.
adipose tissue = high
blood = moderate
dense regular connective tissue = low
stratified squamous epithelium = high
What specialized type of epithelium is specialized for transport by passive processes (diffusion)?
simple squamous epithelium
What type(s) are specialized for more active transport processes?
simple columnar epithelium and simple cuboidal
What specific type of epithelium is most highly specialized for protection and strength, but not absorption or secretion?
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
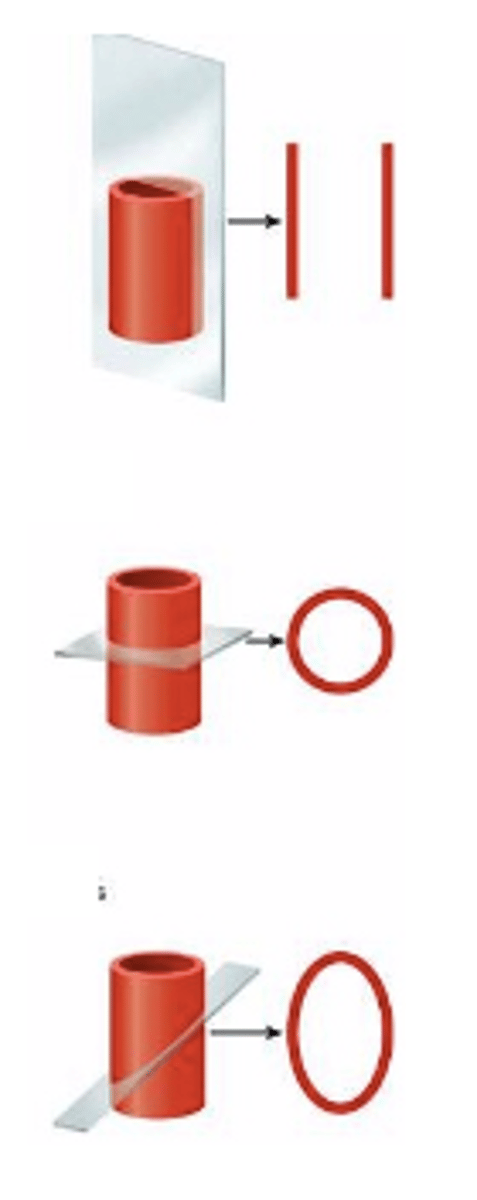
3 Ways to Section Tissue
longitudinal section, cross section, oblique section

