3.18 Secondary Headaches/Ocular Neurology II
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
TBI's will be what type of brain hemorrhages ?
- epidural or subdural hematomas
Epidural hematoma definition
- blood between skull and dura mater - not as common
- convex shaped
Subdural hematomas - description
- blood under dura mater
- concave shaped
Epidural hematomas
- likely to report to OD?
- most often from ...
- no
- break in temporal bone & bleeding of middle meningeal artery
Epidural hematoma signs/symptoms
- compression of CN III
- ipsilateral ptosis, fixed/dilated pupil, down & out eye
- contralateral vision deficits
Subdural hematoma signs/symptoms
- midline anatomical shifts
- homonymous hemianopia (same side of VF impacted)
2 types of acquired brain injury
- subarachnoid hemorrhage/ruptured aneurysm
- intracerebral hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage/ruptured aneurysm headache
- pain severity ?
- quality
- can happen in what demographic ?
- sudden and severe
- worst headache of life
- young healthy adults
Posterior communicating artery (PComA) Aneurysm
- located near what CN?
- associations
- III
- nausea, vomiting, stiff neck, diplopia, photophobia, seizure, confusion, loss of consciousness, sudden death
Posterior communicating artery aneurysm
- visual symptoms are ...
- if pupil involvement with CN III palsy presents, what to do?
- if it involves CN III - leads to dilated, unresponsive pupil, ptosis, and eye position down and out
- medical emergency and requires immediate ER referral for potential life saving surgery
Intracranial hemorrhage = what?
stroke
Meningitis
- what is this?
- inflammation (swelling) of protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord
Meningitis
- demographics
- babies/young children, immune compromised
What does meningococcal vaccine protect against ?
just bacterial, not viral or other ones
Meningitis headache characteristics
associations
- throughout head, can radiate down back and other parts of body
- fever, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, photophobia, confusion

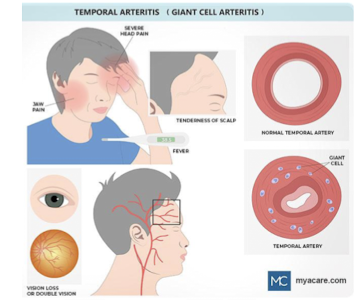
What is Giant Cell Arteritis?
Vasculitis of medium and large arteries in body,
especially around the scalp, temples, head, neck, upper body and arms (but can be anywhere)
Ocular Sx of GCA
Ophthalmic artery or tributaries can be affected
High risk for partial or complete vision loss
VF defects typically altitudinal or complete
Systemic Sx of GCA
Increased risk of stroke, other ischemia
High systemic morbidity and/or mortality risk
Constitutes a true ocular and systemic urgency
Tests for GCA
Eye tests: VA, pupils, EOMs, visual fields, dilated
fundus exam, OCT
Labs: erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Possible: ultrasound of temporal artery
Definitive test: biopsy of temporal artery
GCA management
Urgent testing- same day by PCP or send to ER
High dose IV or oral steroids
