Tissues and Integumentary Unit 2 Test Corrections #1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Tissues are a group of cells that all share the same function.
Tissues are made up of cells and tissues make up organs
What is the definition of tissue?
The four tissue types are connective, epithelial, nervous and muscle
What are four primary tissue types?
The characteristics for epithelial tissue are:
Avascular (no blood vessels) thus is thin
Characterized based on numbers of layers and shape of cells
Has one surface not in contact with other tissue types
Protects and specializes in diffusion
What are the characteristics for epithelial tissue?
The characteristics of each muscle type are:
Skeletal: striated and voluntary
Smooth: nonstriated, voluntary, found in digestive tract and blood vessels
Cardiac: striated, involuntary, found in the heart only
Describe the characteristics of each muscle type:
The characteristics for connective tissue are:
Has living cells and extracellular matrix
What are the characteristics of connective tissue?
The chemical found in your hair, nails and skin is keratin
What is the waterproof chemical found in your hair, nails and skin?
The four membranes to remember are:
Mucous, Serous, Cutaneous and Synovial
What are the four membranes to remember?
The mucous membrane is:
Moist
Specializes in secretion and absorption
What are the characteristics for the mucous membrane?
The serous membrane:
Lines internal organs
Serous fluid between each tissue layer
What are the characteristics for the serous membrane?
The cutaneous membrane is a:
Dry membrane
Provides protection
What are the characteristics for the cutaneous membrane?
The synovial membrane is the:
Only connective tissue membrane
Found in the joints
What are the characteristics for the synovial membrane?
The sebaceous gland produces oil
What does the sebaceous gland produce?
The sweat gland produces sweat, releases water and cools the body
What does the sweat gland produce?
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer
Which type of skin cancer is the most dangerous?
These three things give our skin color:
Melanin (tan/black)
Carotene (orange)
Hemoglobin (pink/red)
What three things give our skin color?
First degree burn is:
Redness of the skin
Itching
Pain
Hot to touch (epidermis and top of dermis)
What are the characteristics for first degree?
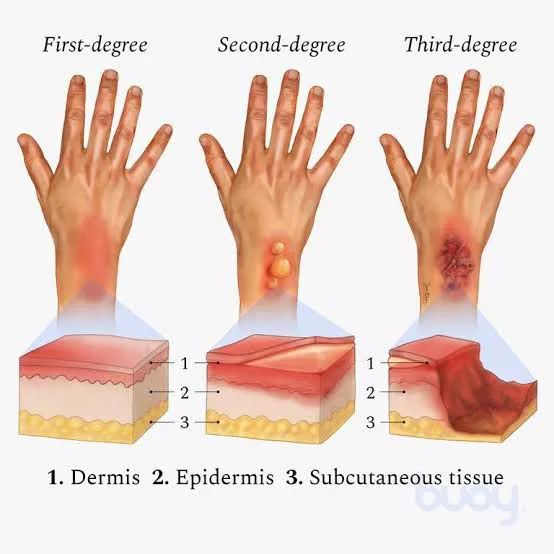
Second degree burn is:
Blisters
Epidermis and dermis
What are the characteristics for second degree burn?
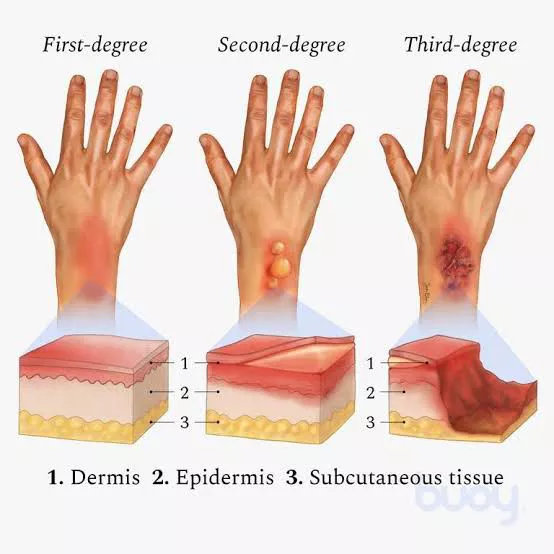
Third degree burn is:
Charred skin (black or white)
Down into the subcutaneous tissues
What are the characteristics for third degree burn?
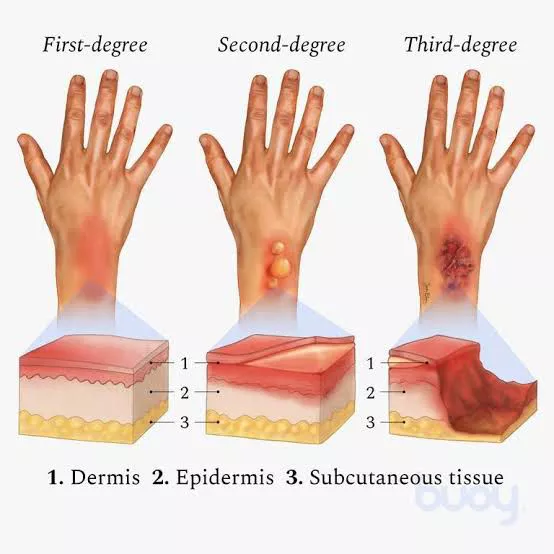
Third degree is serious because it:
Destroys entire skin layer
Opens up to infections
Severe water loss
Replaced with scar tissue mostly
Why is third degree burn so serious? What problems arise as a result?
Each letter stands for:
A = Asymmetry
B = Border
C= Color
D=- Diameter
E = Evolving
What does each letter of ABCDE stand for in cancer detection?
REMEMBER: Metastasis is an action and malignant is a characteristic
What do you need to remember about metastasis and malignant?
Some characteristics for cancer cells that make them different from normal cells is:
Normal cells do a specific job, cancer cells lose that function
Normal cells divide in an controlled manner, cancer cells divide uncontrollably
What are some characteristics for cancer cells that make them different from normal cells?
Mutations cause cells to lose control of the cell division process by:
Cells have proteins (genes) that control the cell cycle and act like breaks and accelerator pedals
Accelerator pedal proteins stimulate cell division so when they are mutated to be on too much, you can get too much cell division
Mutations cause cells to lose control of the cell division process by:
p53 triggers apoptosis or programmed cell death if there is irreparable damage to the cell’s DNA
If it isn’t functioning, then the cell will not trigger apoptosis and can begin accumulating damage, which can lead to mutations in cell cycle control proteins, inevitably causing uncontrolled cell growth
Why is p53 important for normal cells? Why can it lead to cancer if it is mutated?
The difference is:
Benign - will not spread, encapsulated
Malignant - the characteristic of cancer that means it can spread to other tissues and organs
Describe the difference between a benign and a malignant tumor:
Non-cancerous
What is benign?
Malignant is cancerous
What is malignant?
Dyplasia is:
Cells that don’t look how they do under the microscope
The abnormal growth of cells within a tissue
What is dysplasia?
A carcinogen is any substance or activity that can cause cancer or increase the risk of developing cancer
What is a carcinogen?