Basic call structure and measurements
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the three phases of an echolocation call when a bat is foraging?
1) Search Phase (longer calls with narrow bandwidth)
2) Approach Phase (increased bandwidth, duration may decrease)
3) Terminal Phase / Feeding Buzz (very high bandwidth and repetition rate, durations decreases)
What effect does the Doppler Shift have on echolocation?
As the source of sound travels towards the listener, frequency increases. A bat flying directly towards the detector may have slightly (+0.55kHz) increased frequency
Define Harmonics
Multiples of the same call in multiples of the original (fundamental or 1st harmonic) frequency
Define Type A, B, C, and D Social Calls
Type A: Aggression
Type B: Distress
Type C: Co-ordination
Type D: Advertisement/agonistic
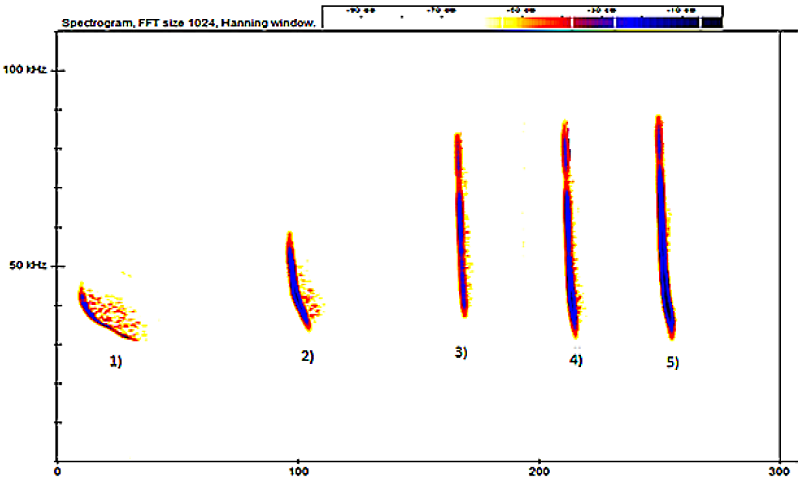
What does a Spectrogram show?
Frequency over time with intensity represented by colour
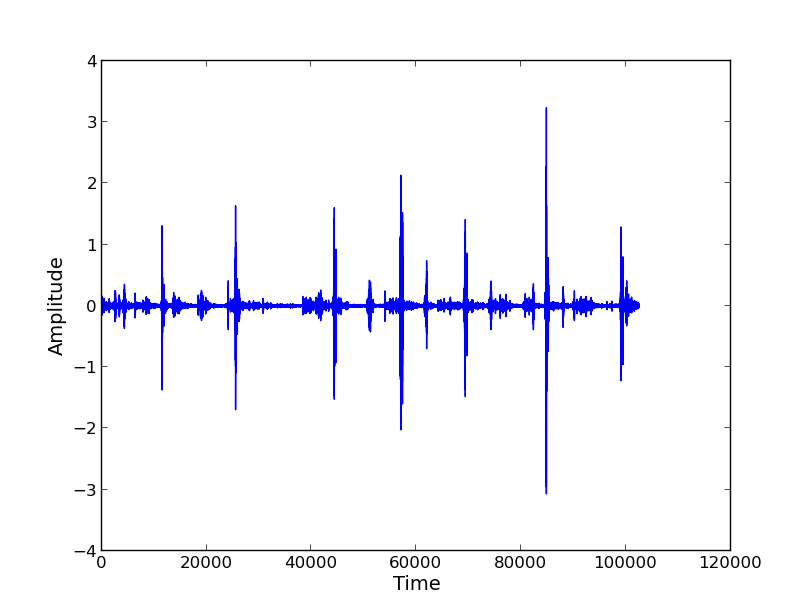
What does an Oscillogram show?
Amplitude over time - useful for trying to find where the call occurs during a sequence
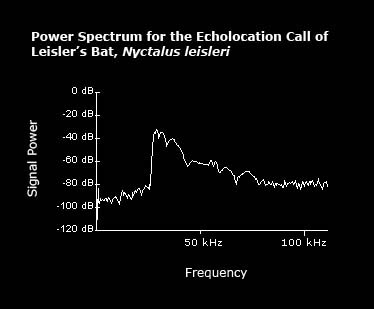
What does a Power Spectrum show?