2 Types of microscopes
light microscope
scanning electron microscope (SEM) 3D visualization
4 steps for slide preparation
embedding (in paraffin or freeze)
sectioning (slicing)
fixing (dehydration/add alcohol)
staining
6 types of histological analysis
composition analysis
tissue culture
histopathology (tissues gone rogue)
marking/tagging
fluorescence
video
Nervous Tissue Specialization
specialized for communication by electrical and chemical signals
2 components make up nervous tissue
neurons (nerve cells)
- integration of stimuli
neuroglia (glial)
- protect and assist neurons
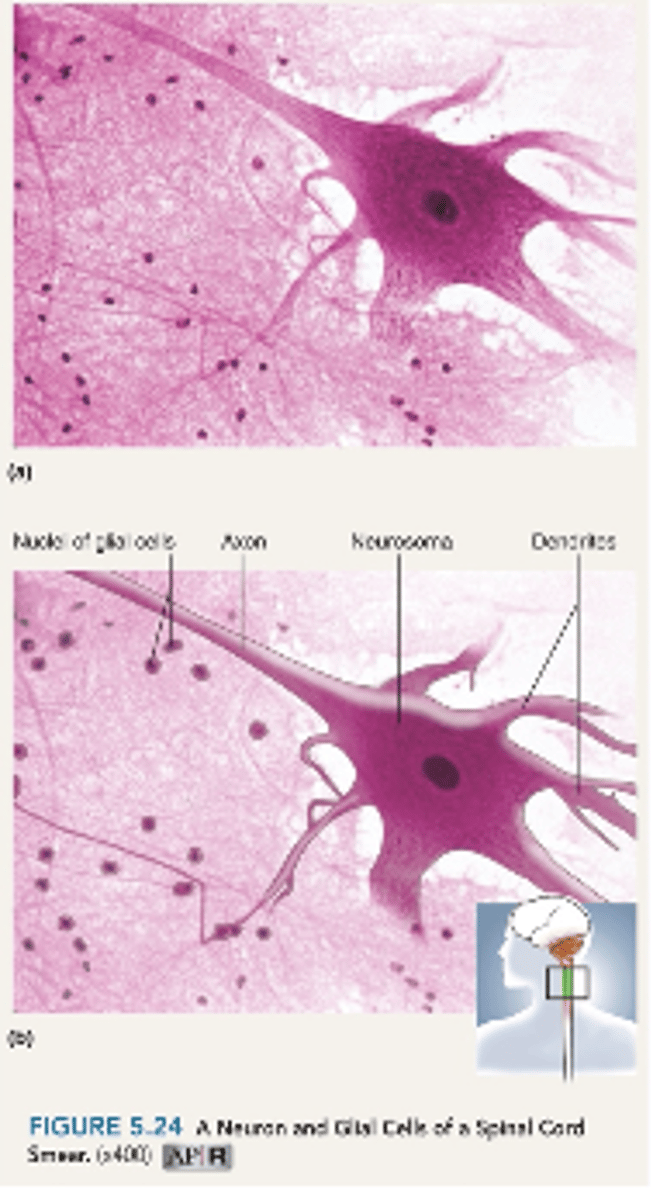
Nerve Tissue
