Cardiovascular System: Electrical Conduction of the Heart
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
It is responsible for the spark that initiates conraction of the heart
Electrical Conduction System
It is a measure of electrical activity in the Heart
Electrocardiogram
Part of electrical conduction of the heart located in the right atrium, considered as the start of of electrical conduction of the heart
SinoAtrial Node +
Main Pacemaker of the heart
SinoAtrial Node =
what part of the heart prevents the transmission of signals from right to left and vice versa
Septum
Both prevents electrical signals from transmitting directly from the right side of the heart to the left side and vice versa.
Interatrial Septum and Interventricular Septum
These specialized tract of cells are responsible for carrying signal from SA Node to Left Atrium to ensure they are contracting properly
Bachmann Bundle
These pathways are responsible for transmitting the signals from SA Node down to the atrioventricular node.
Internodal Pathways
Part of electrical conduction of the heart located in the right atrium near the coronary sinus and tricuspid valve
AtrioVentricular Node+
Its purpose is to delay the signal from SA Node briefly before sending it the Ventricles to give time to atria to ensure it contract properly and eject all the blood in it down to the ventricle, completely filling it subsequently before firing the ventricle
AtrioVentricular Node =
High speed transmission cells that come off the AV Node and branch of into 2
Bundle of His +
Partially travel into interatrial septum down into interventricular septum that serves as THE ONLY route for signal transmission between atria and ventricle
Bundle of His =
These cells are responsible for carrying the signal from Bundle of his to Right Ventricle
Right Bundle Branch
These cells are responsible for carrying the signal from Bundle of his to Left Ventricle
Left Bundle Branch
Due to sheer size of left bundle branch, its first branch has a fan like appearance to it that’s responsible for carrying signal to posterior and inferior portions of left ventricle
Left Posterior Fascicle +
It is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart that is the most difficult ot develop a block
Left Posterior Fascicle =
Due to sheer size of left bundle branch, this single stranded fiber that’s responsible for carrying signal to anterior and superior portions of left ventricle
