Honors Chemistry Unit 5: Period Table
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Coloumbic attraction
The force of attraction between positive and negative charges
Coulombic attraction will increase due to
an increase in protons
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
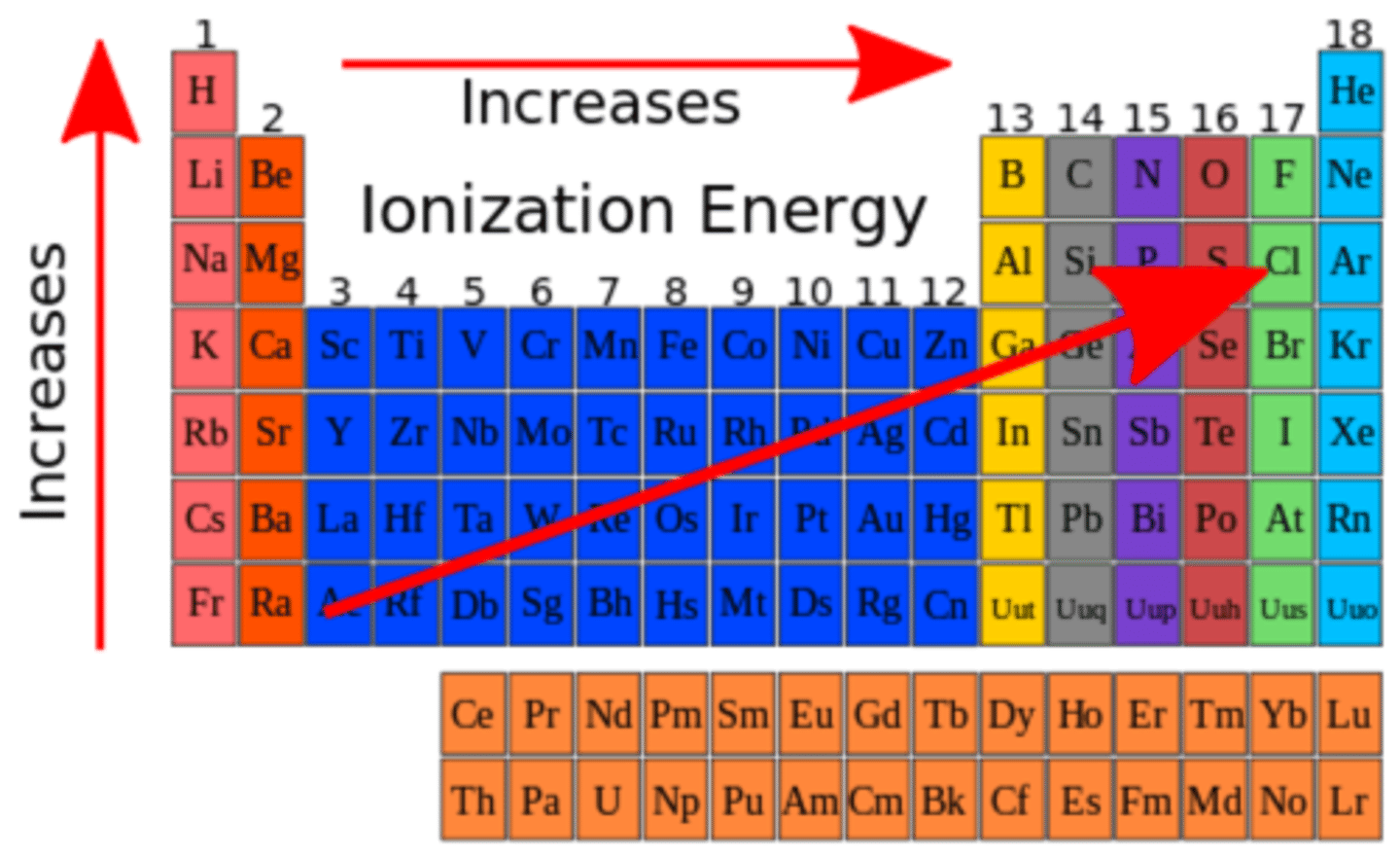
ionization energy increases as you move to the...
right on the periodic table
ionization energy decreases as you move...
