Control of Gene Expression in Molecular Mechanisms of Disease
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Nucleus
Site where transcription occurs in eukaryotic cells.
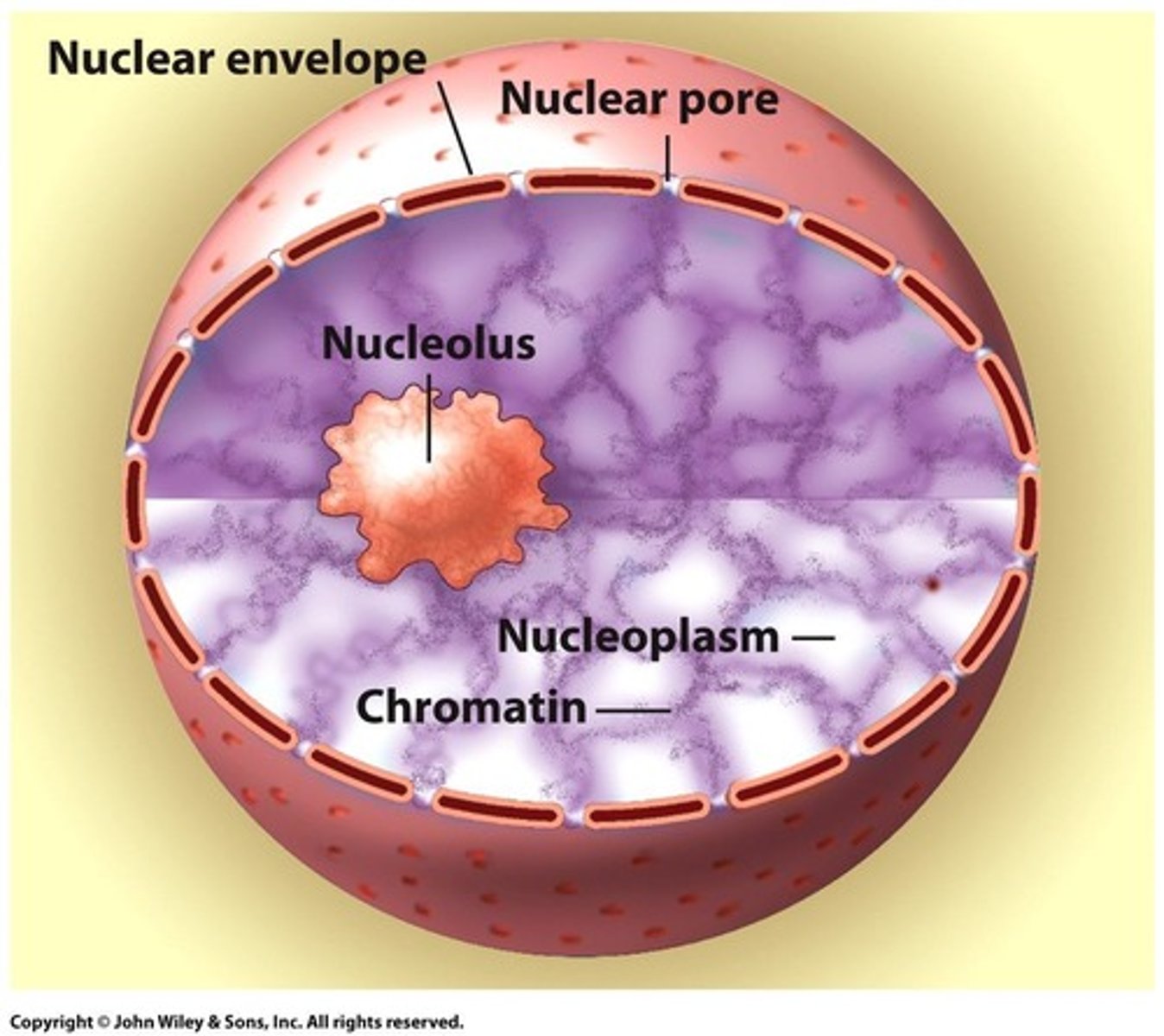
Chromatin
Tightly packed DNA and protein complex in the nucleus.
