Reproduction + Development
5.0(2)Studied by 12 people
Card Sorting
1/48
Last updated 4:09 PM on 3/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Prenatal Development
The single-celled zygote forms a multicellular organism with specialized cells through the processes of: **mitosis and differentiation**
By the end of the 8th week of pregnancy the embryo is called a **fetus** and all of the major structures are present
When the zygote is implanted in the uterine wall a temporary organ called the **placenta** is formed from maternal and embryonic tissues
The developing embryo is attached to the placenta by the **umbilical cord,** this cord contains blood vessels
The fetus is surrounded by a membrane called the **amnion** which is filled with **amniotic fluid**
The fluid protects the fetus by giving it a stable environment and absorbing shock
zygote 🡪 multiple identical cells 🡪 differentiated cells (tissues) 🡪 organs 🡪organ systems 🡪 individual
By the end of the 8th week of pregnancy the embryo is called a **fetus** and all of the major structures are present
When the zygote is implanted in the uterine wall a temporary organ called the **placenta** is formed from maternal and embryonic tissues
The developing embryo is attached to the placenta by the **umbilical cord,** this cord contains blood vessels
The fetus is surrounded by a membrane called the **amnion** which is filled with **amniotic fluid**
The fluid protects the fetus by giving it a stable environment and absorbing shock
zygote 🡪 multiple identical cells 🡪 differentiated cells (tissues) 🡪 organs 🡪organ systems 🡪 individual
2
New cards
Umbilical Cord
two arteries and a vein connects the fetus to the placenta
* **There is NO exchange of blood between the embryo and the mother!**
* **There is NO exchange of blood between the embryo and the mother!**
3
New cards
Placenta
**site of diffusion**
* **Oxygen & nutrients diffuse from the mother’s blood vessels, across the placenta, and into the baby’s blood vessels**
* **Wastes diffuse from the baby’s blood vessels into the mother’s blood vessels**
* **Oxygen & nutrients diffuse from the mother’s blood vessels, across the placenta, and into the baby’s blood vessels**
* **Wastes diffuse from the baby’s blood vessels into the mother’s blood vessels**
4
New cards
Human gestation
* the period between fertilization and birth
* approximately 38-40 weeks
* When gestation is complete the baby passes through the **cervix** and then through the **vagina**
* approximately 38-40 weeks
* When gestation is complete the baby passes through the **cervix** and then through the **vagina**
5
New cards
Teratogens
* **Substances that may harm the developing fetus and result in the formation of birth defects**
* **Include alcohol, certain drugs/medications, infections, and certain chemicals**
* **Include alcohol, certain drugs/medications, infections, and certain chemicals**
6
New cards
Fertilization
the fusion of the sperm cell nucleus with the egg cell nucleus to produce a zygote (fertilized egg)
* IF fertilization takes place, it occurs in the **oviduct**
* The egg cell is viable for approximately 24 hours after ovulation
Sperm + ovum 🡪 zygote
* IF fertilization takes place, it occurs in the **oviduct**
* The egg cell is viable for approximately 24 hours after ovulation
Sperm + ovum 🡪 zygote
7
New cards
Implantation
* After approximately a week, the developing embryo is implanted into the **uterus**
**Embryo**: conception to 8 weeks
**Embryo**: conception to 8 weeks
8
New cards
Identical twins (monozygotic)
One egg is fertilized by one sperm
Embryo splits into two during the early stages of development
Have identical genes and must be of the same sex
(Incidence: about 3 in every 1000 births)
Embryo splits into two during the early stages of development
Have identical genes and must be of the same sex
(Incidence: about 3 in every 1000 births)
9
New cards
**Fraternal twins (dizygotic)**
Two eggs are ovulated and are each fertilized by a different sperm cell.