down the periodic table
atomic radius
the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron
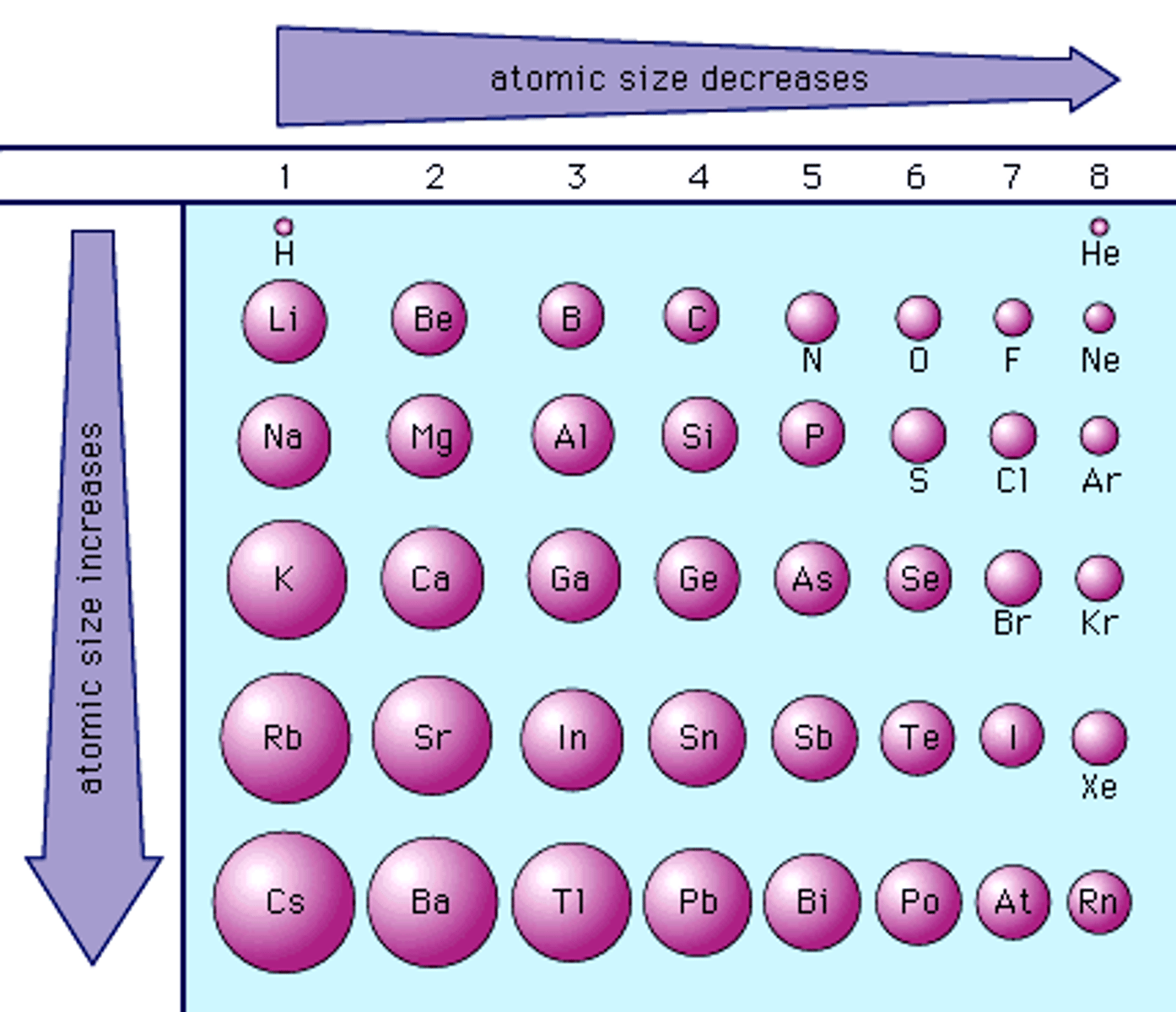
atomic radius increases as you move...
down the periodic table
Atomic Radius will decrease as you move left to right across a period due to...
decreases in energy levels
a larger atomic radius will have...
more energy levels
a smaller atomic radius will have...
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract a shared electron toward itself
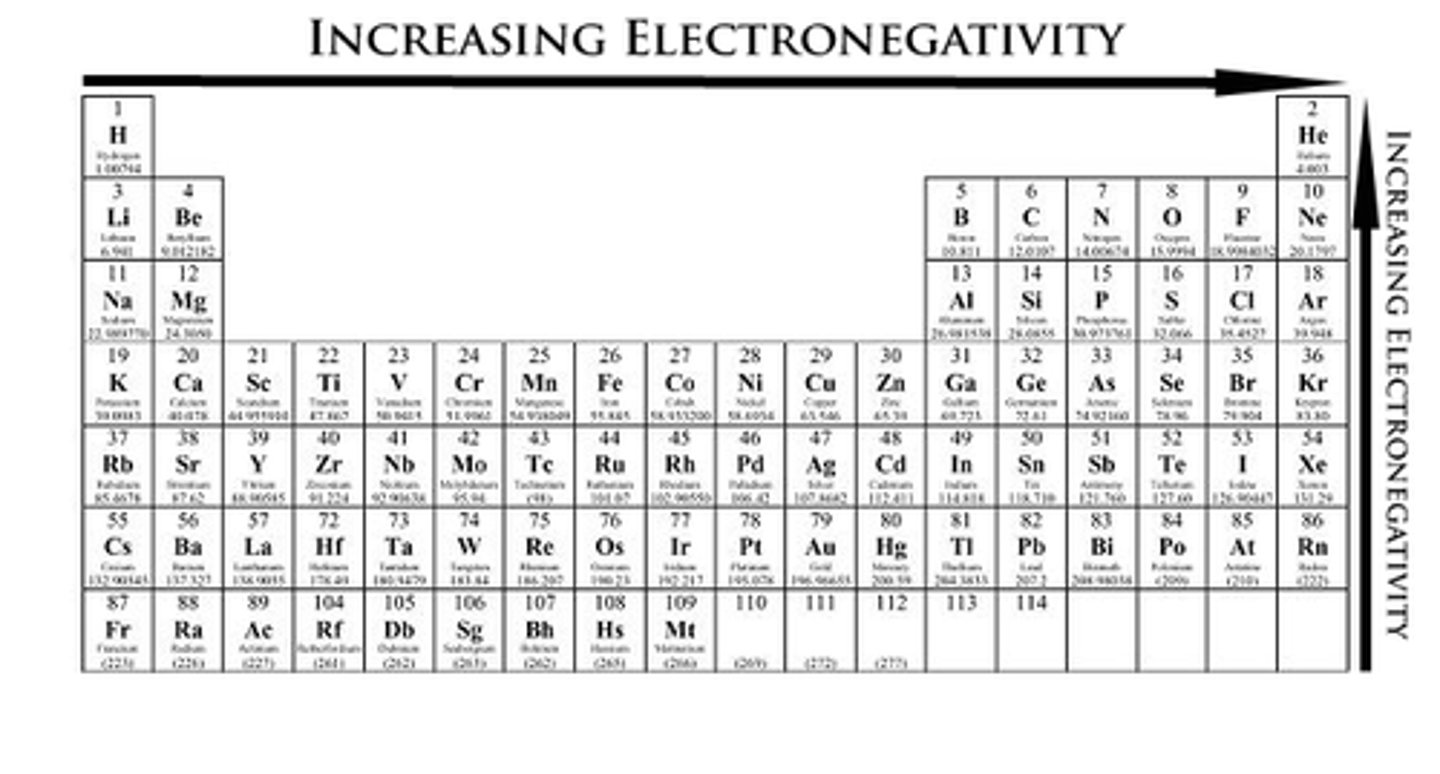
electronegativity increases as you move to the...