Left Anterior Fascicle
These are coming off each branch of Bundle of His and the fascicles are the cells that connect w/ myocyte
Purkinje Fibers +
These are the ones that initialize depolarization of the myocardium
Purkinje Fibers =
This ability of each myocyte in the heart is what dictates the heart rate with our patient
Pacemaker ability +
This is the backup system of the heart if one node failed to transmit signal downward to contract the heart, so that the next node to it takes over to be the pacemaker
Pacemaker ability =
Pacemaker rate of the heart gets ____ as we move lower throughout the conduction of the heart
slower
Pacemaker rate of SA Node
60 - 100 bpm
Pacemaker rate of AV Node
45 - 50 bpm
Pacemaker rate of Bundle of his and its branches (Right Bundle Branch, Left Bundle Branch)
40 - 45 bpm
Pacemaker rate of Purkinje Fibers
20 - 40 bpm
minerals like Na+, K+, Ca++, Mg++, Cl - play major role in electrophysiology of the heart, they are called ____
eletcrolytes
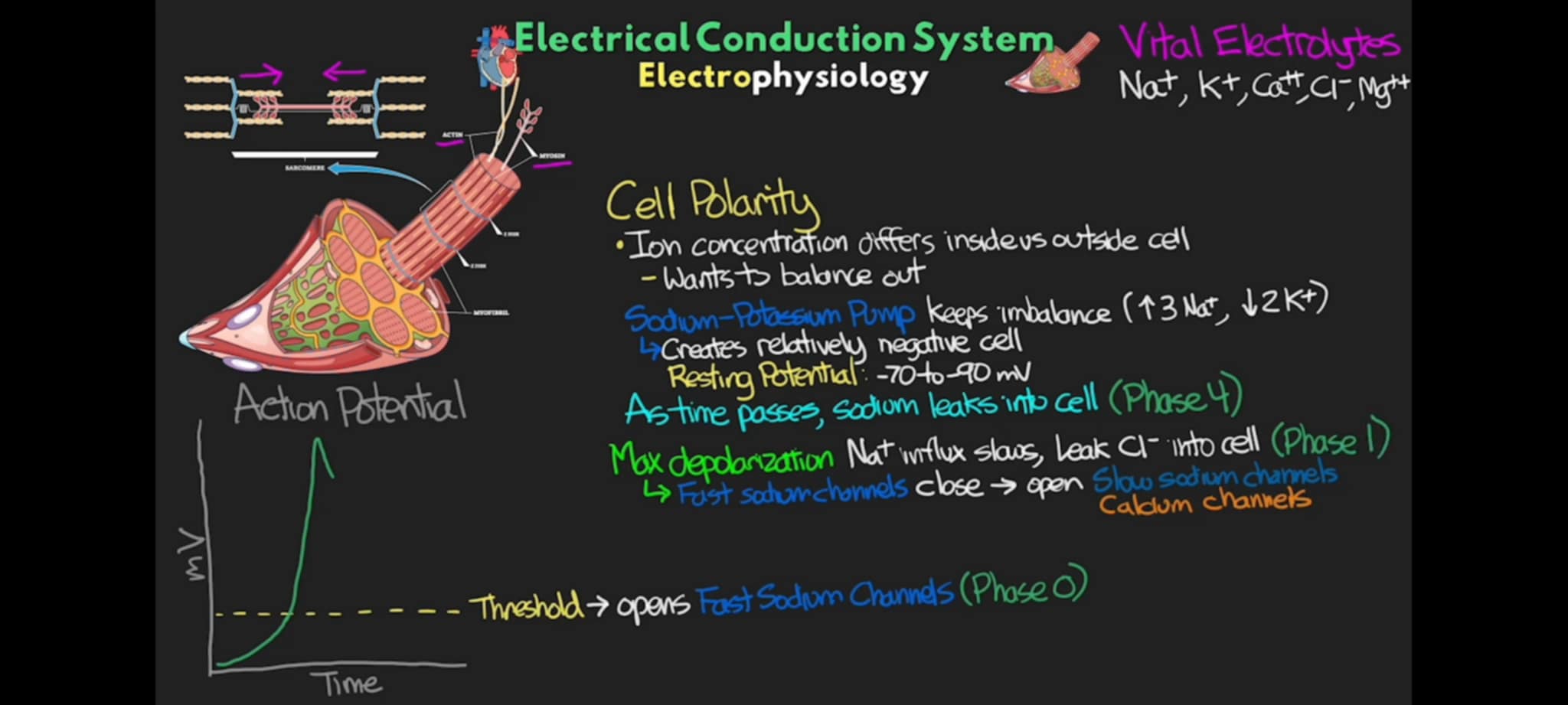
Ion concentration differs inside vs outside of cells that wants to balance out, it is called
Cell Polarity
What mechanism makes the cell polarity possible inside the cells?
Sodium - Potassium Pump
It Pumps out 3 Na+ ions and brings back 2 K+ ions with help of ATP, making the inside of the cell less positive and more negative due to slightly less positive charge of the K than Na.
Na - K Pump +
It creates a relatively negative charge inside the cell compared to the more positive external environment of the cell
Na - K Pump =
Resting Potential of Cardiac Cells
-70 mV to -90 mV

what phase of action potential occurs when there is slow rise of polarity from its resting potential to a certain threshold, once the threshold is achieved, a specialized set of Fast Na+ Channel open up, causing influx of excitatory Na+ ions to flow and make the cell match the positive external environment. This is the sharp rise of polarity to the max at the beginning
Phase 0
what does it mean when the environment inside the cell matches the positive outside environment of the cell?
Depolarization
what phase of action potential occurs when the cell reaches its peak charge the Na+ influx is slowed down and start to have a leak of Cl - ions and the presence of Cl - closes this Na+ channels and opens up channel for Slow Na+ Channel, and Ca++ Channel. This is the slight dip in the chart after the sharp rise due to large influx of Na+.