No more related than any other sibling in the family (can be of the same or different sexes)
Maternal age, genetics, use of assisted reproductive technologies are factors
varies by geography and ranges from 6 to over 20 per 1,000 deliveries
No more related than any other sibling in the family (can be of the same or different sexes)
Maternal age, genetics, use of assisted reproductive technologies are factors
varies by geography and ranges from 6 to over 20 per 1,000 deliveries
10
New cards
Embryonic Development
A series of **cell divisions** and **differentiation** into various tissues and organ systems
11
New cards
Embryo
**a multicellular organism in the early stages of development**
The beginning developmental processes are always the same in all animals:
1) **rapid mitotic cell divisions** (cleavage)
2) **growth**
3) **differentiation**
The beginning developmental processes are always the same in all animals:
1) **rapid mitotic cell divisions** (cleavage)
2) **growth**
3) **differentiation**
12
New cards
**Cleavage**
* **The cells divide rapidly with little time in between for growth**
* **The cells become smaller and smaller**
* **The cells divide until they become a solid ball called a morula**
* **Cells continue to divide and are pushed to the outside to form a fluid-filled ball of cells called a blastula**
* **The cells become smaller and smaller**
* **The cells divide until they become a solid ball called a morula**
* **Cells continue to divide and are pushed to the outside to form a fluid-filled ball of cells called a blastula**
13
New cards
Gastrulation
**The cells further divide until they fold in on each other called invagination**
* **This forms 2 cell layers**
* **The outside layer is called** the **ectoderm** layer
* **The inside layer is the endoderm layer**
* **As cells continue to divide a third cell layer forms in the middle: mesoderm**
* **This forms 2 cell layers**
* **The outside layer is called** the **ectoderm** layer
* **The inside layer is the endoderm layer**
* **As cells continue to divide a third cell layer forms in the middle: mesoderm**
14
New cards
Differentiation
* the changing of unspecialized embryonic cells into the specialized cells, tissues and organs of a multicellular animal
* the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm **differentiates** to form tissue and organs systems
* **Each cell contains the same genes, but different**
genes are __**expressed**__ in different cells (embryonic cells use different portions of their genetic information)
* **The type of cell that forms through differentiation is controlled by genes, hormones and cell location**
* the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm **differentiates** to form tissue and organs systems
* **Each cell contains the same genes, but different**
genes are __**expressed**__ in different cells (embryonic cells use different portions of their genetic information)
* **The type of cell that forms through differentiation is controlled by genes, hormones and cell location**
15
New cards
Germ Layers
**Ectoderm: Outer layer**
**Endoderm: Inner Layer**
**Mesoderm: Middle Layer**
**Endoderm: Inner Layer**
**Mesoderm: Middle Layer**
16
New cards
Ectoderm
* forms nervous system including brain,
spinal cord and nerves
* forms skin, sweat glands, hair, nails
spinal cord and nerves
* forms skin, sweat glands, hair, nails
17
New cards
Endoderm
* forms lining of digestive tract and associated organs (liver, pancreas)
* forms lining of respiratory tract
* forms lining of respiratory tract
18
New cards
Mesoderm
* forms bones and muscles
* forms blood and blood vessels
* forms reproductive and excretory systems
* forms blood and blood vessels
* forms reproductive and excretory systems
19
New cards
Menstrual Cycle
a series of changes controlled by **hormones** that help prepare the female uterus for a possible pregnancy
The cycle is controlled by hormones of the **pituitary gland** in the brain and **ovaries**
The menstrual cycle occurs in 4 stages
Begins at **puberty**
Usually lasts 28 days, but can vary due to illness & other factors
**Stops** when a women is **pregnant**
**Humans and primates** are the only mammals to have a menstrual cycle
**Stops permanently** during **menopause**
The cycle is controlled by hormones of the **pituitary gland** in the brain and **ovaries**
The menstrual cycle occurs in 4 stages
Begins at **puberty**
Usually lasts 28 days, but can vary due to illness & other factors
**Stops** when a women is **pregnant**
**Humans and primates** are the only mammals to have a menstrual cycle
**Stops permanently** during **menopause**
20
New cards
Stage 1 - Follicle stage
Lasts 10-14 days
Ovarian hormones (**estrogen and progesterone**) are in **low** concentrations
Pituitary gland produces **FSH** (follicle stimulating hormone) which **causes a follicle** (egg cell capsule) **to form**
as the follicle grows it makes **increased amounts of estrogen**
* **estrogen** has a **negative feedback** effect on the pituitary that **stops FSH secretion**