Amplitude over frequency - useful for identifying the Frequency of Maximum Energy (FMaxE) or ‘peak’ frequency
Define Inter-pulse Interval (IPI)
The time between repeated calls
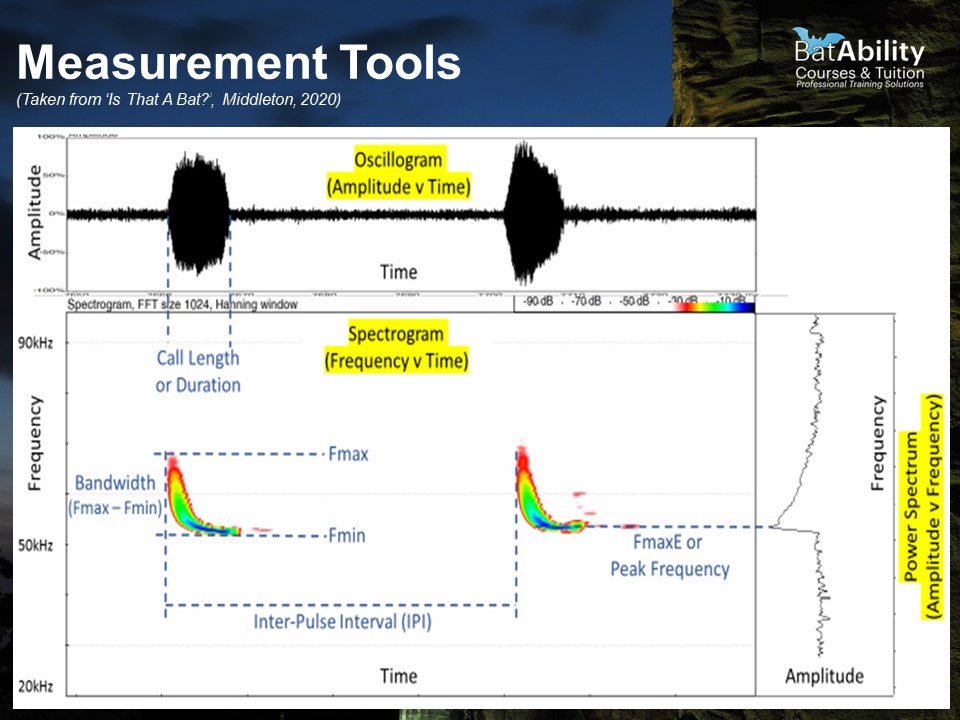
Define call duration (‘Dur’)
The duration of the call, in milliseconds
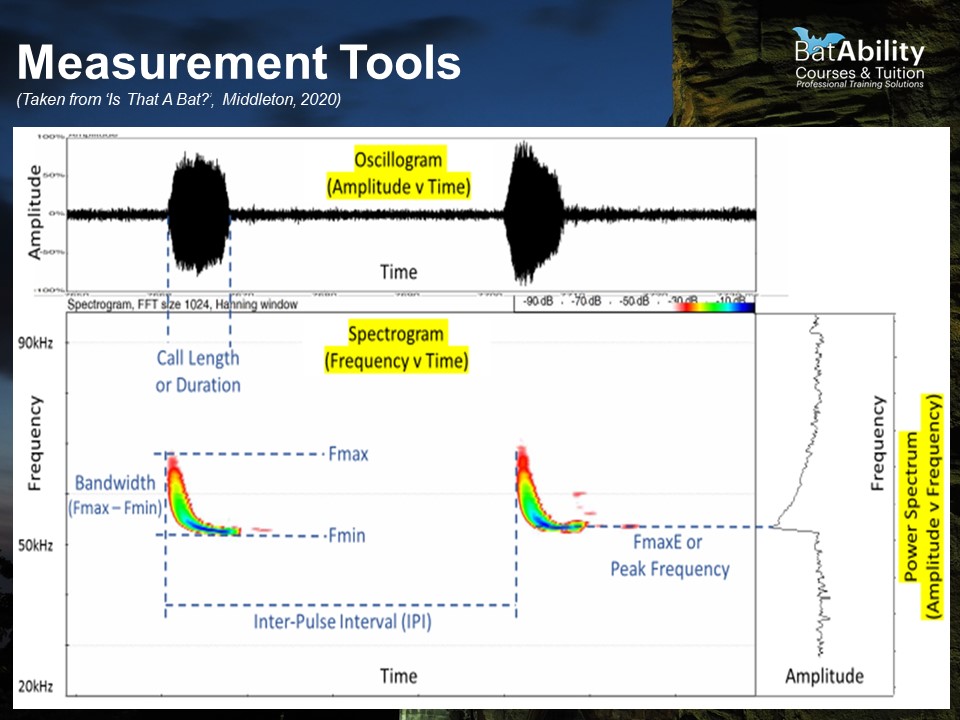
Define the Maximum Frequency (FMax)
The maximum frequency achieve at any point during the call, i.e. the top of the call shape