In 2017, FDA approved tx tocilizumab injection
for steroid failure cases
Systemic Hypertension Headache Features
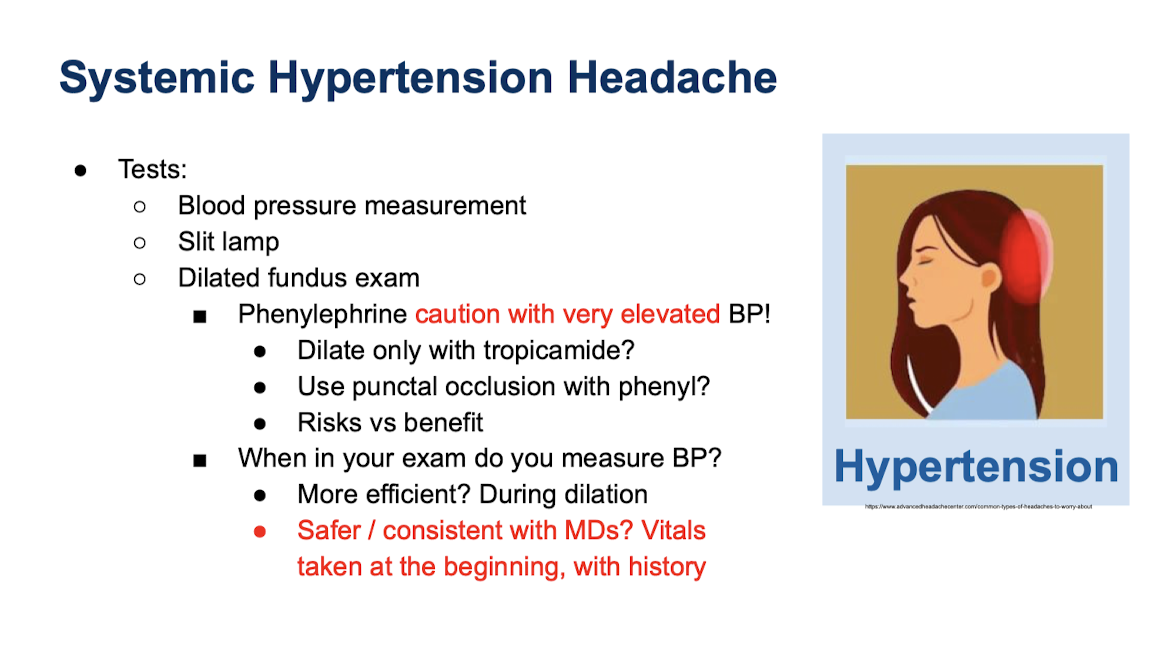
Tests for Systemic Hypertension
Papilledema definition
- term only used when optic nerve swelling is caused by raised intracranial pressure (ICP) usually bilateral
Papilledema
- most common demographic?
- women child bearing age
Papilledema
- symptoms
- HA
- nausea/vomiting
- shoulder/neck pain
- tinnitus
2 types of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION)
these both cause what?
- arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (AAION)
- non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)
optic nerve edema
AAION
- caused by ...
- what percent of cases?
- cause ?
GCA, temporal cell arteritis
10%
acute ischemia of posterior ciliary arteries or ophthalmic artery due to inflammation
AAION ocular findings
- sudden, painless loss of vision
- amaurosis fugax can happen before
- optic nerve edema
- CWS
- VF defects
- + RAPD in affected eye
AAION systemic findings (GCA)
- HAs, fatigue, fever, scalp tenderness, jaw pain, pain/stiffness in neck
Non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION)
- demographics?
- ocular findings
- 95% men
- painless altitudinal VF defect upon waking, 25% have central vision loss
- optic nerve edema obviously
- RAPD affected eye
NAION
- risk factors
- small, crowded nerve w/disc at risk (C/D <0.20)
- diabetes, HTN
how to rule out AAION ?
- ESR/CRP
Optic neuritis
-cause ?
- acute demyelinating or idiopathic optic neuropathy most often secondary to MS
optic neuritis symptoms ocular
- swollen nerve
- retrobulbar optic neuritis
- macular star shaped exudates
- pallor
- pain on eye movement
- unilateral vision loss
- reduced contrast
Optic neuritis treatment
- usually self resolving
- treat underlying MS
- IV steroids sometimes considered
Horner's Syndrome
- primary symptoms
- secondary symptoms
- ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis, anisocoria greater in dark
disrupts sympathetic pupil pathway
- conjunctival hyperemia
Myasthenia Gravis
- cause
- ocular signs
- antibodies inhibit ACh released from nerve endings leading to muscle weakness
- EOM weakness
- ptosis one or both eyes
- blurry or double vision
Myasthenia Gravis systemic signs
- difficulty swallowing
- impaired speech (dysarthria)
- shortness of breath
Myasthenia gravis extra tests to perform
- prolonged upgaze test
- ice pack test (measure palpebral aperture size before and after ice pack) - if more than 2 mm change it's positive
Sympathetic system problem with pupils and anisocoria
greater anisocoria in dark
Parasympathetic system problem with pupils and anisocoria
greater anisocoria in light
Exam techniques to distinguish small crowded optic nerve from early optic nerve edema (swelling)
- + SVP is good sign which disappears with disc swelling
- observe smallest arteries as they cross into disc
- OCT
- B scan