Nucleolus
Region in nucleus where ribosomal RNA is synthesized.
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane surrounding the nucleus, continuous with ER.
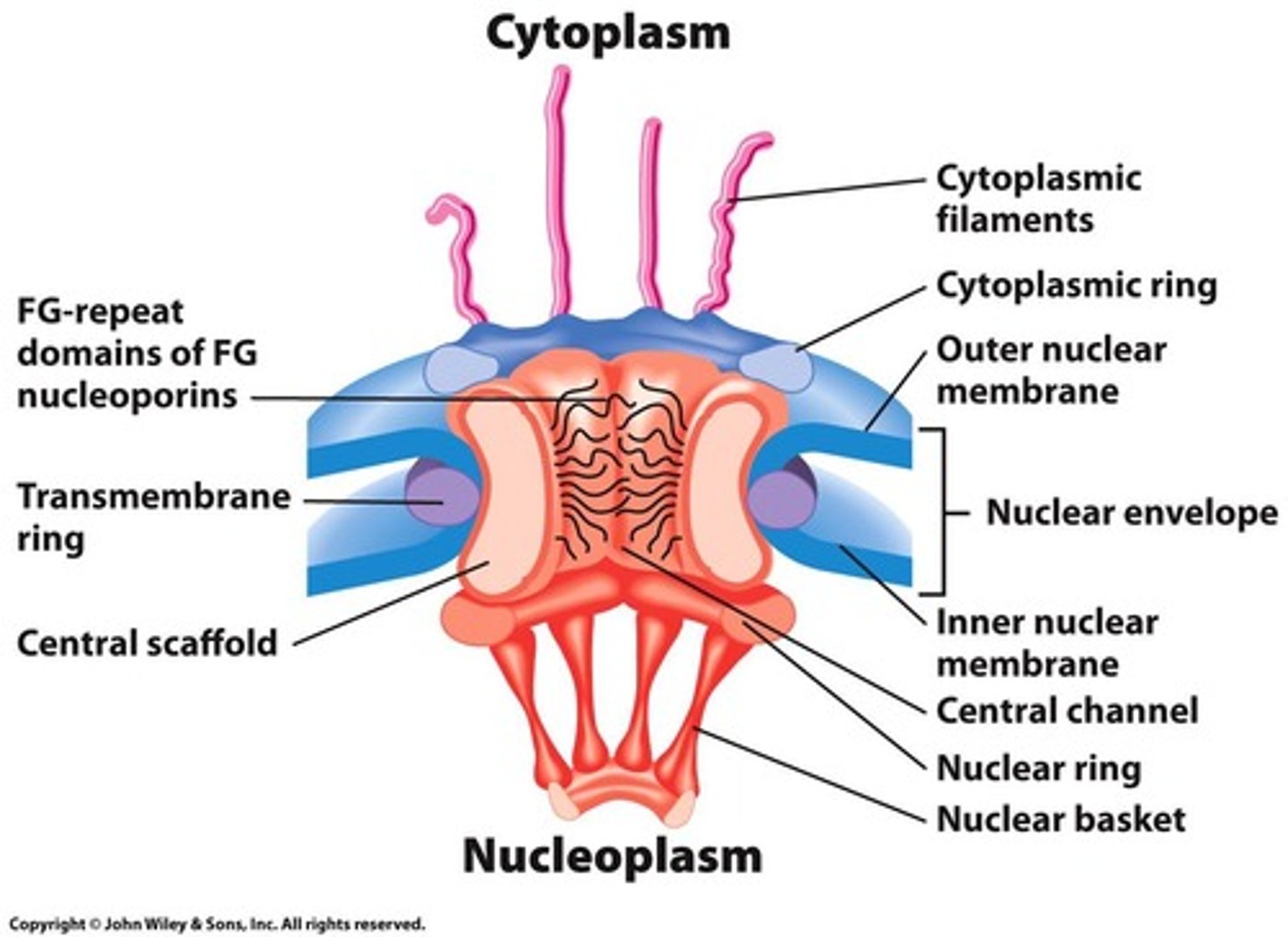
Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
Gateway for RNA and proteins across nuclear envelope.