* **estrogen** causes the **uterine lining** (endometrium) to **grow thicker**
Ovarian hormones (**estrogen and progesterone**) are in **low** concentrations
Pituitary gland produces **FSH** (follicle stimulating hormone) which **causes a follicle** (egg cell capsule) **to form**
as the follicle grows it makes **increased amounts of estrogen**
* **estrogen** has a **negative feedback** effect on the pituitary that **stops FSH secretion**
* **estrogen** causes the **uterine lining** (endometrium) to **grow thicker**
21
New cards
Stage 2 – Ovulation (middle of cycle)
* increased estrogen from the follicle stimulates the pituitary gland to produce **LH (luteinizing hormone)**
* **LH surge causes the follicle to rupture and the egg cell is sent to the oviduct=ovulation**
* **LH surge causes the follicle to rupture and the egg cell is sent to the oviduct=ovulation**
22
New cards
Stage 3 – Corpus Luteum Stage
13-14 days
**ruptured follicle** heals inside the ovary forming the **corpus luteum**
corpus luteum produces **progesterone**
**progesterone** maintains the **added growth of the uterine lining**
**ruptured follicle** heals inside the ovary forming the **corpus luteum**
corpus luteum produces **progesterone**
**progesterone** maintains the **added growth of the uterine lining**
23
New cards
If fertilization takes place:
* An embryo in the uterus will secrete a chemical called **hCG** (human chorionic gonadotropin)
* **hCG** prevents the corpus luteum from decomposing which maintains **progesterone** levels
* The **uterine lining** is **not shed**
* hCG is the chemical that is detected by pregnancy tests
* **hCG** prevents the corpus luteum from decomposing which maintains **progesterone** levels
* The **uterine lining** is **not shed**
* hCG is the chemical that is detected by pregnancy tests
24
New cards
Stage 4 - Menstruation
* if an embryo __**is not present**__, approximately 2 weeks after ovulation the **corpus luteum decomposes**
* **estrogen & progesterone levels decrease**
* **uterine lining is shed** and moves out through the vagina (menstruation)
* **pituitary increases** the release of **FSH** & a new follicle matures – the cycle continues throughout the woman’s reproductive years
* **estrogen & progesterone levels decrease**
* **uterine lining is shed** and moves out through the vagina (menstruation)
* **pituitary increases** the release of **FSH** & a new follicle matures – the cycle continues throughout the woman’s reproductive years
25
New cards
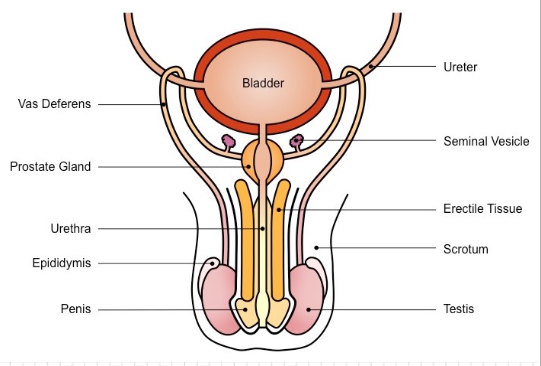
Male reproductive system
**Testes** – the male gonad; produce sperm and testosterone
* Located outside of the body in structure called the **scrotum**
* Lower temperature is best for sperm production and storage
* Testes are 3°C lower than body temp
Mature sperm are stored in the **epididymis**
* The sperm is transported from the testes (testicles) to the **vas deferens**
* **vas deferens:** tubes that connect to urethra
Glands that add fluid are the ***Cowper’s gland, seminal vesicles*** and ***prostate***
* Fluid nourishes and transports sperm, protects sperm from acidity of female reproductive tract
* Sperm + seminal fluid = **semen**
* Located outside of the body in structure called the **scrotum**
* Lower temperature is best for sperm production and storage
* Testes are 3°C lower than body temp
Mature sperm are stored in the **epididymis**
* The sperm is transported from the testes (testicles) to the **vas deferens**
* **vas deferens:** tubes that connect to urethra
Glands that add fluid are the ***Cowper’s gland, seminal vesicles*** and ***prostate***
* Fluid nourishes and transports sperm, protects sperm from acidity of female reproductive tract
* Sperm + seminal fluid = **semen**
26
New cards
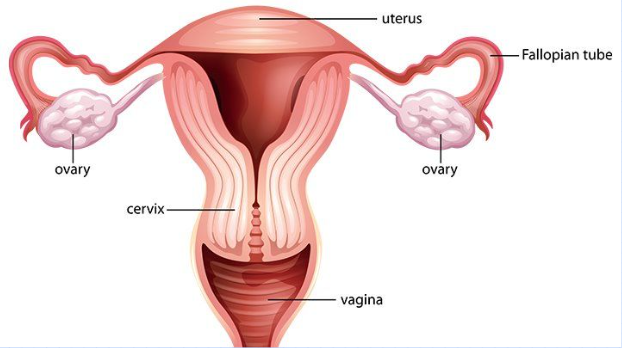
Female reproductive system
**Ovaries**
**Oviduct** (fallopian tube)
**Uterus**
**Cervix**
**Vagina**
**Oviduct** (fallopian tube)
**Uterus**
**Cervix**
**Vagina**
27
New cards
vas deferens
tubes that connect to urethra
28
New cards
**Ovaries**
the female gonad; produce egg cells (ova) and hormones estrogen and progesterone
29
New cards
**Oviduct**
a tube that carries the egg cell (ovum) to the uterus;
******site of fertilization of the egg cell**
* Cilia draws ovulated egg cell into the oviduct
******site of fertilization of the egg cell**
* Cilia draws ovulated egg cell into the oviduct
30
New cards
**Uterus**
a thick, muscular, pear shaped organ (aka womb)
* A baby develops here
* A baby develops here
31
New cards
**Cervix**
narrow neck that is the opening to the uterus
32
New cards
**Vagina**
the birth canal
33
New cards
Meiosis
the process by which **gametes** (egg and sperm) are formed \n Meiosis only occurs in the **gonads** (ovaries and testes)
34
New cards
In meiosis, the **chromosomes replicate once**, and the **cell divides twice…**
**Result = 4 new cells, each with ½ the number of chromosomes as the parent cell**
**The 4 cells are monoploid (aka haploid): have one set of chromosomes**
**The rest of the body cells are diploid: have the full number of chromosomes (2 sets)**
The chromosomes are genetically different from the chromosomes of the parent cell