Cell types
- neurons (nerve cell)
- glial cells
Nerve cell structure
- nucleus and long cell processes
- dendrite (signal towards cell body)
- axon (signal away from cell body)
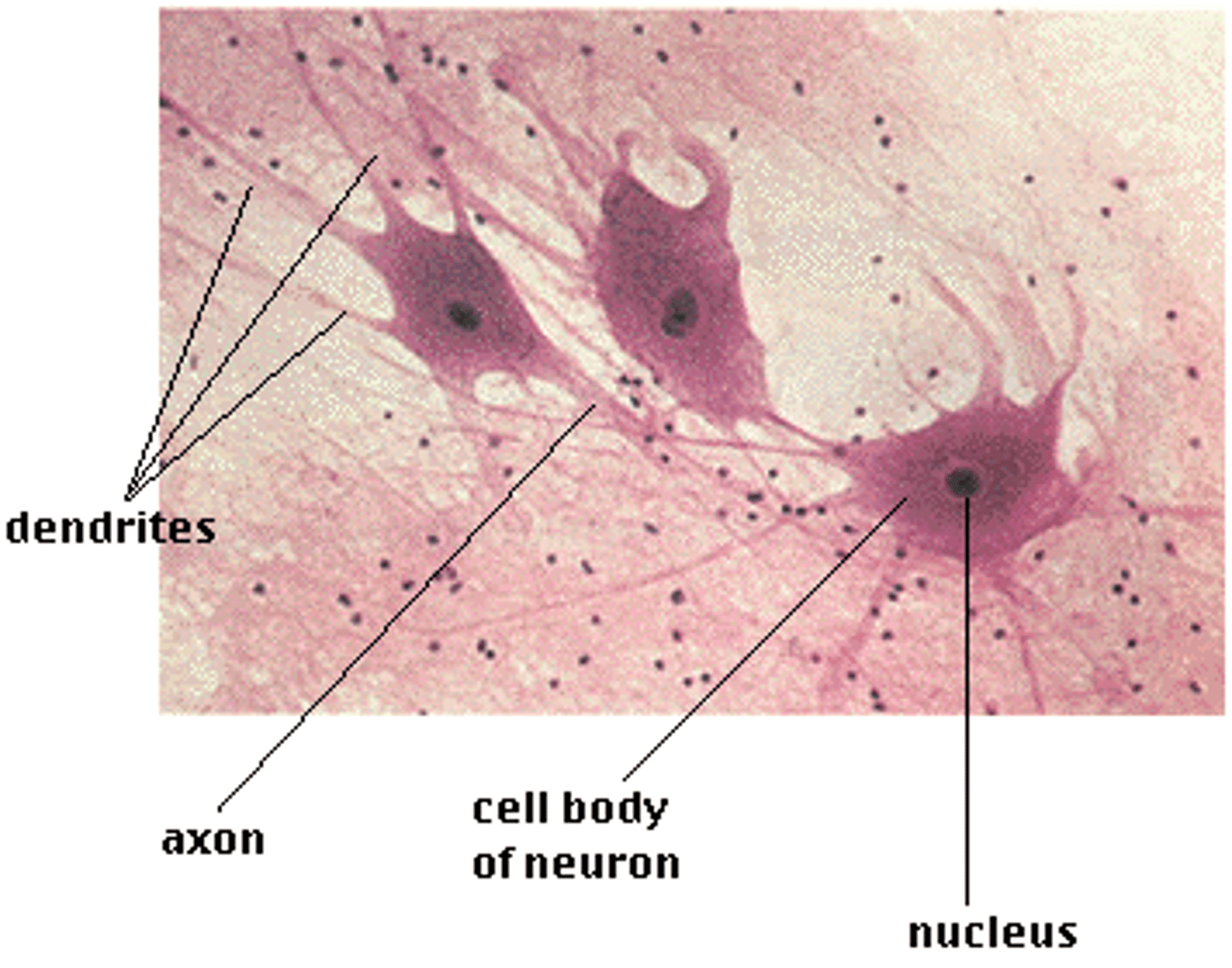
2 places to find nervous tissue
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
excitability in nervous tissue
- a characteristic of all living cells
- developed to the highest degree in nervous and muscular tissue
membrane potential in nervous tissue
electrical charge difference (voltage) that occurs across the plasma membranes is the basis for the excitation
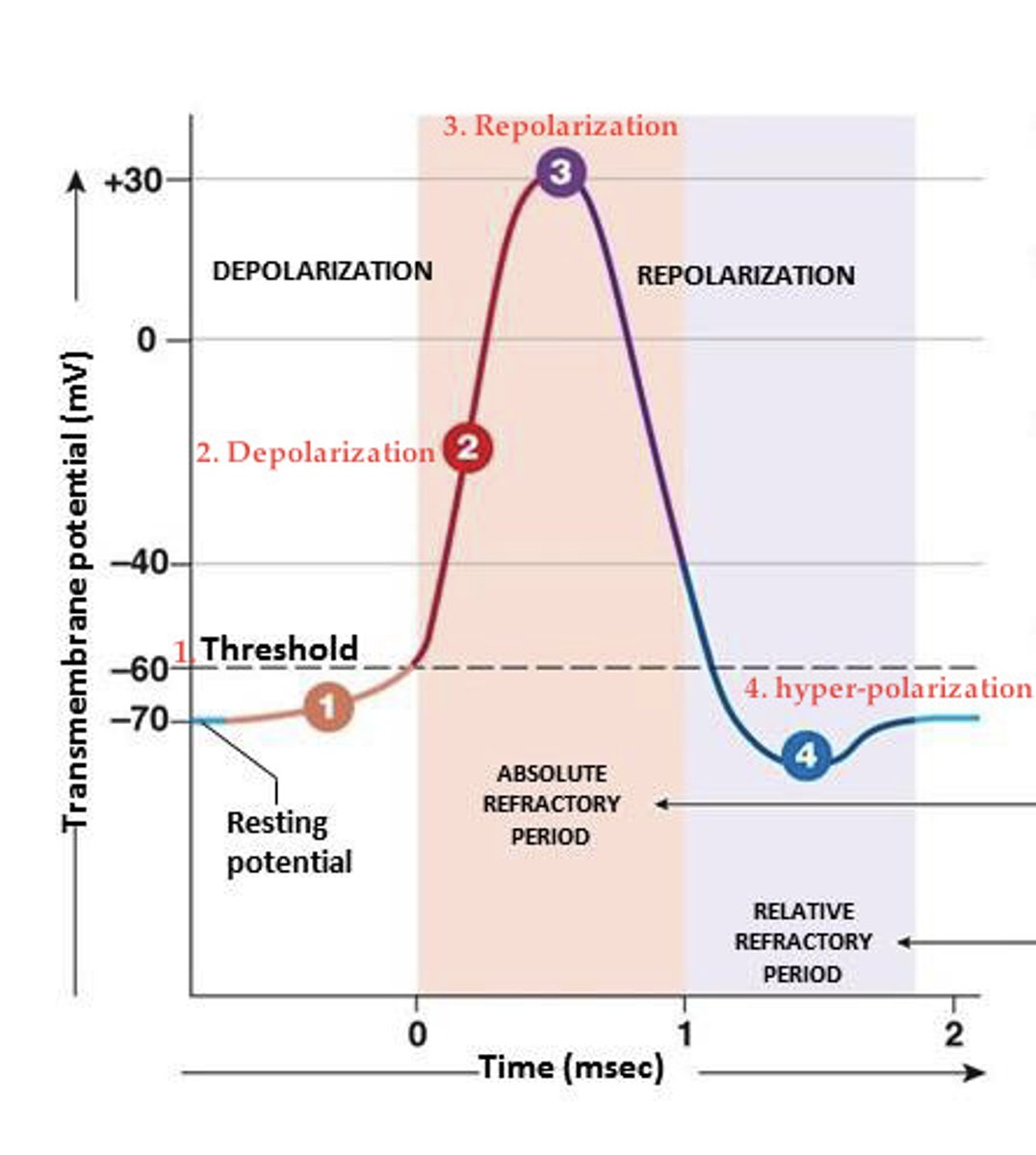