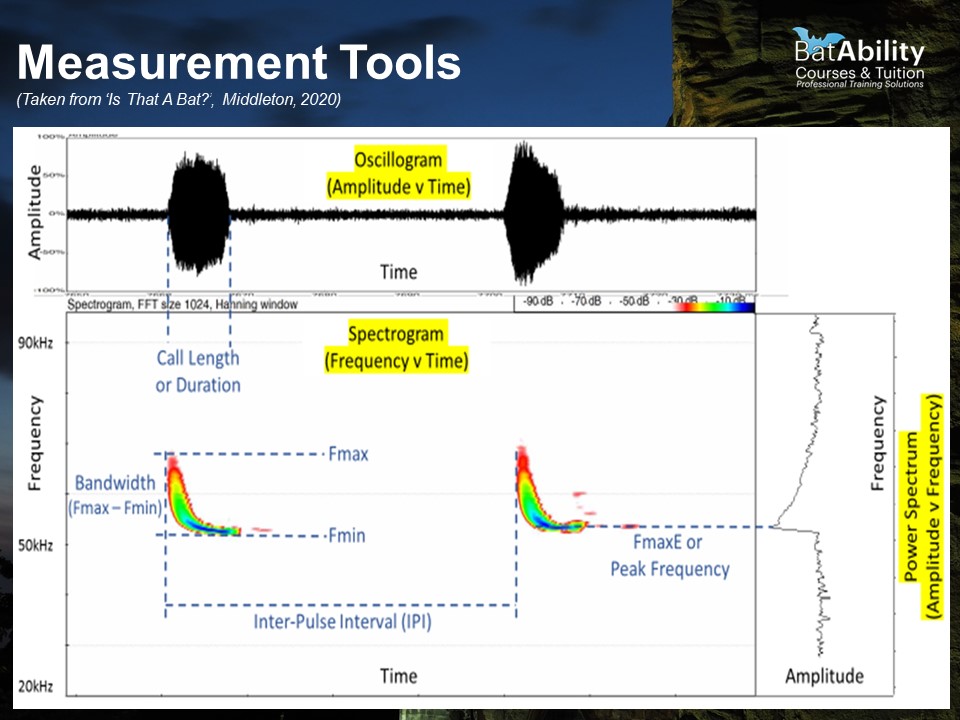
Define the minimum frequency (FMin)
The lowest frequency achieved during the call
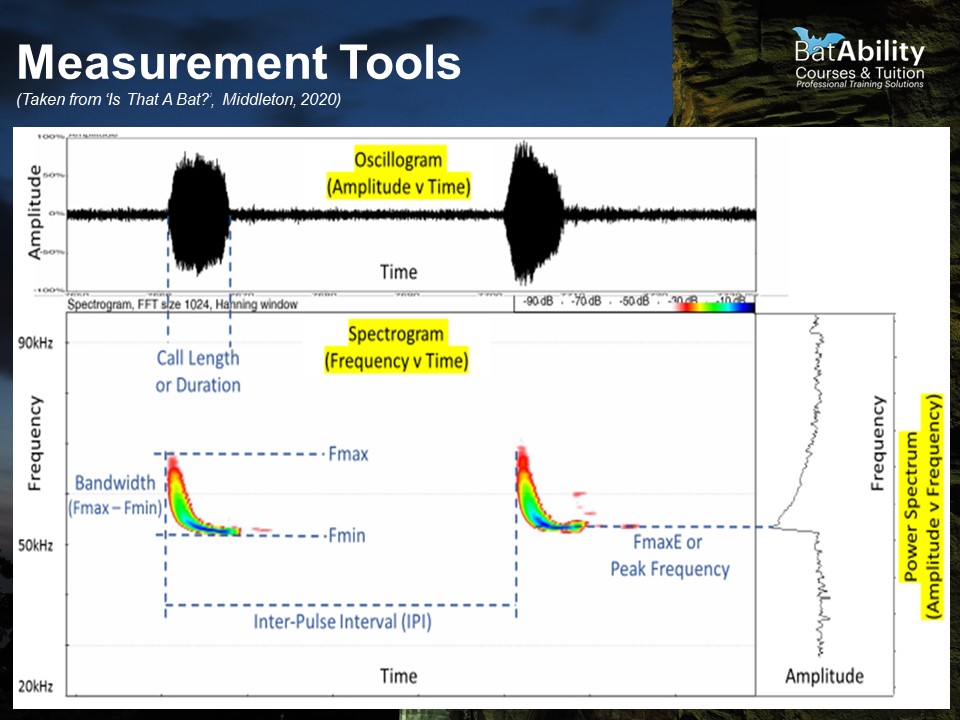
Define call bandwidth
The range between the Fmin and Fmax, i.e. the distance the call extends in frequencies. For Myotis spp., calls are very long in bandwidth
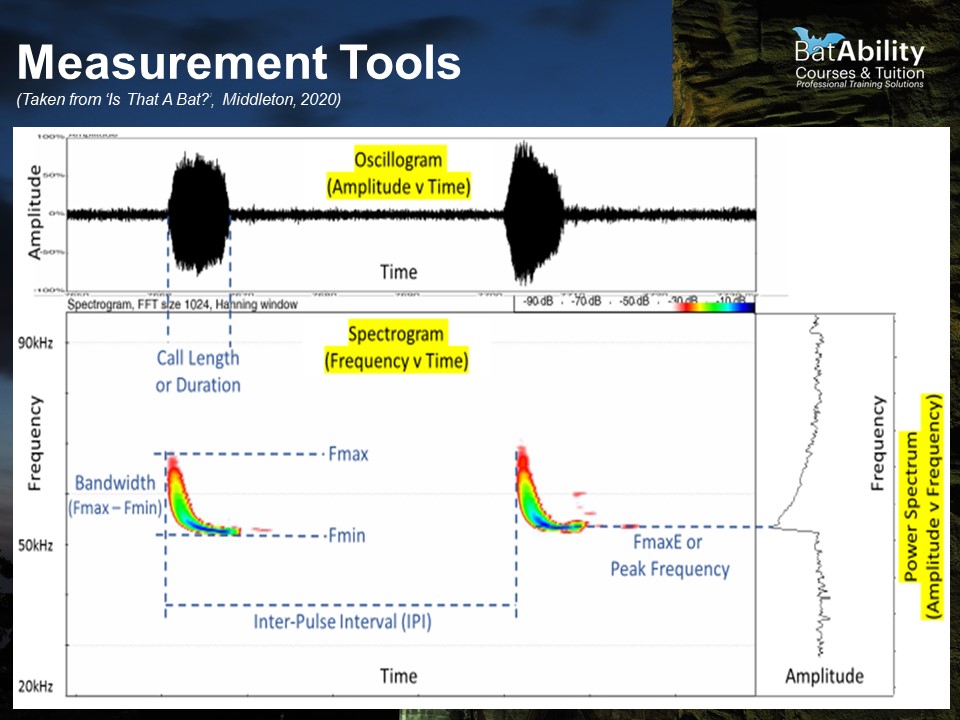
Define Frequency of Maximum Energy (FMaxE)