right of the period table
electronegativity decreases as you move...
down the period table
photoelectric effect
refers to the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
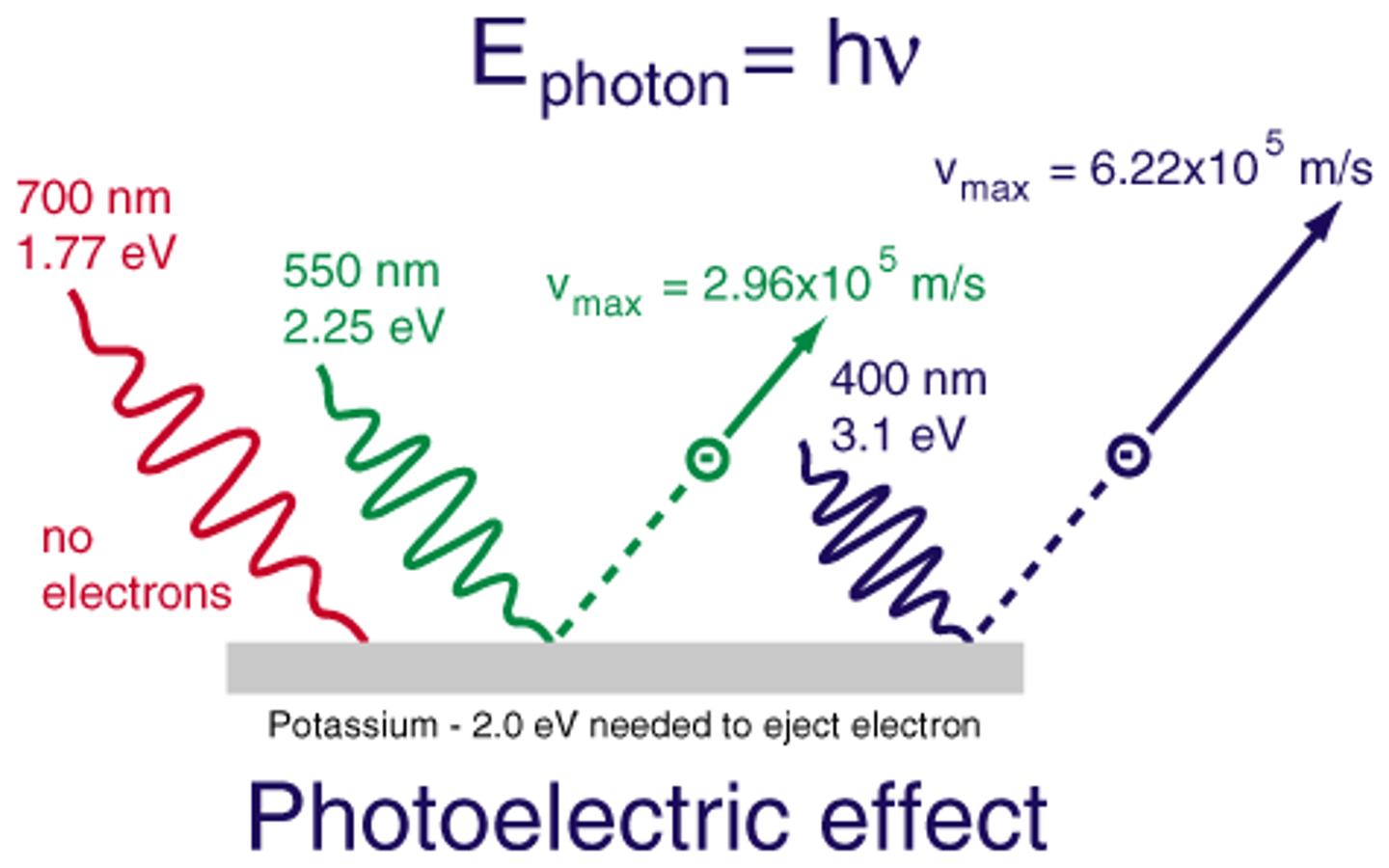
photoelectric effect major findings
high light energy photons can be absorbed by electrons and cause them to be removed from an atoms
Which electrons will be ripped off the atom 1st?
electrons farthest from the nucleus (least binding energy)
Which electrons were traveling the slowest speed at the end and why?
Electrons that are closest to the nucleus, energy from the photon was used to overcome the binding energy of those electrons and only a little is left over to be converted to Kinetic energy.