chemical communication in nervous tissue
occurs at synapses between neurons or between neurons and other effector tissues
effector = muscle or gland
2 excitable tissue types
nervous and muscle tissue
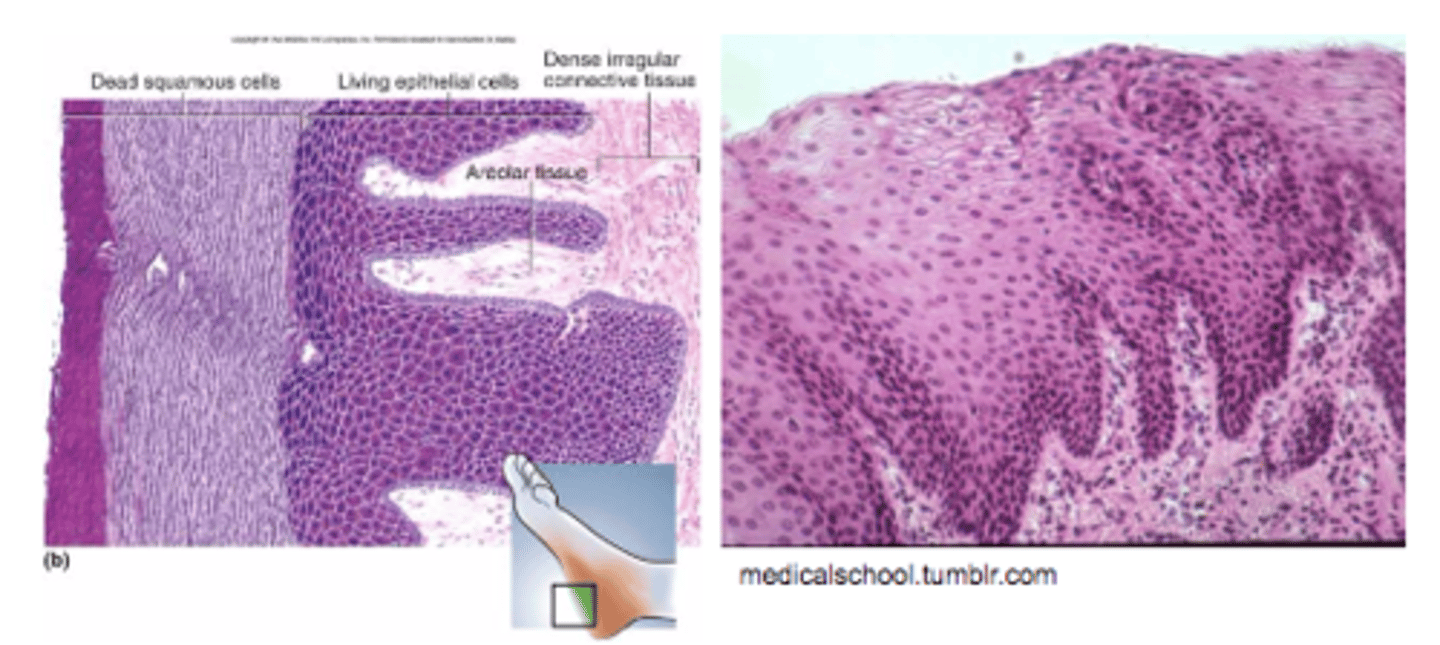
Integument Epithelial Tissue
excellent protection bad at transport
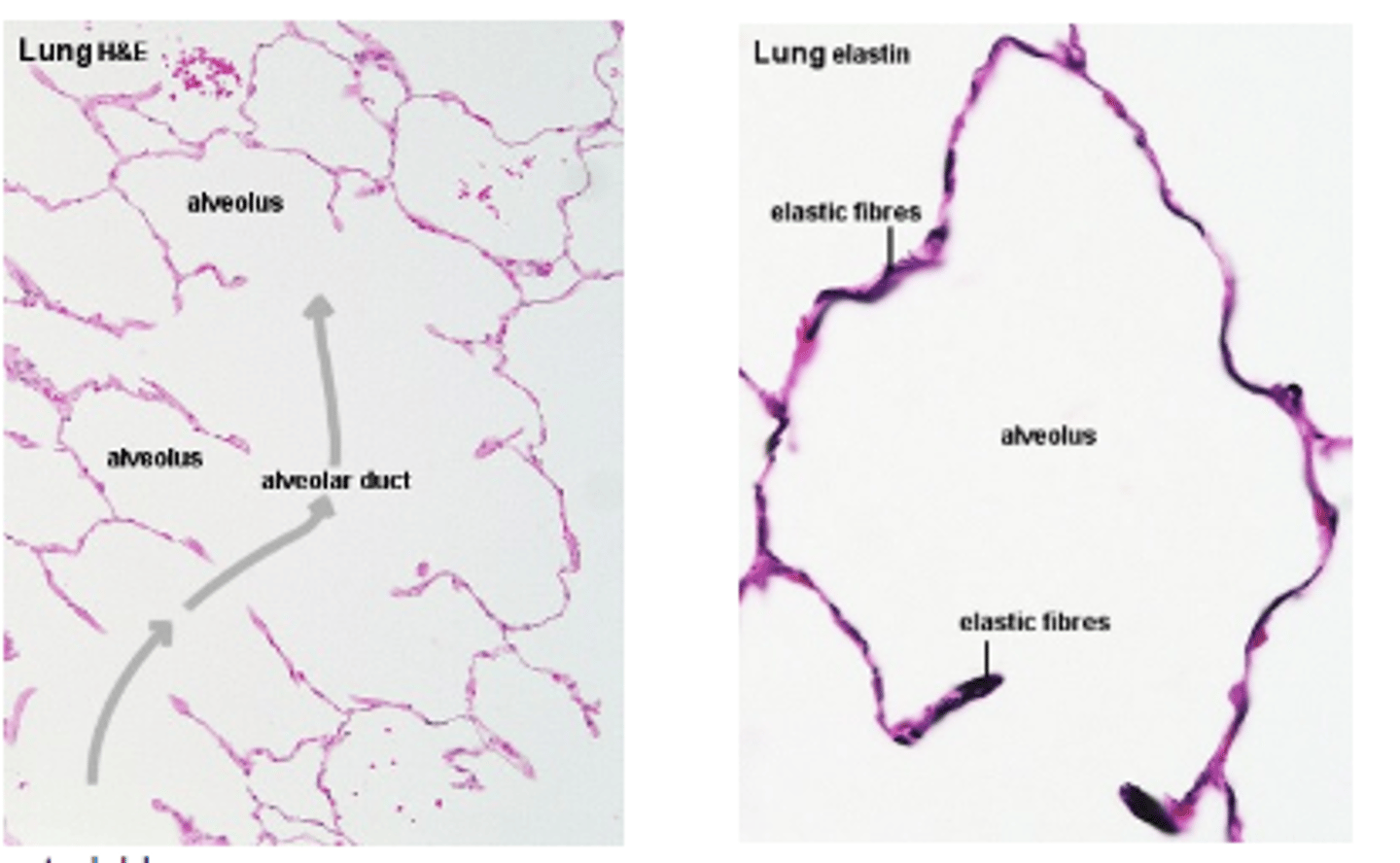
Pulmonary Alveoli Epithelial Tissue
excellent transport/diffusion bad at protection
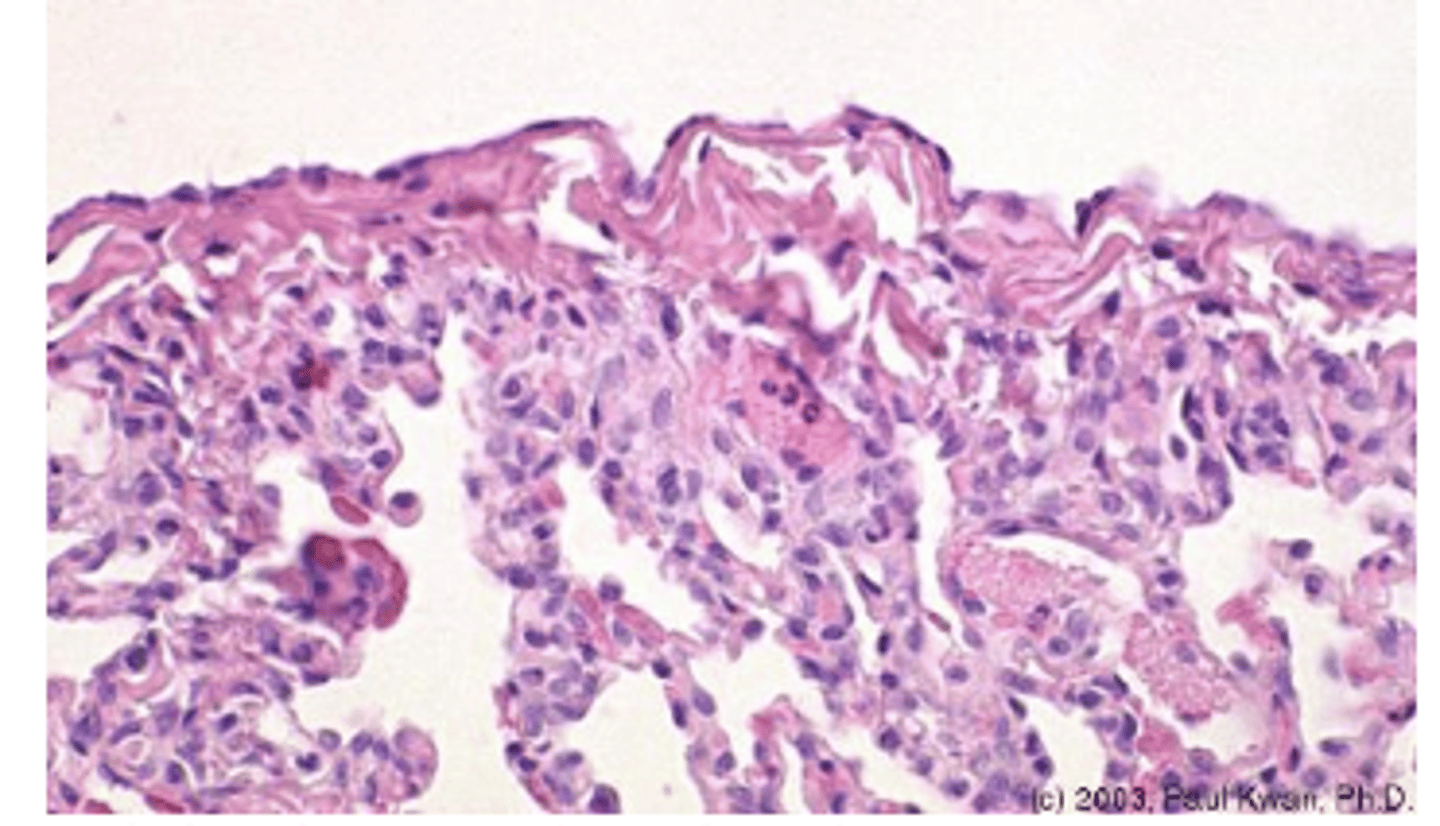
Mesothelia Epithelial TIssue
Internal non free surface type
- lines organs (serous membranes)
- visceral vs. parietal layers
- heart (pericardium), lungs (pleura), viscera (peritoneum)