The point of highest amplitude, i.e. the frequency at which the bat exerts the most energy into the call and produces the loudest sound
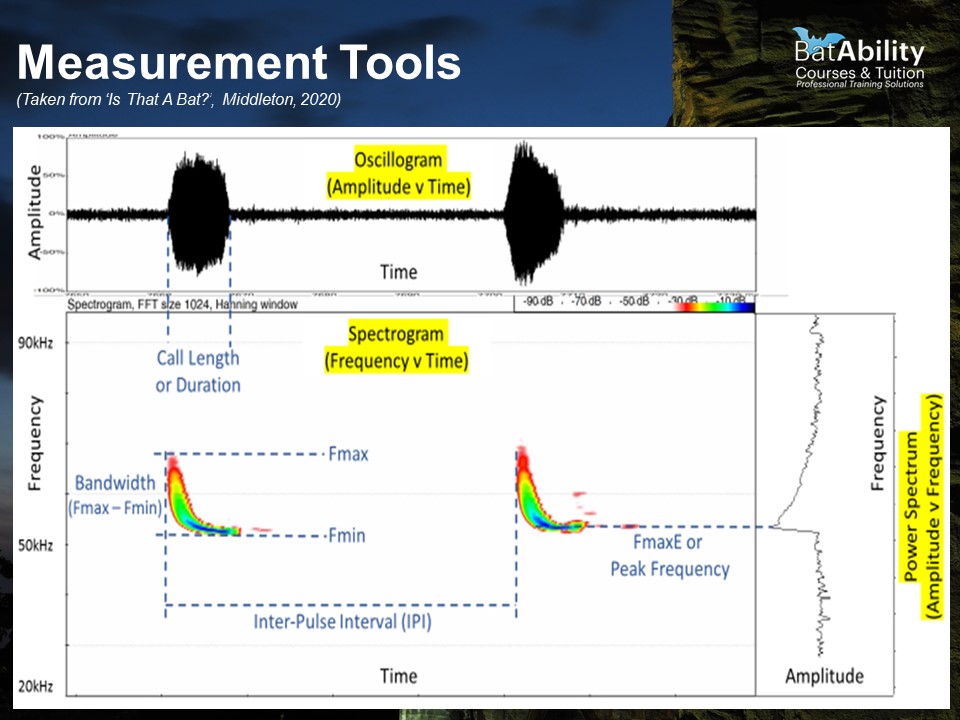
How to measure IPI
Select the a point at the start of the first call in a sequence, then select the start of the final call in the sequence.
Measure the distance (ms) between the two points, then divide this by the number of gaps between calls.
OR
Simply measure the time from the start of one call to the start of the next