Phase 1
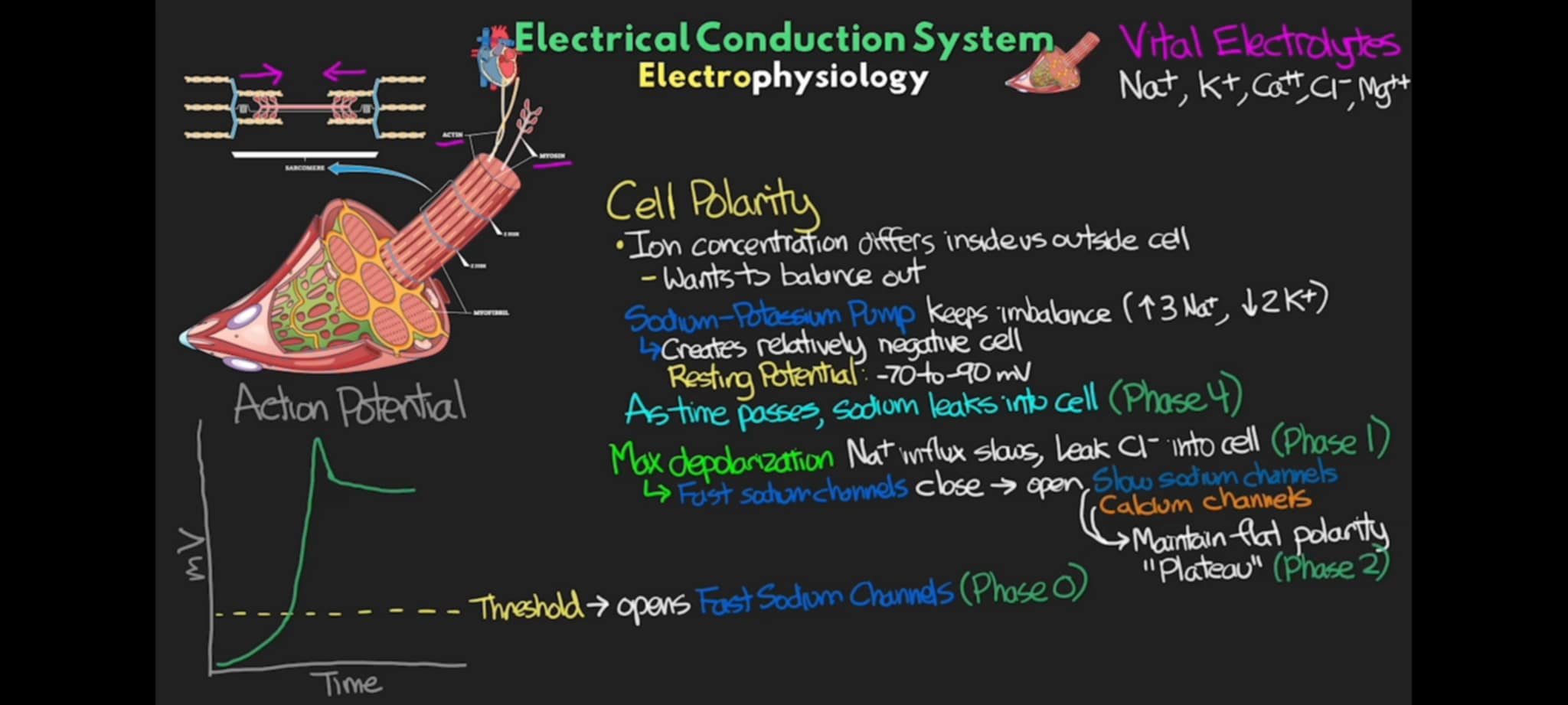
what phase of action potential occurs when the cell slowly lets in Na+ and lets in Ca++ that maintain a flat polarity
Phase 2 (Plateau Phase)
This mineral plays a vital role for the myosin and actin to bind, hence they contract.