Glandular Epithelia and their shapes
sweat gland = exocrine gland
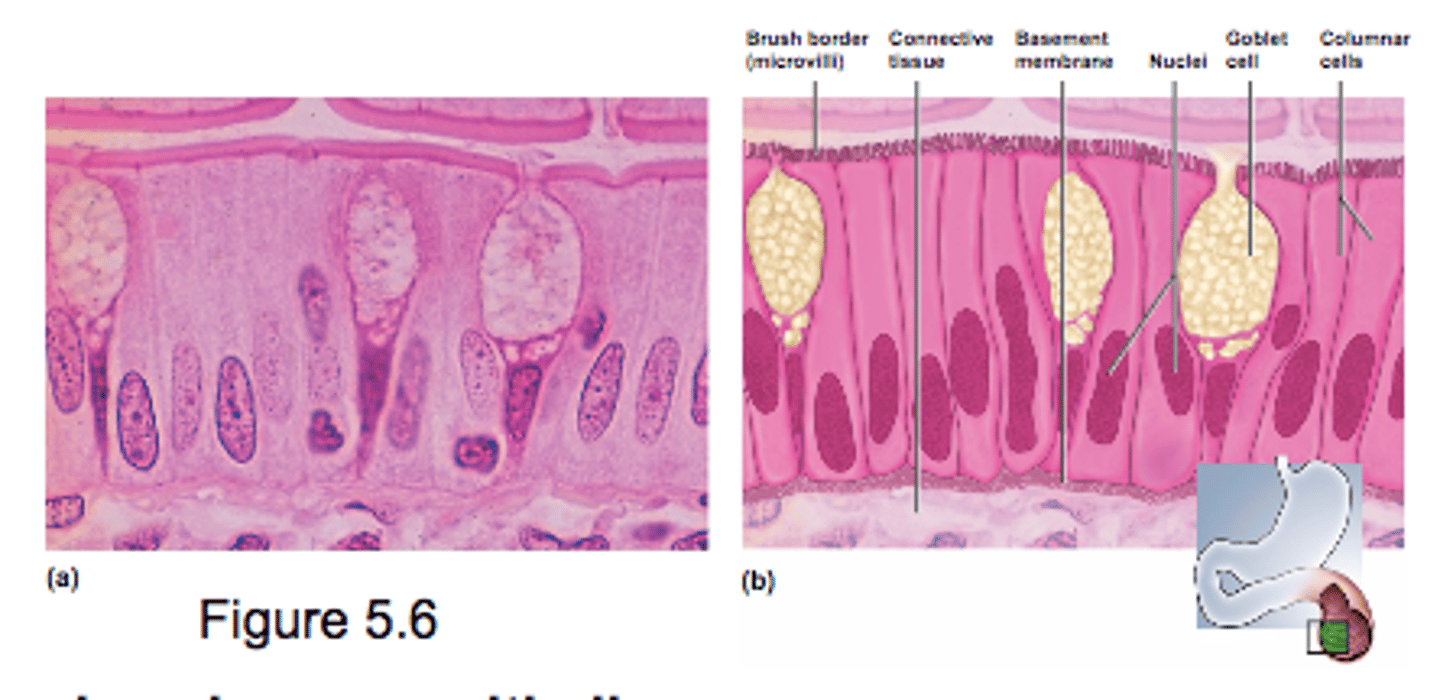
Simple Columnar Epithelium
-single row of tall, narrow cells & single row of nuclei
- active transport process (secretion and absorption)
- some protection
What are the three primary types of fibers found within the matrix of various connective tissues?
what macromolecule are they made of?
elastic fiber - in matrix (extracellular material)
reticular fiber - in matrix (extracellular material)
collagen - in matrix (extracellular material)
protein
What molecule differentiates outside skin of cheek from inside skin of mouth?
what macrololecules is it?
keratinized is outside skin, non-keratinized is inside skin
keratin is the protein/molecule that differentiates the two
protein
What specific tissue type is primarily associated with lymphatic organs such as the spleen?
reticular tissue
What two categories of cells are found within nervous tissue?
neurons and neuroglial cells
What unique type of epithelium is associated with the lining of much of the urinary system, such as the bladder?
is it stratified?
what special ability does it have?
transitional epithelial (only in urinary tract)
yes stratified
able to change from round to flat when stretched
3 types of cartilage
hyaline cartilage
elastic cartilage
fibrocartilage
What specific epithelial tissue appears stratified but in actuality is not stratified?
pseudostratified epithelia (looks multilayered but isnt)
What are the three subtypes of muscle tissue?
cardiac
smooth
skeletal
are hormones secreted from endocrine glands or exocrine glands?
endocrine glands
What type of epithelium lines internal/visceral organs (heart, lung, digestive)?
mesothelial: internal non free-surface type (simple squamous)
Are sweat glands exocrine or endocrine?
exocrine glands
By weight or volume, what is the most common general protein in the human body?
what color is it?
collagen
white