**The 4 cells are monoploid (aka haploid): have one set of chromosomes**
**The rest of the body cells are diploid: have the full number of chromosomes (2 sets)**
The chromosomes are genetically different from the chromosomes of the parent cell
35
New cards
First Meiotic Division
Interphase I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
36
New cards
**Interphase I**
**chromosomes and centrioles replicate**
37
New cards
Prophase I
* chromosomes condense
* centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
* spindle fibers form, attach to centromeres of chromatids
* each pair of chromatids lines up with its __homologous pair__ = __**synapsis**__
* centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell
* spindle fibers form, attach to centromeres of chromatids
* each pair of chromatids lines up with its __homologous pair__ = __**synapsis**__
38
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
* chromosomes that are __**similar**__ in terms of size, shape and genetic content
* In each pair, one chromosome came from the mother (maternal); one chromosome came from the father (paternal)
* In each pair, one chromosome came from the mother (maternal); one chromosome came from the father (paternal)
39
New cards
Synapsis
pairing of homologous chromosomes
40
New cards
Crossing over
exchange of segments of chromosomes during synapsis;
results in recombination of the genes
results in recombination of the genes
41
New cards
Genetic Recombination
Genetic Recombination is the result of crossing over
**Because of crossing over, each gamete (egg or sperm cell) receives a unique set of genes from their parents**
**Because of crossing over, each gamete (egg or sperm cell) receives a unique set of genes from their parents**
42
New cards
Chiasmata
Points at which crossing over and exchange of genetic material occur between the chromosomal strands
43
New cards
Metaphase 1
tetrads line up in the middle of the cell
44
New cards
Anaphase 1
* homologous chromosomes separate
* \*\*\* This is called disjunction
* \*\*\* This is called disjunction
45
New cards
Telophase 1
* two daughter cells are formed;
* \*each has half the number of chromosomes, but they are still replicated
* \*each has half the number of chromosomes, but they are still replicated
46
New cards
Second Meiotic Division
* just like mitosis
* duplicated chromosomes separate - but they are actually recombined due to crossing over
* duplicated chromosomes separate - but they are actually recombined due to crossing over
47
New cards
Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
__**Mitosis -**__
1. Daughter cells are genetically identical to parent cells: same # and types of chromosomes
2. 2 diploid cells are formed
3. Occurs in growth & repair of body cells
4. Chromosomes replicate once; cell divides once
5. Homologous chromosomes do not pair; no recombination of genes
__**Meiosis -**__
1. Daughter cells are not genetically identical to parent cells: have ½ the number of chromosomes and they have different genetic combinations
2. 4 monoploid cells are formed
3. Forms gametes (egg & sperm cells) in the gonads
4. Chromosomes replicate once; cell divides once
5. Synapsis, crossing over and genetic recombination of genes
1. Daughter cells are genetically identical to parent cells: same # and types of chromosomes
2. 2 diploid cells are formed
3. Occurs in growth & repair of body cells
4. Chromosomes replicate once; cell divides once
5. Homologous chromosomes do not pair; no recombination of genes
__**Meiosis -**__
1. Daughter cells are not genetically identical to parent cells: have ½ the number of chromosomes and they have different genetic combinations
2. 4 monoploid cells are formed
3. Forms gametes (egg & sperm cells) in the gonads
4. Chromosomes replicate once; cell divides once
5. Synapsis, crossing over and genetic recombination of genes
48
New cards
Oogenesis
* the production of egg cells (ova) in the ovary of the female
* cytoplasm is divided unequally
* one of the daughter cells receives most of the cytoplasm – the small cells are called polar bodies
* the large egg cell formed contains yolk to nourish the developing embryo before the placenta forms
* the polar bodies disintegrate
* for each cell that undergoes meiotic division, there is only 1 ovum (egg cell) produced
* cytoplasm is divided unequally
* one of the daughter cells receives most of the cytoplasm – the small cells are called polar bodies
* the large egg cell formed contains yolk to nourish the developing embryo before the placenta forms
* the polar bodies disintegrate
* for each cell that undergoes meiotic division, there is only 1 ovum (egg cell) produced
49
New cards
Spermatogenesis
* The production of sperm in the testes
* The division of the cytoplasm is equal
* For each cell, there are 4 sperm produced
* The division of the cytoplasm is equal
* For each cell, there are 4 sperm produced