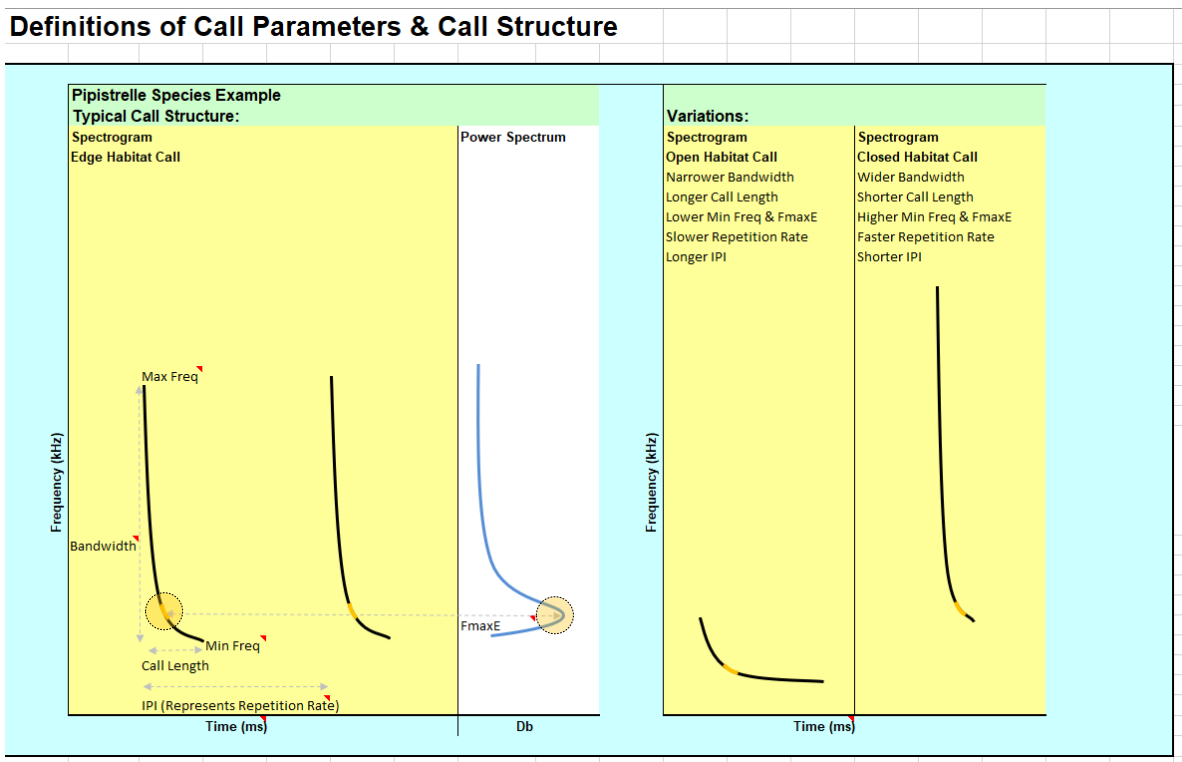
How does call structure vary according to the habitat type?
In open habitats, calls will be longer duration and shorter bandwidth to aid navigation.
In edge habitats, duration may decrease and bandwidth increased to gain more detail.
In cluttered habitats, calls are shortest and have the highest bandwidth as the bat increases repetition rate while avoiding obstacles.
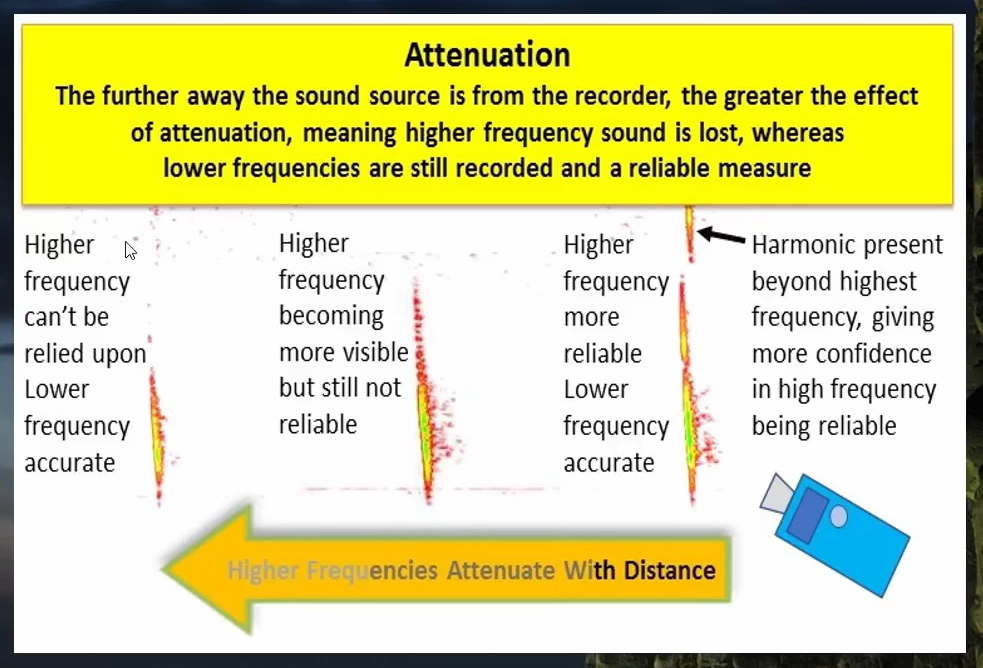
Define attenuation
The tendency for quieter or distant calls to be lost at higher frequency
Define clipping
Very loud calls may cause the power spectrum to fail to record correctly and display a single band instead of a call

Define comb filtering
When calls appear to be separated due to the sound reflecting off surfaces such as water
Define aliasing
Calls appear to be repeated but upside down, occurs due to high amplitude often alongside clipping