Why do groups of elements act similar?
they have the same amount of valence electrons
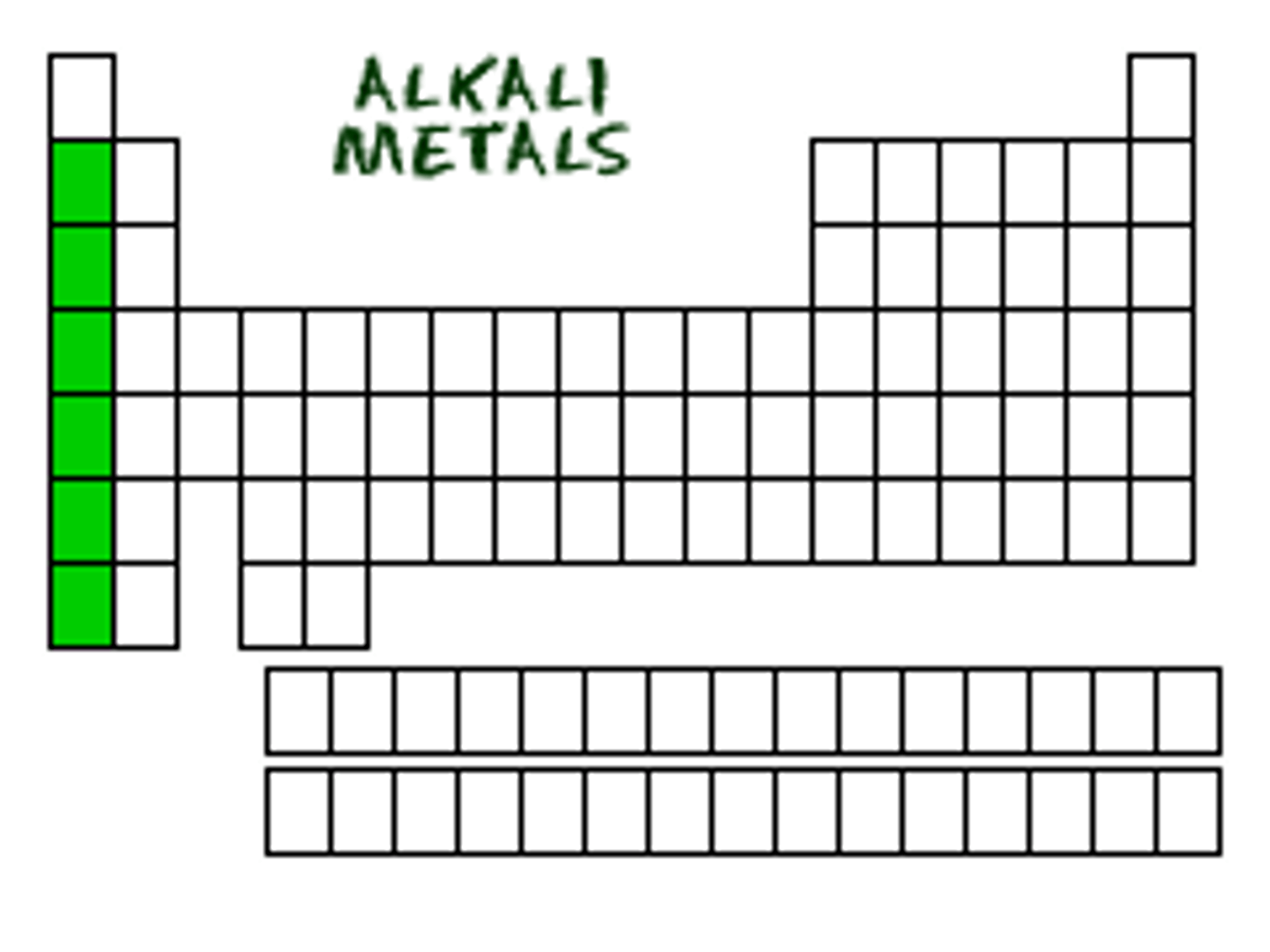
akali metals
group 1, one valence electrons, reacts violently with water, highly reactive
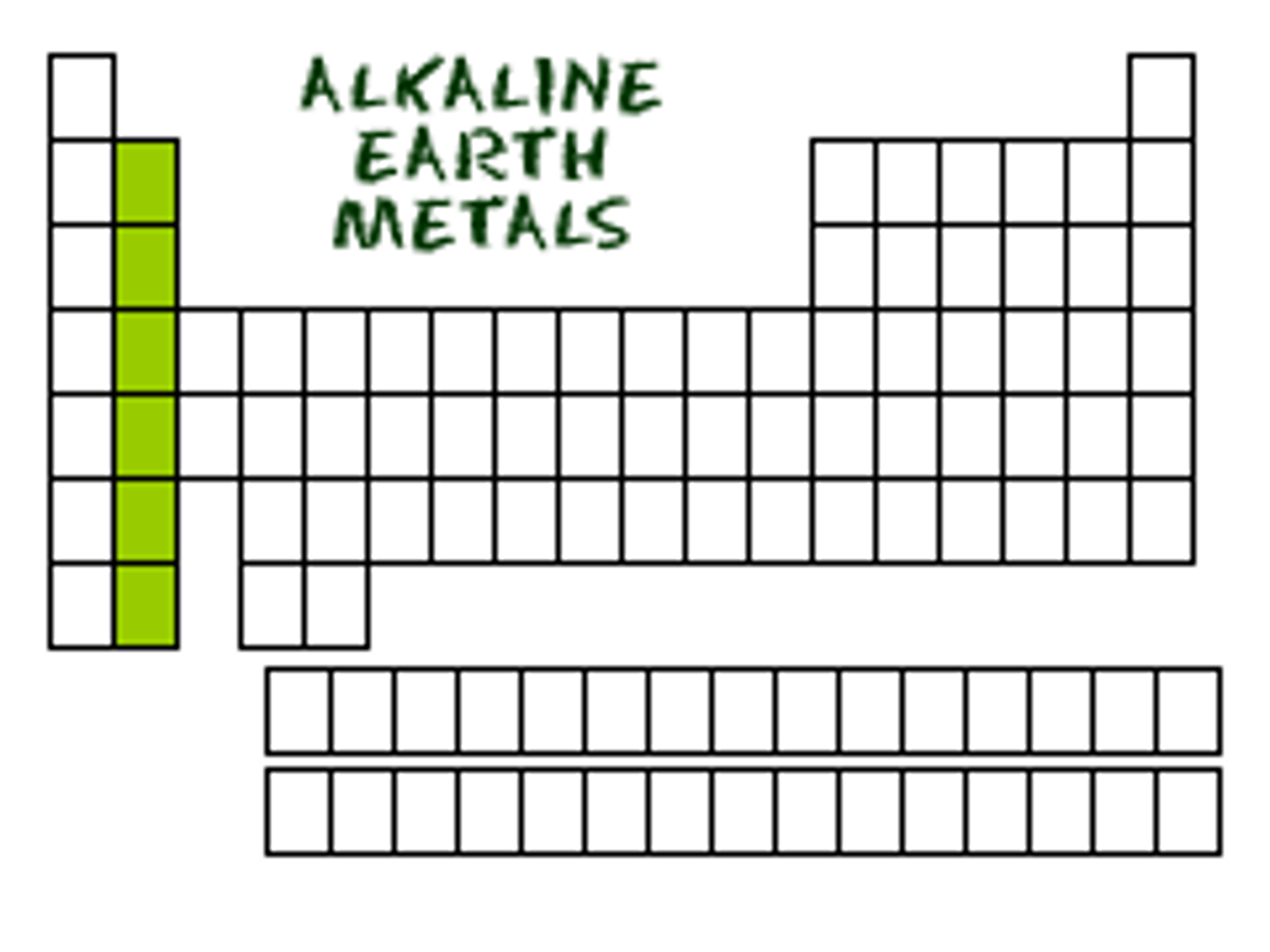