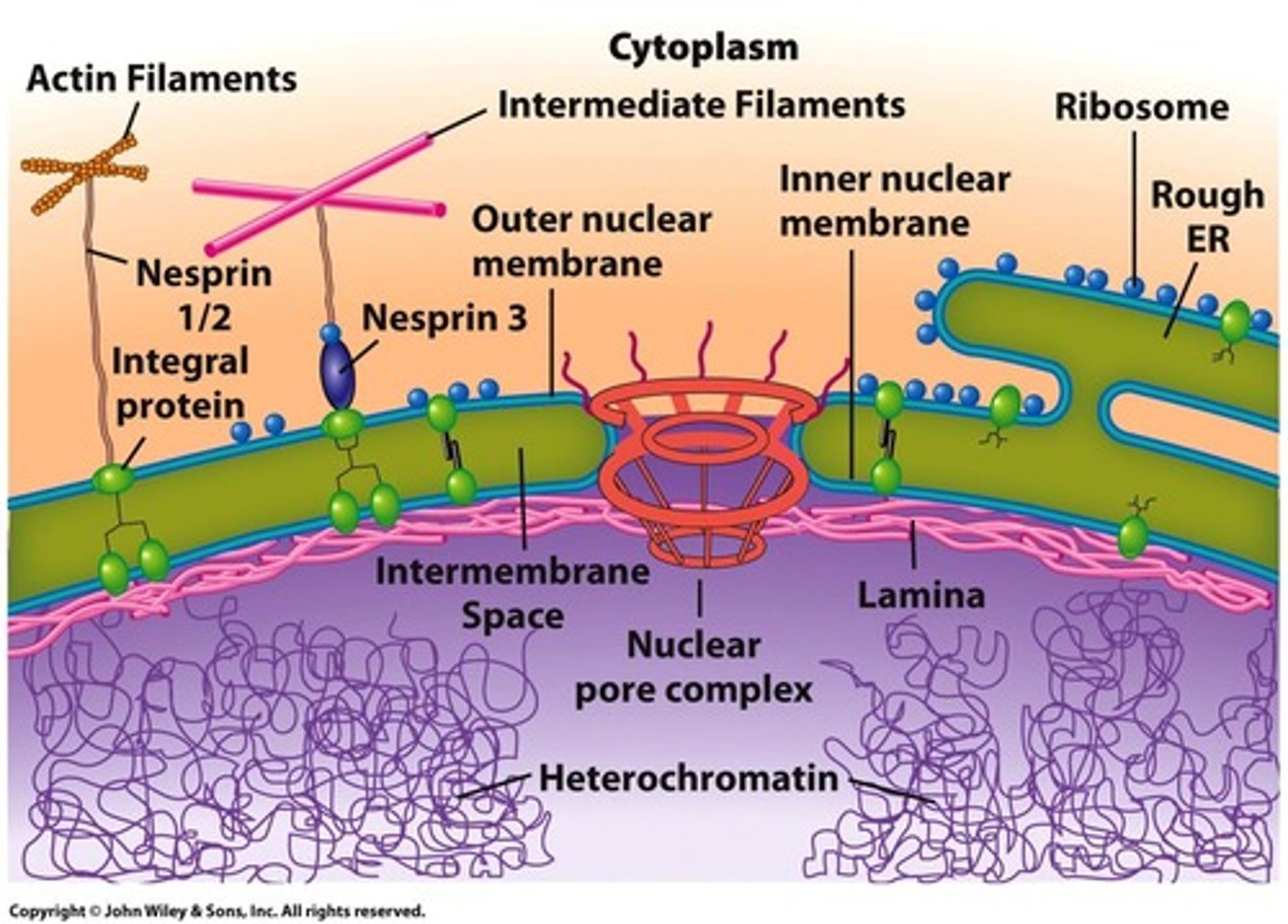
Nucleoporins
Proteins composing the nuclear pore complex.
Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS)
Amino acid sequence directing proteins into the nucleus.
Nuclear Export Signal (NES)
Sequence that facilitates protein export from the nucleus.
Importins
Receptors that transport proteins into the nucleus.
Exportins
Transport receptors that ferry proteins out of the nucleus.
mRNA Export
Transport of mature mRNA as ribonucleoproteins.
Transcriptional State
Expression level of genes in a cell type.
Transcription Factors (TF)
Proteins that regulate transcription of specific genes.
General Transcription Factors
Bind to core promoter sites, assist RNA Pol.
Activators
Transcription factors that stimulate gene transcription.
Repressors
Transcription factors that inhibit gene transcription.
DNA-binding Domain
Region of TF that interacts with specific DNA sequences.
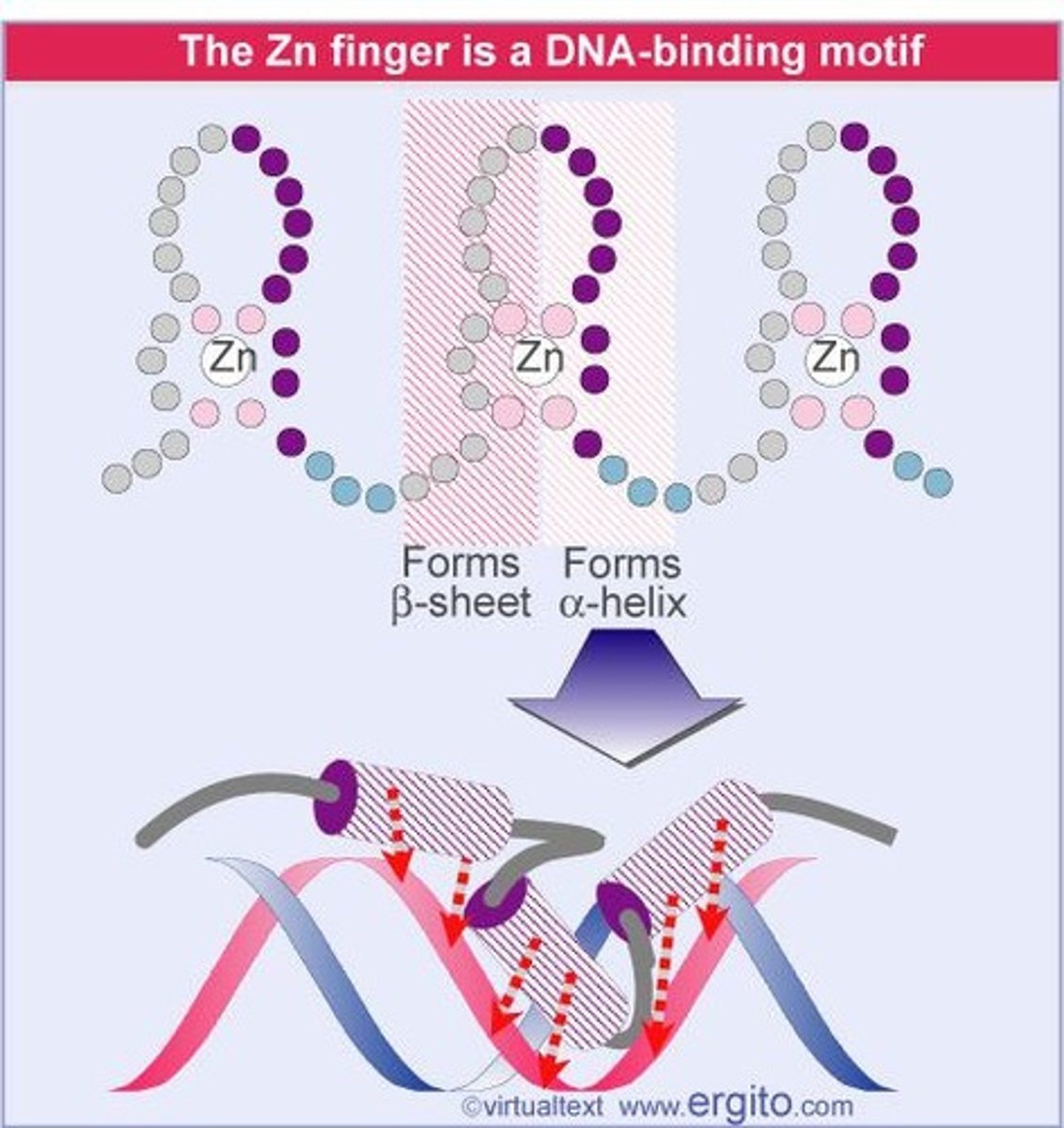
Zinc Fingers
DNA-binding motif using zinc ions for stability.
Helix-Loop-Helix (HLH)