Calcium
what phase of action potential occurs when there is now a physical contraction due to influx of Ca++
Phase 2
T or F: the more Ca++ we have inside the cell, the stronger and longer the contraction is
T
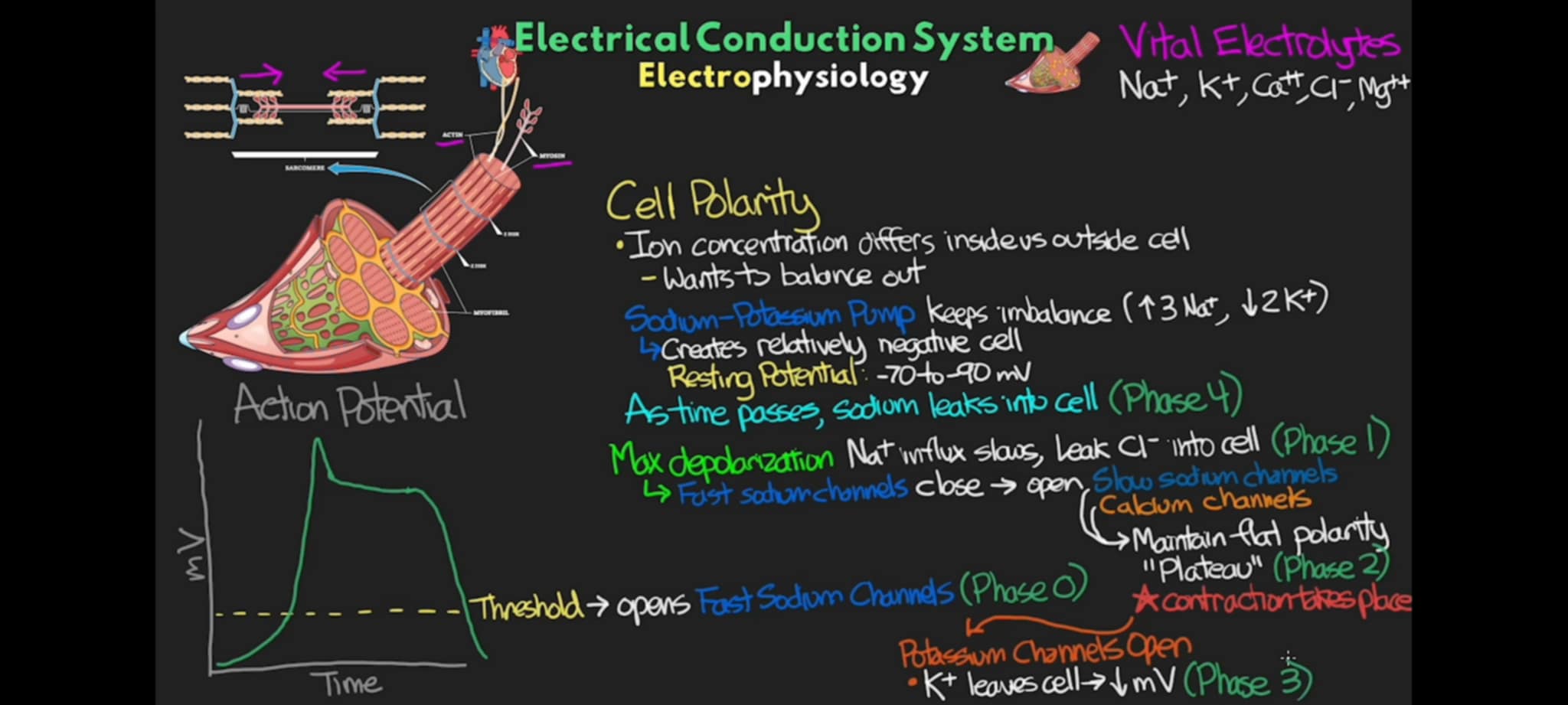
what phase of action potential occurs when there is now an open K channels that allow K to leave the cell, resulting in quick drop on polarity (mV) of the cell, making the cell more negative inside.