akaline earth metals
group 2, solids at room temperature, mallable, good conductors
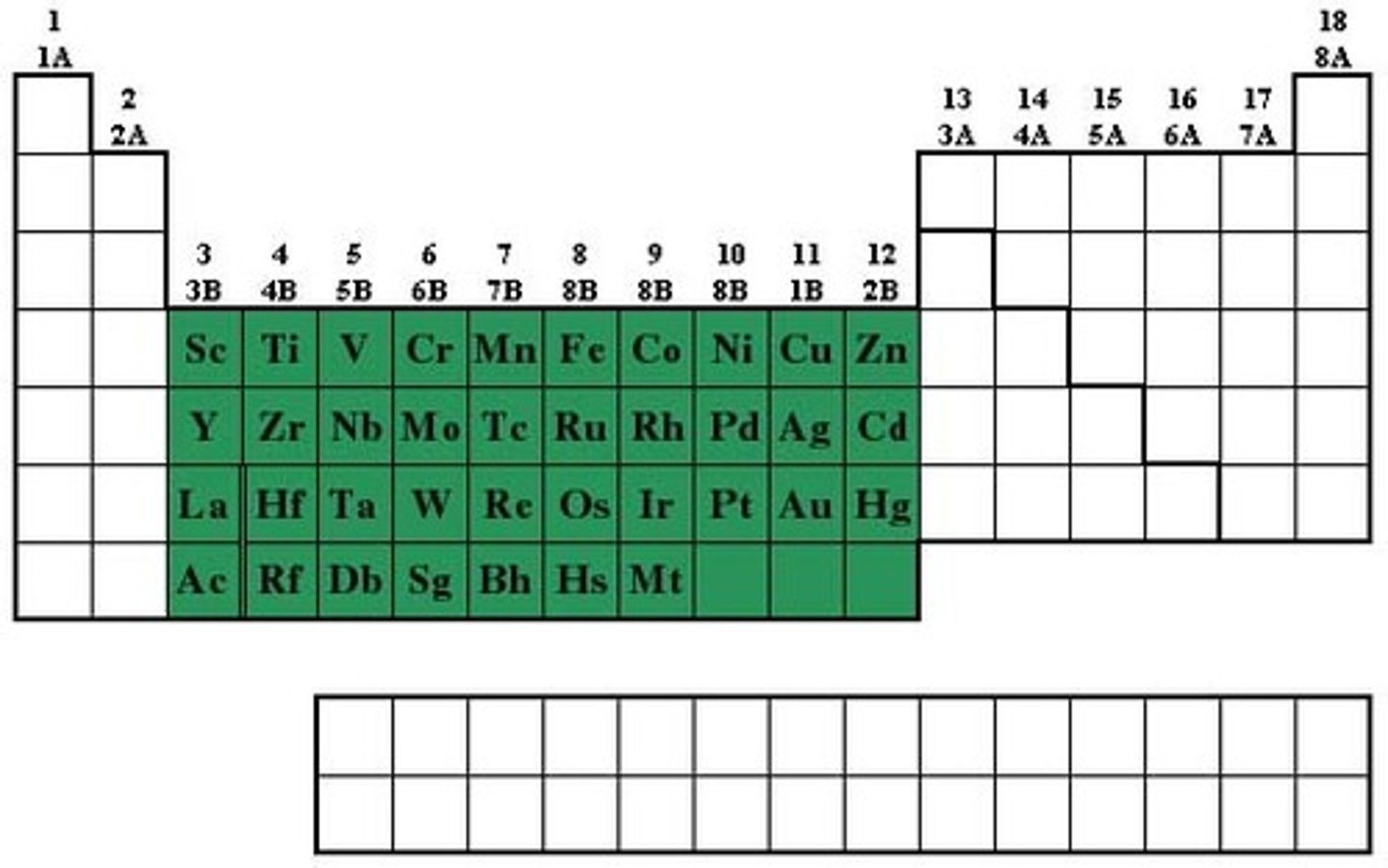
transition metals
Groups 3-12, 1-2 valence electrons, less reactive than alkali-earth metals, shiny, good conductor of thermal energy and electrical current, high density