Motif with two alpha helices separated by a loop.
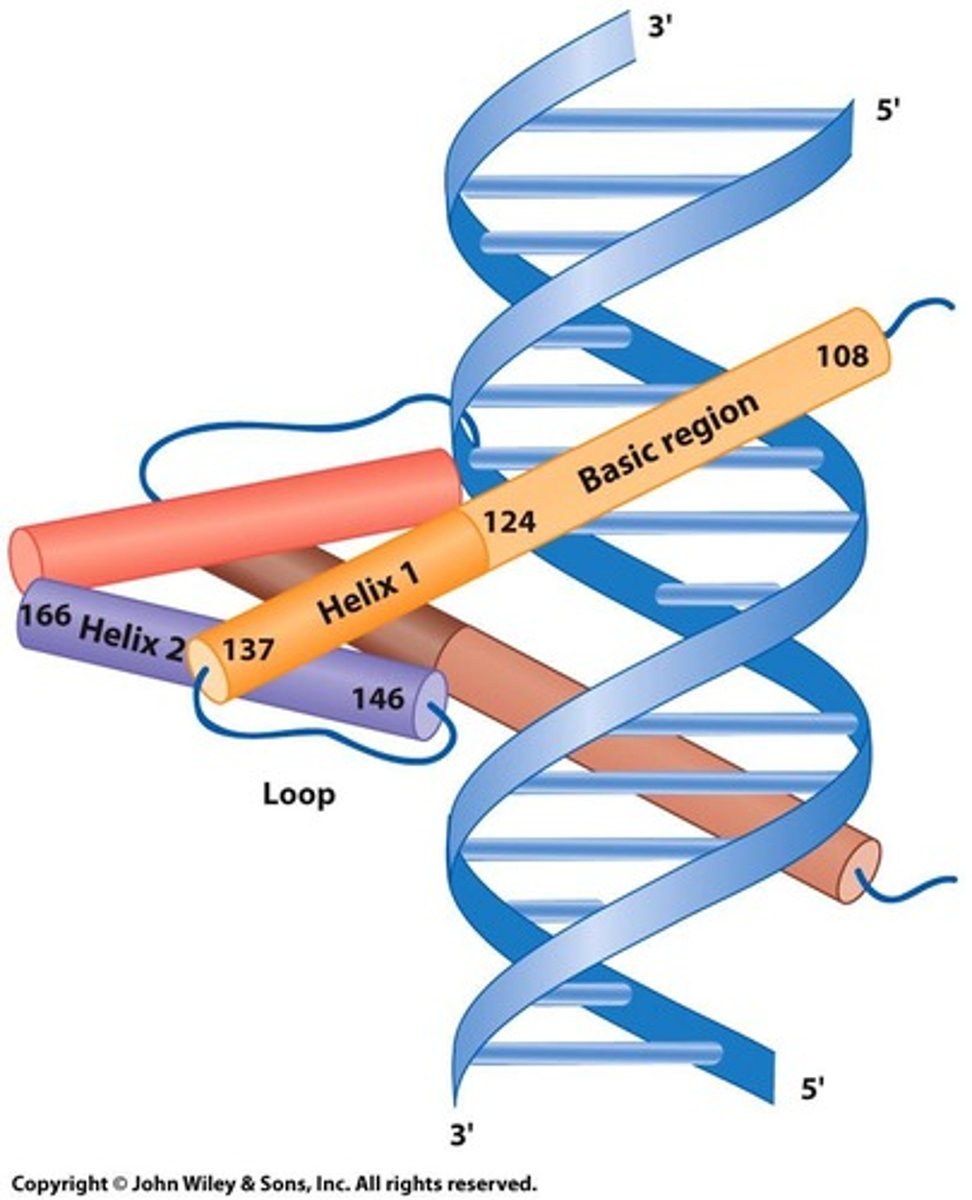
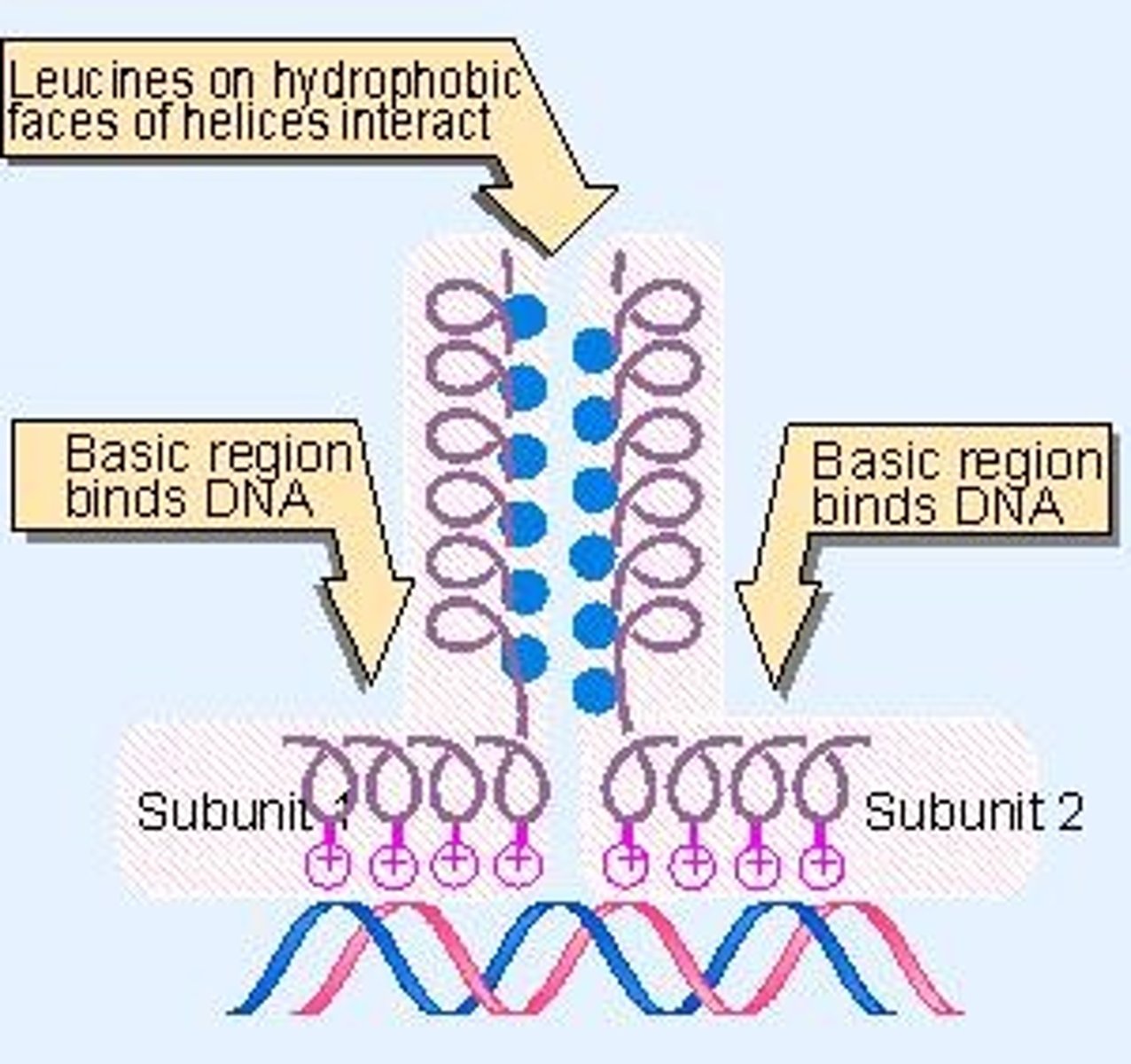
Leucine Zipper
Dimerization motif with leucine every seventh amino acid.
Response Elements
DNA sequences where transcription factors bind.
Proximal Promoter Elements
Regulatory sequences near the transcription start site.
Distal Promoter Elements
Regulatory sequences located far from the promoter.
Enhancer Sites
Regions that increase transcription from a distance.
Co-activators
Proteins that enhance gene expression without binding DNA.
Histone Acetyltransferases (HATs)
Enzymes that add acetyl groups to histones.
Chromatin Relaxation
Process that makes DNA more accessible for transcription.
Mediator Complex
Multi-subunit protein complex essential for transcription.
SWI/SNF Complex
Chromatin remodeling complex that increases transcription accessibility.
Acetyl Group