Phase 3 +
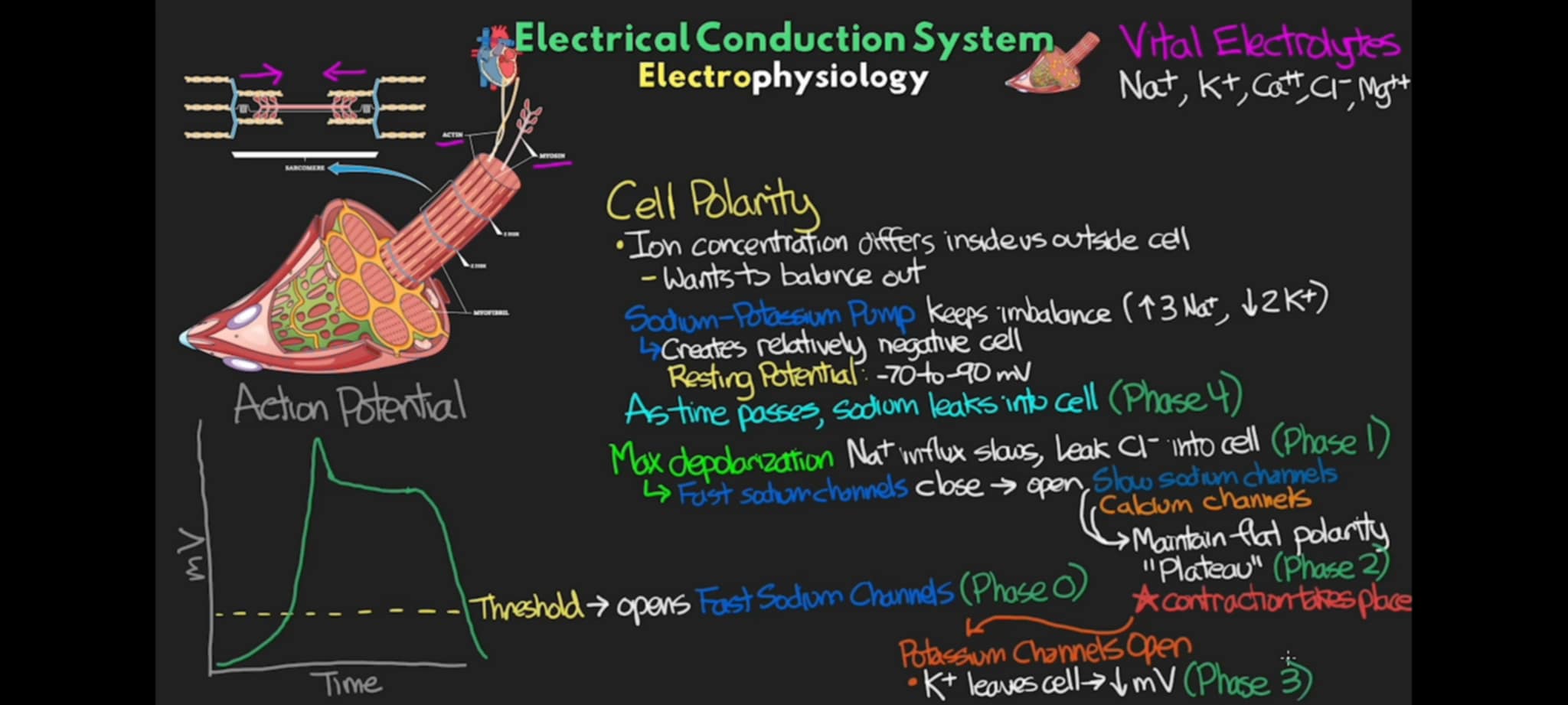
What does it mean when the cells got back to its resting potential or even beyond its resting potential, it does this so that it doesn’t overdrive and fry itself or not continually use itself at a fast pace that accelerates its wear and tear. Its a regulating mechanism inside our cells to preserve itself for its longevity
Repolarization
what phase of action potential of the cell where repolarization occurs and the cell is back to its resting potential of -70 mV to -90 mV where all the ion channels have been closed