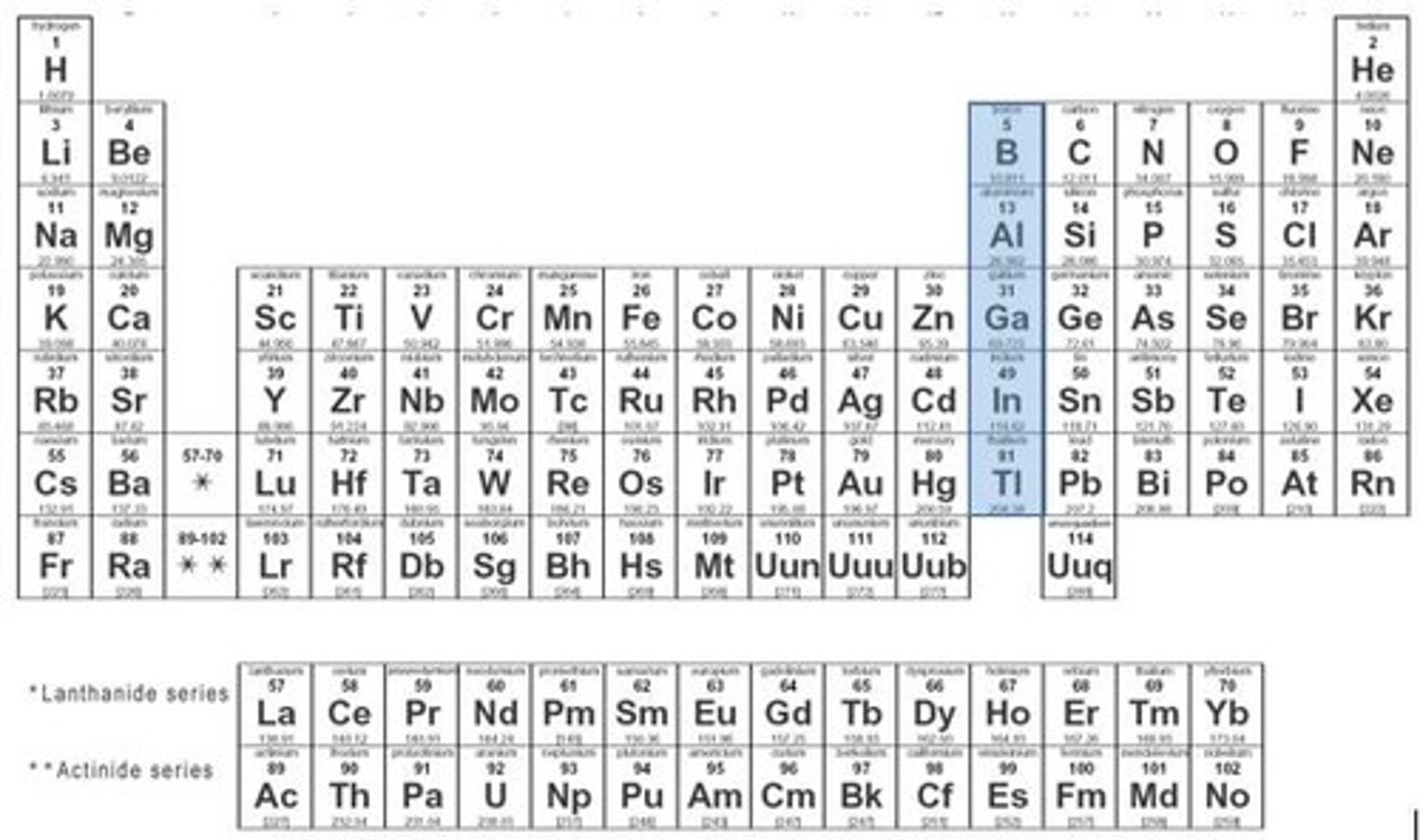
boron family
group 13, 3 valence electrons, metalloids and metals, hard, brittle, low melting/boiling points, good conductors
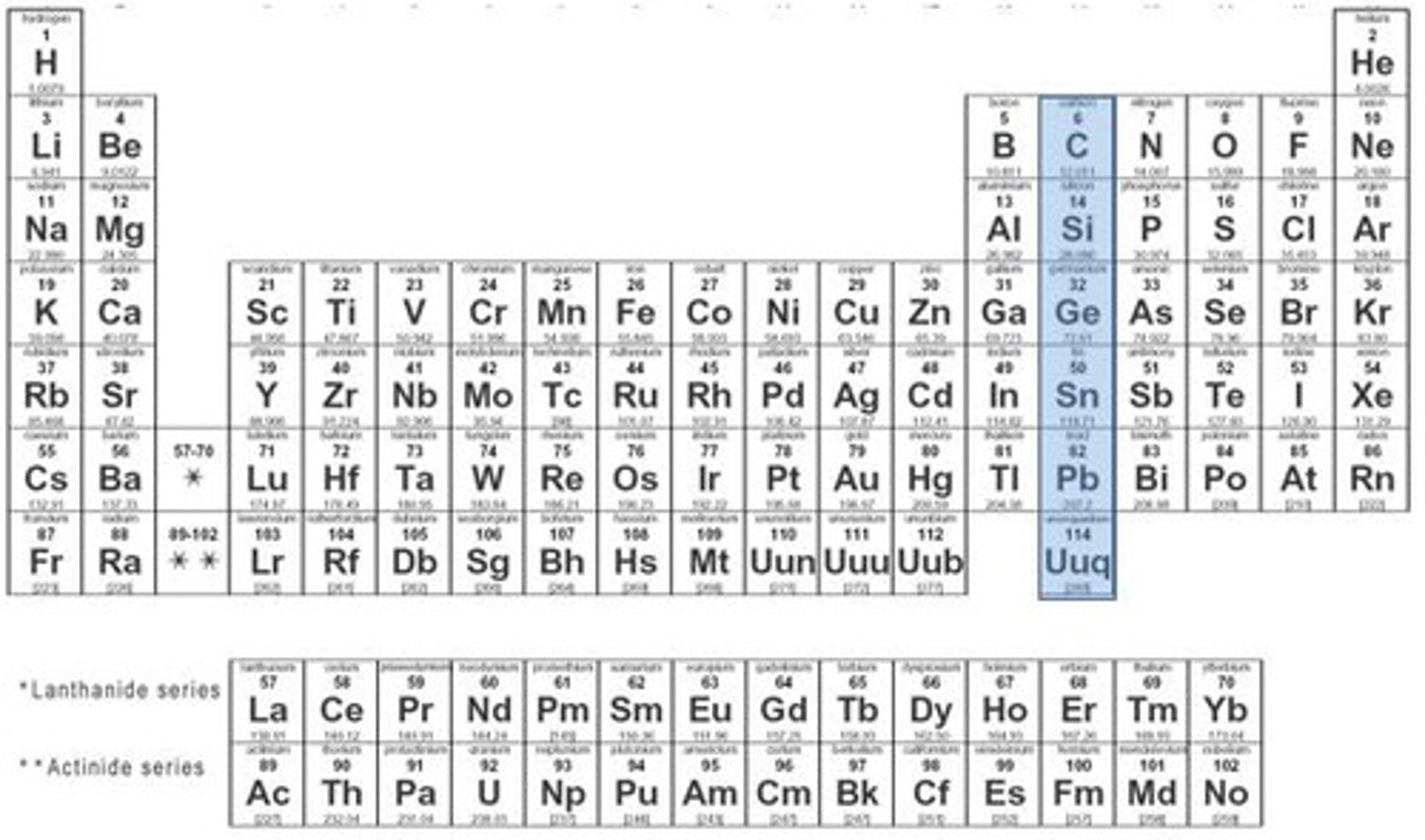
carbon family