Reduces histone positive charge, enhancing DNA accessibility.
Chromatin Remodeling Complexes
Facilitate access to DNA for transcription machinery.
CBP
Coactivator that acetylates histones for transcription.
SWI/SNF
Coactivator that remodels chromatin structure.
mRNA Processing
Modifications required for mRNA to exit nucleus.
snRNPs
Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in splicing.
SR Proteins
Enhance splice site activation by binding ESEs.
hnRNP
Repress splice sites by binding to ESSs.
Exon/Intron Splicing Enhancers
Sequences that promote splicing activation.
Exon/Intron Splicing Silencers
Sequences that inhibit splicing activation.
Translation Initiation
First step in protein synthesis from mRNA.
mRNA Localization
Targeting mRNAs to specific cellular locations.
mRNA Stability
Determines how long mRNA persists in cytoplasm.
5' and 3' UTRs
Regulatory regions influencing mRNA translation.
eIF2
Initiation factor phosphorylated to inhibit translation.
Ferritin
Protein that sequesters iron in high levels.
Iron Regulatory Protein (IRP)
Regulates ferritin mRNA translation based on iron levels.
Poly(A) Tail
Length affects mRNA stability and degradation rate.
Deadenylase
Enzyme that shortens the poly(A) tail.
AU-rich Elements (AREs)
Sequences that destabilize mRNA and promote degradation.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
Regulate gene expression by targeting mRNA 3' UTR.
Small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
Inhibit gene expression by degrading specific mRNAs.
RNA Interference (RNAi)
Mechanism by which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression.
Proteasomes
Cellular complexes that degrade unneeded proteins.
Ubiquitin Ligases
Attach ubiquitin to proteins for degradation.
Polyubiquitination
Process of adding multiple ubiquitin molecules to proteins.
P-bodies
Cytoplasmic granules where mRNA degradation occurs.