Phase 3 =
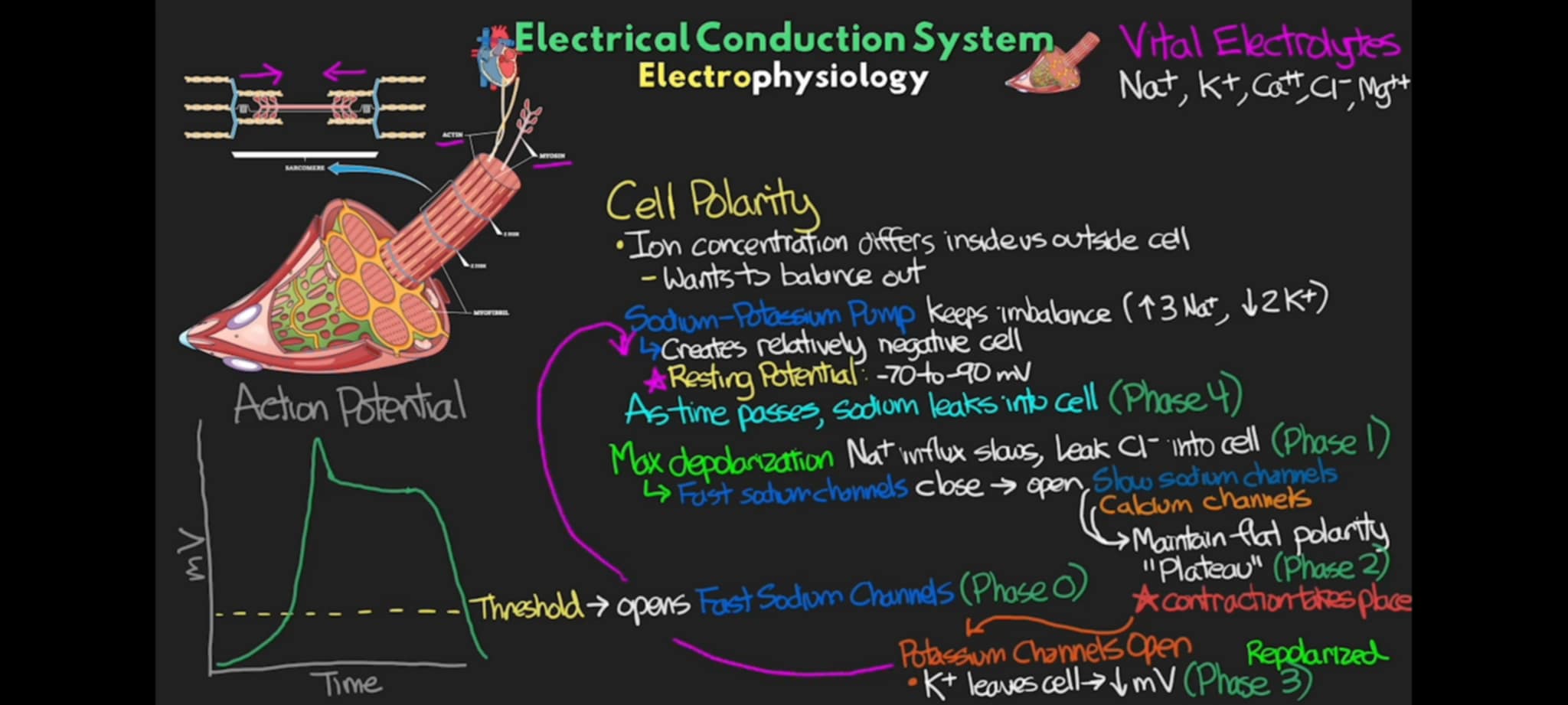
what phase of action potential of the cell where Na+ leaks into cell as time passes and breaks the threshold wherein it becomes the catalyst for fast Na+ ion channel to open, causing rapid influx of excitatory Na+ ions to flow inside the cell and make it more positive in phase 0
phase 4
Where does the fastest phase 4 happens in the electrical conduction system of the heart?
SINOATRIAL NODE
T or F: Phase 4 tends to get slower as we get distal to SA NODE that leads to slower heartbeat
T