group 14, 4 valence electrons, metals, non-metals, and metalloids, have half-filled s & p sublevels, fairly stable and unreactive.
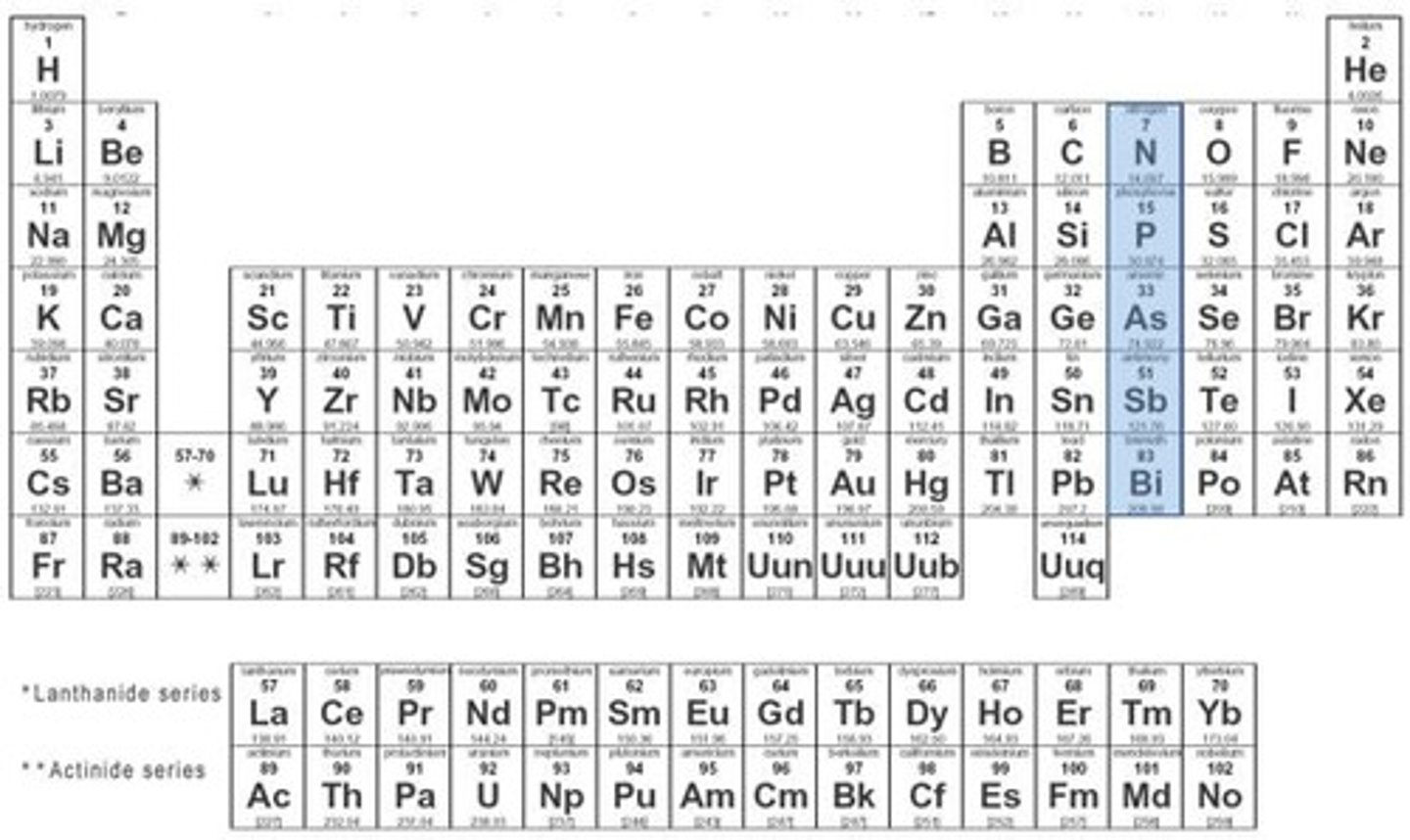
nitrogen family
group 15, 5 valence electrons, solid at room temperature
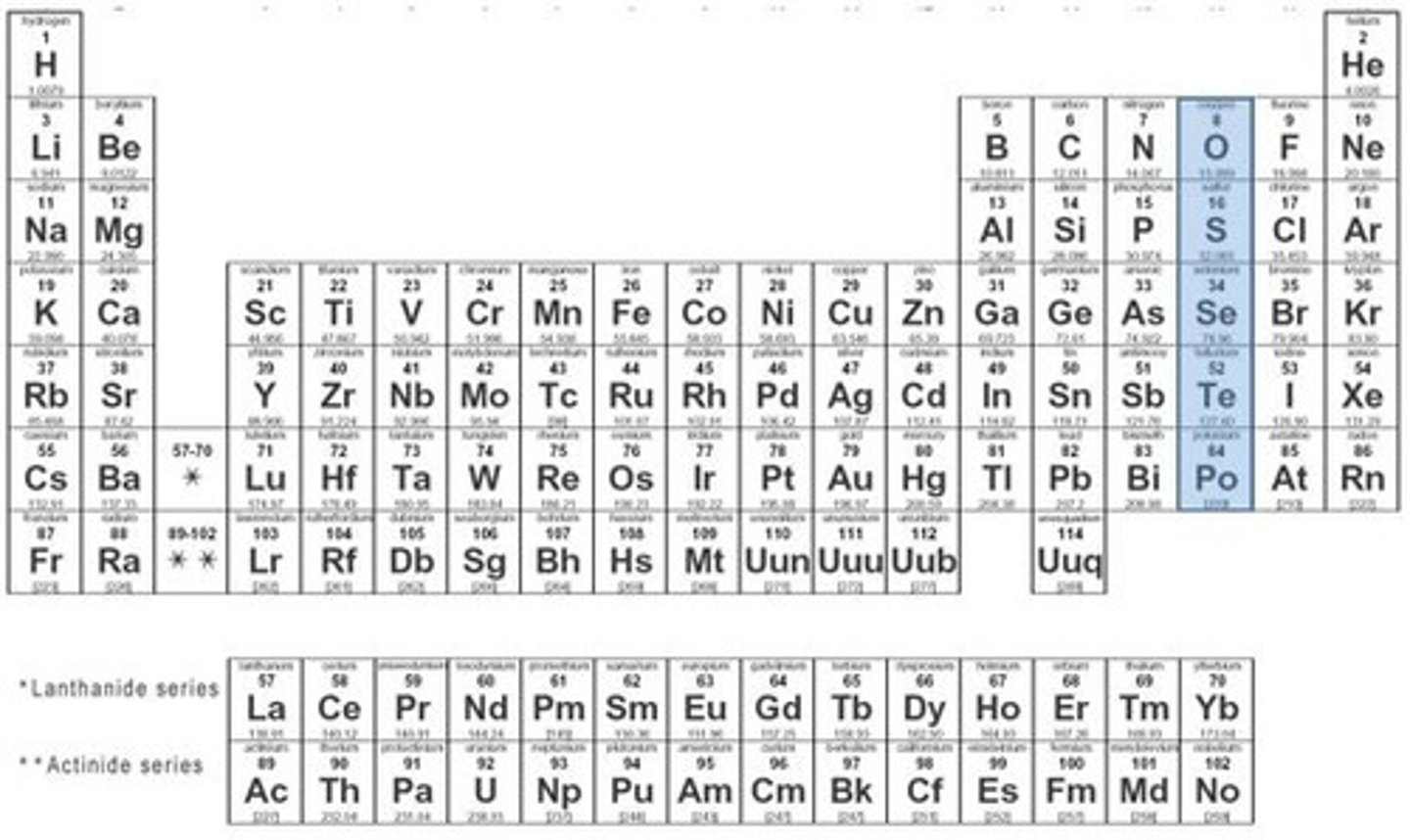
oxygen family
group 16; 6 valence electrons
halogens
group 17, 7 valence electrons, Very reactive, Contains nonmetals
Nobel Gases
group 18, 8 valence electrons, Very unreactive gases, have full S & P sublevels
Lanthanoids
Elements 57-71
Actinoids
Elements 89-103